Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
3 2 Formulae Magnetism
Cargado por
NathanianDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
3 2 Formulae Magnetism
Cargado por
NathanianCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
3.
2 Magnetism
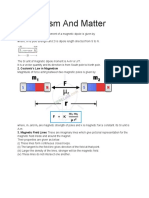
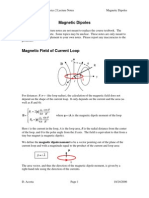
Current Loop as a Magnetic Dipole & Dipole Moment:
Magnetic Dipole Moment is A B I M=IA n SI unit is A m2.
TIP: When we look at any one side of the loop carrying current, if the current is in anticlockwise direction then that side of the loop behaves like Magnetic North Pole and if the current is in clockwise direction then that side of the loop behaves like Magnetic South Pole.
Current Solenoid as a Magnetic Dipole or Bar Magnet:
B
x x x x x x x
Bar Magnet:
Geographic Length
Magnetic Length
Magnetic Dipole Moment is M = m.2l. l
Coulombs Law in Magnetism:
0 m1 m2 F= 4 r
2
m1
m2
(where k = 0 / 4 is a constant and 0 = 4 x 10-7 T m A-1)
In vector form
F=
0 m1 m2 r 4 r
2
F=
0 m1 m2 r 4 r3
B=H r = B / B0
(where is the permeability of the medium)
or
r = / 0
I=M/V I = m(2l) / A(2l) = m / A cm = I / H
r = 1 + cm
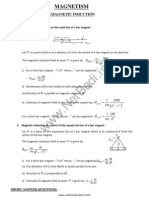
Magnetic Field due to a Magnetic Dipole (Bar Magnet):
i) At a point on the axial line of the magnet:
0 2 M x 4 (x l )
2 2 2
BP =
BN BQ BS y
O
If l << x, then BP 0 2 M 4 x3
ii) At a point on the equatorial line of the magnet: B Q= 0 M 4 (y
2+
BP = B N - B S BS BN N P
l l)
2 3/2
l x
If l << y, then BP 0 M 4 y3
Magnetic Field at a point on the axial line acts along the dipole moment vector. Magnetic Field at a point on the equatorial line acts opposite to the dipole moment vector.
Torque on a Magnetic Dipole (Bar Magnet) in Uniform Magnetic Field:
M
2l
mB
M
mB
S
t
Torque = Magnetic Force x t = mB (2l sin ) = M B sin distance
t = MxB
Direction of Torque is perpendicular and into the plane containing M and B.
Work done on a Magnetic Dipole (Bar Magnet) in Uniform Magnetic Field:
dW = td = M B sin d
2
mB
d 1 2
mB
W = M B sin d
1
mB mB
B
W = M B (cos1 - cos 2)
If Potential Energy is arbitrarily taken zero when the dipole is at 90 then P.E in rotating the dipole and inclining it at an angle is , Potential Energy = - M B cos Note: Potential Energy can be taken zero arbitrarily at any position of the dipole.
Curies Law:
Magnetic susceptibility of a material varies inversely with the absolute temperature. I H / T or I / H 1 / T cm 1 / T cm = C / T (where C is Curie constant) Curie temperature for iron is 1000 K, for cobalt 1400 K and for nickel 600 K.
H/T
Hysteresis Loop or Magnetisation Curve:
I B
E D
También podría gustarte
- MagnetismDocumento19 páginasMagnetismAkash Kumar UpadhyayAún no hay calificaciones
- MagnetismDocumento42 páginasMagnetismAditya BansalAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and MatterDocumento15 páginasMagnetism and MatterJinshy VinodAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 MagnetismDocumento21 páginas4 MagnetismShristyAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and MatterDocumento16 páginasMagnetism and Matterarghyabhai685Aún no hay calificaciones
- 4 MagnetismDocumento17 páginas4 MagnetismThinkershub11Aún no hay calificaciones
- PHY13 Lesson 1 MagnetismDocumento48 páginasPHY13 Lesson 1 MagnetismAmante Rivera JrAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab Mannual-Stewart and Gee's-2Documento17 páginasLab Mannual-Stewart and Gee's-2Sitaramaraju VengalarajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter Formulas DownlaodDocumento17 páginasPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 5 Magnetism and Matter Formulas Downlaodksdb50% (2)
- CBSE Notes Class 12 Physics MagnetismDocumento12 páginasCBSE Notes Class 12 Physics MagnetismTanuja MagarAún no hay calificaciones
- Created by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreDocumento21 páginasCreated by C. Mani, Principal, K V No.1, AFS, Jalahalli West, BangaloreAnaya SajilalAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 4 Deflection Magneto Meter PDFDocumento11 páginas04 4 Deflection Magneto Meter PDFReddyvari VenugopalAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and MatterDocumento4 páginasMagnetism and MatterShaurya SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 3 Magnetic Induction PDFDocumento6 páginas04 3 Magnetic Induction PDFReddyvari VenugopalAún no hay calificaciones
- IITJEE 2014-Physics-School Handout-Magnetism and MatterDocumento10 páginasIITJEE 2014-Physics-School Handout-Magnetism and MatterDikshant GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Electricity and MagnetismDocumento16 páginasElectricity and MagnetismHazel Riyenzi100% (1)
- 4 Moving Charges and MagnetismDocumento7 páginas4 Moving Charges and MagnetismRajender ReddyAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetic Field and Magnetic Force: B V F FDocumento21 páginasMagnetic Field and Magnetic Force: B V F FscholsarAún no hay calificaciones
- MAGNETOSTATIC NOTESDocumento12 páginasMAGNETOSTATIC NOTESthiripura sundariAún no hay calificaciones
- Permanent MagnetDocumento15 páginasPermanent MagnetthinkiitAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and MatterDocumento3 páginasMagnetism and MatterArchana RachelAún no hay calificaciones
- Prhysic Report Magnetic FieldDocumento4 páginasPrhysic Report Magnetic FieldSot MeowAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetic InductionDocumento6 páginasMagnetic InductionYugandhar Veeramachaneni0% (1)
- Magnetism & MatterDocumento17 páginasMagnetism & Matterkartiksingh46648Aún no hay calificaciones
- 17 MagnetostaticsDocumento29 páginas17 MagnetostaticsChirag HablaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulae Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocumento14 páginasFormulae Magnetic Effect of CurrentNathanian81% (16)
- Deflection Magneto MeterDocumento11 páginasDeflection Magneto MeterYugandhar Veeramachaneni79% (14)
- Magnetic Dipole Interactions and MomentsDocumento10 páginasMagnetic Dipole Interactions and MomentsMarina RukavinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism MatterDocumento18 páginasMagnetism MatterSri D0% (1)
- WWW - Thinkiit.in: Magnetic Effects of Current, Magnets and Magnetic MaterialsDocumento14 páginasWWW - Thinkiit.in: Magnetic Effects of Current, Magnets and Magnetic MaterialsthinkiitAún no hay calificaciones
- NMR SpectrosDocumento137 páginasNMR Spectroskangalbert86Aún no hay calificaciones
- MRI NotesDocumento33 páginasMRI Notesmishs14Aún no hay calificaciones
- SDASDASDSADocumento17 páginasSDASDASDSAAkash BidhuriAún no hay calificaciones
- MagnetismDocumento6 páginasMagnetismMohammed Aftab AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 33Documento12 páginasCH 33ybobbyxAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and MatterDocumento21 páginasMagnetism and MatterDeept azaadAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Mapping Magnetic Field Lines of A Bar MagnetDocumento18 páginasPhysics Mapping Magnetic Field Lines of A Bar Magnet7H VENOM TMAún no hay calificaciones
- AP Physics B - Magnetic Fields and ForcesDocumento21 páginasAP Physics B - Magnetic Fields and ForcesAudrey Patrick KallaAún no hay calificaciones
- Moving Charges and Magnetism: Right-Hand Thumb RuleDocumento6 páginasMoving Charges and Magnetism: Right-Hand Thumb RuleSahil SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Eth 25262 01Documento138 páginasEth 25262 01Bubun Kumar PradhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Vibration Magneto MeterDocumento5 páginasVibration Magneto MeterYugandhar Veeramachaneni100% (3)
- 01 Magnetism TheoryDocumento13 páginas01 Magnetism TheoryAnonymous Ob697T5oBlAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetic Properties GuideDocumento19 páginasMagnetic Properties Guideavi taylorAún no hay calificaciones
- Current Carrying ConductorsDocumento12 páginasCurrent Carrying ConductorsYugandhar Veeramachaneni33% (3)
- 08electromagnetism - 193-dsDocumento6 páginas08electromagnetism - 193-dskushwah_770145566Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Moving Charges and MagnetrismDocumento13 páginasPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 4 Moving Charges and MagnetrismTanishq AryanAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 5 Vibration Magneto Meter PDFDocumento5 páginas04 5 Vibration Magneto Meter PDFReddyvari VenugopalAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics XIDocumento33 páginasPhysics XIPavithra PrakashAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and MatterDocumento4 páginasMagnetism and MatterPranshu PatelAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and Matter Class XIIDocumento12 páginasMagnetism and Matter Class XIIAditya DasksgAún no hay calificaciones
- Phy CHP 5 NotesDocumento21 páginasPhy CHP 5 Notesayaan ahmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism FORMULADocumento1 páginaMagnetism FORMULAMoni Kakati0% (1)
- Magnetic Force and TorqueDocumento56 páginasMagnetic Force and TorqueAlvin Dave GalasinaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Indah Permata Sari - Resume Medan MagnetDocumento13 páginasIndah Permata Sari - Resume Medan MagnetIndah Permata sariAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and Matter: Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2024Documento2 páginasMagnetism and Matter: Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2024Aryan ChaturvediAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetism and Matter Class 12 EamcetDocumento103 páginasMagnetism and Matter Class 12 Eamcetsai mukeshAún no hay calificaciones
- 3.e by M by Thomson MethodDocumento4 páginas3.e by M by Thomson MethodRavi Kanth M NAún no hay calificaciones
- HKPhO 18FJDFYJGJGHJHJHJGYJGYHFJFTJRTJFGJFGNGJYJTYJTYJTYDocumento23 páginasHKPhO 18FJDFYJGJGHJHJHJGYJGYHFJFTJRTJFGJFGNGJYJTYJTYJTYSumihar SimangunsongAún no hay calificaciones
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsDe EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 2 UV-Visible SpectrometryDocumento32 páginasUnit 2 UV-Visible SpectrometryKrishnanand NagarajanAún no hay calificaciones
- Uni 3 Infra Red SpectrometryDocumento21 páginasUni 3 Infra Red SpectrometryNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Some atomisation-excitation sources used in atomic emission spectrometry are:- Flame - Electric spark- Electric arc- Inductively coupled plasma (ICP)- Microwave plasma- Glow discharge lamps- LasersDocumento26 páginasSome atomisation-excitation sources used in atomic emission spectrometry are:- Flame - Electric spark- Electric arc- Inductively coupled plasma (ICP)- Microwave plasma- Glow discharge lamps- LasersVelpuri Venkatappaiah67% (3)
- Experiment 9Documento17 páginasExperiment 9NathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 2 Evaluation of Analytical Data IDocumento15 páginasUnit 2 Evaluation of Analytical Data INathanian75% (4)
- Unit 3 Potentiometry-II (PH Metry)Documento24 páginasUnit 3 Potentiometry-II (PH Metry)Nathanian100% (1)
- UNIT 14 Introductio To Analytical Instruments - Doc 12.5Documento14 páginasUNIT 14 Introductio To Analytical Instruments - Doc 12.5NathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 8Documento8 páginasExperiment 8NathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosDocumento9 páginasNuclear Magnetic Resonance SpectrosSougata DasAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 1 General Aspects of Separation MethodsDocumento21 páginasUnit 1 General Aspects of Separation MethodsNathanian100% (1)
- Infrared SpectrosDocumento38 páginasInfrared Spectrosfazraz100% (11)
- Unit 12 NMR SpectrometryDocumento32 páginasUnit 12 NMR SpectrometryNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 7Documento10 páginasExperiment 7NathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT 4 Raman Spectroscopy 12309Documento24 páginasUNIT 4 Raman Spectroscopy 12309NathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 8 Atomic Fluorescence SpectrometryDocumento23 páginasUnit 8 Atomic Fluorescence SpectrometryNathanian100% (12)
- Unit 6 Applications of Fluorimetry and PhosphorimetryDocumento30 páginasUnit 6 Applications of Fluorimetry and PhosphorimetryNathanian100% (1)
- Unit 6 Kineti Methods BacDocumento25 páginasUnit 6 Kineti Methods BacNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 11 Applications of AAS and AESDocumento22 páginasUnit 11 Applications of AAS and AESNathanian75% (4)
- Unit 13 MASS SpectrometryDocumento19 páginasUnit 13 MASS SpectrometryNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 5 Liquid Column ChromatographyDocumento18 páginasUnit 5 Liquid Column ChromatographyNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT 12 ElectrophoresisDocumento17 páginasUNIT 12 ElectrophoresisNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 9 Ion Exchange ChromatographyDocumento35 páginasUnit 9 Ion Exchange ChromatographyNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 9 Atomic AbsorptionDocumento26 páginasUnit 9 Atomic AbsorptionNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 7 Flame PhotometryDocumento32 páginasUnit 7 Flame PhotometryRia Agnez100% (8)
- Unit 4 Raman SpectrosDocumento22 páginasUnit 4 Raman SpectrosNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 9 Applications of Polarography, Amperometric Titrations and VoltammetryDocumento15 páginasUnit 9 Applications of Polarography, Amperometric Titrations and VoltammetryNathanian100% (9)
- Unit 10-Size Exclusion Chromatography After CorrectionDocumento23 páginasUnit 10-Size Exclusion Chromatography After CorrectionNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 8 High Performance Liquid Chromatography HPLCDocumento57 páginasUnit 8 High Performance Liquid Chromatography HPLCNathanianAún no hay calificaciones
- All Items List For Pre-Comm Man-Hour EstimationDocumento97 páginasAll Items List For Pre-Comm Man-Hour Estimationmusab shabbirAún no hay calificaciones
- GMORS Rubber Especification O Rings Guidebook AS568ADocumento90 páginasGMORS Rubber Especification O Rings Guidebook AS568AfeltofsnakeAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 - The Structure of The Atom p3Documento7 páginasChapter 2 - The Structure of The Atom p3lhmooAún no hay calificaciones
- 06.GTA-06 (p1) Question Paper BT1Documento16 páginas06.GTA-06 (p1) Question Paper BT1Motivational BabaAún no hay calificaciones
- Isolation of Plant Genomic Dna by Ctab MethodDocumento4 páginasIsolation of Plant Genomic Dna by Ctab MethodVikram ArjunAún no hay calificaciones
- Lithium-Ion Battery Instantaneous Available Power Prediction Using Surface Lithium Concentration of Solid Particles in A Simplified Electrochemical ModelDocumento10 páginasLithium-Ion Battery Instantaneous Available Power Prediction Using Surface Lithium Concentration of Solid Particles in A Simplified Electrochemical Modelಅಭಿಷೇಕ್ ಕನ್ನಡಿಗAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 7 Revision Practice TestDocumento19 páginasCH 7 Revision Practice Testpedro pascalAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Motion GraphsDocumento2 páginasPhysics Motion GraphsRaymond NguyenAún no hay calificaciones
- Mass WastingDocumento64 páginasMass WastingEkala XuhalxAún no hay calificaciones
- Package-08 TR (R1)Documento2 páginasPackage-08 TR (R1)Antony Prashanth OliveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA)Documento3 páginasDifferential Thermal Analysis (DTA)peeyush01gargAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 - Material Selection For Urea ServiceDocumento17 páginas7 - Material Selection For Urea ServicedennykvgAún no hay calificaciones
- Acknowledging Help for a Landslide Analysis ProjectDocumento7 páginasAcknowledging Help for a Landslide Analysis ProjectabishrantAún no hay calificaciones
- Investigations On The Theory of The Brownian MovementDocumento11 páginasInvestigations On The Theory of The Brownian MovementRafael Poerschke100% (1)
- Drug Excipient InteractionsDocumento18 páginasDrug Excipient InteractionsAsika TamilAún no hay calificaciones
- MSDS PAC10 Poly Aluminium ChlorideDocumento5 páginasMSDS PAC10 Poly Aluminium ChlorideWirawan Adi Setya RAún no hay calificaciones
- Work, Energy & Power: Honors PhysicsDocumento20 páginasWork, Energy & Power: Honors PhysicsFebry ArdiansyahAún no hay calificaciones
- Lect 6 Extra Examples PDFDocumento5 páginasLect 6 Extra Examples PDFZaidoon MohsinAún no hay calificaciones
- DPP - NomenclatureDocumento44 páginasDPP - NomenclatureMohit KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocumento9 páginasDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineTorkhani RachelAún no hay calificaciones
- Scope Location 1 TC-6212Documento33 páginasScope Location 1 TC-6212NISAR AHMEDAún no hay calificaciones
- SOP BioreaktorDocumento17 páginasSOP BioreaktorElma PuspaningtyasAún no hay calificaciones
- Solved Thermodynamics ProblemsDocumento26 páginasSolved Thermodynamics Problemsjerwinmancenido100% (1)
- Ashrae Cleanroom Design Guide ReducDocumento450 páginasAshrae Cleanroom Design Guide ReducDavraceAún no hay calificaciones
- Genesis Tank - Catalog (2023)Documento10 páginasGenesis Tank - Catalog (2023)Uttam KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Bakut Abraham, Sani Uba and Abdulkadir IbrahimDocumento11 páginasBakut Abraham, Sani Uba and Abdulkadir Ibrahimibro4khadAún no hay calificaciones
- Water Treatment SchemesDocumento26 páginasWater Treatment SchemesCao Xuan CanhAún no hay calificaciones
- G12 General Physics 2 Q3W2Documento7 páginasG12 General Physics 2 Q3W2Nicole Angela BartosisAún no hay calificaciones
- Problems For PracticeDocumento2 páginasProblems For PracticeFisher TigerAún no hay calificaciones
- CHE 46: Biochemical EngineeringDocumento30 páginasCHE 46: Biochemical EngineeringJunn Edgar LibotAún no hay calificaciones