Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Definition of Business Policy
Cargado por
Jessica LaguatanDescripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Definition of Business Policy
Cargado por
Jessica LaguatanCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
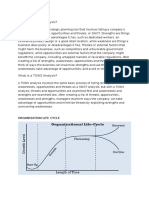
Definition of Business Policy Business Policy defines the scope or spheres within which decisions can be taken by the
subordinates in an organization. It permits the lower level management to deal with the problems and issues without consulting top level management every time for decisions. Business policies are the guidelines developed by an organization to govern its actions. They define the limits within which decisions must be made. Business policy also deals with acquisition of resources with which organizational goals can be achieved. Business policy is the study of the roles and responsibilities of top level management, the significant issues affecting organizational success and the decisions affecting organization in long-run.
Features of Business Policy An effective business policy must have following features1. Specific- Policy should be specific/definite. If it is uncertain, then the implementation will become difficult. 2. Clear- Policy must be unambiguous. It should avoid use of jargons and connotations. There should be no misunderstandings in following the policy. 3. Reliable/Uniform- Policy must be uniform enough so that it can be efficiently followed by the subordinates. 4. Appropriate- Policy should be appropriate to the present organizational goal. 5. Simple- A policy should be simple and easily understood by all in the organization. 6. Inclusive/Comprehensive- In order to have a wide scope, a policy must be comprehensive. 7. Flexible- Policy should be flexible in operation/application. This does not imply that a policy should be altered always, but it should be wide in scope so as to ensure that the line managers use them in repetitive/routine scenarios. 8. Stable- Policy should be stable else it will lead to indecisiveness and uncertainty in minds of those who look into it for guidance. Difference between Policy and Strategy The term policy should not be considered as synonymous to the term strategy. The difference between policy and strategy can be summarized as follows1. Policy is a blueprint of the organizational activities which are repetitive/routine in nature. While strategy is concerned with those organizational decisions which have not been dealt/faced before in same form. 2. Policy formulation is responsibility of top level management. While strategy formulation is basically done by middle level management. 3. Policy deals with routine/daily activities essential for effective and efficient running of an organization. While strategy deals with strategic decisions. 4. Policy is concerned with both thought and actions. While strategy is concerned mostly with action. 5. A policy is what is, or what is not done. While a strategy is the methodology used to achieve a target as prescribed by a policy.
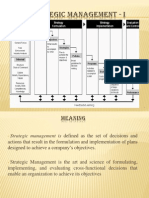
Strategic Management - An Introduction Strategic Management is all about identification and description of the strategies that managers can carry so as to achieve better performance and a competitive advantage for their organization. An organization is said to have competitive advantage if its profitability is higher than the average profitability for all companies in its industry. Strategic management can also be defined as a bundle of decisions and acts which a manager undertakes and which decides the result of the firms performance. The manager must have a thorough knowledge and analysis of the general and competitive organizational environment so as to take right decisions. They should conduct a SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats), i.e., they should make best possible utilization of strengths, minimize the organizational weaknesses, make use of arising opportunities from the business environment and shouldnt ignore the threats. Strategic management is nothing but planning for both predictable as well as unfeasible contingencies. It is applicable to both small as well as large organizations as even the smallest organization face competition and, by formulating and implementing appropriate strategies, they can attain sustainable competitive advantage. 6. Strategic Management is a way in which strategists set the objectives and proceed about attaining them. It deals with making and implementing decisions about future direction of an organization. It helps us to identify the direction in which an organization is moving. 7. Strategic management is a continuous process that evaluates and controls the business and the industries in which an organization is involved; evaluates its competitors and sets goals and strategies to meet all existing and potential competitors; and then reevaluates strategies on a regular basis to determine how it has been implemented and whether it was successful or does it needs replacement. 8. Strategic Management gives a broader perspective to the employees of an organization and they can better understand how their job fits into the entire organizational plan and how it is co-related to other organizational members. It is nothing but the art of managing employees in a manner which maximizes the ability of achieving business objectives. The employees become more trustworthy, more committed and more satisfied as they can co-relate themselves very well with each organizational task. They can understand the reaction of environmental changes on the organization and the probable response of the organization with the help of strategic management. Thus the employees can judge the impact of such changes on their own job and can effectively face the changes. The managers and employees must do appropriate things in appropriate manner. They need to be both effective as well as efficient. 9. One of the major role of strategic management is to incorporate various functional areas of the organization completely, as well as, to ensure these functional areas harmonize and get together well. Another role of strategic management is to keep a continuous eye on the goals and objectives of the organization.
Strategic decisions are the decisions that are concerned with whole environment in which the firm operates, the entire resources and the people who form the company and the interface between the two. Characteristics/Features of Strategic Decisions a. Strategic decisions have major resource propositions for an organization. These decisions may be concerned with possessing new resources, organizing others or reallocating others. b. Strategic decisions deal with harmonizing organizational resource capabilities with the threats and opportunities. c. Strategic decisions deal with the range of organizational activities. It is all about what they want the organization to be like and to be about. d. Strategic decisions involve a change of major kind since an organization operates in ever-changing environment. e. Strategic decisions are complex in nature.
f. Strategic decisions are at the top most level, are uncertain as they deal with the future, and involve a lot of risk. g. Strategic decisions are different from administrative and operational decisions. Administrative decisions are routine decisions which help or rather facilitate strategic decisions or operational decisions. Operational decisions are technical decisions which help execution of strategic decisions. To reduce cost is a strategic decision which is achieved through operational decision of reducing the number of employees and how we carry out these reductions will be administrative decision.
10 Axioms of Financial Management The Ten Axioms The Foundations of Financial Decision Making 1. The Risk-Return Trade-off The more risk an investment has, the higher its expected return should be If you bet on a horse, you want greater odds on the long shot If you invest in a risky business (Semiconductor, oil wells, junk bonds), you should demand a greater return Every decision you make should be evaluated for risk 2. The Time Value of Money A dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received in the future If you receive a dollar today, you can invest it and earn more Because of inflation, a dollar you receive today will buy more than a dollar you receive in the future So the sooner you get the money, the better The sooner you invest your money, the better (i.e. retirement) 3. Cash is King You can not spend profit or net income. These are paper figures only Cash is what is received by the firm and can be reinvested or used to pay bills Cash flow does not equal net income; there are timing differences in accrual accounting between when you record a transaction and when you receive or pay the cash 4. Incremental Cash Flows Its only the increase or decrease in cash that really counts Its the difference between cash flows if the project is done versus if the project is not done Consider all related cash flows, i.e., equip., inventory, etc. Brief case example 5. Curse of Competitive Markets Its hard to find and maintain exceptionally profitable projects High profits attract competition How to keep very profitable projects Product differentiation (Kleenex, Xerox) Low cost (Costco, Honda) Service and quality (Mercedes, Lexus) Give examples for each of the above 6. Efficient Capital Markets The markets are quick and the prices are right Information is incorporated into security prices at the speed of light! Assuming the information is correct, then the prices will reflect all publicly available information regarding the value of the firm Example: announcing a stock split 7. The Agency Problem Managers are typically not the owners of a company Managers may make decisions that are in their best interests and not in line with the long term best interests of the owners Example, cutting Research and Development costs on new products to maximize
current income Pay for performance; stock options 8. Taxes Bias Business Decisions Because cash is king, we must consider the after-tax cash flow on an investment The tax consequences of a business decision will impact (reduce) cash flow Companies are given tax incentives by the government to influence their decisions Examples : investment tax credit and environmental credits reduce taxes; purchase of Prius 9. All Risk is Not Equal Some risk can be diversified away and some cannot Dont put all your eggs in one basket Diversification creates offsets between good results and bad results Example: drilling for oil wells 10. Ethical Behavior Means Doing the Right Thing Ethical Dilemmas are everywhere in finance; just read the news (back date stock options, Madoff) Unethical behavior eliminates trust, results in loss of public confidence Shareholder value suffers and it takes a long time to recover Social responsibility means firms have to be responsible to more than just owners - all stakeholders!
También podría gustarte
- Making Strategy Work (Review and Analysis of Hrebiniak's Book)De EverandMaking Strategy Work (Review and Analysis of Hrebiniak's Book)Aún no hay calificaciones
- Diff BW Policy & StrategyDocumento2 páginasDiff BW Policy & StrategyJoyalAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate Strategy: A Handbook for EntrepreneursDe EverandCorporate Strategy: A Handbook for EntrepreneursAún no hay calificaciones
- Strategic Decisions, Levels of StrategyDocumento13 páginasStrategic Decisions, Levels of Strategykafi70156Aún no hay calificaciones
- Unit-I: Concept of Strategy: The Term Strategy Is Derived From A Greek WordDocumento22 páginasUnit-I: Concept of Strategy: The Term Strategy Is Derived From A Greek Wordsumeetgoyal16Aún no hay calificaciones
- B PolicyDocumento10 páginasB PolicyGaurav SirohiAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Policy SpecificDocumento42 páginasBusiness Policy SpecificManish SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is A SWOT AnalysisDocumento31 páginasWhat Is A SWOT AnalysisJagdish SainiAún no hay calificaciones
- BPSM NotesDocumento3 páginasBPSM Notesankit1844Aún no hay calificaciones
- Bus 402 Business Policy APRIL SIX 2023Documento24 páginasBus 402 Business Policy APRIL SIX 2023jonelouis440Aún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To StrategyDocumento17 páginasIntroduction To StrategyYogita soniAún no hay calificaciones
- Name: Kenneth Arvin Sedon Course: Bsa Iii Topic: Purpose of Strategic Business AnalysisDocumento5 páginasName: Kenneth Arvin Sedon Course: Bsa Iii Topic: Purpose of Strategic Business AnalysisKenneth Arvin SedonAún no hay calificaciones
- Scope of Strategic Management, Business Policy, Strategic Decision Making ProcessDocumento3 páginasScope of Strategic Management, Business Policy, Strategic Decision Making ProcessQay AbbeAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit I Notes Business PolicyDocumento19 páginasUnit I Notes Business PolicyJunaid SiddiquiAún no hay calificaciones
- Bba 202 SUMMER 2014Documento5 páginasBba 202 SUMMER 2014ManishSinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Business PolicyDocumento8 páginasBusiness PolicyOm PriyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Of Reaching There - Strategy Includes Both The Fixation of Objectives As Well The Medium To Be Used To Realize ThoseDocumento5 páginasOf Reaching There - Strategy Includes Both The Fixation of Objectives As Well The Medium To Be Used To Realize ThoseVishruti SinhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Strategic ManagementDocumento128 páginasStrategic ManagementKylaAún no hay calificaciones
- What Are The Characteristics of A Good StrategyDocumento8 páginasWhat Are The Characteristics of A Good StrategyJayson Tom Briva CapazAún no hay calificaciones
- Bba 6 Unit 1 Notes BP&SDocumento19 páginasBba 6 Unit 1 Notes BP&Ssanket12032002Aún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate Strategy ExamDocumento11 páginasCorporate Strategy Examtiko sikharulidze100% (2)
- Topic IiDocumento17 páginasTopic IiLianne PadillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Material of B.P.S. Unit-1Documento18 páginasMaterial of B.P.S. Unit-1Uday OdedaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Business PolicyDocumento22 páginasBusiness PolicyMarjorie San GabrielAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 1 - Introduction To Strategic ManagementDocumento12 páginasUnit 1 - Introduction To Strategic Managementjalaja muniraju100% (1)
- Business Policy and Strategic AnalysisDocumento36 páginasBusiness Policy and Strategic AnalysisSandeep GhatuaryAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 2Documento6 páginasLecture 2Shuja MirAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Business PolicyDocumento7 páginasIntroduction To Business PolicyMazumder Suman100% (1)
- Definition of Business PolicyDocumento10 páginasDefinition of Business Policyvarun rajAún no hay calificaciones
- Mission: StatementDocumento13 páginasMission: Statementzulfi12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- MB0052 - Solved Q.-4 To 6Documento4 páginasMB0052 - Solved Q.-4 To 6Ankur BhavsarAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Policy and StrategyDocumento9 páginasBusiness Policy and StrategyJerissa Joy TaongAún no hay calificaciones
- Strategy Refers To Top Management's Plans To Develop and Sustain Competitive Advantage - A State Whereby A Firm'sDocumento9 páginasStrategy Refers To Top Management's Plans To Develop and Sustain Competitive Advantage - A State Whereby A Firm'sGennelyn Grace PenaredondoAún no hay calificaciones
- SM Unit !&@Documento11 páginasSM Unit !&@sankalp mohantyAún no hay calificaciones
- Advantages and Limitations of Strategic ManagementDocumento4 páginasAdvantages and Limitations of Strategic ManagementSuchir100% (3)
- SWOT AnalysisDocumento18 páginasSWOT AnalysisEshita NaiduAún no hay calificaciones
- Q1. Explain The Corporate Strategy in Different Types of OrganizationDocumento8 páginasQ1. Explain The Corporate Strategy in Different Types of OrganizationRamesh ChandAún no hay calificaciones
- BPSM Notes of Unit 1Documento6 páginasBPSM Notes of Unit 1Arpita DevAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 6: Financial StatementsDocumento7 páginasLesson 6: Financial StatementsDorhea Kristha Guian SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Bpms AssignmentDocumento13 páginasBpms AssignmentKarmdeep GarhwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Policy & Strategy Notes (2019) (Vi - Sem - BMS - SSCBS - Du)Documento62 páginasBusiness Policy & Strategy Notes (2019) (Vi - Sem - BMS - SSCBS - Du)Sanya GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Strama Module 1 Quiz 1Documento3 páginasStrama Module 1 Quiz 1Dianne F. ManiquizAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Policy and Strategy-1Documento29 páginasBusiness Policy and Strategy-1Nishaath ShareefAún no hay calificaciones
- BPSM Unit IDocumento12 páginasBPSM Unit Irohitkumarc4ppAún no hay calificaciones
- Myat Pwint PhyuDocumento10 páginasMyat Pwint PhyuAung Kyaw Soe SanAún no hay calificaciones
- Definitions of Business PolicyDocumento4 páginasDefinitions of Business PolicyMathew JcAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Strategic Performance ManagementDocumento11 páginasIntroduction To Strategic Performance ManagementKelvin MasekoAún no hay calificaciones
- MGT 215Documento4 páginasMGT 215Jasper Kim Jon EnriqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Strategic Management - WalmartDocumento7 páginasStrategic Management - WalmartKanika ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- Q1. Explain The Corporate Strategy in Different Types of OrganizationDocumento8 páginasQ1. Explain The Corporate Strategy in Different Types of OrganizationVishal TiwaraeAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Policy & Strategic Management: Assignment: Submitted To: DR - Ruchi SinghDocumento22 páginasBusiness Policy & Strategic Management: Assignment: Submitted To: DR - Ruchi SinghRishabh RastogiAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Business PolicyDocumento14 páginasIntroduction To Business PolicyMazumder SumanAún no hay calificaciones
- Mba - Iiird Semester Gauhati University Business Policy and Strategic ManagementDocumento42 páginasMba - Iiird Semester Gauhati University Business Policy and Strategic ManagementArjun GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- MB0052Documento8 páginasMB0052Rakesh KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- BBA Strategic Management - IDocumento135 páginasBBA Strategic Management - IbijayAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 1 - Business Policy-1Documento30 páginasUnit 1 - Business Policy-1sodusfurikAún no hay calificaciones
- Do Not Share Any One: Q1. Explain The Corporate Strategy in Different Types of OrganizationDocumento8 páginasDo Not Share Any One: Q1. Explain The Corporate Strategy in Different Types of Organizationnetworker91Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mba Iii Semester Strategic Management and Social Capital (MBA008A) ObjectivesDocumento20 páginasMba Iii Semester Strategic Management and Social Capital (MBA008A) ObjectivesGauravsAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Policy - Definition and FeaturesDocumento8 páginasBusiness Policy - Definition and FeaturesSudhanshu RoxxAún no hay calificaciones
- 2exam LogisticsDocumento6 páginas2exam LogisticsJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- HBODocumento7 páginasHBOJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- ValuesDocumento11 páginasValuesJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- ValuesDocumento11 páginasValuesJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- EthicsDocumento1 páginaEthicsJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- Ethics FinalsDocumento1 páginaEthics FinalsJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- Ethics FinalsDocumento1 páginaEthics FinalsJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- The 4 Sections and The 14 Principles of The Toyota WayDocumento6 páginasThe 4 Sections and The 14 Principles of The Toyota WayJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- IB FinalDocumento1 páginaIB FinalJessica LaguatanAún no hay calificaciones
- NPS Transaction Statement For Tier I AccountDocumento2 páginasNPS Transaction Statement For Tier I AccountAkash RahangdaleAún no hay calificaciones
- ch03 Part10Documento6 páginasch03 Part10Sergio HoffmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Dave Ramsey EText PacketDocumento287 páginasDave Ramsey EText PacketSoumi Vesali0% (1)
- Continuity and Change in Philanthropic Housing Organisations The Octavia Hill Housing Trust and The Guinness TrustDocumento21 páginasContinuity and Change in Philanthropic Housing Organisations The Octavia Hill Housing Trust and The Guinness TrustGillian WardellAún no hay calificaciones
- Ib Club Careers - Interview Tips PDFDocumento9 páginasIb Club Careers - Interview Tips PDFqcrvtbAún no hay calificaciones
- IAS 41 - Agriculture PDFDocumento14 páginasIAS 41 - Agriculture PDFJanelle SentinaAún no hay calificaciones
- City of Lawrence, MA - Property Valuation FAQDocumento1 páginaCity of Lawrence, MA - Property Valuation FAQDan RiveraAún no hay calificaciones
- The Capital Asset Pricing Model (Chapter 8)Documento47 páginasThe Capital Asset Pricing Model (Chapter 8)kegnataAún no hay calificaciones
- Cases For Digest in Commercial LawDocumento1 páginaCases For Digest in Commercial LawLizzette GuiuntabAún no hay calificaciones
- Product Development ProposalDocumento9 páginasProduct Development ProposalMHar Jo MondanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mfrs 15 2sept2014Documento132 páginasMfrs 15 2sept2014Raja Afiah Raja AbdullahAún no hay calificaciones
- Budgeting and Budgetary ControlDocumento2 páginasBudgeting and Budgetary ControlpalkeeAún no hay calificaciones
- The Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), Short-Sale Restrictions and Related IssuesDocumento8 páginasThe Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM), Short-Sale Restrictions and Related Issuessunny_medipalliAún no hay calificaciones
- Trainning and Development in Axis Bank: Title PageDocumento55 páginasTrainning and Development in Axis Bank: Title PageRakesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- A Business PlanDocumento27 páginasA Business Planaparnadas_sitAún no hay calificaciones
- Money Management and Trading PsychologyDocumento10 páginasMoney Management and Trading PsychologyEmerson100% (1)
- Chapter 9Documento34 páginasChapter 9carlo knowsAún no hay calificaciones
- CLSP Unit 2Documento59 páginasCLSP Unit 2Shikhar BavejaAún no hay calificaciones
- Investment Application Form Meezan Savings PlanDocumento2 páginasInvestment Application Form Meezan Savings PlanSalman Arshad100% (1)
- Jean Marie Part 2 - The InterviewsDocumento5 páginasJean Marie Part 2 - The Interviewsekramcal100% (1)
- TAX 1 Mini Digest Part 2Documento6 páginasTAX 1 Mini Digest Part 2Lilu BalgosAún no hay calificaciones
- The Laboratory BudgetDocumento25 páginasThe Laboratory Budgetmaria emailAún no hay calificaciones
- TITAN Project BoopathiDocumento70 páginasTITAN Project BoopathiNagaraj Boopathi50% (2)
- Association of Indigenous Universal Banks Petition President Akufo-AddoDocumento11 páginasAssociation of Indigenous Universal Banks Petition President Akufo-AddoGhanaWeb EditorialAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 2 - Financial Statement and Ratio AnalysisDocumento14 páginasAssignment 2 - Financial Statement and Ratio AnalysisGetto PangandoyonAún no hay calificaciones
- Income Under The Head SalariesDocumento21 páginasIncome Under The Head SalariesAnupam BaliAún no hay calificaciones
- Data AnanysisDocumento14 páginasData AnanysisDrishty BishtAún no hay calificaciones
- CSS Profile InstructionsDocumento10 páginasCSS Profile InstructionsVickyAún no hay calificaciones
- Aviation Rental Business - PlanDocumento35 páginasAviation Rental Business - PlanBoki BorisAún no hay calificaciones
- A Project Report: Company Guide Mr. Vishwas SoniDocumento49 páginasA Project Report: Company Guide Mr. Vishwas SoniSushank Agrawal0% (1)
- Sales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinDe EverandSales Pitch: How to Craft a Story to Stand Out and WinCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2)
- SYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsDe EverandSYSTEMology: Create time, reduce errors and scale your profits with proven business systemsCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (48)
- Scaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0De EverandScaling Up: How a Few Companies Make It...and Why the Rest Don't, Rockefeller Habits 2.0Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)De EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on Strategy (including featured article "What Is Strategy?" by Michael E. Porter)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (11)
- Artificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (104)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2)
- The Ruler's Guide: China's Greatest Emperor and His Timeless Secrets of SuccessDe EverandThe Ruler's Guide: China's Greatest Emperor and His Timeless Secrets of SuccessCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (14)
- 2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesDe Everand2022-2023 Price Action Trading Guide for Beginners in 45 MinutesCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (4)
- Harvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsDe EverandHarvard Business Review Project Management Handbook: How to Launch, Lead, and Sponsor Successful ProjectsCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (15)
- Learn and Understand Business AnalysisDe EverandLearn and Understand Business AnalysisCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (31)
- How to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffDe EverandHow to Grow Your Small Business: A 6-Step Plan to Help Your Business Take OffCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (61)
- Small Business For Dummies: 5th EditionDe EverandSmall Business For Dummies: 5th EditionCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (10)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantDe EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (387)
- The Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerDe EverandThe Toyota Way (Second Edition): 14 Management Principles from the World's Greatest ManufacturerCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (121)
- HBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeDe EverandHBR's 10 Must Reads on AI, Analytics, and the New Machine AgeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (69)
- Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdDe EverandLean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, 2nd EdCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (17)
- Strategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe EverandStrategic Analytics: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (46)
- Strategy Skills: Techniques to Sharpen the Mind of the StrategistDe EverandStrategy Skills: Techniques to Sharpen the Mind of the StrategistCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5)
- Elevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingDe EverandElevate: The Three Disciplines of Advanced Strategic ThinkingCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (3)
- Summary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyDe EverandSummary of Richard Rumelt's Good Strategy Bad StrategyCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceDe EverandPower and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial IntelligenceCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (38)
- Systems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessDe EverandSystems Thinking: A Guide to Strategic Planning, Problem Solving, and Creating Lasting Results for Your BusinessCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (80)
- The Heart of Business: Leadership Principles for the Next Era of CapitalismDe EverandThe Heart of Business: Leadership Principles for the Next Era of CapitalismCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (32)
- Learning to Think Strategically: 4th EditionDe EverandLearning to Think Strategically: 4th EditionCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (6)
- Jim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryDe EverandJim Collins' Good to Great Why Some Companies Make the Leap ... And Others Don’t SummaryCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (3)
- Why Digital Transformations Fail: The Surprising Disciplines of How to Take Off and Stay AheadDe EverandWhy Digital Transformations Fail: The Surprising Disciplines of How to Take Off and Stay AheadCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (9)
- How to Think Strategically: Upskilling for Impact and Powerful StrategyDe EverandHow to Think Strategically: Upskilling for Impact and Powerful StrategyAún no hay calificaciones