Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Suggested Pfmea Evaluation Criteria
Cargado por
trfcpropDescripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Suggested Pfmea Evaluation Criteria
Cargado por
trfcpropCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
POTENTIAL FAILURE MODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS 3RD EDITION
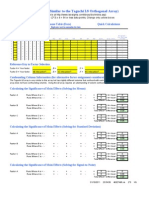
SUGGESTED PFMEA SEVERITY EVALUATION CRITERIA
Criteria: Severity of Effect
This ranking results when a potential failure mode results in a final customer and/or a manufacturing/assembly plant defect. The final customer should always be considered first. If both occur, use the higher of the two severities.
Criteria: Severity of Effect
This ranking results when a potential failure mode results in a final customer and/or a manufacturing/assembly plant defect. The final customer should always be considered first. If both occur, use the higher of the two severities.
Effect Hazardous without warning Hazardous with warning Very High
(Customer Effect) Very high severity ranking when a potential failure mode affects safe vehicle operation and/or involves non-compliance with government regulation without warning. Very high severity ranking when a potential failure mode affects safe vehicle operation and/or involves non-compliance with government regulations with warning. Vehicle/item inoperable (loss of primary function). Vehicle/item operable but at a reduced level of performance. Customer very dissatisfied. Vehicle/item operable but Comfort/Convenience item(s) inoperable. Customer dissatisfied. Vehicle/item operable but Comfort/Convenience item(s) operable at a reduced level of performance. Fit and Finish/Squeak and Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by most customers (greater than 75%). Fit and Finish/Squeak and Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by 50% of customers. Fit and Finish/Squeak and Rattle item does not conform. Defect noticed by discriminating customers (less than 25%). No discernable effect.
(Customer Effect) Or may endanger operator (machine or assembly) without warning.
Ranking 10
Or may endanger operator (machine or assembly) with warning. Or 100% of product may have to be scrapped, or vehicle/item repaired in repair department with a repair time greater than one hour. Or product may have to be sorted and a portion (less than 100%) scrapped, or vehicle/item repaired in repair department with a repair time between a half-hour and an hour. Or product may have to be sorted and a portion (less than 100%) scrapped, or vehicle/item repaired in repair department with a repair time less than a half-hour. Or 100% of product may have to be reworked, or vehicle/item repaired offline but does not go to repair department. Or the product may have to be sorted, with no scrap, and a portion (less than 100%) reworked. Or a portion (less than 100%) of the product may have to be reworked, with no scrap, on-line but out-of-station. Or a portion (less than 100%) of the product may have to be reworked, with no scrap, on-line but in-station. Of slight inconvenience to operation or operator, or no effect.
High
Moderate
Low Very Low Minor Very Minor None
5 4 3 2 1
Extract taken from the FMEA 3rd Edition (QS-9000) reference manual
Page 1 of 2
POTENTIAL FAILURE MODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS 3RD EDITION
SUGGESTED PFMEA OCCURRENCE EVALUATION CRITERIA
Probability Very High: Persistent Failures High: Frequent Failures Moderate: Occasional Failures Likely Failure Rates* > 100 per thousand pieces 50 per thousand pieces 20 per thousand pieces 10 per thousand pieces 5 per thousand pieces 2 per thousand pieces 1 per thousand pieces 0.5 per thousand pieces 0.1 per thousand pieces < 0.01 per thousand pieces Ranking 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Low: Relatively Few Failures Remote: Failure is Unlikely
SUGGESTED PFMEA DETECTION EVALUATION CRITERIA
Detection Almost Impossible Very Remote Remote Very Low Low Moderate Moderately High High Criteria Absolute certainty of non-detection Controls will probably not detect Controls have poor chance of detection Controls have poor chance of detection Controls may detect Controls may detect Controls have a good chance to detect Controls have a good chance to detect Controls almost certain to detect Controls certain to detect X X Inspection Types A B C X X X X X Suggested Range of Detection Methods Ranking
Cannot detect or is not checked. Control is achieved with indirect or random checks only. Control is achieved with visual inspection only. Control is achieved with double visual inspection only. Control is achieved with charting methods, such as SPC (Statistical Process Control). Control is based on variable gauging after parts have left the station, or Go/No Go gauging performed on 100% of the parts after the parts have left the station. Error detection in subsequent operations, OR gauging performed on setup and first piece check (for set-up causes only). Error detection in-station, or error detection in subsequent operations by multiple layers of acceptance: supply, select, install, verify. Cannot accept discrepant part. Error detection in-station (automatic gauging with automatic stop feature). Cannot pass discrepant part. Discrepant part cannot be made because item has been error-proofed by process/product design.
10 9 8 7 6 5
Very High Very High
X X
2 1
Extract taken from the FMEA 3rd Edition (QS-9000) reference manual
Page 2 of 2
También podría gustarte
- Forever Requirements - ChryslerDocumento35 páginasForever Requirements - ChryslerR H100% (1)
- Effective FMEAs: Achieving Safe, Reliable, and Economical Products and Processes using Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisDe EverandEffective FMEAs: Achieving Safe, Reliable, and Economical Products and Processes using Failure Mode and Effects AnalysisCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)
- Burst Builds - Launch Ramp-Up SuccessDocumento32 páginasBurst Builds - Launch Ramp-Up SuccessKaya Eralp AsabAún no hay calificaciones
- Roush Paint Appearance Standard AS 100 1 PDFDocumento6 páginasRoush Paint Appearance Standard AS 100 1 PDFBESAún no hay calificaciones
- Sampling PlanDocumento6 páginasSampling PlanGaurang DaveAún no hay calificaciones
- Production Part Approval Process A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDe EverandProduction Part Approval Process A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionAún no hay calificaciones
- Supplier Requirement ManualDocumento8 páginasSupplier Requirement Manualdavid4asiaAún no hay calificaciones
- 8 Run DOE TemplateDocumento10 páginas8 Run DOE Templatesumitjain2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Supplier Quality ManualDocumento32 páginasSupplier Quality ManualEliane CostaAún no hay calificaciones
- Good Distribution Practices A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDe EverandGood Distribution Practices A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionAún no hay calificaciones
- GM 1927 Supplier Quality ManualDocumento109 páginasGM 1927 Supplier Quality ManualCarlos CarranzaAún no hay calificaciones
- ISO 13485 Quality Management System A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionDe EverandISO 13485 Quality Management System A Complete Guide - 2021 EditionAún no hay calificaciones
- MTU Friedrichshafen Supplier Evaluation CriteriaDocumento8 páginasMTU Friedrichshafen Supplier Evaluation Criteriacastor2010Aún no hay calificaciones
- Supplier Quality Improvement - ChecklistDocumento16 páginasSupplier Quality Improvement - ChecklistmuneerppAún no hay calificaciones
- PPAP-APQP Guide B45157 - Rev-ADocumento29 páginasPPAP-APQP Guide B45157 - Rev-AMoti Ben-ZurAún no hay calificaciones
- Variable MSA 4th Edition Blank TemplateDocumento1 páginaVariable MSA 4th Edition Blank TemplateSachin RamdurgAún no hay calificaciones
- GS-0002D, Design FMEADocumento26 páginasGS-0002D, Design FMEAmesa142100% (1)
- Quality Engineer or Supplier Quality or Failure Analysis EngineeDocumento3 páginasQuality Engineer or Supplier Quality or Failure Analysis Engineeapi-121417252Aún no hay calificaciones
- Register Forum Home Page Post Attachment Files All Help Lost PasswordDocumento3 páginasRegister Forum Home Page Post Attachment Files All Help Lost PasswordKirthivasanAún no hay calificaciones
- Design of Experiments (DOE) TutorialDocumento4 páginasDesign of Experiments (DOE) Tutorialmpedraza-1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quality Control PlanDocumento1 páginaQuality Control PlanScha Affin100% (1)
- Process Capability Study 1500Documento6 páginasProcess Capability Study 1500sebastian lureAún no hay calificaciones
- PPAP Manual Supplier QualityDocumento51 páginasPPAP Manual Supplier QualityGuru PrasadAún no hay calificaciones
- APQP Phase 2 Checklist 26OCT2018 7.2.5Documento26 páginasAPQP Phase 2 Checklist 26OCT2018 7.2.5Mani Rathinam RajamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)Documento22 páginasAdvanced Product Quality Planning (APQP)mjapmgAún no hay calificaciones
- Checklist Control PlanDocumento1 páginaChecklist Control PlanRAJASEKARSUBHUAún no hay calificaciones
- ? What Are The Existing Controls, Ns What Are The Actions ForDocumento10 páginas? What Are The Existing Controls, Ns What Are The Actions ForPk NimiwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Supplier Deviation Request FormDocumento1 páginaSupplier Deviation Request FormBESAún no hay calificaciones
- APQP Phases ActivitiesDocumento1 páginaAPQP Phases Activitiesaorto3919Aún no hay calificaciones
- Iso 8015 - 1985-12-15Documento7 páginasIso 8015 - 1985-12-15Ionut FarcasAún no hay calificaciones
- Failure Analysis of Overhead Transmission Line Compression ClampsDocumento26 páginasFailure Analysis of Overhead Transmission Line Compression ClampsRK KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To MTripleP IMetalDocumento21 páginasIntroduction To MTripleP IMetalKrishna Mohan T.RAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem SolvingDocumento31 páginasProblem SolvingSudhagarAún no hay calificaciones
- PPAP PriruckaDocumento10 páginasPPAP PriruckaKin MattAún no hay calificaciones
- Apqp Advanced Product Quality PlanningDocumento27 páginasApqp Advanced Product Quality PlanningRajesh KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Valmet Automotive Quality Management March 2015 PDFDocumento32 páginasValmet Automotive Quality Management March 2015 PDFEdgar Mugabi TusuubiraAún no hay calificaciones
- List of Questions To Ask Your AS9100 Consultant ENDocumento2 páginasList of Questions To Ask Your AS9100 Consultant ENNarasimharaghavanPuliyurKrishnaswamyAún no hay calificaciones
- Minimum Automotive Quality Management System Requirements For Sub-Tier Suppliers - AUG 14 PDFDocumento9 páginasMinimum Automotive Quality Management System Requirements For Sub-Tier Suppliers - AUG 14 PDFFer Jesus Nieves UribeAún no hay calificaciones
- Jishu Hozen Audit Sheet CountermeasuresDocumento7 páginasJishu Hozen Audit Sheet CountermeasuresharshavardhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Warm-Up - Day 2: Place Self Others Team Purpose AgendaDocumento85 páginasWarm-Up - Day 2: Place Self Others Team Purpose AgendaSanjeev SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- APQPStatus Reporting GuidelinesDocumento19 páginasAPQPStatus Reporting GuidelinesskluxAún no hay calificaciones
- Format No-Blank/Dir: Detail Inspection ReportDocumento18 páginasFormat No-Blank/Dir: Detail Inspection ReportRock RockyAún no hay calificaciones
- Cooper Industries PPAP Forms KitDocumento25 páginasCooper Industries PPAP Forms KitAshutosh SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 ApqpDocumento30 páginas1 ApqpVIPIN YADAVAún no hay calificaciones
- 5.2 Process Capability Analysis Rev2ADocumento8 páginas5.2 Process Capability Analysis Rev2APollyAún no hay calificaciones
- 8D - One Page 8-D Report Rev 007 Duplicate PKG ID-UNITDocumento7 páginas8D - One Page 8-D Report Rev 007 Duplicate PKG ID-UNITEdgar LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Supplier Apqp Gated ReviewDocumento1 páginaSupplier Apqp Gated Reviewtanto_deep_15Aún no hay calificaciones
- Measurement System Analyses Gauge Repeatability and Reproducibility Methods PDFDocumento8 páginasMeasurement System Analyses Gauge Repeatability and Reproducibility Methods PDFFortune FireAún no hay calificaciones
- DFMEA Tutorial: Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis GuideDocumento18 páginasDFMEA Tutorial: Design Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Guidepiero_rsAún no hay calificaciones
- APQP OS Procedure ExampleDocumento8 páginasAPQP OS Procedure Exampleali qaAún no hay calificaciones
- Continental GQA 150429Documento22 páginasContinental GQA 150429dywonAún no hay calificaciones
- Ppap - Aiag ManualDocumento102 páginasPpap - Aiag Manualquintozh100% (1)
- Repair and Modification of Printed Boards and Electronic AssembliesDocumento6 páginasRepair and Modification of Printed Boards and Electronic AssembliesArvind NangareAún no hay calificaciones
- Master Form VDADocumento4 páginasMaster Form VDAapi-3856433Aún no hay calificaciones
- Apqp Status LogDocumento1 páginaApqp Status Logsathyabalaraman67% (3)
- BCSP CSP Exam Study GuideDocumento578 páginasBCSP CSP Exam Study GuideengineeramujtabaAún no hay calificaciones
- QSWI 30-2-0 - Rev F - Risk Management .Docxnov122021083716Documento18 páginasQSWI 30-2-0 - Rev F - Risk Management .Docxnov122021083716uday yadavAún no hay calificaciones
- 2022-CSSGB-BoK Six SigmaDocumento7 páginas2022-CSSGB-BoK Six SigmaHarika KalluriAún no hay calificaciones
- Process Safety Management GuideDocumento39 páginasProcess Safety Management Guidesl1828100% (6)
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis by BoschDocumento52 páginasFailure Mode and Effects Analysis by Boschwawawa1100% (1)
- RCFA and 5-Whys Tips for Successful UseDocumento12 páginasRCFA and 5-Whys Tips for Successful UseadiljredsAún no hay calificaciones
- Failure Mode Effects Analysis in Half The TimeDocumento25 páginasFailure Mode Effects Analysis in Half The TimeRowdyRaheelAún no hay calificaciones
- Implement and monitor WHS practicesDocumento90 páginasImplement and monitor WHS practicesbrooke luffyAún no hay calificaciones
- The Basics of Healthcare Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocumento89 páginasThe Basics of Healthcare Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisAnita Sriwaty PardedeAún no hay calificaciones
- Supra Saeindia 2017 Rule BookDocumento152 páginasSupra Saeindia 2017 Rule BookMeet ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- APQP-PPAP - Workbook ExampleDocumento37 páginasAPQP-PPAP - Workbook ExampleVIBHOR50% (2)
- 48bbc11943003 PDFDocumento10 páginas48bbc11943003 PDFAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA AAún no hay calificaciones
- Customer Specific Requirements - PPAP (2014!03!05)Documento7 páginasCustomer Specific Requirements - PPAP (2014!03!05)diablo2250Aún no hay calificaciones
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) : SIT IN PROJECT GROUPS (But Not Necessarily Teams)Documento23 páginasFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) : SIT IN PROJECT GROUPS (But Not Necessarily Teams)James CalosAún no hay calificaciones
- E-Book 02 Mine ClosureDocumento55 páginasE-Book 02 Mine Closuremalshang9039Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt Mock ExamDocumento30 páginasLean Six Sigma Green Belt Mock ExamKhatija KamAún no hay calificaciones
- 3296-RLCSF3-3-17-0014 - Ram Study Report Rev 2Documento156 páginas3296-RLCSF3-3-17-0014 - Ram Study Report Rev 2anub0025100% (1)
- Hazop Distill La Ti On ColumnDocumento41 páginasHazop Distill La Ti On Columnnaila nisar100% (3)
- DP Failure Mode Effects Analysis Assurance Framework Risk Based GuidanceDocumento93 páginasDP Failure Mode Effects Analysis Assurance Framework Risk Based GuidanceLuanda Barboza100% (2)
- Six Sigma Green Belt Exam Study NotesDocumento11 páginasSix Sigma Green Belt Exam Study NotesKumaran VelAún no hay calificaciones
- Achieving Maintenance Operations Excellence Through The RCM ProgramDocumento7 páginasAchieving Maintenance Operations Excellence Through The RCM ProgramflavianosamelAún no hay calificaciones
- P&G Case StudyDocumento15 páginasP&G Case StudyallamelshehamyAún no hay calificaciones
- Quality PressDocumento56 páginasQuality PressEddie Kuang100% (1)
- HIRARCDocumento60 páginasHIRARCnazatussimaz100% (1)
- DFMEA - Manual PDFDocumento24 páginasDFMEA - Manual PDFDevendra GandhiAún no hay calificaciones
- Safety in Chemical and Hydrocarbon Process Industry - Change ManagementDocumento14 páginasSafety in Chemical and Hydrocarbon Process Industry - Change ManagementV. BalasubramaniamAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter Nine Failure Rate, Reliability and MaintainabilityDocumento24 páginasChapter Nine Failure Rate, Reliability and MaintainabilitySimachew AddisuAún no hay calificaciones
- APQP & Control Plan Training - Presentation Slides - Working TemplateDocumento149 páginasAPQP & Control Plan Training - Presentation Slides - Working TemplateTeeva Battumalai100% (2)
- IPPTChap011 Rev 5th EdDocumento26 páginasIPPTChap011 Rev 5th EdMirek LíbalAún no hay calificaciones
- PT Pos Indonesia FMEA and FTA Analysis of Delivery FailuresDocumento7 páginasPT Pos Indonesia FMEA and FTA Analysis of Delivery FailuresHamda AidilAún no hay calificaciones
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumDe EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumCalificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (12)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveDe EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveAún no hay calificaciones
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityDe EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsDe EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (722)
- CompTIA Security+ Get Certified Get Ahead: SY0-701 Study GuideDe EverandCompTIA Security+ Get Certified Get Ahead: SY0-701 Study GuideCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (2)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewDe EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2)
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldDe EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (54)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyDe EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (51)
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyDe EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (227)
- Alibaba: The House That Jack Ma BuiltDe EverandAlibaba: The House That Jack Ma BuiltCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (29)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessDe EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessAún no hay calificaciones
- 8-Bit Apocalypse: The Untold Story of Atari's Missile CommandDe Everand8-Bit Apocalypse: The Untold Story of Atari's Missile CommandCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (10)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderDe EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (398)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andDe EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (708)
- The Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldDe EverandThe Master Algorithm: How the Quest for the Ultimate Learning Machine Will Remake Our WorldCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (107)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldDe EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (4)
- The Corporate Startup: How established companies can develop successful innovation ecosystemsDe EverandThe Corporate Startup: How established companies can develop successful innovation ecosystemsCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (6)
- Blood, Sweat, and Pixels: The Triumphant, Turbulent Stories Behind How Video Games Are MadeDe EverandBlood, Sweat, and Pixels: The Triumphant, Turbulent Stories Behind How Video Games Are MadeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (335)
- Data-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseDe EverandData-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (12)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyDe EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (24)