Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
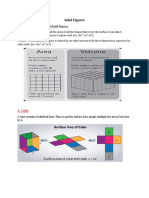
Learn how to calculate the area of plane shapes like triangles, rectangles, circles and more using formulas
Cargado por
udhayausDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Learn how to calculate the area of plane shapes like triangles, rectangles, circles and more using formulas
Cargado por
udhayausCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
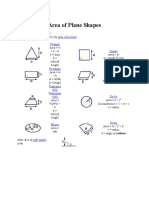
Area of Plane Shapes
Learn more about Area, or try the Area Calculator.
Triangle
Area = b h
b = base h = vertical height Rectangle
Area = a2
a = length of side
Square
Parallelogram
Area = w h
w = width h = height Trapezoid (US) Trapezium (UK)
Area = b h
b = base h = vertical height Circle
Area = (a+b) h
h = vertical height
Area =
r2
Circumference = 2r r = radius Sector
Ellipse
Area =
ab
Area = r2
r = radius = angle in radians
Note: h is at right angles to b:
Example: What is the area of this rectangle?
The formula is:
Area = w h
w = width h = height We know w = 5 and h = 3, so:
Area = 5 3 = 15
Example: What is the area of this triangle?
Height = h = 12 Base = b = 20
Area = b h = 20 12 = 120
A harder example:
Example: Sam cuts grass at $1 per 10m2 How much does Sam earn cutting this area:
Let's break the area into two parts:
Area of A = a2 = 20m 20m = 400m2 Area of B = b h = 20m 14m = 140m2
So the total area is: Part B is a triangle. Viewed sideways it has a base of 20m and a height of 14m.
Part A is a square:
Area = Area of A + Area of B = 400m2 + 140m2 = 540m2 Sam earns = $1 540m2 / 10m2 = $54
Sam earns $1 per 10m2
Waterplane Area Calculation with Simpsons Rule
Naval architects will always have to deal with ship form calculations. These include the calculations of areas of waterplane, transverse sections to obtain the curve of sectional areas, the calculation of hydrostatic properties of the ship such as the displacement, the center of buoyancy, the center of floatation, the transverse metacenter above the keel and etc. In this post, I am going to explain how in Naval Architecture studies we use Simpson's rules to calculate the waterplane area and the position of its centroid of area and finally, the second moments of area for a boat.
For example, we get the ordinates (in meters) of the waterplane of a boat which is defined by a series of half breadth ordinates at 2 meters separation, as follows:
For illustration, I have drawn or sketched the waterplane using pencil on a piece of paper.
To carry out the ship or boat form calculation, I use Microsoft Excel. I entered the half bread ordinates of the boat in a table and perform the calculation as depicted on the table below:
As explained by E. C. Tupper on page 55 of Introduction to Naval Architecture, The column F(A) represents SM x y; F(M) = SM x lever x y;F(I)long = SM x lever x lever x y and F(I) trans = SM x y 3. From the summations in the table: The area of the waterplane (for both sides of the boat) = 2/3 x 2 x 67.2 = 89.599 square meters. The centroid of the area is 2 x 21/67.2 = 0.625 m forward of amidships. The longitudinal second moment of area about amidships = 2/3 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 284.4 = 1516.799 m 4 The minimum longitudinal second moment will be about the centroid of area and given by: IL = 1516.8 - 89.599 (0.625)2 = 1481.647 m4 The ship form calculations can be carried out not only by Simpson's rules but also by Trapezoidal, Tchebycheff's rules. With the use of computer spreadsheet program like Microsoft Excel and Lotus 123, the calculation can be done and modified in real-time easily. by Charles Roring Watch the video of ship displacement calculation on the following posts: Ship Displacement Calculation Ships Displacement Calculation using Simpson's Rule
También podría gustarte
- Navigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsDe EverandNavigation & Voyage Planning Companions: Navigation, Nautical Calculation & Passage Planning CompanionsAún no hay calificaciones
- Hull Geometric Calculations and Hydrostatic CurvesDocumento41 páginasHull Geometric Calculations and Hydrostatic Curvessmartfox91Aún no hay calificaciones
- 05 - MensurationDocumento28 páginas05 - Mensurationthinkiit88% (8)
- Mensuration Tricks, Formulas & Examples: Add CommentDocumento19 páginasMensuration Tricks, Formulas & Examples: Add CommentGirdhar GopalAún no hay calificaciones
- Surface Area of Common SolidsDocumento17 páginasSurface Area of Common Solidsalpha_beta48Aún no hay calificaciones
- VISTAS Institute Basic Ship TheoryDocumento15 páginasVISTAS Institute Basic Ship TheoryDeepak PooranachandranAún no hay calificaciones
- Volumes, Surface Areas and Radian Measure: Review of Areas and Perimeters of Planar FiguresDocumento15 páginasVolumes, Surface Areas and Radian Measure: Review of Areas and Perimeters of Planar Figuresmasyuki1979Aún no hay calificaciones
- Unit-I 1. Explain About Lines Plan of A Ship? AnsDocumento14 páginasUnit-I 1. Explain About Lines Plan of A Ship? AnsDeepak Pooranachandran100% (1)
- Surface Area of Common SolidsDocumento6 páginasSurface Area of Common SolidsAlmario SagunAún no hay calificaciones
- Simpsons Rule NotesDocumento3 páginasSimpsons Rule NotesSherwin Bonsol Arevalo100% (1)
- Calculation of Cross Sectional AreaDocumento3 páginasCalculation of Cross Sectional AreaShivantha HettiarachchiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 - GeometryDocumento28 páginasChapter 2 - GeometryAnna MethyldaAún no hay calificaciones
- MensurationDocumento20 páginasMensurationmaheshgullanki100% (1)
- NA2 Chapter 4Documento27 páginasNA2 Chapter 4Enrique J. Carrillo GómezAún no hay calificaciones
- Surface Area & Volume Surface Area & Volume of 3-D Objects: ObjectiveDocumento4 páginasSurface Area & Volume Surface Area & Volume of 3-D Objects: ObjectiveShrey GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mensuration Formulas GuideDocumento13 páginasMensuration Formulas GuideRitsikaGurram0% (1)
- Chapter 20Documento24 páginasChapter 20KyrieAún no hay calificaciones
- Surveying m5Documento23 páginasSurveying m5Er Anoop SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Earthworks FormulasDocumento4 páginasEarthworks FormulasJithesh SukumaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Differential Calculus 2Documento38 páginasDifferential Calculus 2Anonymous ktESLM3TdAún no hay calificaciones
- BoomerangDocumento6 páginasBoomerangapi-198258118Aún no hay calificaciones
- CuboDocumento14 páginasCuboapi-397491176Aún no hay calificaciones
- Area and Perimeter For SSC ExamsDocumento62 páginasArea and Perimeter For SSC ExamsHema Latha100% (1)
- Surface Area and VolumeDocumento9 páginasSurface Area and VolumeJASMINE JEANNE C. DELGADOAún no hay calificaciones
- g10m MeasurementDocumento20 páginasg10m Measurementapi-235269401Aún no hay calificaciones
- Triangle Square: Example: What Is The Area of This Rectangle?Documento3 páginasTriangle Square: Example: What Is The Area of This Rectangle?walyatAún no hay calificaciones
- Area × B × H Area A: Triangle SquareDocumento3 páginasArea × B × H Area A: Triangle SquareNikhil KhandelwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Area of Plane ShapesDocumento5 páginasArea of Plane ShapesNanettePascualAún no hay calificaciones
- Heron's Formula SolutionsDocumento23 páginasHeron's Formula SolutionsAjayAún no hay calificaciones
- Half PDFDocumento183 páginasHalf PDFTanveer Ali100% (2)
- Mensuration Formulas PDFDocumento3 páginasMensuration Formulas PDFMm DasAún no hay calificaciones
- Estimation ManualDocumento33 páginasEstimation Manualmerreik100% (1)
- Intro To Agri-Fisheries - Midterm (Week 1 To 4)Documento81 páginasIntro To Agri-Fisheries - Midterm (Week 1 To 4)nellrose emlanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Volume Calculation LectureDocumento5 páginasVolume Calculation LectureRoua NawafAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocumento14 páginasPhysics Tutorial 1 SolutionsBonaventure MasekoAún no hay calificaciones
- Answer: Option B Explanation:: A - B - C - DDocumento10 páginasAnswer: Option B Explanation:: A - B - C - DrajgogoiAún no hay calificaciones
- Hide Answer Here Is The Answer and ExplanationDocumento32 páginasHide Answer Here Is The Answer and ExplanationvenugopalAún no hay calificaciones
- Aerodynamics HW SolutionsDocumento1 páginaAerodynamics HW SolutionsFearless713Aún no hay calificaciones
- AreaDocumento15 páginasAreanavyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aptitude FormulasDocumento9 páginasAptitude FormulasPRAKASHAún no hay calificaciones
- MensurationDocumento19 páginasMensurationAtishay JainAún no hay calificaciones
- Constellation Design ReportDocumento13 páginasConstellation Design ReportJoão JúniorAún no hay calificaciones
- Design of Structure-1 - 2 (Design Steps)Documento27 páginasDesign of Structure-1 - 2 (Design Steps)Minhaz KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- SHIP FORM CALCULATIONSDocumento41 páginasSHIP FORM CALCULATIONSNgurah BuanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz 5 Math Splbe 2016Documento7 páginasQuiz 5 Math Splbe 2016benAún no hay calificaciones
- Quantitative AptitudeDocumento5 páginasQuantitative AptitudeAaron BrownAún no hay calificaciones
- 05 - Simpson's RuleDocumento18 páginas05 - Simpson's RuleGoldy26Aún no hay calificaciones
- Calculate Cut and Fill Volumes for Roadway DesignDocumento3 páginasCalculate Cut and Fill Volumes for Roadway DesignnorizhnbAún no hay calificaciones
- EXAMPLES-2.4: (1.) Rectangular SectionDocumento3 páginasEXAMPLES-2.4: (1.) Rectangular SectionJuanithaAún no hay calificaciones
- MAT120 Summer2023 Assignment1 Sec 02Documento4 páginasMAT120 Summer2023 Assignment1 Sec 02rafin0830Aún no hay calificaciones
- Area of ShapesDocumento9 páginasArea of ShapesUmesh Chikhlikar100% (1)
- Answer: ExplanationDocumento30 páginasAnswer: ExplanationSirSmirkAún no hay calificaciones
- GEOMETRY FORMULA GUIDEDocumento27 páginasGEOMETRY FORMULA GUIDEMubassher Ahmed Shoaib100% (1)
- The Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsDe EverandThe Surprise Attack in Mathematical ProblemsCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1)
- A Complete Course in Physics ( Graphs ) - First EditionDe EverandA Complete Course in Physics ( Graphs ) - First EditionAún no hay calificaciones
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersDe EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersAún no hay calificaciones
- SGS Annual 2015 Form III Mathematics ExamDocumento28 páginasSGS Annual 2015 Form III Mathematics ExamAce EduCoachingAún no hay calificaciones
- AreaDocumento13 páginasAreaamitjustamitAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Geometrical Ideas: Class VI. Maths WorksheetDocumento3 páginasBasic Geometrical Ideas: Class VI. Maths Worksheetbhaskar51178Aún no hay calificaciones
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date I. Lesson Title Ii. Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Iii. Content/Core ContentDocumento4 páginasLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date I. Lesson Title Ii. Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melcs) Iii. Content/Core ContentMarjury Bernadette BuenAún no hay calificaciones
- Geom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketDocumento22 páginasGeom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketAnela100% (1)
- Grade 6 3rd Periodical Test TOT OUTPUTDocumento6 páginasGrade 6 3rd Periodical Test TOT OUTPUTGiechris RubiaAún no hay calificaciones
- 11th Science MHT Cet Triumph Mathematics McqsDocumento17 páginas11th Science MHT Cet Triumph Mathematics Mcqsashok Pradhan100% (4)
- IGCSE Math Mock Exam Worked SolutionsDocumento11 páginasIGCSE Math Mock Exam Worked SolutionsZunaira SafdarAún no hay calificaciones
- Find Area of Polygons and Surface AreasDocumento8 páginasFind Area of Polygons and Surface AreasyadavdevenderAún no hay calificaciones
- Ellipse DPTDocumento2 páginasEllipse DPTAgam PrakashAún no hay calificaciones
- CBSE Maths Mock PaperDocumento34 páginasCBSE Maths Mock PaperDivyansh GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bazele AutoCAD-ului 2002Documento105 páginasBazele AutoCAD-ului 2002Mircea AlexandruAún no hay calificaciones
- MCQ in Spherical Trigonometry Part 1 - ECE Board Exam - Pinoybix EngineeringDocumento5 páginasMCQ in Spherical Trigonometry Part 1 - ECE Board Exam - Pinoybix EngineeringMari CarAún no hay calificaciones
- The 48 Special Crystal Forms ExplainedDocumento8 páginasThe 48 Special Crystal Forms ExplainedCJPATAGANAún no hay calificaciones
- G8 and G9 Math OlympicsDocumento9 páginasG8 and G9 Math OlympicsMariel VillanuevaAún no hay calificaciones
- MC35 Geometry Ch04 Handout-209Documento6 páginasMC35 Geometry Ch04 Handout-209SCARLETT CARSONAún no hay calificaciones
- Hyperboloids of RevolutionDocumento27 páginasHyperboloids of Revolutionapi-253076004Aún no hay calificaciones
- Worksheet 19: Symmetry and Loci: Extended Revision Exercises: Shape, Space and MeasuresDocumento4 páginasWorksheet 19: Symmetry and Loci: Extended Revision Exercises: Shape, Space and Measuresmk hatAún no hay calificaciones
- Comprehensive Exam ProblemsDocumento8 páginasComprehensive Exam ProblemsApril Bacaser DancilAún no hay calificaciones
- M9 Herons Formula WS - 28 Aug 2023 - 1693222117566 - HomqgDocumento3 páginasM9 Herons Formula WS - 28 Aug 2023 - 1693222117566 - HomqgAaravamudhan BadrinarayananAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 13 ExercisesDocumento3 páginasChapter 13 ExercisesnopeAún no hay calificaciones
- PDF Detailed Lesson Plan in Math V - CompressDocumento5 páginasPDF Detailed Lesson Plan in Math V - CompressKATRINA GARCIAAún no hay calificaciones
- AUC Sheet SolutionDocumento67 páginasAUC Sheet SolutiontanmayAún no hay calificaciones
- A Complete Guide On Advance Maths For SSC ExaminationsDocumento3 páginasA Complete Guide On Advance Maths For SSC ExaminationsPrakhar tiwariAún no hay calificaciones
- Elements of Plane TrigonometryDocumento275 páginasElements of Plane TrigonometryMannyAún no hay calificaciones
- Geometric Design - The BasicsDocumento26 páginasGeometric Design - The BasicsMary Carmen Andreu Merino100% (1)
- HW30 - Week 32 - Relation Between Sides and Angles in TrianglesDocumento4 páginasHW30 - Week 32 - Relation Between Sides and Angles in TrianglesDemir BasaktarAún no hay calificaciones
- Quick Practice Test # 1: Date: 25-May-2020Documento5 páginasQuick Practice Test # 1: Date: 25-May-2020RhombiAún no hay calificaciones
- 2014 Intermediate Individual Solutions (English) PDFDocumento8 páginas2014 Intermediate Individual Solutions (English) PDFalex jobogAún no hay calificaciones