0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
51 vistas14 páginasRecyclerView Con Swipe
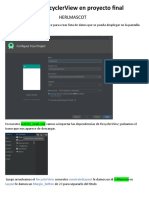
El documento describe cómo implementar un RecyclerView en Android utilizando Kotlin, incluyendo la configuración de dependencias, la creación de interfaces para los elementos y la implementación de un adaptador. También se detalla la funcionalidad de deslizamiento para eliminar elementos y la creación de un adaptador de RecyclerView con soporte para deslizamiento. Finalmente, se presentan ejemplos de código para la configuración y uso del RecyclerView y su adaptador en una actividad principal.
Cargado por
Eric RiveraDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd
0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
51 vistas14 páginasRecyclerView Con Swipe
El documento describe cómo implementar un RecyclerView en Android utilizando Kotlin, incluyendo la configuración de dependencias, la creación de interfaces para los elementos y la implementación de un adaptador. También se detalla la funcionalidad de deslizamiento para eliminar elementos y la creación de un adaptador de RecyclerView con soporte para deslizamiento. Finalmente, se presentan ejemplos de código para la configuración y uso del RecyclerView y su adaptador en una actividad principal.
Cargado por
Eric RiveraDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd