Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
D5 Water
Cargado por
ErnestomalamionDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
D5 Water
Cargado por
ErnestomalamionCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
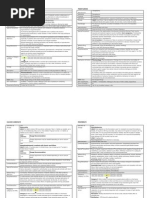
D5 WATER Contents
Per 100 mL Dextrosemonohydrate 5 g, Naacetate anhydrous189 mg, KCl 141 mg,Na phosphatemonobasic 21.4 mg,MgCl 2 hexahydrate30.5 mg, mono K phosphate 15 mg,sodiummetabisulphite(approx 2 mEq/L) 20mg. Electrolytes in1000 mL Na 25 meq,K 20 meq, Mg 3 meq,acetate 23 meq, Cl22 meq, phosphate 3meq
Indications Maintenance therapyin dehydration. Fluid& electrolytemaintenance.Used in thetreatment of diarrhea
Precautions Hyperkalemia inanuria or oliguria dueto renal impairmentor dehydration andincreased BUN due toreduced urinaryoutput, surgery &tissue damage.Pregnancy. Nametabisulfite maycause allergic typereactions includinganaphylacticsymptoms & life-threatening or lesssevere asthmaticepisodes
Adverse Reaction Hyperkalemia,hypernatremia /hyperchloremia &conditions arisingfrom them eg.edema, certaincardiac diseases.Rarely ,hypermagnesemia /hyperphosphatemia
Drug Interaction Amrinone lactate.
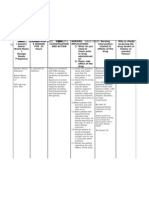
Normal Saline Solution
Other Names 0.9% Sodium Chloride Solution
Classification 1. Isotonic volume expander 2. Electrolyte replacement
Action 1. Normal Saline is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for fluid and electrolyte replenishment. 2. It contains no antimicrobial agents.
3. The pH is 5.0 (4.5 to 7.0). 4. It contains 9 g/L Sodium Chloride with an osmolarity of 308 mOsmol/L. 5. It contains 154 mEq/L Sodium and Chloride.
Indications 1. It is indicated as a source of water and electrolytes. 2. In general, intravenous lines should not be started unless the patient currently, or may soon need either fluid replenishment or medication administration. 3. If used to replenish fluids, a large bore IV (18G or more) should be started, hung with a 1000 mL bag of saline. 4. If saline is being started for medication administration maintain at TKVO, or consider using a saline lock instead of intravenous line. Contraindications 1. Severe Hypertension 2. Pulmonary edema
Precautions 1. If administering a fluid bolus check BP and lung sounds every 250cc. Discontinue bolus if pulmonary edema is discovered, or once BP is in therapeutic range (generally SBP above 90 mm/Hg). Avoid hypervolemia. 2. It should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with congestive heart failure, severe renal insufficiency and in clinical states in which there exists edema with sodium retention. 3. In patients with diminished renal function, administration of Normal Saline may result in sodium retention.
Adverse Reactions 1. Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation, and hypervolemia. 2. If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures and save remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
Interactions/Compatibility/Stability 1. Compatible with most, if not all, EMS medications. Check individual medications before administration. 2. Avoid excessive heat. It is recommended the product be stored at room temp. (25`C) brief exposure up to 40`C does not adversely affect the product.
Special Considerations Be aware that hypertonic (1.8%) and hypotonic (0.45%) saline solutions exist. Ensure appropriate concentration before use.
Dosages 20cc/kg of lean body weight for hypovolemic hypotension. Repeat once prn, then consider use of blood products.
También podría gustarte
- Drug AnalysisDocumento3 páginasDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Methylprednisolone AlphapharmDocumento5 páginasMethylprednisolone AlphapharmMarthin TheservantAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug StudyDocumento13 páginasDrug StudyAldrin Ian Oraza AlpeAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study Ko ToDocumento4 páginasDrug Study Ko ToGian Carlo FernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- D5W (Dextrose 5%) ClassDocumento4 páginasD5W (Dextrose 5%) ClassHanilyn ArdinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Dextrose 50 InjectionDocumento6 páginasDextrose 50 InjectionLip StickAún no hay calificaciones
- MorphineDocumento2 páginasMorphineNinoska Garcia-Ortiz80% (5)
- Drug Study FDocumento3 páginasDrug Study FFatima Love Ariate-ArcasetasAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolDocumento3 páginasDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128Aún no hay calificaciones
- D5WDocumento1 páginaD5WBreena Reubee EstilloreAún no hay calificaciones
- Iron SucroseDocumento3 páginasIron SucroseAtul KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug AnalysisDocumento3 páginasDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento2 páginasNursing Care PlanCindy Mae Quinga100% (2)
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocumento15 páginasDrug Study On Emergency DrugsDennise Juayang100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocumento5 páginasDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioAún no hay calificaciones
- Generic Name:: ClassificationsDocumento4 páginasGeneric Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsAún no hay calificaciones
- DRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)Documento1 páginaDRUG Kalium Durule (Potasium Chloride)rholiboiAún no hay calificaciones
- LOPERAMIDEDocumento3 páginasLOPERAMIDEfaye kimAún no hay calificaciones
- ClonidineDocumento2 páginasClonidineFlora Angeli PastoresAún no hay calificaciones
- OfloxacinDocumento2 páginasOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- CyclosporineDocumento2 páginasCyclosporineMuhammad ArsalanAún no hay calificaciones
- HydrocortisoneDocumento4 páginasHydrocortisoneiammaiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Monograph XareltoDocumento2 páginasDrug Monograph XareltoBenAún no hay calificaciones
- Folic AcidDocumento2 páginasFolic AcidConn_Casipe_8158100% (1)
- Doxorubicin: Mechanism of ActionDocumento3 páginasDoxorubicin: Mechanism of ActionGeorge FogAún no hay calificaciones
- Sodium BicarbonateDocumento1 páginaSodium BicarbonateALbinong VelascoAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaDrug StudycliffordbuenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Captopril Drug StudyDocumento7 páginasCaptopril Drug StudyKimzie Joy Basco100% (1)
- Filgastrim (GCSF)Documento3 páginasFilgastrim (GCSF)Kyla Barrera TabungarAún no hay calificaciones
- IrbesartanDocumento3 páginasIrbesartanapi-3797941Aún no hay calificaciones
- Drug StudyDocumento3 páginasDrug StudyLarah Mae AndogAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricDocumento3 páginasDrug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricJhon Jade PalagtiwAún no hay calificaciones
- Pyridoxine (B6)Documento1 páginaPyridoxine (B6)Amanda CoadAún no hay calificaciones
- Antimalarial DrugsDocumento7 páginasAntimalarial DrugsHilmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Case Presentation Hypokalemic ManDocumento61 páginasCase Presentation Hypokalemic ManHussain AzharAún no hay calificaciones
- Felodipine CefuroximeDocumento3 páginasFelodipine CefuroximecotyboyAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug StudyDocumento2 páginasDrug StudyemmanuelmyagokayeAún no hay calificaciones
- ClonidineDocumento1 páginaClonidineKhryss Paula BaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug AnalysisDocumento18 páginasDrug AnalysisArt Christian RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Bearse Tablet InsertDocumento2 páginasBearse Tablet InsertLeonard ByunAún no hay calificaciones
- Atropine SulfateDocumento1 páginaAtropine SulfateTrishaaMayolAún no hay calificaciones
- AldactoneDocumento2 páginasAldactoneianecunarAún no hay calificaciones
- Bicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyDocumento1 páginaBicillin C-R Penicillin G: Drug StudyChristine Pialan Salimbagat100% (1)
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocumento4 páginasMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenAún no hay calificaciones
- Intravenous ImmunoglobulinDocumento5 páginasIntravenous ImmunoglobulinTeslim RajiAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Study - BaclofenDocumento5 páginasDrug Study - BaclofenRocco WalksAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Potassium Chloride KCLDocumento1 páginaDrug Potassium Chloride KCLSrkocher100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocumento5 páginasDrug StudyBridgette ArañesAún no hay calificaciones
- As Pi LetDocumento7 páginasAs Pi Letianecunar100% (1)
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocumento1 páginaDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- IV Fluid TonicityDocumento4 páginasIV Fluid TonicityDarylSteffiAún no hay calificaciones
- Case Study NCM 118Documento14 páginasCase Study NCM 118Romzy BasañesAún no hay calificaciones
- HypermagnesemiaDocumento2 páginasHypermagnesemiaapi-3712326100% (1)
- Drug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento8 páginasDrug Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesKhim CaronanAún no hay calificaciones
- Management of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticleDocumento4 páginasManagement of Potassium Disorders 17706 ArticlealeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ringer Fund inDocumento2 páginasRinger Fund inMuhammad FauziAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug StudyDocumento28 páginasDrug StudyJheryck SabadaoAún no hay calificaciones
- DrugsDocumento116 páginasDrugsRyan FlahertyAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug StudyDocumento20 páginasDrug StudyBrylle CapiliAún no hay calificaciones
- Sodium BicarbonateDocumento8 páginasSodium BicarbonateRaf AylaniAún no hay calificaciones