Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011
Cargado por
Jill Peary RajuDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011
Cargado por
Jill Peary RajuCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
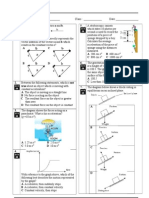
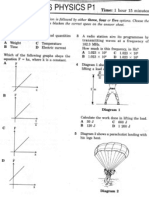
SECTION A 40 marks Each question is followed by four options.
Choose the best option for each question then blacken the correct space on the answer sheet. 1 Which of the following does not relate to physics field? A. movement of gas particle. B. phenomenon of rainbow. C. covalent and ionic bonding. D. to produce more shiny diamond Which of the following physical quantities consists of derived quantities? A Temperature, time, force B Electric current, length, time C Force, velocity, electric charge D Velocity, force, length Which of the following is a derived physical quantity? A. mass C. electric current B. temperature D. weight Which of the following is a scalar quantity? A Distance C B Velocity D Acceleration Force
3.
5.
Which of the following value of prefix is correct? Prefix Value of prefix A Giga 10 8 B Desi 10-1 C Milli 10-6 D Nano 10-7 A radio station transmit a radio waves at 90.3 MHz. What is the frequency in units of Hz ? A. 90.3 X 104 Hz C. 90.3 X 106 Hz 5 B. 90.3 X 10 Hz D. 90.3 X 107 Hz 9 E. 90.3 X 10 Hz The equatorial diameter of earth is 12 760 000 m. Which is written with the correct prefix? A. 1.276 Mm. C. 0.1276 Gm B. 0.01276 Gm D. 12.76 m Which of the following is the correct converted unit ? A 1 000 mm3 = 1.0 x 10 -4 m3 B 100 mm3 = 1.0 x 10-2 m3 C 450 mm3 = 4.5 x 10-7 m3 D 45 mm3 = 4.5 x 10 -6 m3 A physical quantity is defined as the product of velocity and time. What is the S.I. unit of this quantity? A. kg m s-2 C. m s-1 B. kg m s-1 D. m10.
7.
8.
9.
10.
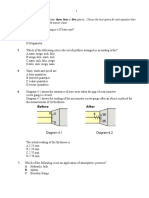
Diagram 1 shows the scales on a pair of analogue stop watch and digital stop watch . 1
Digital stop watch Diagram 1 Which comparison is correct about the sensitivity of the analogue stop watch and digital stop watch when measuring time? Analogue stop watch Digital stop watch
Analogue stop watch
Low sensitivity
Low sensitivity
Low sensitivity
High sensitivity
C.
High sensitivity
Low sensitivity
D.
High sensitivity
High sensitivity
Vernier Callipers
Diagram 2 11. The vernier calliper reading in Diagram 2 is A. 0.05 cm C. B. 0.35 cm D. 0.55 cm 1.50 cm
Four students A, B, C and D use metre rule (R), vernier callipers (V) and micrometer screw gauge (M), to measure the thickness of a book. The measurements obtained are recorded in a table below. Which record is correct? R ( cm ) V ( cm ) M ( cm )
12.
4.213
4.21
2
4.2
4.2
4.21
4.213
4.213
4.2
4.21
4.21
4.213
4.2
13.
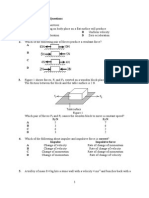
Diagram 3 below shows a method of estimating the diameter of a wire using a ruler 20 turns Rod
Ruler The diameter of the wire is A 0.12 cm B 0.13 cm 14.
Wire Diagram 3 C D 0.27 cm 0.28 cm
The equation below shows the relationship between image distance, v with magnification, M, for a convex lens. v 10 = 10 M Which of the following graphs shows the relationship between v and M for the above equation? A C
15
Which of the following is not a purpose of plotting graph in scientific investigation? A Giving a consistent measurement B Finding relationship between two variables C Find the values that out of range D Interpreting data Which of following describe vector quantities A. Energy is needed to melt the ice B. The thrust needed to launched rocket. C. Capacitance of capacitor D. Speed of the car. Diagram 4 shows the journey of a bus from city A to reach city D.
16
17.
Diagram 4
What is the displacement of the bus? A 60 km B 100 km 18.
C D
128 km 220 km
Diagram 5 shows a graph of velocity against time for the motion of a bus.
How far does the bus reaches a steady velocity? A. 10 m C. 100 m B. 20 m D. 200 m 19. Diagram 6 shows a obtained from an experiment 4
travel before it
ticker tape that was Diagram 5 by using a
trolley A of mass 2 kg and a trolley B. Trolley A was released from one end of platform so that it moves downwards and collides with the stationary trolley B. After the collision they stick and move together. What is the mass of trolley B?
Before collision Diagram 6 A 0.5 kg C. 1.5 kg B 1.0 kg D. 2.0 kg Diagram 7 shows a Formula-1 racing car.
After collision
20.
Diagram 7 Why does the cars design engineer use light composite materials for making the body of the car although its engine is powerful ? A Acceleration increases if mass decreases. B A small mass produces a large force. C A large force produces a large inertia. D The cost of composite material of small mass is low. 21. Diagram 8 below shows two objects with different masses are dropped simultaneously from a height. Which quantity is same for both of the objects?
Diagram 8
A B 22.
Weight Velocity
C D
Final velocity Rate of change of velocity
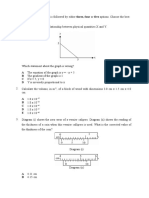
The graph in Diagram 9 below representing the motion of a vehicle.
Diagram 9
What is the acceleration and displacement of the vehicles? Acceleration/ ms-2 Displacement/ m A 4 800 B 6 600 C 4 400 D 6 400
23.
Diagram 10 is a velocity-time graph showing motion of a car.
Diagram 10 Which statement describes the motion of the car? OX XY A Uniform acceleration Uniform deceleration
Uniform velocity
Uniform deceleration
Uniform acceleration
Uniform velocity
Uniform velocity
Uniform acceleration
24.
Diagram 11 shows a car is accelerating with a frictional force of 6000 N acting on it. 6
Accelerati on
Diagram11 Friction force
What is the force exerted by the engine of the car ? A. equal to 6000 N B. greater than 6000 N C. smaller than 6000 N D. 0N 25. Diagram 12 shows Proton Exoras crumple zone.
Diagram 12 What happen if there is no crumple zone for the cars? A Time of impact will increase and increase the level of injuries B Time of impact will increase and increase the impulsive force to the car C Time of impact will decrease and increase the impulsive force to the car D Time of impact will decrease and avoid the driver from injuries 26 The following item is for safety features in vehicles, except. A rubber bumper B larger rim C anti-scatter windscreen D Anti-Lock-Breaking System (ABS) A force can do the following except. A move a stationary object B stop a moving object C decelerate a moving object D alters the quantity of matters of the object Diagram 13 shows trolley A and B of same mass on a frictionless plane. Trolley A moves and collides with the stationary trolley B.
27.
28 .
Before collision plasticine
After collision
Diagram 13 Which of the following statements is true? A The collision is an elastic collision B Both trolleys do not undergo changes in momentum C The total momentum before and after the collision is the same D The total kinetic energy before and after the collision is conserved 29. Diagram 14 shows a coconut falling from a tree.
Diagram 14
Which accelerationtime graph represents the motion of the coconut?
A Accelerati on Acceleration C
time
time
Accelerati on
Acceleratio n
time
time
30.
Diagram 15 shows a boy walking, thrown forward when he accidentally kicked a stone
Diagram 15 Which of the following physics concept is responsible for the boy thrown forward? A Momentum C. Impulse B Inertia D. Energy 31. A Which of the following has the highest net force? C
32.
Diagram 16 shows a tape charts. Every strip has 5 ticks
Length/ cm
Diagram 16
Time/ t
If 50 Hz frequency is used, calculate the acceleration A 20.0 cms-2 C 160.0 cms-2 -2 B 100.0 cms D 200.0 cms-2 -2 E 250.0 cms 33. Which of the velocity-time graph below shows a movement of a car which is slowing down and then stops? velocity A C velocit y
time
tim e velocit
velocit
time
tim e
10
34.
Kasim kicks a stationary ball of mass 1.2 kg with a force of 15 N and the time of impact between his boots and the ball is 0.2 s. Calculate the maximum velocity achieved by the ball. A 2.5 ms-1 C 25.0 ms-1 B 15.0 ms-1 D 30.0 ms-1 E 90.0 ms-1 A coconut falls from a tree of height 2.3 m. Which of the following quantities relating to the coconut remains unchanged during the fall? A The gravitational potential energy of the coconut B The velocity of the coconut. C The acceleration of the coconut. D The displacement of the coconut. The diagram below show the forces acting on a block. Which block experiences the highest net force? A
35.
36.
37.
Between the following statements, which is not true about an object which is moving with constant acceleration? A. The object is moving in a straight line B. No force is acting on the object C. The resultant force on the object is greater than zero D. The resultant force on the object is constant Diagram 17 below shows two vectors a and b.
38.
Diagram 17
11
Which of the following correctly represents the vector addition of the vectors a and b which results in the resultant vector c? A C
39.
Diagram 18 shows two objects being dropped during the moon exploration.
plasticine
feather Diagram 18
Moon surface Which of the is true when both objects were dropped? A. The velocity of plasticine and feather are constant. B. The rate of change of velocity of plasticine and feather are the same. C. The momentum of plasticine and feather are the same. D. The plasticine dropped faster than the feather 40. Diagram 19 shows an aeroplane flying horizontally with increasing velocity.
12
Lift
Thrust
Drag
Diagram 19 Weight Which of the following statement is correct? A Weight > Lift B Lift > Weight Section B (30 marks) Answer all questions 1. Diagram 1 shows a micrometre screw gauge when the jaws are closed.
C D
Drag = Thrust Thrust > Drag
Diagram 1 a) Name the part label R. .. [1 mark] What is the function of the part label R? [1 mark] What is the value of zero error shown by the micrometre above? [1 mark] Identify the sensitivity of the micrometre screw gauge [1 mark]
b)
c)
d)
13
Diagram 2a(i) 2.
Diagram 2a(ii)
Diagram 2a(i) shows a boy pushing a shopping cart at the start of a shopping trip and Diagram 2a(ii) shows the cart at the end of the shopping trip. (a). (i) Define mass. . [1 mark] State whether mass is scalar quantity or a vector quantity. [1 mark] (b) (i) Compare the mass of the cart in Figure 2a(i) and Figure 2a(ii). [1 mark] Which cart would be more difficult to start moving? . [1 mark] Which cart would be more difficult to stop once its moving? .. [1 mark] Based on your answers in b(i)-(iii), state the relationship between mass and the rate of change in motion. [1 mark] .Name the physics concept involved in (b). .. [1 marks]
(ii)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(c)
14
Tanker with 5 small tank Diagram 2b(i) (d)
Tanker with 1 big tank Diagram 2b(ii)
Diagram 2b(i) and Figure 2b(ii) show tankers with the same capacity but built differently. Which tanker is safer to be used? [1 mark]
3.
Diagram 3.1 and 3.2 show two watermelons fall off a table and drop on to surface A and surface B respectively.
Surface A
Surface B
(a). Diagram 3.1 by impulse? What is meant
Diagram 3.2
[1 mark] (b) With reference to Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2, (i) Compare the force on the watermelons that strike on Surface A and Surface B. [1 mark] (ii) . (iii). [1 mark] State the relationship between the force produced in a collision and the time of impact. (c) [1 mark] Mark with a ( ) for the correct statement about the change of momentum of the watermelons in both situations above. The change of momentum of the watermelon in Diagram 3.1 is greater than that of the watermelon in Diagram 3.2. Compare the time of impact of the watermelons on Surface A and Surface B.
15
The change of momentum of the watermelon in Diagram 3.2 is greater than that of the watermelon in Diagram 3.1. The change of momentum of the watermelon in Diagram 3.1 is equal to that of the watermelon in Diagram 3.2. [1 mark] Suggest a suitable material for surface B. [1 mark]
(d)
Diagram 3.3 By referring to the Diagram 3.3, explain how the driver is able to avoid serious injuries when the car stopped suddenly. . . [2 marks] A boy with mass 50 kg climbs up a 2.5 m wall from the ground level and jump down as shown in Diagram 4.
4.
Diagram 4
(a)
(i)
Name the energy gained by the boy before the jump? ................. [ 1 mark ] State the energy change experienced by the boy before the leg hit the ground.
(ii)
16
[ 1 mark] (b) Based on the information given on Diagram 4, calculate (i) the speed of the boy just before his legs touch the ground.
[ 2 marks] (ii) the impulsive force produced when the time of action between his legs and the ground is 0.03 s.
(c)
[ 2 marks ] Impulsive force can caused severe damage. Suggest a method to reduce the impact of the impulsive force in eggs drop competition from a height during a science carnival. Your answer should base on the following criteria (i) The eggs casing . Reason . [ 2 marks] Method for soft landing Reason [ 2 marks]
(ii)
5.
Diagram 5.1 shows a goal keeper catch a ball using a pair of gloves. The ball is stopped within 0.5 s. Diagram 5.2 shows a taut racket string is used to hit a tennis ball. The time taken by the racket to hit the ball is 0.01 s. The ball moves at high velocity.
Diagram 5.1 (a) What is meant by velocity? Diagram 5.2
. [ 1 mark ] 17
(b)
Based on Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2, compare the types of surface used to catch and hit a ball with the time taken. Relate the reaction time and the force to deduce a relevant physics concept. . [5 marks ] Before starting a volleyball match, the ball that will be used must have suitable air pressure. Explain why a low pressured ball is not suitable to be used in volleyball match. . . [4 marks]
(c)
(d)
Diagram 5.3 Diagram 5.3 shows a model of a car. As an engineer, you are given a task to modify the car to be a racing car for a Formula One Grand Prix at Sepang Circuit. Suggest modifications that need to be done on the car so that (i) The car can move faster and stable while it is being driven (ii) The car is comfortable and does not bounce when passes bumpy track (iii) The cars driver is safe if any accident happens. Reason
Modification
18
[10 marks ] END OF QUESTION PAPER Prepared by Jill Peary Raju
Checked by
En Hanapi Ketua Panitia Fizik
Verified by
En Yazi Bujang Ketua Bidang Sains Dan Matematik
19
También podría gustarte
- Final Exam f4 2014Documento21 páginasFinal Exam f4 2014Mohd AzlanAún no hay calificaciones
- Fizik KiDocumento9 páginasFizik KiKiTTyAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Form 4 Modul WAJADocumento14 páginasPhysics Form 4 Modul WAJARamanath RamAún no hay calificaciones
- MODUL 1 FizikDocumento14 páginasMODUL 1 FizikMohd HafizuddinAún no hay calificaciones
- Assessment ChapterDocumento34 páginasAssessment ChapterfazilarazaliAún no hay calificaciones
- Fizik Kertas 1 Ogos 2013 1 Jam 30 MinitDocumento21 páginasFizik Kertas 1 Ogos 2013 1 Jam 30 MinitSue Suraya NazaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Kubong, LimbangDocumento14 páginasSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Kubong, LimbangDuong Han CalebAún no hay calificaciones
- Paper 1 Physics Form4 SBP 2007 Mid YearDocumento19 páginasPaper 1 Physics Form4 SBP 2007 Mid Yearruslawati100% (3)
- Paper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Documento15 páginasPaper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Junaidah Mohamad RamliAún no hay calificaciones
- © Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P) : 1 SulitDocumento17 páginas© Navision (M) Sdn. Bhd. (690640-P) : 1 Sulitcool0311Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective QuestionDocumento17 páginasPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2 Objective Questionqalanis67% (9)
- Physics Y10 Term 2 Exam Paper1Documento14 páginasPhysics Y10 Term 2 Exam Paper1Ezra Loganathan MuniandiAún no hay calificaciones
- Modul 1 f4f5Documento13 páginasModul 1 f4f5Tamil ArasuAún no hay calificaciones
- Modul 1Documento13 páginasModul 1Ms PaulinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Paper 1: Introduction To Physics: Physical Quantity Type of Physical Quantity S.I. UnitDocumento5 páginasPaper 1: Introduction To Physics: Physical Quantity Type of Physical Quantity S.I. UnitLily Suhany MahmoodAún no hay calificaciones
- T-Forces and Motion AssessmentDocumento12 páginasT-Forces and Motion AssessmentGan Hock KiamAún no hay calificaciones
- Test 1 Socrative Review - Velocity - BlankDocumento5 páginasTest 1 Socrative Review - Velocity - Blank양원진Aún no hay calificaciones
- IGCSE Physics ExamDocumento24 páginasIGCSE Physics Examkamalharmoza100% (3)
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Physics Part A: Objective QuestionDocumento8 páginasChapter 1: Introduction To Physics Part A: Objective QuestionMohamad Rizal MukhtarAún no hay calificaciones
- Section ADocumento3 páginasSection ASyah NuriAún no hay calificaciones
- FizikDocumento36 páginasFizikLileng LeeAún no hay calificaciones
- This Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options. Choose The Best Option For Each Question Then Blacken The Correct Space On The Answer Sheet. Answer All QuestionsDocumento8 páginasThis Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options. Choose The Best Option For Each Question Then Blacken The Correct Space On The Answer Sheet. Answer All Questionsjoe zulkefliAún no hay calificaciones
- USTH B1 ExerciceMechanics Part1 QuestionDocumento8 páginasUSTH B1 ExerciceMechanics Part1 QuestionCó Tên KhôngAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 9 Physics QuestionDocumento24 páginasGrade 9 Physics QuestionTsegaye D LemmaAún no hay calificaciones
- PRE-MOCK HPHS-Physics-32025003CS202o2Documento16 páginasPRE-MOCK HPHS-Physics-32025003CS202o2Zubia WaheedAún no hay calificaciones
- Form 4 Physics Standard Is Ed Test 2 2011Documento4 páginasForm 4 Physics Standard Is Ed Test 2 2011ject83Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physics 2019 1st TermDocumento3 páginasPhysics 2019 1st TermsulayajannyAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Cambridge Igcse Year 10 Paper 1Documento18 páginasPhysics Cambridge Igcse Year 10 Paper 1Adibah AliasAún no hay calificaciones
- Physic's Paper 1 Form4-08Documento15 páginasPhysic's Paper 1 Form4-08Salmizam IzamAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Test 2Documento4 páginasPhysics Test 2WeteachAún no hay calificaciones
- Physic Paper 1Documento16 páginasPhysic Paper 1Thana SegarAún no hay calificaciones
- B. Meter: Introductory Physics 1 Test #1 - Unit 1 To 3 Multiply Choices - Answer All QuestionsDocumento7 páginasB. Meter: Introductory Physics 1 Test #1 - Unit 1 To 3 Multiply Choices - Answer All Questionscondoleeza smithAún no hay calificaciones
- Mesl 2019 PDFDocumento10 páginasMesl 2019 PDFSolayao, Jan Marvin J.Aún no hay calificaciones
- SPM 4531 2006 Physics p1 BerjawapanDocumento12 páginasSPM 4531 2006 Physics p1 Berjawapanpss smk selandarAún no hay calificaciones
- 2010 Final Paper (Repaired)Documento15 páginas2010 Final Paper (Repaired)Syed OmerAún no hay calificaciones
- PhysicsDocumento9 páginasPhysicsNaleep GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mid 2nd Term Mathayom 2 ScienceDocumento8 páginasMid 2nd Term Mathayom 2 ScienceAbdullohAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Assignment 1 - FIC1502 - 2021Documento10 páginas1 Assignment 1 - FIC1502 - 2021Tshepiso MaileAún no hay calificaciones
- Section A Answer All QuestionsDocumento7 páginasSection A Answer All QuestionsNAJMILAún no hay calificaciones
- Simple Machine PDFDocumento7 páginasSimple Machine PDFAnonymous 6MSekAxCnZ100% (1)
- MSTE Problem Set 2 - NopassDocumento15 páginasMSTE Problem Set 2 - Nopassminstacey7Aún no hay calificaciones
- FZK Upp2 2011Documento16 páginasFZK Upp2 2011Amalina KamarudinAún no hay calificaciones
- A A PHYSICS MODEL EXAM 2011 Model TwoDocumento9 páginasA A PHYSICS MODEL EXAM 2011 Model TwoKerod MohamedAún no hay calificaciones
- Peperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011Documento17 páginasPeperiksaan Pertengahan Tahun 2011Sue Suraya NazaAún no hay calificaciones
- PhysDocumento10 páginasPhysahmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Ujian Bulanan 1 Fizik Tingkatan 4 2013Documento5 páginasUjian Bulanan 1 Fizik Tingkatan 4 2013Siti Aminah Alwi100% (1)
- 103 F 05 Exam 1Documento7 páginas103 F 05 Exam 1Raufzha AnandaAún no hay calificaciones
- 8c Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento36 páginas8c Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsMunad E Ali100% (1)
- Mathematics Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocumento6 páginasMathematics Surveying and Transportation EngineeringMEGAN MUTAAún no hay calificaciones
- Name: - Form: - Date: - Lesson 1 - Linear Motion A) IntroductionDocumento26 páginasName: - Form: - Date: - Lesson 1 - Linear Motion A) Introductionpallz007Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Paper 1 Form 4Documento21 páginasPhysics Paper 1 Form 4Salmizam Izam0% (1)
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 1 Objective QuestionsDocumento9 páginasPhysics Form 4 Chapter 1 Objective Questionsqalanis100% (2)
- Physics Grade IX Paper I (A) April 2021 AKDocumento10 páginasPhysics Grade IX Paper I (A) April 2021 AKHaseeb MirzaAún no hay calificaciones
- SECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DDocumento17 páginasSECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DNurlailie Md JamilAún no hay calificaciones
- End Sem PaperDocumento13 páginasEnd Sem PaperKasani Tirumala tejaAún no hay calificaciones
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3De EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Calificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2De EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Ujian 1 Sains Form 1 2017Documento8 páginasUjian 1 Sains Form 1 2017Jill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- RPPTB Science Form 5Documento28 páginasRPPTB Science Form 5Jill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminar Kertas 3 Fizik SPMDocumento26 páginasSeminar Kertas 3 Fizik SPMMaZs AmIrulAún no hay calificaciones
- Bahulu's HouseDocumento137 páginasBahulu's Houseaim_nainaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Intro To PhysicsDocumento33 páginas1 Intro To Physicsharshasoni100% (6)
- Ujian Penggal 1 2014 SN p2Documento13 páginasUjian Penggal 1 2014 SN p2Jill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- CH1SCIENTIFICINVESTIGATIONDocumento6 páginasCH1SCIENTIFICINVESTIGATIONAmsyidi AsmidaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bimbingan Malam 2012 Soalan 10Documento8 páginasBimbingan Malam 2012 Soalan 10Jill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Soalan 11 Sains f5Documento8 páginasSoalan 11 Sains f5Jill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Documento17 páginasPhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiAún no hay calificaciones
- Trial Physics 2012Documento11 páginasTrial Physics 2012Jill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics f4 2013Documento29 páginasYearly Lesson Plan Physics f4 2013Jill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics f4 2013 EditedDocumento9 páginasYearly Lesson Plan Physics f4 2013 EditedJill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- 7.2 Ohms Law 09Documento12 páginas7.2 Ohms Law 09Jill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Modul SC GraphDocumento2 páginasModul SC GraphJill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.9 Equilibrium of ForceDocumento4 páginas2.9 Equilibrium of ForceJill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Exercise 1Documento1 páginaExercise 1Elvon EdwardAún no hay calificaciones
- 3.1 PressureDocumento15 páginas3.1 PressureJill Peary RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Lateral Earth PressureDocumento2 páginasLateral Earth PressureLaura HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Soil Structure and FabricDocumento33 páginasSoil Structure and FabricVigknaraja JagathesanAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulation of Soap PDFDocumento4 páginasFormulation of Soap PDFNelson StangAún no hay calificaciones
- Samlerapport DeepWind 2013Documento274 páginasSamlerapport DeepWind 2013jormaeherAún no hay calificaciones
- BirefringenceDocumento9 páginasBirefringenceDoug Bank100% (1)
- O A T A O Oatao: Pen Rchive Oulouse Rchive UverteDocumento16 páginasO A T A O Oatao: Pen Rchive Oulouse Rchive UverteamirulhaqimAún no hay calificaciones
- ICSECM-2017 Chameera UdawatthaDocumento11 páginasICSECM-2017 Chameera UdawatthaSavinda SenevirathneAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 3: Mass Transfer Coefficients: Lecture No. 5Documento3 páginasModule 3: Mass Transfer Coefficients: Lecture No. 5walisyhAún no hay calificaciones
- Mayas Online Mechanics Review ClassDocumento23 páginasMayas Online Mechanics Review ClassVon Andrei MedinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aryabhata Biography: Major WorksDocumento2 páginasAryabhata Biography: Major WorksrajeshAún no hay calificaciones
- Ferroelectricity in HfO2Documento6 páginasFerroelectricity in HfO2Basharat AhmadAún no hay calificaciones
- TGS WW Training PTDocumento220 páginasTGS WW Training PTCleverson Jose Godinho100% (2)
- Fountain: Date: 08-Apr-18Documento20 páginasFountain: Date: 08-Apr-18MikhaelA.RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Active Force on Retaining Wall Supporting Φ Backfill Considering Curvilinear Rupture SurfaceDocumento10 páginasActive Force on Retaining Wall Supporting Φ Backfill Considering Curvilinear Rupture SurfaceLawrence CainAún no hay calificaciones
- Mark Scheme (Results) : October 2017Documento24 páginasMark Scheme (Results) : October 2017Ahmed AmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Exercise 1 PDFDocumento12 páginasExercise 1 PDFAnjali GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fourth Quarter ExaminationDocumento10 páginasFourth Quarter ExaminationJay Ronnie PranadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Asme II Part A (A 36) - 2010Documento6 páginasAsme II Part A (A 36) - 2010Nila GamaAún no hay calificaciones
- NIRMAL-Guidelines-Mini Project or Internship Assessment Report (KEE-354)Documento7 páginasNIRMAL-Guidelines-Mini Project or Internship Assessment Report (KEE-354)anurudhAún no hay calificaciones
- Max - Maier - Applications of Stimulated Raman Scattering PDFDocumento23 páginasMax - Maier - Applications of Stimulated Raman Scattering PDFAkriti SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculating Grease QuantityDocumento2 páginasCalculating Grease Quantitykamal arabAún no hay calificaciones
- BS en Iso 8990 - 1996Documento27 páginasBS en Iso 8990 - 1996danielAún no hay calificaciones
- An Overview of Acoustics and Lighting Design in Architecture Course ManualDocumento67 páginasAn Overview of Acoustics and Lighting Design in Architecture Course ManualDanielle Kiara ZarzosoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter3 PDFDocumento62 páginasChapter3 PDFKensleyTsangAún no hay calificaciones
- Final Exam 2010 SolnDocumento7 páginasFinal Exam 2010 SolnSimon AlmeidaAún no hay calificaciones
- Store CardDocumento4 páginasStore CardAinurrofikBinSuja'iAún no hay calificaciones
- DXX-790-960/1710-2180-65/65-15i/17.5i i-M/M: Electrical Electrical Properties PropertiesDocumento2 páginasDXX-790-960/1710-2180-65/65-15i/17.5i i-M/M: Electrical Electrical Properties Propertiespuljke100% (1)
- SKF 925 Catalogue Bearing PDFDocumento30 páginasSKF 925 Catalogue Bearing PDFIrfan Aditya Dharma100% (1)
- Curved BeamDocumento85 páginasCurved Beamanon_651663167Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ch09 TestbankDocumento61 páginasCh09 Testbanklimpaj35Aún no hay calificaciones