Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Quiz 1
Cargado por
Emy BahariDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Quiz 1
Cargado por
Emy BahariCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
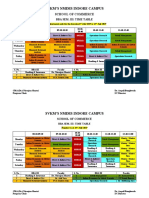
KOLEJ TEKNOLOGI ALPHA PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS (ECO1033)
KOLEJ TEKNOLOGI ALPHA PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS SEMESTER 1 2011/2012
QUIZ 1
NAME MATRIC IC NO. HP NO.
: __________________________________________ : __________________________________________ : __________________________________________ : __________________________________________
INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS: 1) ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS. 2) PLEASE CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER.
1. The fact that human wants cannot be fully satisfied with available resources is called the problem of:
KOLEJ TEKNOLOGI ALPHA PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS (ECO1033)
a. Scarcity. b. Choices. c. Opportunity cost. d. None of above. 1. All of the following can be considered a student's costs of going to college, except: a. Textbooks. b. Tuition and fees. c. Room and board (that costs her about the same as she was paying before entering college). d. The student's time, which can no longer be devoted to earning a salary. 1. Given the decreasing opportunity cost, the Production Possibilities Frontier is: a. Convex. b. Concave. c. Linear. d. Vertical linear. 1. Which of the following is true regarding the Production Possibilities Frontier Model of the economy? a. Any point along the PPF represents an efficient level of production. b. Any point in the area below the PPF represents a combination of production that is not feasible. c. The opportunity cost of producing one more unit of one of the goods represented in the PPF remains the same at any point along the PPF. d. Increases in the resources available for production will cause the PPF to shift towards the origin. 1. Economic growth in the economy can be portrayed in the Production Possibilities Frontier model as a: a. Movement up and to the left along the PPF. b. Shift of the PPF away from the origin. c. Movement down and to the right along the PPF. d. Shift of the PPF towards the origin.
1. Microeconomics is the study of: a. How governments can get the economy out of a recession.
KOLEJ TEKNOLOGI ALPHA PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS (ECO1033)
b. Economy-wide phenomena, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. c. How households and firms make decisions and how they interact in markets. d. How governments can reduce inflation. 1. Which of the following is an example of a normative statement? a. Higher interest rates will cause people to borrow and invest less. b. The government should increase spending during recessions, so that the economy recovers quickly. c. When the price of a good increases, consumers respond by reducing the quantity that they want to purchase of the good. d. Over the past 50 years, the number of women that participate in the labor force has increased dramatically. 1. Factors of production are: a. The coefficients in a production function. b. The characteristics of a market that determine how much is produced. c. The inputs used to produce goods and services. d. The outputs from a production function. 1. An increase in demand means that: a. When the price drops consumers are willing to purchase greater quantities of the good. b. Consumers are willing to purchase greater quantities of the good at any given price. c. When the price rises, consumers are willing to purchase greater quantities of the good. d. Consumers make the price drop by buying greater quantities of the good. 1. If the demand for coffee decreases as income decreases, coffee is: a. A normal good. b. A substitute good. c. A complementary good. d. An inferior good.
1. If good B is a substitute for good A, and the price of good B increases: a. The quantity demanded of good A will decrease. b. The demand for good A will increase.
KOLEJ TEKNOLOGI ALPHA PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS (ECO1033)
c. The price of good A will tend to decrease. d. The quantity demanded of good B will increase. 1. Movement along the demand curve for high rise apartments will be cause by a change in: a. Price of the single-storey link houses. b. Consumers income. c. Consumers taste and preference. d. Price of the high rise apartments. 1. When the price of a good increases:
a. The quantity supplied of the good will increase. b. The quantity supplied of the good will decrease. c. The supply curve of the good will shift to the right. d. The supply curve of the good will shift to the left. 1. All of the following are held to be constant when the supply curve for a product is drawn,
except: a. The price of the product. b. The state of the technology. c. The number of the producers. d. The price of inputs used to make the product.
1. A shift to either the left or right of a supply curve is called: a. A change in quantity demanded. b. A change in supply. c. A change in demand. d. A change in quantity supplied.
1. A new technology that helps firms reduce production costs will cause a:
a. Movement down and to the left along the supply curve. b. Movement up and to the right along the supply curve.
c. Shift to the right of the supply curve. d. Shift to the left of the supply curve. 1. If the price in a market happens to be below equilibrium, there will be a ________ in the market, and the price will tend to ________.
KOLEJ TEKNOLOGI ALPHA PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS (ECO1033)
a. Surplus, Drop. b. Surplus, Rise. c. Shortage, Drop. d. Shortage, Rise. 1. If the price in a market happens to be above equilibrium, there will be a ________ in the market, and the price will tend to ________. a. Surplus, Drop. b. Surplus, Rise. c. Shortage, Drop. d. Shortage, Rise. 1. Suppose the price of corn syrup increases. Given that corn syrup is a major ingredient in the production of soft drinks, how will this affect the equilibrium price and quantity in the soda market? a. The equilibrium price will increase and the equilibrium quantity will decrease. b. The equilibrium price will decrease and the equilibrium quantity will increase. c. Both the equilibrium quantity and price will increase. d. Both the equilibrium quantity and price will decrease. 1. When college students leave town for the semester break, the demand for meals at the local restaurants declines. This results in: a. A decrease in equilibrium price and an increase in quantity. b. An increase in equilibrium price and quantity. c. A decrease in equilibrium price and quantity. d. An increase in equilibrium price, and a decrease in quantity. 1. If a price floor is in place and it is binding, the market will: a. Remain in equilibrium, unaffected by the price floor. b. Experience a shortage. c. Experience a surplus. d. Adjust its equilibrium point toward the price floor.
1. If a price ceiling is in place and it is binding, the market will: a. Remain in equilibrium, unaffected by the price floor. b. Experience a shortage.
KOLEJ TEKNOLOGI ALPHA PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS (ECO1033)
c. Experience a surplus. d. Adjust its equilibrium point toward the price floor. 1. Black markets are associated with: a. Minimum price and resulting product surpluses. b. Minimum price and resulting product shortages. c. Maximum price and resulting product surpluses. d. Maximum price and resulting product shortages.
1. If a tax is imposed on buyers of a good, the ________ curve of the good will shift ________ by the amount of the tax. a. Demand, Upward. b. Demand, Downward. c. Supply, Upward. d. Supply, Downward. 1. If a tax is imposed on sellers of a good, the ________ curve of the good will shift ________ by the amount of the tax. a. Demand, Upward. b. Demand, Downward. c. Supply, Upward. d. Supply, Downward. 1. Subsidies given to vegetable farmers will result in: a. A shift in the supply curve of vegetables. b. A shift in the demand curve for vegetables. c. A movement along the supply curve of vegetables. d. A movement along the demand curve of vegetables. 1. Consumer surplus is the: a. Difference between what the consumer is willing to pay and what the consumer has to pay. b. Surplus of goods the consumer has after consuming all he/she needs from them. c. Excess number of goods consumers purchase over and above what they really need. d. Excess number of units firms produce over and above what consumers want to purchase.
KOLEJ TEKNOLOGI ALPHA PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS (ECO1033)
1. The consumer surplus can be expressed graphically as the area: a. Above the supply curve and below the price. b. Above the supply curve and below the demand curve. c. Below the supply curve and above the horizontal axis. d. Below the demand curve and above the price of the good. 1. The producer surplus can be expressed graphically as the area:
a. Above the supply curve and below the price. b. Above the supply curve and below the demand curve. c. Below the supply curve and above the horizontal axis. d. Below the demand curve and above the price of the good. 1. The producer surplus represents the: a. Production in a market over and above what consumers wish to purchase. b. Difference between the price of the good and the cost to the seller. c. Left over of raw materials and other inputs that firms have after producing the good. d. Left over of the good that remains unsold after the holiday season.
GOOD LUCK
También podría gustarte
- Econ202 Tt1 2012f HellmanDocumento12 páginasEcon202 Tt1 2012f HellmanexamkillerAún no hay calificaciones
- MIT11 203F10 ExamprepDocumento9 páginasMIT11 203F10 Examprepecobalas7Aún no hay calificaciones
- MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Mankiw 7th 1Documento10 páginasMULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Mankiw 7th 1Mỹ HoàiAún no hay calificaciones
- Microeconomics Practical Exercises: Topic 1 - 4 Section 1: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento12 páginasMicroeconomics Practical Exercises: Topic 1 - 4 Section 1: Multiple Choice QuestionsNgoc NguyenAún no hay calificaciones
- University of Santo Tomas Elective Eit / PeDocumento6 páginasUniversity of Santo Tomas Elective Eit / PeBella AdrianaAún no hay calificaciones
- BFI Final Exam Mock 1Documento5 páginasBFI Final Exam Mock 1yenninhchuAún no hay calificaciones
- Quiz 7Documento1 páginaQuiz 7chipcanes32Aún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Quiz 1Documento1 páginaPractice Quiz 1chipcanes32Aún no hay calificaciones
- Half-Yearly Examination Paper 2014 Class Xii Subject: EconomicsDocumento10 páginasHalf-Yearly Examination Paper 2014 Class Xii Subject: EconomicsNisha JainAún no hay calificaciones
- Economic Analysis for Business Decisions QuizDocumento22 páginasEconomic Analysis for Business Decisions Quizravi kangneAún no hay calificaciones
- Answer-Assignment Two, Essentials-Spring 2023Documento4 páginasAnswer-Assignment Two, Essentials-Spring 2023Mostafa ElzanklonyAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem Set 3 - SolutionDocumento10 páginasProblem Set 3 - SolutionlaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Solutions: ECO 100Y Introduction To Economics Midterm Test # 1Documento12 páginasSolutions: ECO 100Y Introduction To Economics Midterm Test # 1examkillerAún no hay calificaciones
- Economics MCQsDocumento168 páginasEconomics MCQsSanjeev Subedi83% (23)
- 經濟學原理一作業三Documento8 páginas經濟學原理一作業三Agus Be PeAún no hay calificaciones
- Economics MCQsDocumento14 páginasEconomics MCQsAsad AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 2 Demand & Supply PDFDocumento6 páginasAssignment 2 Demand & Supply PDFhemantAún no hay calificaciones
- Supply and Demand Problem Sets EconomicsDocumento5 páginasSupply and Demand Problem Sets Economicsjesse jamesAún no hay calificaciones
- 1Documento12 páginas1loctorAún no hay calificaciones
- Shift The Supply Curve To The Right: An Increase in Price Increases RevenueDocumento10 páginasShift The Supply Curve To The Right: An Increase in Price Increases RevenueAhmed Mahmoud AbouzaidAún no hay calificaciones
- Microeconomics Multiple Choice Chapter ReviewDocumento10 páginasMicroeconomics Multiple Choice Chapter ReviewMii AnnAún no hay calificaciones
- RYERSON ECN 104 INTRODUCTORY MICROECONOMICSDocumento19 páginasRYERSON ECN 104 INTRODUCTORY MICROECONOMICSzodiac1b1100% (1)
- Test Sample (Nov2021)Documento7 páginasTest Sample (Nov2021)2021492824Aún no hay calificaciones
- Econ RevisionDocumento6 páginasEcon Revisionelserry.comAún no hay calificaciones
- Economics 100 Quiz 1Documento15 páginasEconomics 100 Quiz 1Ayaz AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Economics Multiple CDocumento20 páginasEconomics Multiple CZuriel Azameti100% (1)
- Pe Final Mocktest - Fow9Documento12 páginasPe Final Mocktest - Fow9wwwpa2005Aún no hay calificaciones
- Review - Part 1Documento12 páginasReview - Part 1K61BF Lê Ngọc Gia HânAún no hay calificaciones
- EconomicsDocumento4 páginasEconomicsjanemarielle100% (2)
- Trial balance quizDocumento4 páginasTrial balance quizNguyen Ho Tu Anh (K16 HCM)Aún no hay calificaciones
- Economics PRICE CHANGE TESTDocumento4 páginasEconomics PRICE CHANGE TESTyiAún no hay calificaciones
- Sample Micro-Macro Questions EnglishDocumento3 páginasSample Micro-Macro Questions EnglishAhmed HajiAún no hay calificaciones
- Fa 2Documento5 páginasFa 2Amit SemwalAún no hay calificaciones
- NUS EC1301 Mid-Term Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento10 páginasNUS EC1301 Mid-Term Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsLiu XinchengAún no hay calificaciones
- M4 App. EconDocumento19 páginasM4 App. EconPIVY IVYAún no hay calificaciones
- NUS EC1301 Mid-Term Exam QuestionsDocumento11 páginasNUS EC1301 Mid-Term Exam QuestionsYin Hau100% (2)
- AP Microeconomics Midterm Exam Practice TestDocumento18 páginasAP Microeconomics Midterm Exam Practice TestKenny Cohen100% (1)
- Tutorial 2 SECTION D (T1 2020)Documento5 páginasTutorial 2 SECTION D (T1 2020)jaiveer gurjarAún no hay calificaciones
- School of Education: City College of TagaytayDocumento3 páginasSchool of Education: City College of TagaytayAmparo Christine Recon-PanganibanAún no hay calificaciones
- Abm Module 3 NewDocumento21 páginasAbm Module 3 NewAiza BelandoAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Economics MCQs With AnswersDocumento32 páginasBasic Economics MCQs With AnswersNasir Nadeem73% (30)
- Practice Economics QuizDocumento9 páginasPractice Economics Quizhadia jawadAún no hay calificaciones
- Mid-Term Exam (With Answers)Documento12 páginasMid-Term Exam (With Answers)Wallace HungAún no hay calificaciones
- Principles of MicroeconomicsDocumento16 páginasPrinciples of MicroeconomicsAnonymous GAulxiI100% (4)
- AP宏观经济新试题2021 答案Documento22 páginasAP宏观经济新试题2021 答案seoyoon1012Aún no hay calificaciones
- EcoDocumento10 páginasEcomainhhs180252Aún no hay calificaciones
- Practice 2 - ECON1010Documento6 páginasPractice 2 - ECON1010veres.tankerAún no hay calificaciones
- ECO 100 Quiz 1 02 2020 Your Name Your Student NumberDocumento12 páginasECO 100 Quiz 1 02 2020 Your Name Your Student NumberbalalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Economic AssignmentDocumento5 páginasEconomic AssignmentAlbamiish Ibnu MohamedAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 4 Elasticity Test and AnswerDocumento13 páginasChapter 4 Elasticity Test and AnswerWendors Wendors100% (3)
- Principles of Economics Practice Exam 2015 QuestionsDocumento6 páginasPrinciples of Economics Practice Exam 2015 Questionsjess100% (1)
- Managerial Economics: Incremental Profit from Customizing InstrumentsDocumento8 páginasManagerial Economics: Incremental Profit from Customizing Instrumentsajeet gautam67% (3)
- Part I: Multiple Choice (60% - 2% Each) - On A Scantron, Clearly Mark The Single Best AnswerDocumento8 páginasPart I: Multiple Choice (60% - 2% Each) - On A Scantron, Clearly Mark The Single Best Answerhyung_jipmAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 4 Activities 1-6Documento10 páginasModule 4 Activities 1-6Daisy Ann Cariaga SaccuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial 3 Answer EconomicsDocumento9 páginasTutorial 3 Answer EconomicsDanial IswandiAún no hay calificaciones
- A level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe EverandA level Economics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsCalificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (1)
- Essentials of Development Economics, Third EditionDe EverandEssentials of Development Economics, Third EditionCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Edit Resume Tomato PurpleDocumento1 páginaEdit Resume Tomato PurpleEmy BahariAún no hay calificaciones
- Edit Cover Letter StolzlDocumento1 páginaEdit Cover Letter StolzlRadwan AlahmhAún no hay calificaciones
- Edit Resume AvenirDocumento2 páginasEdit Resume AvenirAhsan ShahidAún no hay calificaciones
- Beach ResortDocumento130 páginasBeach ResortEmy BahariAún no hay calificaciones
- EXERCISE. Production and CostsDocumento3 páginasEXERCISE. Production and CostsEmy BahariAún no hay calificaciones
- EXERCISE. Production and CostsDocumento3 páginasEXERCISE. Production and CostsEmy BahariAún no hay calificaciones
- Positive and Normative EconomicsDocumento3 páginasPositive and Normative EconomicsEmy BahariAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial 2Documento2 páginasTutorial 2Emy BahariAún no hay calificaciones
- More Unanswered QuestionsDocumento8 páginasMore Unanswered QuestionspermaculturistAún no hay calificaciones
- Week 8Documento2 páginasWeek 8Nikunj D Patel100% (1)
- Economic History of The PhilippinesDocumento4 páginasEconomic History of The PhilippinesClint Agustin M. RoblesAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 1 Business EthicsDocumento21 páginasLesson 1 Business EthicsRiel Marc AliñaboAún no hay calificaciones
- Ec 23Documento1 páginaEc 23Jimuel Sanchez CayabasAún no hay calificaciones
- Macroeconomic Analysis of USA: GDP, Inflation & UnemploymentDocumento2 páginasMacroeconomic Analysis of USA: GDP, Inflation & UnemploymentVISHAL GOYALAún no hay calificaciones
- Five Key Sources of Critical Success FactorsDocumento2 páginasFive Key Sources of Critical Success FactorsHanako ChinatsuAún no hay calificaciones
- EVENT Marketing Generates New BusinessDocumento26 páginasEVENT Marketing Generates New Businesssuruchi100% (1)
- 801 Value Added TaxDocumento4 páginas801 Value Added TaxHarold Cedric Noleal OsorioAún no hay calificaciones
- Machu Picchu ToursDocumento14 páginasMachu Picchu ToursCarmen RosasAún no hay calificaciones
- Fujitsu Case StudyDocumento8 páginasFujitsu Case StudySyaza MohammadAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Activity 1 MRLFJRDDocumento1 página10 Activity 1 MRLFJRDMurielle FajardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Time-Table - BBA 3rd SemesterDocumento2 páginasTime-Table - BBA 3rd SemesterSunny GoyalAún no hay calificaciones
- America Turning Japanese? Global Debt Deflation & Manipulated Asset MarketsDocumento20 páginasAmerica Turning Japanese? Global Debt Deflation & Manipulated Asset Marketsaao5269Aún no hay calificaciones
- Accounting-ABM WorksheetDocumento5 páginasAccounting-ABM WorksheetPrincess AlontoAún no hay calificaciones
- SHASHIKANT SHARMA CVDocumento3 páginasSHASHIKANT SHARMA CVsanamsharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Parag Milk & Namaste India Milk Dairy by Manish Kumar Rajpoot (MBA)Documento17 páginasParag Milk & Namaste India Milk Dairy by Manish Kumar Rajpoot (MBA)Manish Kumar Rajpoot100% (1)
- The World Trade Organiation and World Trade Patterns: Chapter - 40Documento8 páginasThe World Trade Organiation and World Trade Patterns: Chapter - 40Halal BoiAún no hay calificaciones
- Jagath Nissanka,: Experience Key Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocumento2 páginasJagath Nissanka,: Experience Key Roles and ResponsibilitiesJagath NissankaAún no hay calificaciones
- GIDB3647341-Money WorksheetDocumento6 páginasGIDB3647341-Money WorksheetAnonymous GxsqKv85GAún no hay calificaciones
- Tax 2 - Midterm ExamDocumento2 páginasTax 2 - Midterm ExamMichelle MatubisAún no hay calificaciones
- Immelt's Reinvention of GEDocumento5 páginasImmelt's Reinvention of GEbodhi_bg100% (1)
- Marx Alienated LaborDocumento5 páginasMarx Alienated LaborDanielle BenderAún no hay calificaciones
- Indian Automotive Industry Overview and MG Motors PerformanceDocumento51 páginasIndian Automotive Industry Overview and MG Motors PerformanceYatharth Sharma0% (1)
- Customer Perception of Service Quality at Indian Overseas BankDocumento96 páginasCustomer Perception of Service Quality at Indian Overseas BankRenjith K PushpanAún no hay calificaciones
- Signature Global Park 5 Apartment Details and Payment PlansDocumento2 páginasSignature Global Park 5 Apartment Details and Payment Planssanyam ralliAún no hay calificaciones
- IBT-REVIEWERDocumento10 páginasIBT-REVIEWERBrenda CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Ud. Wirastri Jurnal Penerimaan Kas Desember 2015Documento40 páginasUd. Wirastri Jurnal Penerimaan Kas Desember 2015Raihan FatihaAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Ricardian ModelDocumento51 páginas2 Ricardian Modelkeshni_sritharan100% (1)
- Aberdeenshire Council Local Development Plan 2021 - TurriffDocumento9 páginasAberdeenshire Council Local Development Plan 2021 - TurriffMy TurriffAún no hay calificaciones