Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Pressure drop calculation through pipes
Cargado por
Bhala VenksDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Pressure drop calculation through pipes
Cargado por
Bhala VenksCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Pressure drop calculation
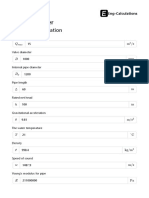
Find out more about flow calculation using GlobalSpec search engine! The most frequently used calculation in fluid dynamics probably is the calculation of pressure drop through a pipe or channel. Also when the difference in pressure is known the same calculation is used to calculate possible flow rate through pipe. This calculator can be used for both laminar and turbulent flow regime. It can calculate pressure drop or flow rate through a pipe including friction losses and local pressure losses calculation. Explanation of used values Q volumetric flow rate G mass flow rate L pipe lenght D pipe diameter kr pipe roughness V velocity A area lambda friction coefficient Re Reynolds number delta boundary layer thickness rho fluid density view table ni kinematic viscosity view table mi dynamic viscosity view table ksi minor loss coefficient p1 pressure on the inlet p2 pressure on the outlet p1-p2 pressure drop Appliance Pressure drop calculator is based on the Bernouly equation for calculation of pressure difference between two points of one stream line, includung pressure losses due to friction and minor losses (like losses in bends, valves etc.). The pressure difference due to change of height is not included in this version of calculator. Also this calculator can be used for flow through pipe calculation when pressure difference is known. Units of measure are both in SI and English system. Pressure drop calculator can be used for calculation of:
volumetric flow - Q mass flow - G pressure on the inlet - p1 pressure on the outlet - p2 pressure drop - dp
velocity - V cross section area - A Reynolds number - Re friction coefficient - lambda boundary layer thickness - delta
For calculation of those values, necessary values for input are:
pipe diameter - D pipe lenght - L pipe roughness - kr kinematic viscosity - ni, or dynamic viscosity mi minor losses coefficient - ksi fluid density - rho
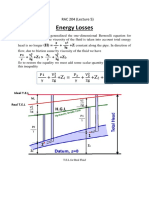
Theory In this calculator well known equations have been used. Here you can find all of them for your review. First of all, pressure drop through the pipe due to friction and local losses can be calculated as follows:
where is: Dp - pressure drop rho - fluid density view table Q - volumetric flow rate D - pipe diameter lambda - friction coefficient L - pipe lenght sum ksi - the sum of minor losses coefficient To calculate mass flow rate following equation is to be used: where is: G - mass flow rate For pressure drop calculation because of friction, viscocity of fluid has to be known. Relation between dynamic and kinematic viscosity is as follows: where is: mi - dynamic viscosity view table mi - kinematic viscosity view table Velocity of flowing fluid is calculated based on the continuity equation: where the cross section of round pipe is:
To find out if the flow is laminar or turbulant, Reynolds number must be calculated: Friction coefficient for laminar flow is: for flow in hidraulicaly smooth pipe (Blasius equation):
for turbulant flow with Re<100 000 (Prandtl equation):
for turbulant flow with Re>100 000 (Karman equation):
The boundary layer thickness (delta) can be calculated based on the Prandtl equation as: and when the boundary layer thickness is bigger than pipe roughness and if the flow is turbulent, than it can be considered as flow in hydraulicaly smooth pipe and Blasius equation is used. Help Although, use of pressure drop calculator is mainly straight forward, some tips might be useful. First of all, select if calculation if for pressure drop, or flow rate through pipe calculation. If calculation is for pressure drop than volumetric or mass flow rate must be entered. Using input values button, you can select which one is to input. For flow rate calculation, pressure drop must be entered, together with either pressure on the inlet, or on the outlet. In both cases lenght, diameter and pipe roughness, viscosity (kinematic or dynamic) and density of flowing fluid must be known. This calculator is also considering, pressure drop due to minor losses. It is calculated, based on the value of minor losses coefficient (ksi), which must be entered. Pressure difference due to change in geodetic height is not in the calculation in this calculator. As a result beside pressure drop or flow rate, this calculator is giving values of velocity, cross section area, friction coefficinet, Reynolds number,
boundary layer thickness and low regime.
También podría gustarte
- Orifice Plate Flow Calculator Pressure DropDocumento6 páginasOrifice Plate Flow Calculator Pressure Droplutfi awnAún no hay calificaciones
- Using The Moody DiagramDocumento6 páginasUsing The Moody DiagramDorothy AmpomahAún no hay calificaciones
- Design of LPG Refigeration System: 1. Copper TubesDocumento20 páginasDesign of LPG Refigeration System: 1. Copper TubesJeevan Landge PatilAún no hay calificaciones
- Hazen WilliamsDocumento2 páginasHazen WilliamssushilkumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Pipeline profile and reservoir water levelsDocumento7 páginasPipeline profile and reservoir water levelsPhyu Mar Thein KyawAún no hay calificaciones
- Design Data HandbookDocumento21 páginasDesign Data HandbookSourabh PradhanAún no hay calificaciones
- The Principle of Temperature Calculation: Rolling LibraryDocumento2 páginasThe Principle of Temperature Calculation: Rolling LibrarycguillermosmAún no hay calificaciones
- Pipe Flow Friction Factor Calculations With Excel Spreadsheets 3 June 15 Final PDFDocumento29 páginasPipe Flow Friction Factor Calculations With Excel Spreadsheets 3 June 15 Final PDFFernando GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- 76-Numericals On Heat exchanger-06-Nov-2019Material - I - 06-Nov-2019 - Heat - Exchanger PDFDocumento39 páginas76-Numericals On Heat exchanger-06-Nov-2019Material - I - 06-Nov-2019 - Heat - Exchanger PDFsiva yandraAún no hay calificaciones
- Piping Hydraulic CalculationDocumento3 páginasPiping Hydraulic Calculationntah84Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fluid Mechanics Tutorial 8C Pumped Piped Systems: Let's Start by Examining The Meaning of Specific Speed of PumpsDocumento17 páginasFluid Mechanics Tutorial 8C Pumped Piped Systems: Let's Start by Examining The Meaning of Specific Speed of Pumps12Aún no hay calificaciones
- Calculation of Flow Rate For Orifice Venturi or Flow Nozzle Meter Si UnitsDocumento18 páginasCalculation of Flow Rate For Orifice Venturi or Flow Nozzle Meter Si UnitsPrakash WarrierAún no hay calificaciones
- Instructional Manual For Cooling Tower (Heat Transfer)Documento7 páginasInstructional Manual For Cooling Tower (Heat Transfer)ramniwas123Aún no hay calificaciones
- Buckling of Columns PDFDocumento11 páginasBuckling of Columns PDFAhmedHatifAún no hay calificaciones
- FTFS Chap20 P032Documento23 páginasFTFS Chap20 P032AbdulAbdulAún no hay calificaciones
- Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Cost EstimationDocumento5 páginasShell and Tube Heat Exchanger Cost EstimationFebry AhmadAún no hay calificaciones
- Heat Exhanger Individual ReportDocumento16 páginasHeat Exhanger Individual ReportMusa OtoAún no hay calificaciones
- Measurement of Condensation Heat Transfer Coefficient Inside A Vertical Tube in The Presence of Noncondensable Gas PDFDocumento11 páginasMeasurement of Condensation Heat Transfer Coefficient Inside A Vertical Tube in The Presence of Noncondensable Gas PDFmintuAún no hay calificaciones
- 5.3 Design of Waste Heat Boiler: (13) : DataDocumento7 páginas5.3 Design of Waste Heat Boiler: (13) : Datamoni beeAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculating Two-Phase Pressure Drop (Editado)Documento8 páginasCalculating Two-Phase Pressure Drop (Editado)anon_37067086Aún no hay calificaciones
- Friction LossesDocumento34 páginasFriction LossesTahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Pressuredrop Calculations by Kern Method SRRDocumento18 páginasPressuredrop Calculations by Kern Method SRRrajeev50588Aún no hay calificaciones
- Orifice MeterDocumento9 páginasOrifice MeterEran LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- AutoPIPE QuickStart - Model Modification - WorkbookDocumento63 páginasAutoPIPE QuickStart - Model Modification - WorkbookJames100% (1)
- Fabrication Strainers Mesh SizingDocumento6 páginasFabrication Strainers Mesh SizingArun GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Gas Line Pressure LossesDocumento4 páginasGas Line Pressure Lossesyash saragiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic T2: Flow in Pipes and Channels AUTUMN 2013Documento30 páginasTopic T2: Flow in Pipes and Channels AUTUMN 2013Bernard PalmerAún no hay calificaciones
- Equivalent MethodDocumento8 páginasEquivalent MethodAjaykumar TiwariAún no hay calificaciones
- Camphor BallsDocumento8 páginasCamphor BallsGurunath EpiliAún no hay calificaciones
- Total Head Calculation of Pipe Line and Pump StationDocumento7 páginasTotal Head Calculation of Pipe Line and Pump Stationthakur_raghabAún no hay calificaciones
- Orifice Sizing PrinciplesDocumento12 páginasOrifice Sizing Principlesjlcheefei9258100% (1)
- 4.1.3 Step-by-Step CalculationDocumento11 páginas4.1.3 Step-by-Step Calculationmohamed nizal100% (1)
- Water Hammer: Values For CalculationDocumento3 páginasWater Hammer: Values For CalculationEng-CalculationsAún no hay calificaciones
- SN74LVC07Documento23 páginasSN74LVC07abcdAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 5 2Documento15 páginasLecture 5 2IbrahimDewaliAún no hay calificaciones
- Heat Exchanger Design OptimizationDocumento27 páginasHeat Exchanger Design OptimizationUsama AkramAún no hay calificaciones
- 5.4.3. Power Requirements For Pumping Liquids: 5.4. Pumps and CompressorsDocumento3 páginas5.4.3. Power Requirements For Pumping Liquids: 5.4. Pumps and Compressorsamir885Aún no hay calificaciones
- Liquid Valve CV CalcDocumento4 páginasLiquid Valve CV Calcamit_kt1973Aún no hay calificaciones
- Compute Time To Drain or Empty A Tank, Pond, or ReservoirDocumento5 páginasCompute Time To Drain or Empty A Tank, Pond, or ReservoirJayakrishnan RadhakrishnanAún no hay calificaciones
- Viscous Pipe Flow GuideDocumento57 páginasViscous Pipe Flow GuidehananAún no hay calificaciones
- Solutions 3 17Documento2 páginasSolutions 3 17EDM MAGIC100% (1)
- Heater Lowers Methanol Temp from 95C to 40CDocumento30 páginasHeater Lowers Methanol Temp from 95C to 40CHamdan ShdAún no hay calificaciones
- Vacuum Systems PDFDocumento12 páginasVacuum Systems PDFSnigdha YadavAún no hay calificaciones
- Appreciation: Fluid Friction TestDocumento10 páginasAppreciation: Fluid Friction TestLuqman Yusof100% (1)
- Calculation of time needed to mix liquids with pitch blade impellersDocumento10 páginasCalculation of time needed to mix liquids with pitch blade impellershadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Pressure Loss - SwitchyardDocumento1 páginaPressure Loss - Switchyardkarthikraja21Aún no hay calificaciones
- Simulation of Distillation For ACETONE-BENZENE-CHLOROFORMDocumento8 páginasSimulation of Distillation For ACETONE-BENZENE-CHLOROFORMfjcgAún no hay calificaciones
- Projectile MotionDocumento11 páginasProjectile MotionRamachandran VenkateshAún no hay calificaciones
- Pressure Vessel-Tank Sizing: Engineer's Aide Reference GuideDocumento27 páginasPressure Vessel-Tank Sizing: Engineer's Aide Reference GuideUsman ArifAún no hay calificaciones
- PRESSURE DROP CALCULATION FOR DRILL WATER PIPEDocumento9 páginasPRESSURE DROP CALCULATION FOR DRILL WATER PIPEdasubhaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Orifice SizingDocumento2 páginasOrifice SizingXheikhKaleemAún no hay calificaciones
- Bilge System DesignDocumento40 páginasBilge System DesignTegar LanangAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedDocumento3 páginasTutorial Topic 2 2020 RevisedTara PillayAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 Calculation Compressed Air System Principal DimensionDocumento16 páginas5 Calculation Compressed Air System Principal DimensionAtandho Gama MagwasyarAún no hay calificaciones
- Compressor SizeDocumento3 páginasCompressor SizeSubhash KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Drawing Autocad 2dDocumento5 páginasDrawing Autocad 2dMuhammad Muzamil MazriAún no hay calificaciones
- Pressure Drop Calculation - Theory: View TableDocumento13 páginasPressure Drop Calculation - Theory: View Tableray_k_917775% (4)
- Pressure Drop CalculationDocumento8 páginasPressure Drop Calculationmazumdar_satyajitAún no hay calificaciones
- Pressure Drop CalculationDocumento13 páginasPressure Drop CalculationknsaravanaAún no hay calificaciones
- ME 311-Fluid MechanicsDocumento2 páginasME 311-Fluid Mechanicssaeed al-zahraniAún no hay calificaciones
- Certificate of Compliance: Certificate Number Report Reference Issue DateDocumento2 páginasCertificate of Compliance: Certificate Number Report Reference Issue DateAob AprilAún no hay calificaciones
- Code-A: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005, Ph. 011-47623456Documento48 páginasCode-A: Aakash Tower, 8, Pusa Road, New Delhi-110005, Ph. 011-47623456Sujit LawareAún no hay calificaciones
- Control Valve Specification SheetDocumento1 páginaControl Valve Specification SheetJuan Krloz CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (States of Matter) - Notes2Documento2 páginasChapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings (States of Matter) - Notes2charan213Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pressure Regulators Selection Guidelines & CriteriaDocumento17 páginasPressure Regulators Selection Guidelines & CriteriaTala RamezaniAún no hay calificaciones
- The Particulate Nature of MatterDocumento15 páginasThe Particulate Nature of Matterabhilasha sharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- ScheduleDocumento2 páginasSchedulecbcyouthygnAún no hay calificaciones
- NFPA 15 SummaryDocumento13 páginasNFPA 15 SummarySam Low100% (2)
- Engineering All in OneDocumento245 páginasEngineering All in OneozchrisAún no hay calificaciones
- Cooling System WA600!6!22272Documento15 páginasCooling System WA600!6!22272Ventsislav VenevAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Sheet BPH 60 250.40 T PDFDocumento3 páginasData Sheet BPH 60 250.40 T PDFzajednosexAún no hay calificaciones
- Pressure Loss Experiment Gunt Hamburg HM 150.29Documento2 páginasPressure Loss Experiment Gunt Hamburg HM 150.29eldwin_dj7216Aún no hay calificaciones
- Egr SystemDocumento5 páginasEgr SystemAbhishek SainiAún no hay calificaciones
- Table 6.1 results of multi-pump test experimentDocumento1 páginaTable 6.1 results of multi-pump test experimentShahruzi MahadzirAún no hay calificaciones
- 41 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamics PDFDocumento5 páginas41 ThermoDynamics ThermoDynamics PDFmozam haqAún no hay calificaciones
- Well Data Sheet: Customer InformationDocumento2 páginasWell Data Sheet: Customer InformationmghareebAún no hay calificaciones
- Assembly Manual PROSLIDE ToboganDocumento59 páginasAssembly Manual PROSLIDE Tobogansilvia caicedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Pipe Sizing ASHRAEDocumento2 páginasPipe Sizing ASHRAESabir Mohamed Abdelhalim100% (2)
- AG 200-800 Series PilotsDocumento13 páginasAG 200-800 Series Pilotstxlucky80Aún no hay calificaciones
- BS Pani Fluid MechDocumento362 páginasBS Pani Fluid MechAnukool VikramAún no hay calificaciones
- Bernoulli Equation ExperimentDocumento1 páginaBernoulli Equation ExperimentMohamed GdAún no hay calificaciones
- 02 Feedstocks & ProductsDocumento135 páginas02 Feedstocks & ProductsciclointermedioAún no hay calificaciones
- Optimize Vertical Lift PerformanceDocumento27 páginasOptimize Vertical Lift PerformanceMira MirzabaevaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bosch 24i RSF Combination Boiler Installation ManualDocumento36 páginasBosch 24i RSF Combination Boiler Installation Manualsliding_doorsAún no hay calificaciones
- P011-0003, Symbols & Legends (3,3)Documento1 páginaP011-0003, Symbols & Legends (3,3)Mubashir fareedAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaporation 2Documento18 páginasEvaporation 2Kuma Gloria100% (1)
- WATER CONTAMINATION OF STEAM TURBINE LUBE OILSDocumento6 páginasWATER CONTAMINATION OF STEAM TURBINE LUBE OILSIlham Surya HadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Filtration Solutions enDocumento12 páginasFiltration Solutions enIon Vasilica BrosuAún no hay calificaciones
- Pressure Regulator of CNG Vehicles: National Standard of The People's Republic of ChinaDocumento9 páginasPressure Regulator of CNG Vehicles: National Standard of The People's Republic of ChinaSarwat Naim SiddiquiAún no hay calificaciones