Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Kornet, Tow & Milan
Cargado por
rgrsantosDescripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Kornet, Tow & Milan
Cargado por
rgrsantosCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
KORNET-E ANTI-ARMOUR GUIDED MISSILE, RUSSIA Kornet E is the name given to the export version of the Russian Kornet
missile system. The system, first shown in 1994, has been developed by the KBP Instrument Design Making Bureau, Tula, Russia and is in production and service with the Russian Army and has been sold to the Syrian Army. Kornet is a third generation system, developed to replace the Fagot and Konkurs missile systems in the Russian Army. It is designed to destroy tanks, including those fitted with explosive reactive armor (ERA), fortifications, entrenched troops as well as small-scale targets. The system can be fitted to a variety of tracked and wheeled vehicles, including the BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicle, as well as serving as a standalone, portable system. The self-propelled Kornet missile system is manufactured by the Volsk Mechanical Plant, Volsk, Russian Federation. It was reported in April 2005 that the Kornet E missile system has been ordered by the government of Eritrea. Greece has purchased 500 examples Kornet - E Anti Tank Guided Missile. Missile The launcher fires Kornet missiles with tandem shaped charge HEAT warheads to defeat tanks fitted with ERA or with high explosive/incendiary (thermobaric effect) warheads, for use against bunkers, fortifications and fire emplacements. Armor penetration for the HEAT warhead is stated to be 1,200mm. Range is 5km. The missile has semi-automatic command-to-line-ofsight (SACLOS) laser beam riding guidance, flying along the line of sight to engage the target head on in a direct attack profile. Launcher The tripod launcher includes optical sight, thermal sight, laying drives, missile launch mechanism and missiles kept in storage and transport containers. The operator uses either optical or thermal sight to detect and track the target. The thermal sight is designated 1PN80 and is produced by the State Institute of Applied Optics (NPO GIPO) of Kazan, Russia. Vehicle Mounts The Kornet anti-tank guided weapon system is mounted on a cross-country, armored chassis based on the BMP-3 infantry fighting vehicle which entered production in the late 1980s and is in service with the Russian Army. BMP-3 is a tracked, armored, amphibious vehicle. It has a 500hp diesel engine, weighs 18.7t and is capable of a maximum speed of 70km/hr and range of 600km. The vehicle is equipped with night vision devices. The self-propelled Kornet missile system has the capability for automatic loading and the simultaneous launching of two missiles at a single target. 16 missiles can be carried. It has a crew of two.
TOW 2 HEAVY ANTI-TANK MISSILE, USA The BGM-71 TOW wire-guided heavy anti-tank missile is produced by Raytheon Systems Company. The weapon is used in anti-armor, anti-bunker, anti-fortification and antiamphibious landing roles. TOW is in service with over 45 armed forces and is integrated on over 15,000 ground, vehicle and helicopter platforms worldwide. The TOW missile system has been in service since 1970 with more than 650,000 missiles produced. Current production versions are: TOW 2A (BGM-71E), which entered production in 1987 with over 118,000 missiles delivered; TOW 2B (BGM-71F), which entered production in 1991 with over 40,000 missiles delivered and is designed to complement rather than replace TOW 2A; TOW 2B Aero; and TOW 2A Bunker Buster. The missiles can be fired from the ground using a tripod-mounted launch tube or installed on vehicles. The TOW missile system can be fitted as a single-tube pedestal mount on military vehicles or as 2-tube or 4-tube under-armor systems on vehicles such as the Improved TOW Vehicle M901, Desert Warrior, Piranha, US Marine Corps LAV, Dardo Hitfist and Bradley M2/M3. TOW Anti-Tank Guided Missile The missile has command to line-of-sight guidance. The weapons operator uses a telescopic sight to view a point on the target and then fires the missile. The missile has a two-stage ATK (Alliant Techsystems) solid propellant rocket motor. The operator continues to view and track the target through the sight. Guidance signals from the guidance computer are trans mitted along two wires, which spool from the back of the missile to the control system on the missile. The Chandler Evans CACS-2 control system uses differential piston type actuators. TOW missile warheads are supplied by Aerojet of Sacramento, California, with production facilities in Socorro, New Mexico. The missile is fitted with a high intensity thermal beacon, which provides a long-wave infrared tracking source and a xenon beacon for short-wave tracking. This dual-tracking system provides increased resistance to electro-optical and infrared countermeasures. TOW 2A Anti-Tank Guided Missile For penetration of tanks protected with explosive reactive armor (ERA), TOW 2A is equipped with a tandem warhead. A small disrupter charge detonates the reactive armor and allows the main shaped charge to penetrate the main armor.
MILAN ANTI-TANK GUIDED MISSILE SYSTEM, EUROPE MILAN is a portable medium-range, anti-tank weapon manufactured by Euromissile, based in Fontenay-aux-Roses in France. Euromissile is a consortium originally set up by AerospatialeMatra of France and DaimlerChrysler Aerospace of Germany, now a subsidiary of the EADS company. "The latest version of MILAN has a new digitized firing post and extended range missile." The missile system activities of Aerospatiale Matra have been merged with Matra BAE Dynamics and Alenia Marconi Systems to form MBDA. The system has also been built under license by Bharat Dynamics in India. The system was developed for the French and German A rmies and over 350,000 missiles and 10,000 launch units have been produced since 1972. MILAN is in service in 41 countries. MILAN 3, armed with a tandem warhead with a new firing post with jam-resistant pulsed-beacon infrared guidance, has been in production since 1996 and has been ordered by France, Cyprus and two other armies. MBDA (EADS Aerospatiale Matra) has proposed a missile system based on the MILAN 3 firing post combined with the Trigat MR missile, to be known as Trigan. Trigan is intended as a replacement for the Trigat MR missile system for the French and German Ministries of Defense, following the withdrawal from the programme of the UK and the Netherlands. MILAN ADT/ER MILAN ADT/ER is the latest version of the missile system with new digitized firing post and new extended range missile. The MILAN ADT firing post has an integrated thermal imager with a video output which allows remote operation. With two missiles, the ADT weighs less than 45kg. Qualification of the ADT firing post is underway and the first guided firing of the missile system took place in May 2006. The MILAN ER missile has a range extended to 3,000m and a new, multi-effect warhead which can penetrate 1,000mm Explosive Reactive Armor (ERA) or Rolled Homogenous Armor (RHA), or more than 3m of reinforced concrete. A direct attack mode has been added as well as improved anti jamming capability. MISSILE
The munition consists of the missile in a waterproof launch tube. MILAN 2 has a single shaped charge warhead for use against very thick and composite armor. MILAN 2T and MILAN 3 missiles are armed with a tandem charge for use against reactive armor. "MILAN ADT has an integrated thermal imager with a video output which allows remote operation." The missile's Artus propulsion system is a dual system supplied by Socit Nationale des Poudres et Explosifs (SNPE) of France, now Eurenco. Eurenco is a company formed from the merger of the explosives and propellants operations of SNPE, Saab and Patria. The first stage burns for 1.5s to eject t he missile from the launcher to a distance of about 3m, and then the second stage burns for 11s giving a speed of over 200m/s and maximum range of 2km for a 12.5s time-of-flight. FIRING POST The firing post consists of a sighting system and a guidance ass embly mounted on a tripod. The infrared localizer measures the angular deviation between the missile and the line of sight to the target. The transmission of guidance data by wire and the new MILAN 3 CCD localizer provide jamming resistance. All existing MILAN firing posts can be easily upgraded to MILAN 3 firing posts, which can fire all MILAN missiles. THERMAL SIGHT The firing post can be equipped with an optional MIRA thermal sight, produced by Thales (formerly Thomson-CSF) Optronique. MIRA has a detection range of 4,000m and field of view of 6 x 3. The mounting bracket is quickly set up without tools or modification to the MILAN firing post. No correlation between the thermal sight and the firing post is necessary. A new-generation thermal sight has been developed for the MILAN 3 firing post, the MILIS from Safran (formerly SAGEM), which has a dual field of view, a detection range of 7km and a recognition range of 2.5km. OPERATION In typical deployment, one squad of two MILAN firing posts can be assigned at company level and three or four squads form a platoon used at regiment or battalion level. The launch crew consists of two: the gunner who carries the firing post and the loader or assistant gunner who carries two missiles. "The launch crew consists of two: the gunner who carries the firing post and the loader who carries two missiles."
The gunner places the sight mark on the base of the target and presses the firing button. The missile is launched from the launch container and the launch tube is ejected to the rear of the launcher. The launcher can then be reloaded. Immediately after launch the fins on the missile open to provide a stabilizing roll to the missile. After the missile is clear of the gunner, the sustainer rocket ignites. The gunner tracks the target simply by maintaining the position of the sight reticle centered on the target during missile flight. During flight the missile is automatically slaved at about 0.5m above the line-of-sight to avoid obstacles. The explosion of the charge occurs at the moment of impact with the target, even at high angles of incidence up to 80. The rate of fire is up to three rounds a minute. Various mounting installations enable MILAN to be used from any vehicle either placed with the tripod on the roof or secured by using a quick-release clamp. Twin turrets have been developed for tracked vehicles allowing the missiles to be fired under armor.
También podría gustarte
- MortarsDocumento12 páginasMortarsAji Wijanarko100% (1)
- CampionDocumento24 páginasCampionJet VissanuAún no hay calificaciones
- 7961 LeslieDocumento22 páginas7961 LesliefortysixetwoAún no hay calificaciones
- LW25mm Bushmaster CannonDocumento2 páginasLW25mm Bushmaster CannonRobert PontissoAún no hay calificaciones
- Composition Document GuideDocumento6 páginasComposition Document GuideGeorge Bailey100% (1)
- Pergolizzi PDFDocumento22 páginasPergolizzi PDFaftetAún no hay calificaciones
- Kestrel TATADocumento4 páginasKestrel TATAAnonymous j7OdBGM100% (1)
- IFV-30 Weapon System: Hard Hitting Power For Infantry Fighting VehiclesDocumento2 páginasIFV-30 Weapon System: Hard Hitting Power For Infantry Fighting VehiclesOsorio LuisAún no hay calificaciones
- Gaav Uav FalcoDocumento2 páginasGaav Uav Falcotomay777Aún no hay calificaciones
- Carl-Gustaf Multi-Purpose Weapon System Product SheetDocumento8 páginasCarl-Gustaf Multi-Purpose Weapon System Product SheetRenganathan V SankaranAún no hay calificaciones
- General Dynamics - Phalanx Close-In Weapon System (Ciws)Documento1 páginaGeneral Dynamics - Phalanx Close-In Weapon System (Ciws)YamveaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vulcano 127Documento2 páginasVulcano 127PPI_PerugiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Trackfire RWS Provides Cutting-Edge Performance for Land and Naval ForcesDocumento8 páginasTrackfire RWS Provides Cutting-Edge Performance for Land and Naval ForcesOsorio Luis100% (1)
- GATR Fact SheetDocumento2 páginasGATR Fact SheetsorinartistuAún no hay calificaciones
- 30herje45t Jetk, Jmpeo4mjpoe4mjpe4omjpe4t5omjop - 40mm Mk44 Bushmaster Cannon PDFDocumento2 páginas30herje45t Jetk, Jmpeo4mjpoe4mjpe4omjpe4t5omjop - 40mm Mk44 Bushmaster Cannon PDFsd_hosseini_88Aún no hay calificaciones
- TM-9-1290-262-10 Aiming CircleDocumento95 páginasTM-9-1290-262-10 Aiming CircleHari IswantoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tank Guns and AmmunitionDocumento27 páginasTank Guns and Ammunitionhaftom gebrehiwot50% (2)
- Catalogo OnlineDocumento22 páginasCatalogo OnlineLuis Gabriel Gomez100% (1)
- Rafael ASPRO-HDocumento2 páginasRafael ASPRO-Hradamantys4371Aún no hay calificaciones
- Dagr LGRDocumento2 páginasDagr LGRtomay777Aún no hay calificaciones
- Carl-Gustaf M4 Training MhowDocumento134 páginasCarl-Gustaf M4 Training Mhowwmsenevirathneuk100% (1)
- Excalibur OverviewDocumento10 páginasExcalibur Overviewjarod437Aún no hay calificaciones
- BAE SYSTEMS MjolnerDocumento4 páginasBAE SYSTEMS Mjolnergun100% (1)
- PGK Precision Artillery KitDocumento2 páginasPGK Precision Artillery KithdslmnAún no hay calificaciones
- ST Engineering Light Infantry WeaponsDocumento12 páginasST Engineering Light Infantry WeaponsMario Lopez100% (1)
- Rooikat 76 PDFDocumento2 páginasRooikat 76 PDFfuckscribAún no hay calificaciones
- DRDC - Defensive Aids Suite TechnologyDocumento60 páginasDRDC - Defensive Aids Suite TechnologyHunter_TothAún no hay calificaciones
- AIFV PumaDocumento2 páginasAIFV PumaMiriam MoralesAún no hay calificaciones
- 105/120/125 MM PELE Firing Results: Dr. Lutz Börngen, Wolfgang SteinDocumento29 páginas105/120/125 MM PELE Firing Results: Dr. Lutz Börngen, Wolfgang SteinRamonAún no hay calificaciones
- 25mm Fact SheetDocumento2 páginas25mm Fact Sheetdangerdan97Aún no hay calificaciones
- Denel Dynamics Product BrochureDocumento36 páginasDenel Dynamics Product BrochureYannis Hadgopoulos100% (1)
- Pressed 1Documento8 páginasPressed 1mjd rAún no hay calificaciones
- 20x102mm Fact SheetDocumento2 páginas20x102mm Fact SheetHossam AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Lav-30 Tow Weapon System: Missile Power For Light Armored VehiclesDocumento2 páginasLav-30 Tow Weapon System: Missile Power For Light Armored VehiclesOsorio LuisAún no hay calificaciones
- CtaDocumento34 páginasCtasmayarcad100% (1)
- Armored Knight ASVDocumento2 páginasArmored Knight ASVmrzcmi2259100% (2)
- Artillery RT180-1 PDFDocumento2 páginasArtillery RT180-1 PDFBazil001Aún no hay calificaciones
- MK90 Propellant Powers HYDRA-70 Rocket MotorDocumento1 páginaMK90 Propellant Powers HYDRA-70 Rocket Motorhdslmn100% (1)
- Rafael TrophyDocumento2 páginasRafael Trophyradamantys4371Aún no hay calificaciones
- Baes 020780Documento12 páginasBaes 020780Bagas Putra Pramuarsa100% (1)
- RBS15 Mk3: Anti-Ship Missile System With Land Attack CapabilityDocumento12 páginasRBS15 Mk3: Anti-Ship Missile System With Land Attack CapabilityMad MinuteAún no hay calificaciones
- Eurenco PropellantDocumento6 páginasEurenco PropellantManish Singh AdhikariAún no hay calificaciones
- 25mm MK2 MPT-SD Multipurpose Tracer-Self DestructDocumento2 páginas25mm MK2 MPT-SD Multipurpose Tracer-Self DestructMF84Aún no hay calificaciones
- 25 MM BushmasterDocumento2 páginas25 MM BushmasterMatthew Moonie HerbertAún no hay calificaciones
- 30x173 - MK46 Mod1 - Sea Evaluation - NAVSEA - 2007 PDFDocumento22 páginas30x173 - MK46 Mod1 - Sea Evaluation - NAVSEA - 2007 PDFAnonymous jIzz7woS6100% (1)
- R400BrochureUSA DagorDocumento2 páginasR400BrochureUSA Dagor陈旭100% (1)
- General Dynamics - MACS M231/M232A1 Modular Artillery Charge SystemDocumento1 páginaGeneral Dynamics - MACS M231/M232A1 Modular Artillery Charge SystemYamvea100% (1)
- Artillery RT180 1Documento2 páginasArtillery RT180 1VINOD KHALSEAún no hay calificaciones
- GRM 20Documento2 páginasGRM 20jakalae5263Aún no hay calificaciones
- Rafael ASPRO-PDocumento2 páginasRafael ASPRO-Pradamantys4371Aún no hay calificaciones
- Hellfire Missile PropulsionDocumento2 páginasHellfire Missile Propulsionsabet100% (3)
- Land Rovers That Fire MissilesDocumento33 páginasLand Rovers That Fire MissilesОстап МещеряковAún no hay calificaciones
- General Dynamics A139 MMGDocumento2 páginasGeneral Dynamics A139 MMGeternal_harpyAún no hay calificaciones
- MOWAG Piranha 3 Brochure GDELSDocumento6 páginasMOWAG Piranha 3 Brochure GDELSRifleman_ron100% (1)
- Starstreak: High Velocity Missile (HVM)Documento2 páginasStarstreak: High Velocity Missile (HVM)adnan putraluhsyAún no hay calificaciones
- Javelin 162 BrochureDocumento2 páginasJavelin 162 Brochurescifidiscovery100% (2)
- Brimstone DataDocumento2 páginasBrimstone Databobmartin00Aún no hay calificaciones
- 120mm FSAPDS Mk-II amn for MBT Arjun defeats tank armourDocumento1 página120mm FSAPDS Mk-II amn for MBT Arjun defeats tank armourHossam AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematical Ideas 13th Edition Miller Test BankDocumento36 páginasMathematical Ideas 13th Edition Miller Test Bankrenteinculpsezkj100% (39)
- Singing of National Anthem in TamilDocumento4 páginasSinging of National Anthem in TamilThavam RatnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Remote Controlled Stabilized Machine Gun PlatformDocumento2 páginasRemote Controlled Stabilized Machine Gun PlatformU Aye KoAún no hay calificaciones
- The Greatest Story Never Told 2018 - 2019Documento149 páginasThe Greatest Story Never Told 2018 - 2019extemporaneous100% (7)
- Newyork Review of Books 8 October 2015Documento60 páginasNewyork Review of Books 8 October 2015Hugo Coelho100% (1)
- Bilal DoaDocumento8 páginasBilal DoaarifAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Kurisa Vs JalandoniDocumento2 páginas3 Kurisa Vs JalandoniRalph FineAccent FragranceAún no hay calificaciones
- PAW Fiction - Tired Old Man (Gary D Ott) - Survival StoryDocumento308 páginasPAW Fiction - Tired Old Man (Gary D Ott) - Survival StoryBruce ArmstrongAún no hay calificaciones
- SkulduggeryDocumento10 páginasSkulduggerylunarhallAún no hay calificaciones
- Albania at War, 1939-1945-Bernd Jürgen FischerDocumento720 páginasAlbania at War, 1939-1945-Bernd Jürgen Fischermeral masterAún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER 28 OUTLINE The Crisis of The Imperial OrderDocumento6 páginasCHAPTER 28 OUTLINE The Crisis of The Imperial OrderRania AbunijailaAún no hay calificaciones
- CW Module 1Documento17 páginasCW Module 1arln mndzAún no hay calificaciones
- Odiseya PDFDocumento170 páginasOdiseya PDFMariam NarimanidzeAún no hay calificaciones
- A Brief History of The UsaDocumento20 páginasA Brief History of The UsaElbert JolioAún no hay calificaciones
- Gabriela SilangDocumento9 páginasGabriela SilangEshaira Morales100% (1)
- A Concise History of Portugal - David Birmingham (Cambridge Concise History)Documento230 páginasA Concise History of Portugal - David Birmingham (Cambridge Concise History)Ronan RyanAún no hay calificaciones
- Oxford University Press - Online Resource Centre - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento4 páginasOxford University Press - Online Resource Centre - Multiple Choice QuestionsRahul GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lighthouse 121312Documento32 páginasLighthouse 121312VCStarAún no hay calificaciones
- NGNL V8Documento203 páginasNGNL V8Zhao Xian75% (4)
- Lista ClintonDocumento427 páginasLista Clintonhilmucor03Aún no hay calificaciones
- CV Jamal Rosi New 2018Documento1 páginaCV Jamal Rosi New 2018berd zainAún no hay calificaciones
- A Princess of Mars by Edgar Rice BurroughsDocumento176 páginasA Princess of Mars by Edgar Rice BurroughsRaphael Bluewolf100% (3)
- AP Syllabus StudentDocumento12 páginasAP Syllabus StudentForrest StarrAún no hay calificaciones
- Opelika Train Depot HistoryDocumento4 páginasOpelika Train Depot HistoryeastalabamaartsAún no hay calificaciones
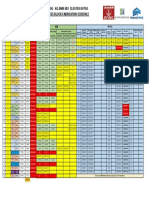
- PT. KARIMUN FPSO FABRICATION SCHEDULEDocumento1 páginaPT. KARIMUN FPSO FABRICATION SCHEDULEMuntaha Aridy SyafitraAún no hay calificaciones
- In General Assembly January Session, A.D. 2020Documento2 páginasIn General Assembly January Session, A.D. 2020Frank MaradiagaAún no hay calificaciones
- No Quarter Prime 4Documento114 páginasNo Quarter Prime 4Saqra Thera100% (2)
- The Future of KurdistanDocumento23 páginasThe Future of KurdistanJerusalem Center for Public AffairsAún no hay calificaciones
- Ultimate Three Kingdoms Guide (Savage Worlds)Documento62 páginasUltimate Three Kingdoms Guide (Savage Worlds)David Martin100% (1)
- Ceylon Light Infantry Volunteers H Company 1882Documento2 páginasCeylon Light Infantry Volunteers H Company 1882Anton EdemaAún no hay calificaciones