Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Teen Pregnancy Causes and Risks
Cargado por
angeline_letranDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Teen Pregnancy Causes and Risks
Cargado por
angeline_letranCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Chapter 2 Review of Related Study
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED STUDY
2.1 TEENAGE PREGNANCY Teenage pregnancy is formally defined as a pregnancy in a young woman who has not reached her 20th birthday when the pregnancy ends, regardless of whether the woman is married or is legally an adult (age 14 to 21, depending on the country). In everyday speech, the speaker is usually referring to unmarried minors who become pregnant unintentionally.
The sexual revolution has ushered in a period in which the average adolescent experiences tremendous pressures to have sexual experiences of all kinds. Filipino teens get a higher exposure to sex from the Internet, magazines, TV shows, movies and other media than decades ago, yet without any corresponding increase in information on how to handle the input. So kids are pretty much left to other kids for opinions and value formation when it comes to sex.
Sexual misinformation is therefore equally shared in the group. Parents at home and teachers in school feel equally inadequate or uneasy to discuss the topic of sex with youngsters. The problem mounts because the barkada (gang) has a more profound influence than parents do and they exert pressure and expect the adolescent to conform to the rest of them.
In fact, female adolescents whose friends engage in sexual behavior were found to be more likely to do the same compared to those who do not associate with such peers. If the teen perceives her peers to look negatively at premarital sex, she was more likely to start sex at a later age.
Teenage Pregnancy: End of the road or Start of a New Life
Chapter 2 Review of Related Study
NUMBERS
Statistics in the United States show that each year, almost 1 million teenage women10 percent of all women aged 15-19 and 19 percent of those who have had sexual intercourse become pregnant and one-fourth of teenage mothers have a second child within two years of their first.
In the Philippines, according to the 2002 Young Adult Fertility and Sexuality Study by the University of the Philippines Population Institute (Uppi) and the Demographic Research and Development Foundation, 26 percent of our Filipino youth nationwide from ages 15 to 25 admitted to having a premarital sex experience. Whats worse is that 38 percent of our youth are already in a live-in arrangement.
The 1998 National Demographic and Health Survey (NDHS) reveals that 3.6 million of our teenagers (thats a whopping 5.2 percent of our population!) got pregnant. In 92 percent of these teens, the pregnancy was unplanned, and the majority, 78 percent, did not even use contraceptives the first time they had sex. Many of the youth are clueless that even on a single intercourse, they could wind up pregnant.
2.2 CAUSE OF EARLY PREGNANCY
In some societies, early marriage and traditional gender roles are important factors in the rate of teenage pregnancy. For example, in some sub-Saharan African countries, early pregnancy is often seen as a blessing because it is proof of the young woman's fertility. In the Indian subcontinent, early marriage and pregnancy is more common in traditional rural communities compared to the rate in cities. The lack of education on safe sex, whether its from parents, Teenage Pregnancy: End of the road or Start of a New Life
Chapter 2 Review of Related Study
schools, or otherwise, is a cause of teenage pregnancy. Many teenagers are not taught about methods of birth control and how to deal with peers who pressure them into having sex before they are ready. Many pregnant teenagers do not have any cognition of the central facts of sexuality. Some teens have said to be pressured into having sex with their boyfriend when the teen was young and yet no one had taught these teens how to deal with this pressure or to say "no". 2.2.1 SEXUALITY According to information available from the Guttmacher Institute, sex by age 20 is the normal age across the world, and countries with low levels of adolescent pregnancy accept sexual relationships among teenagers and provide comprehensive and balanced information about sexuality 2.2.2 CONTRACEPTION Adolescents may lack knowledge of, or access to, conventional methods of preventing pregnancy, as they may be too embarrassed or frightened to seek such information. Contraception for teenagers presents a huge challenge for the clinician. In 1998, the government set a target to halve the under-18 pregnancy rate by 2010. The Teenage Pregnancy Strategy (TPS) was established to achieve this. The pregnancy rate in this group, although falling, rose slightly in 2007, to 41.7 per 1000 women.
2.2.3 AGE DISCREPANCY IN RELATIONSHIPS According to the conservative lobbying organization Family Research Council, studies in the US indicate that age discrepancy between the teenage girls and the men who impregnate them is Teenage Pregnancy: End of the road or Start of a New Life
Chapter 2 Review of Related Study
an important contributing factor. Teenage girls in relationships with older boys, and in particular with adult men, are more likely to become pregnant than teenage girls in relationships with boys their own age. They are also more likely to carry the baby to term rather than have an abortion. A review of California's 1990 vital statistics found that men older than high school age fathered 77 percent of all births to high school-aged girls (ages 1618), and 51 percent of births to junior high school-aged girls (15 and younger). Men over age 25 fathered twice as many children of teenage mothers than boys under age 18, and men over age 20 fathered five times as many children of junior high school-aged girls as did junior high school-aged boys. 2.2.4 SEXUAL ABUSE Studies have found that between 11 and 20 percent of pregnancies in teenagers are a direct result of rape, while about 60 percent of teenage mothers had unwanted sexual experiences preceding their pregnancy. Before age 15, a majority of first-intercourse experiences among females are reported to be non-voluntary; the Guttmacher Institute found that 60 percent of girls who had sex before age 15 were coerced by males who on average were six years their senior. One in five teenage fathers admitted to forcing girls to have sex with them. 2.2.5 DATING VIOLENCE Studies have indicated that adolescent girls are often in abusive relationships at the time of their conceiving. They have also reported that knowledge of their pregnancy has often intensified violent and controlling behaviors on part of their boyfriends. Women under age 18 are twice as likely to be beaten by their child's father than women over age 18. 2.2.6 SOCIOECONOMIC FACTORS Teenage pregnancy has been defined predominantly within the research field and among social agencies as a social problem. A hospital-based cohort study was undertaken over 4 months Teenage Pregnancy: End of the road or Start of a New Life
Chapter 2 Review of Related Study
10
among women admitted to a rural hospital in West Bengal. The study cohort consisted of teenage mothers between 1519 years old and a control cohort of mothers between 2024 years old. Data included demographic variables, available medical records, and complications viz. anemia, preterm delivery, and low birth weight. Anemia was defined as a hemoglobin level below 10 gm% during the last trimester of pregnancy, preterm delivery was defined as occurring within 37 weeks of gestation, and low birth weight was defined as babies weighing less than 2500 grams at birth. 2.2.7 CHILDHOOD ENVIRONMENT Women exposed to abuse, domestic violence, and family strife in childhood are more likely to become pregnant as teenagers, and the risk of becoming pregnant as a teenager increases with the number of adverse childhood experiences. According to a 2004 study, one-third of teenage pregnancies could be prevented by eliminating exposure to abuse, violence, and family strife. 2.2.8 MEDIA INFLUENCE A study conducted in 2006 found that adolescents who were more exposed to sexuality in the media were also more likely to engage in sexual activity themselves.
2.3 RISKS OF EARLY PREGNANCY
There are many reasons teen pregnancies should be avoided. Heres a low down on the facts:
Teenage Pregnancy: End of the road or Start of a New Life
Chapter 2 Review of Related Study
11
RISK FOR MALNUTRITION
Teenage mothers tend to have poor eating habits and are less likely to daily multivitamins to maintain adequate nutrition during
take
recommended
pregnancy. They are also more likely
to smoke, drink or take drugs during pregnancy, which can cause health problems for the baby.
RISK FOR INADEQUATE PRENATAL CARE
Teenage mothers are less likely to seek regular prenatal care which is monitoring the growth of the fetus; keeping the mothers weight in check; mother on nutrition and how she should take care of pregnancy. According to the American Medical herself to
essential and ensure advising a
for the
healthy
Association, babies born to women who do
not have regular prenatal care are 4 times more likely to die before the age of 1 year.
RISK FOR ABORTION
Unplanned pregnancies lead to a higher rate of abortions. In the United
States, nearly 4 in 10
teen pregnancies (excluding those ending in miscarriages) are terminated by abortion. There were about 274,000 abortions among teens in 1996.
In the Philippines, although abortion is illegal, it would shock you to know that we even have a higher abortion rate (25/1,000 women) compared to the (23/1,000 women). For sure, there are United States where abortion is legal
more abortions that happen in our country that are
not even reported. Backdoor abortions are resorted to with untrained hilots with questionable sterility procedures, increasing the possibility for tetanus poisoning and other complications. Teenage Pregnancy: End of the road or Start of a New Life
Chapter 2 Review of Related Study
12
RISK FOR FETAL DEATHS
Statistics of the Department of Health show that fetal deaths are more
likely to happen to
young mothers, and that babies born by them are likely to have low birth weight.
RISK FOR ACQUIRING CERVICAL CANCER The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a sexually-transmitted, wart-forming virus that has been implicated in causing cancer of the cervix. This is the most common secondary to breast cancer. Women who are at who engage in sex before 18, have a cancer in women
increased risk for acquiring this are those
pregnancy at or younger than 18, or have had at
least 5 sexual partners, or have had a partner with at least 5 sexual partners.
If you start sex at an early age, you have a higher likelihood of going sexual partners before you settle down, thus increasing your virus and acquiring cervical cancer. The men can get certainly pass it on to their partners, thus something you would want to gift test women (HPV Using the
through
several
exposure to acquiring the
genital warts from this virus and can
increasing her risk for cervical cancer. Is that
to your wife with on your honeymoon? There is a way to
Digene test) but no test for the man so you cant know if you have it.
condom does not confer protection against acquiring this virus since the condom
cannot cover the testes where the warts can grow and proliferate.
Teenage Pregnancy: End of the road or Start of a New Life
También podría gustarte
- Review of Literature Teenage Pregnancy StatisticsDocumento10 páginasReview of Literature Teenage Pregnancy StatisticsDy Ju Arug ALAún no hay calificaciones
- All Chapter and AppendicesDocumento53 páginasAll Chapter and AppendicesLily SaturnAún no hay calificaciones
- Teenage PregDocumento19 páginasTeenage PregJefferson Beralde100% (1)
- Research Paper-CHAPTER IIDocumento5 páginasResearch Paper-CHAPTER IIkcthon100% (2)
- Status of Teenage PregnancyDocumento20 páginasStatus of Teenage PregnancyCristenAún no hay calificaciones
- Teenage Pregnancy: Effects and Coping StrategiesDocumento10 páginasTeenage Pregnancy: Effects and Coping Strategiesanthony ken jimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 Review of Related Literature ADocumento14 páginasChapter 2 Review of Related Literature ANicole CariasAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1Documento10 páginasChapter 1Reynel Torres CabilbilAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1Documento4 páginasChapter 1Faisal Tuazon IIAún no hay calificaciones
- By Galingan, Daniela B.: Effects of Teenage Pregnancy On The Academic Performance of GirlsDocumento11 páginasBy Galingan, Daniela B.: Effects of Teenage Pregnancy On The Academic Performance of GirlsDaniela Galingan75% (4)
- Factors Contributing to Teenage PregnancyDocumento4 páginasFactors Contributing to Teenage PregnancyRonald Pacquiao MacaseroAún no hay calificaciones
- Teenage Pregnancy Thesis - 01Documento15 páginasTeenage Pregnancy Thesis - 01Jacob Christian75% (44)
- CHAPTER 1 5 Teenage PregnancyDocumento33 páginasCHAPTER 1 5 Teenage PregnancyRainer Mostar67% (3)
- Pre-teen and Teenage Pregnancy: a 21st century realityDe EverandPre-teen and Teenage Pregnancy: a 21st century realityCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (3)
- The Perceptions of Olfu Shs Students Towards The Rising Number of Teenage PregnancyDocumento28 páginasThe Perceptions of Olfu Shs Students Towards The Rising Number of Teenage Pregnancysanshai sabado67% (3)
- Awareness in Teenage PregnancyDocumento24 páginasAwareness in Teenage PregnancyEdwardJohnG.CalubII50% (4)
- The Problem and Its BackgroundDocumento49 páginasThe Problem and Its BackgroundJamie Haravata100% (3)
- Awareness in Teenage PregnancyDocumento7 páginasAwareness in Teenage PregnancyEdwardJohnG.CalubIIAún no hay calificaciones
- RESEARCH CHAPTER 1 AND 2 FinalDocumento36 páginasRESEARCH CHAPTER 1 AND 2 Finaliamthesally yangco100% (1)
- Background of The StudyDocumento3 páginasBackground of The StudyKeena Joy Awisan - Pinas87% (23)
- Thesis Chapter 1Documento8 páginasThesis Chapter 1Chrisly Guadayo100% (2)
- Chapter 2 For Final PrintingDocumento23 páginasChapter 2 For Final PrintingfreyAún no hay calificaciones
- CONTENTDocumento80 páginasCONTENTChristian Sabit100% (3)
- Teen Pregnancy Research Paper.Documento11 páginasTeen Pregnancy Research Paper.Emily Owen63% (8)
- Parents' Perception On Teenage Pregnancy: A Qualitative ResearchDocumento15 páginasParents' Perception On Teenage Pregnancy: A Qualitative ResearchErica Mae Rivarez100% (1)
- Teenage Pregnancy Experiences in BuugDocumento9 páginasTeenage Pregnancy Experiences in BuugBella Marquez100% (3)
- Teen Pregnancy & Poverty CorrelationDocumento3 páginasTeen Pregnancy & Poverty CorrelationAnne Margareth Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Teenage Pregnancy Chapter 1Documento2 páginasTeenage Pregnancy Chapter 1KRIZZEL CATAMINAún no hay calificaciones
- Sample Research About Teenage Pregnancy - NEUDocumento53 páginasSample Research About Teenage Pregnancy - NEUAndy Lalu100% (3)
- Chapter 2 by Ivy and RacelDocumento15 páginasChapter 2 by Ivy and RacelKarl DitanAún no hay calificaciones
- Teen Pregnancy PerceptionsDocumento28 páginasTeen Pregnancy PerceptionsArman Aldana Alibudbud100% (1)
- Project Based Learning Part IIDocumento21 páginasProject Based Learning Part IIcrismedionaAún no hay calificaciones
- Teenage Pregnancy Study in The PhilippinesDocumento9 páginasTeenage Pregnancy Study in The PhilippinesLucky Enriquez100% (4)
- Effects of Early Pregnancy To StudentsDocumento30 páginasEffects of Early Pregnancy To Studentsrejenkaye_0871% (7)
- Students' Perceptions of Teenage PregnancyDocumento8 páginasStudents' Perceptions of Teenage PregnancyKris Mea Mondelo Maca50% (2)
- Teenage PregnancyDocumento19 páginasTeenage PregnancyJai-JaiAdalid100% (1)
- Teenage Pregnancy: Causes and Theoretical FrameworksDocumento38 páginasTeenage Pregnancy: Causes and Theoretical FrameworksAmaya Ladiwan100% (2)
- Final Research ProposalDocumento10 páginasFinal Research ProposalNhaliana Keil Ebajo100% (3)
- Chapter 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ADocumento14 páginasChapter 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ARhen Phol Jay Ventura100% (3)
- Impact of Teenage Pregnancy On Academic Performance of StudentsDocumento42 páginasImpact of Teenage Pregnancy On Academic Performance of StudentsCielo Montecillo100% (1)
- Teen Pregnancy's Impact on EducationDocumento25 páginasTeen Pregnancy's Impact on EducationKian AwilAún no hay calificaciones
- Teenage PregnancyDocumento12 páginasTeenage PregnancyJoemel Baui85% (13)
- Perception of Grade 11 Senior High Schoo PDFDocumento30 páginasPerception of Grade 11 Senior High Schoo PDFGlamorius Enigma0% (1)
- Research Teenage PregnancyDocumento151 páginasResearch Teenage Pregnancyfronda kim clester100% (1)
- Teen Pregnancy's Impact on EducationDocumento22 páginasTeen Pregnancy's Impact on EducationYan ŸanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter IDocumento38 páginasChapter ILouresa Mae TAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1Documento5 páginasChapter 1Kat Sajo50% (2)
- RRL Local and ForeignDocumento13 páginasRRL Local and ForeignDick Jefferson Ocampo Pating100% (1)
- Teenage PregnancyDocumento15 páginasTeenage PregnancyEleasha Baracena100% (2)
- Defense Powerpoint 1-3Documento96 páginasDefense Powerpoint 1-3Rose Dacles90% (20)
- Teenage Pregnancy 3Documento10 páginasTeenage Pregnancy 3Janssene ArambuloAún no hay calificaciones
- University of Perpetual Help System Dalta: Effects of Teenage Pregnancy On The Academic Performance of StudentsDocumento4 páginasUniversity of Perpetual Help System Dalta: Effects of Teenage Pregnancy On The Academic Performance of StudentsKyle Castil100% (1)
- Impact of Early Pregnancy on SocietyDocumento38 páginasImpact of Early Pregnancy on SocietyJD VergaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Review Related Studies Related To Teenage Pregnancy (Foreign)Documento44 páginasReview Related Studies Related To Teenage Pregnancy (Foreign)ruth ann solitarioAún no hay calificaciones
- Practical Research 1 Group2Documento12 páginasPractical Research 1 Group2Ron Marc Maranan78% (9)
- Students Perception On Teenage Pregnancy Among Senior HighDocumento12 páginasStudents Perception On Teenage Pregnancy Among Senior HighClaire CabusasAún no hay calificaciones
- The Impact of Teenage Pregnancy On Formal Education of TeenagersDocumento15 páginasThe Impact of Teenage Pregnancy On Formal Education of TeenagersPhred Woko67% (3)
- Aaa SN PsycDocumento2 páginasAaa SN Psyckingawesome21Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1Documento10 páginasChapter 1Jonathan Delos Reyes100% (1)
- Midterm Examination in Purposive Communication: Name: Philipp Louie G. Cabarrubias Year/Section: BSMT-1 GolfDocumento4 páginasMidterm Examination in Purposive Communication: Name: Philipp Louie G. Cabarrubias Year/Section: BSMT-1 GolfYoj EscarioAún no hay calificaciones
- Crisis Management Covid 19Documento22 páginasCrisis Management Covid 19jon elleAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap 9 The Health Care Delivery SystemDocumento26 páginasChap 9 The Health Care Delivery Systemjocelyn bernardoAún no hay calificaciones
- New Patient History FormDocumento6 páginasNew Patient History Formعبدالله الكافAún no hay calificaciones
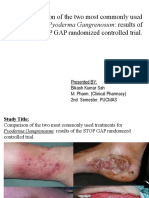
- Pyoderma GangrenosumDocumento18 páginasPyoderma GangrenosumBikash SahAún no hay calificaciones
- Fall Prevention Using TelemonitoringDocumento14 páginasFall Prevention Using Telemonitoringapi-458433381Aún no hay calificaciones
- Hazard Map of Xavier University Main Campus: Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction Mini Task 2Documento5 páginasHazard Map of Xavier University Main Campus: Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction Mini Task 2Princess MarieAún no hay calificaciones
- Review On Nature of Inter Display Between Covid 19 and Systemic DiseaseDocumento9 páginasReview On Nature of Inter Display Between Covid 19 and Systemic DiseaseKhalid NAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Impact On Maternal and Infant Mortality in The United States.Documento7 páginasNursing Impact On Maternal and Infant Mortality in The United States.boniface mogisoAún no hay calificaciones
- Russell BlaylockDocumento3 páginasRussell BlaylockFer TenerifeAún no hay calificaciones
- Musictherapy in Dental Medicine: Dr. Gabriela Iorgulescu, MDD, Ma, Ba, PHDDocumento6 páginasMusictherapy in Dental Medicine: Dr. Gabriela Iorgulescu, MDD, Ma, Ba, PHDMarco Antonio García LunaAún no hay calificaciones
- CHP 1 Worksheet SPRG 18Documento3 páginasCHP 1 Worksheet SPRG 18Gregory ChildressAún no hay calificaciones
- Limitations in Forensic Odontology: Eview RticleDocumento3 páginasLimitations in Forensic Odontology: Eview RticleCikw KuzhaAún no hay calificaciones
- 100837-26 SentieroAdvanced SOH100360 April 2022 EN WebDocumento12 páginas100837-26 SentieroAdvanced SOH100360 April 2022 EN Webrodrigo rodriguez pachonAún no hay calificaciones
- Clostridium BotulinumDocumento37 páginasClostridium Botulinumjoevani_007Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mindsets Matter: A New Framework For Harnessing The Placebo Effect in Modern MedicineDocumento24 páginasMindsets Matter: A New Framework For Harnessing The Placebo Effect in Modern MedicineΑποστολος ΜιχαηλιδηςAún no hay calificaciones
- Code Alert SystemDocumento9 páginasCode Alert SystemSam Tagarda100% (1)
- Dr. H. Pernodjo Dahlan SP.S (K)Documento20 páginasDr. H. Pernodjo Dahlan SP.S (K)hhamiemAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction RHDDocumento5 páginasIntroduction RHDapriellejoyjovenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Informatics 453X Assessment 1 Foundations of HealthDocumento3 páginasNursing Informatics 453X Assessment 1 Foundations of Healthjames mwangiAún no hay calificaciones
- Newborn ResuscitationDocumento57 páginasNewborn ResuscitationmateenAún no hay calificaciones
- Case 3Documento18 páginasCase 3alwaysbeclosing52Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sample Legal Letter of Notice To Principles and School NursesDocumento2 páginasSample Legal Letter of Notice To Principles and School NursesJimUKAún no hay calificaciones
- NMJ Special OncologyDocumento24 páginasNMJ Special OncologyMalcolm LeeAún no hay calificaciones
- To Whom It May ConcernDocumento2 páginasTo Whom It May ConcernIrina PapucAún no hay calificaciones
- EDTA IV and Oral Chelation ProtocolDocumento10 páginasEDTA IV and Oral Chelation ProtocolAla MakotaAún no hay calificaciones
- Igims Directory PDFDocumento28 páginasIgims Directory PDFBambam KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- CISF SCREENING GUIDELINES PRESENTATION - TO BE FOLLOWED BY CISF SECURITY STAFF FOR PASSENGERS WITH DISABILITIES AT INDIAN AIRPORTS - Cisf PPT FinalDocumento36 páginasCISF SCREENING GUIDELINES PRESENTATION - TO BE FOLLOWED BY CISF SECURITY STAFF FOR PASSENGERS WITH DISABILITIES AT INDIAN AIRPORTS - Cisf PPT FinalDisability Rights Alliance100% (1)
- The National Academies PressDocumento203 páginasThe National Academies PressGleiciane SoaresAún no hay calificaciones
- Telepharmacy and Home Delivery Program in SpainDocumento4 páginasTelepharmacy and Home Delivery Program in SpainAthenaeum Scientific PublishersAún no hay calificaciones
- 3D Printing ScriptDocumento2 páginas3D Printing Scriptahmet çelikAún no hay calificaciones