Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
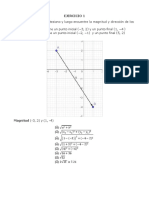
Operaciones Con Vectores
Cargado por
reloj zaachilaTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Operaciones Con Vectores
Cargado por
reloj zaachilaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
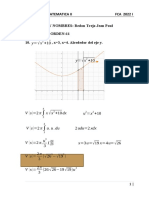
Nombre: Suany Jesamin González Ríos
Matricula: 142433
Grupo: k090
Materia: GEOMETRÍA ANALÍTICA
Unidad 3. Punto y recta en tres dimensiones
Docente: Dr. Ricardo Pérez Águila
Actividad de aprendizaje 2.- Operaciones con Ventores
Oaxaca de Juárez, Oaxaca a 25 de abril de 2022.
CALCULE LAS MAGNITUDES Y LAS DIRECCIONES DE LOS VECTORES
a) (2,2) FORMULA: |v|= √ x 2+ y ² y
Ɵ = tan−1
|v|= √ 22+ 2²
x
|v|= √ 4 +4 2
Ɵ = tan−1
2
|v|= √ 8
Ɵ = tan−1 1
|v|= 2.828
b) (2,2√ 3) FORMULA: |v|= √ x 2+ y 2
√
|v|= 22+ 2(√ 3)²
Ɵ = tan−1
y
x
|v|= √ 2 + 2(1.73)²
2
|v|= √ 22+ 3.46 ² 2√ 3
Ɵ = tan−1
2
|v|= √ 4 +11.97
2(1.73)
|v|= √ 15.97 Ɵ = tan−1
2
|v|= 3.99
3.46
Ɵ = tan−1
2
Ɵ = tan−1 1.73
c) (-3,-3) FORMULA: |v|= √ x + y ²
2
|v|= √ (−3)2 +(−3)² y
Ɵ = tan−1
|v|= √ 9+9 x
|v|= √ 18 −3
Ɵ = tan−1
−3
|v|= 4.242
Ɵ = tan−1 1
ENCUENTRE EL COSENO DEL ANGULO ENTRE LOS VECTORES
U= 2i +3j
V= -7i + j
|U|= √ x 2+ y ² |V|= √ x 2+ y ²
U.V = (U₁*V₁+U₂*V₂)
|U|= √ 22+ 3 ² |V|= √ −72 +1 ²
U.V = (2 * (-7)) + (3 * 1)
U.V = - 14 +3 |U|= √ 4 +9 |V|= √ 4 9+1
U.V = -11 |U|= √ 13 |V|= √ 50
|U|= 3.60 |V|= 7.07
U.V
Cos Ɵ =
|U||V | Ɵ = 64.3990
−11
Cos Ɵ =
3.60∗7.07
−11
Cos Ɵ =
25.452
Cos Ɵ = - 0.4321
MUESTRE QUE LOS VECTORES U=3i + 4j Y V= 4i + 3j SON ORTOGONALES:
U.V = U₁ * V₁ + U₂ * V₂
U.V = (3 * 4) + (4 * 3)
U.V = 12 + 12
U.V = 24
POR LO TANTO NO ES ORTOGONAL
MUESTRE QUE LOS VECTORES U=(2,-3) Y V= (-4,6) SON PARALELOS
U.V = U₁ * V₁ + U₂ * V₂ |U|= √ x 2+ y ² |V|= √ x 2+ y ²
U.V = 2* (-4) + (-3) * 6
|U|= √ 22+(−3) ² |V|= √ −4 2 +6 ²
U.V = -8 + (-18)
|U|= √ 4 +9 |V|= √ 16+36
U.V= -26
|U|= √ 13 |V|= √ 5 2
|U|= 3.60 |V|= 7.21
U.V
Ɵ =cos−1 ( )
|U||V |
−26
Ɵ =cos−1 ( )
(3.60)(7.21) SI SON VECTORES PARALELOS
−26
Ɵ =cos−1 ( )
25.956
Ɵ =cos−1 (−1)
Ɵ = 0°
SEA V= (1,3,-2). ENCUENTRE LA MAGNITUD DE V
|V| = √ x 2+ y 2 + z ²
|V| = 3.7416
|V| = √ 12+ 32+(−2)²
|V| = √ 1+9+ 4
|V| = √ 14
ENCUENTRE UN VECTOR UNITARIO QUE TENGA LA MISMA DIRECCION QUE
V=(2,4,-3)
|V| = √ x 2+ y 2 + z ²
V |V| = √ 22+ 4 2+(−3)²
U=
¿ V ∨¿ ¿ |V| = √ 4 +16+9
2, 4 ,−3
U= |V| = √ 29
√ 29
|V|= 5.38
2 4 −3
U= , ,
√29 √29 √ 29
2 4 −3
U= , ,
5.38 5.38 5.38
BIBLIOGRAFIA.
* Stewart, J. (1999). “Geometría analítica tridimensional y vectores” en Cálculo
trascendentes tempranas. México Thompson Editores, pp. 668; 675; 689-690.
* Zill, D. (2001). “Vectores y el espacio tridimensional” en Cálculo con geometría analítica.
México Grupo Editorial Iberoamérica, pp. 658; 662; 685-691.
También podría gustarte
- Tarea Nro 1 Vectores-FisicaDocumento19 páginasTarea Nro 1 Vectores-FisicaANDERSON CESAR BRACO RUIZAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 CalculoDocumento18 páginasTaller 1 CalculoJulian RiveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercisios Calculo Vectorial 1 (1) 1Documento7 páginasEjercisios Calculo Vectorial 1 (1) 1Acua Tellez Ian EmanuelAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 2. Resolución de Problemas Básicos de Vectores en R 2 y R 3Documento3 páginasEjercicio 2. Resolución de Problemas Básicos de Vectores en R 2 y R 3Señor X100% (1)
- Tarea Matematicas VECTORESDocumento7 páginasTarea Matematicas VECTORESingrid argoteAún no hay calificaciones
- VectoresDocumento7 páginasVectoresMilton HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo 2Documento10 páginasTrabajo 2johan stiven rincon antolinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Avances de La Tarea 2 JANER MORADocumento4 páginasAvances de La Tarea 2 JANER MORAferminAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Unidad 4Documento5 páginasTaller Unidad 4Angie LorenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Modulo 1.2vectoresDocumento7 páginasModulo 1.2vectoresRicardo GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Ejercicios de AfianzamientosDocumento5 páginas1 Ejercicios de AfianzamientosanakarinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vectores, matrices y determinantes en Algebra LinealDocumento12 páginasVectores, matrices y determinantes en Algebra LinealPAOLA ANDREA DUARTE PRADAAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 4 Matematicas IIIDocumento5 páginasTaller 4 Matematicas IIIRicardo BUENDIA SIERRA100% (1)
- Tarea2 622 Gustavo MenesesDocumento11 páginasTarea2 622 Gustavo Menesesgustavojml03Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sadiku Elementos de ElectromagnetismoDocumento5 páginasSadiku Elementos de ElectromagnetismoKarla MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ángulo y suma de vectores 2DDocumento3 páginasÁngulo y suma de vectores 2DacombamAún no hay calificaciones
- Alegbra LienalDocumento4 páginasAlegbra LienalDayana OrtizAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 2Documento1 páginaEjercicio 2Jairo Fragozo garciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller VectoresDocumento10 páginasTaller VectoresAlejandro PantojaAún no hay calificaciones
- V - V - V - TG TG Arctg : 4.1. Encuentre La Magnitud Y Dirección Del Vector Dado. 6.V (-8,9)Documento5 páginasV - V - V - TG TG Arctg : 4.1. Encuentre La Magnitud Y Dirección Del Vector Dado. 6.V (-8,9)josuegallegos169Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 2 - Vectores, Matrices y DeterminantesDocumento10 páginasTarea 2 - Vectores, Matrices y DeterminantesJHOBAN EMEL CAÑIZAREZ PACHECOAún no hay calificaciones
- Cantidades escalares y vectorialesDocumento55 páginasCantidades escalares y vectorialesh .gAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1Documento11 páginasTarea 1Marllel Esthéfany Vásquez GóezAún no hay calificaciones
- Erick - Vazquez - ACTIVIDAD 2 - Geometria AnaliticaDocumento9 páginasErick - Vazquez - ACTIVIDAD 2 - Geometria AnaliticaErick VázquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1 - Vectores, Matrices y DeterminantesDocumento27 páginasTarea 1 - Vectores, Matrices y DeterminantesJhonny PalaciosAún no hay calificaciones
- Tali U1 Ea MarvDocumento12 páginasTali U1 Ea MarvCecilia ReynosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculo de vectores y producto escalarDocumento4 páginasCálculo de vectores y producto escalarJosehiner GuerreroAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios DesarrolladosDocumento4 páginasEjercicios DesarrolladosViviana Zamudio TovarAún no hay calificaciones
- Fase 2 Algebra LinealDocumento21 páginasFase 2 Algebra LinealLorenita HernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- AlgebraDocumento3 páginasAlgebraxXxNightxXxAún no hay calificaciones
- Volumen Con IntegralesDocumento6 páginasVolumen Con IntegralesJean Poul Bedon TrejoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 2 - 05 - Andres BermudezDocumento18 páginasTarea 2 - 05 - Andres BermudezRolandoArturoDiazLariosAún no hay calificaciones
- Aportes 6 Ejercicios.Documento12 páginasAportes 6 Ejercicios.Jose AguirreAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Lineal LeidyDocumento14 páginasAlgebra Lineal LeidyAngelmiro PedrazaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 2 - Vectores J Matrices y Determinantes - John Anderson MartinezDocumento18 páginasTarea 2 - Vectores J Matrices y Determinantes - John Anderson MartinezJohn Anderson Martínez SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea2 622 Gustavo Meneses1Documento10 páginasTarea2 622 Gustavo Meneses1gustavojml03Aún no hay calificaciones
- TC3 1Documento3 páginasTC3 1Shaner H CervantesAún no hay calificaciones
- Matrices y determinantes en álgebra linealDocumento18 páginasMatrices y determinantes en álgebra linealTatiana CamargoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1 Leyver BautistaDocumento18 páginasTarea 1 Leyver BautistaCharlie Puentes Cat100% (1)
- Unidad 1 Algebra Lineal Matrices CompletoDocumento21 páginasUnidad 1 Algebra Lineal Matrices CompletoJimmy francoAún no hay calificaciones
- Revisado 2-TAREA 1Documento4 páginasRevisado 2-TAREA 1Jaime Benavides CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 3 Calculo IntegralDocumento27 páginasUnidad 3 Calculo IntegralyeniferAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 3Documento5 páginasTaller 3Morales GaloAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de VectoresDocumento17 páginasEjercicios de VectoresCronsAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea2 208046 321 Ivan MateusDocumento8 páginasTarea2 208046 321 Ivan Mateusandres felipe arias mateusAún no hay calificaciones
- Ballesta - Jhon - Vectores R2 y R3Documento6 páginasBallesta - Jhon - Vectores R2 y R3Jhon Jairo Ballesta CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra - Javier - MenesesDocumento8 páginasAlgebra - Javier - Menesesjavier andres menesesAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 1 Algebra LinealDocumento5 páginasEjercicio 1 Algebra LinealjairoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea Algebra Magnitud y DireccionDocumento9 páginasTarea Algebra Magnitud y DireccionWilson Audiel Cantillanos Urbina50% (4)
- Tarea 2 - Grupo - 561Documento12 páginasTarea 2 - Grupo - 561Leidy Johana BravoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1 - Vectores, Matrices y DeterminantesDocumento19 páginasTarea 1 - Vectores, Matrices y DeterminantesKatherine TorresAún no hay calificaciones
- Vectores, matrices y determinantes en álgebra linealDocumento5 páginasVectores, matrices y determinantes en álgebra linealÄrlëy BäütïstäAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea1 Grupo 208046 64 ColaborativoDocumento28 páginasTarea1 Grupo 208046 64 ColaborativooswaldoAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 y 2 AlgebnbraDocumento2 páginas1 y 2 AlgebnbraJulio Cesar Rodriguez MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Calculo II - Mi Parte Final TodoDocumento8 páginasTaller Calculo II - Mi Parte Final TodoVictor MerlanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema: Vectores en 2 3: I+ J y V Ai J +V 5Documento9 páginasTema: Vectores en 2 3: I+ J y V Ai J +V 5K̳e̳v̳i̳n̳ O̳g̳m̳Aún no hay calificaciones
- Segundo Aporte Individua1Documento2 páginasSegundo Aporte Individua1usuarioAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 3Documento4 páginasPractica 3FlorDeRosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra LineañDocumento44 páginasAlgebra Lineañcamilo andres covilla pedrzoAún no hay calificaciones
- Gonzalez Suany TE Act1Documento3 páginasGonzalez Suany TE Act1reloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Gonzalez Suany TE Act3Documento3 páginasGonzalez Suany TE Act3reloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Gonzalez Suany TE Act1Documento3 páginasGonzalez Suany TE Act1reloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis de Articulo CientificoDocumento5 páginasAnalisis de Articulo Cientificoreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Gonzalez Suany TE Act2Documento3 páginasGonzalez Suany TE Act2reloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Planeacion FodaDocumento3 páginasPlaneacion Fodareloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- TRANSISTORESDocumento12 páginasTRANSISTORESreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- InfografiaDocumento4 páginasInfografiareloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- DEPARTAMENTALIZACIONDocumento5 páginasDEPARTAMENTALIZACIONreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis de señales electrónicasDocumento5 páginasAnálisis de señales electrónicasreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- ProyectoVidaSuanyDocumento6 páginasProyectoVidaSuanyreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mas Alla de La EticaDocumento3 páginasMas Alla de La Eticareloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Orientada A ObjetosDocumento7 páginasOrientada A Objetosreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aplicacionde DiodosDocumento11 páginasAplicacionde Diodosreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aplicación de diodos en rectificadoresDocumento6 páginasAplicación de diodos en rectificadoresreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- CIRCUITOS BÁSICOS ELECTRÓNICOSDocumento7 páginasCIRCUITOS BÁSICOS ELECTRÓNICOSreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- LINEALgonzalez Suany TE Act1Documento6 páginasLINEALgonzalez Suany TE Act1reloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Herramientas digitales para mejorar la productividad educativaDocumento9 páginasHerramientas digitales para mejorar la productividad educativareloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Interfaces y HerenciaDocumento5 páginasInterfaces y Herenciareloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Plataformas LMSDocumento6 páginasPlataformas LMSreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Orientada A ObjetosDocumento3 páginasOrientada A Objetosreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- MatricesDocumento8 páginasMatricesreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Orientada A ObjetosDocumento7 páginasOrientada A Objetosreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Formas CuadraticasDocumento4 páginasFormas Cuadraticasreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- PLANOSDocumento4 páginasPLANOSreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- OORDENADASDocumento4 páginasOORDENADASreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- ECUACIONESDocumento4 páginasECUACIONESreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Matris InversaDocumento19 páginasMatris Inversareloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- POLINOMIOSDocumento4 páginasPOLINOMIOSreloj zaachilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Programaci N Din Mica DeterministaDocumento40 páginasProgramaci N Din Mica DeterministaJesitita15Aún no hay calificaciones
- 5 - Estudio Armónico de Marea LebuDocumento4 páginas5 - Estudio Armónico de Marea LebuOscar Burgos OrtizAún no hay calificaciones
- Instalacion de Linux Mint Manual PDFDocumento21 páginasInstalacion de Linux Mint Manual PDFぱちん けんかAún no hay calificaciones
- Ley de Proporciones Definidas de ProustDocumento4 páginasLey de Proporciones Definidas de Proustfelixyonathan07Aún no hay calificaciones
- Guía de Estudio Matemática 4Documento4 páginasGuía de Estudio Matemática 4Michael PhillipsAún no hay calificaciones
- Estadística DescriptivaDocumento16 páginasEstadística DescriptivaJohn Eduard RuizAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe Nº01-Perdidas Por Friccion en Tuberias y Accesorios ComercialesDocumento30 páginasInforme Nº01-Perdidas Por Friccion en Tuberias y Accesorios ComercialesMaurizio24100% (2)
- Practica # 3. Determinación Del Calor de ReacciónDocumento7 páginasPractica # 3. Determinación Del Calor de ReacciónSantiago CazorlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bertrand Russell y Los problemas de la filosofíaDocumento82 páginasBertrand Russell y Los problemas de la filosofíapicogordo100% (2)
- Tema 4 - El Solido ElasticoDocumento25 páginasTema 4 - El Solido ElasticoNerea MomeñeAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 2 Mecanica de FluidosDocumento23 páginasPractica 2 Mecanica de FluidosAdolfo AlmonteAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso de Piano Segundo NivelDocumento17 páginasCurso de Piano Segundo NivelJose Israel MaciasAún no hay calificaciones
- Producto Acad Mico 02 TAREA 1Documento14 páginasProducto Acad Mico 02 TAREA 1Q Llanos HenryAún no hay calificaciones
- GeochExp 022Documento22 páginasGeochExp 022Francisco Javier Preciado PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Técnica Orr-Sherby - DornDocumento7 páginasTécnica Orr-Sherby - DornSanti Osorio DiezAún no hay calificaciones
- 06 Campo MagneticoDocumento16 páginas06 Campo MagneticoCkristofer Daniel Yauri PeñafielAún no hay calificaciones
- P5 Estudio Cinetico de Alfa-Amilasa PDFDocumento12 páginasP5 Estudio Cinetico de Alfa-Amilasa PDFlauraAún no hay calificaciones
- Atlas Afiche EcosistemasDocumento1 páginaAtlas Afiche EcosistemasSandra Milena Urbano ApraezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ej 7 Transf D yDocumento17 páginasEj 7 Transf D yDavid JuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- TC2 - Reporte de Evaluación de Proyectos de Inversión - Eq14Documento12 páginasTC2 - Reporte de Evaluación de Proyectos de Inversión - Eq14Montserrat VeraAún no hay calificaciones
- ASME B31 3 Español Apedice SDocumento13 páginasASME B31 3 Español Apedice SADRIANAún no hay calificaciones
- Modelo Agroecologica P 50 Ponedoras PDFDocumento6 páginasModelo Agroecologica P 50 Ponedoras PDFanon_817124399Aún no hay calificaciones
- Integrales Por PartesDocumento3 páginasIntegrales Por Parteslauratmb1211Aún no hay calificaciones
- Guias Matematicas 10 Tercer Periodo 2020 - 1Documento19 páginasGuias Matematicas 10 Tercer Periodo 2020 - 1Yorlan Taborda BetancurAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 7Documento57 páginasUnidad 7ester01phAún no hay calificaciones
- Estandarizacion de Test de Dependencia Al CelularDocumento23 páginasEstandarizacion de Test de Dependencia Al CelularMILUSCA HUMPIRYAún no hay calificaciones
- TaylorDocumento10 páginasTaylorYaquelin Hinojosa BalderasAún no hay calificaciones
- ErocionesDocumento13 páginasErocionesJesús Jaime Gomez LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Sintesis - Analisis de Sistemas de Tubos Tuberias SimplesDocumento3 páginasSintesis - Analisis de Sistemas de Tubos Tuberias SimplesRichard SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- DicDocumento72 páginasDicJesús AlonssAún no hay calificaciones