Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Reviewer in Nutri: Functions
Cargado por
Beverly Manalo0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
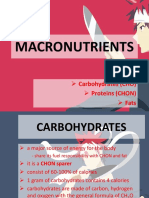
15 vistas4 páginasNutrition involves the study of food and how the body uses it. There are macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that are needed in large amounts, and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals that are needed in small amounts. Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy and can be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides. The main carbohydrates are glucose, fructose, galactose, sucrose, lactose, maltose, starch, and cellulose. Carbohydrates serve important functions like providing energy, sparing protein, fueling the brain and nervous system, regulating fat and cholesterol levels, and storing energy.
Descripción original:
Título original
reviewer-in-nutri (1)
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoNutrition involves the study of food and how the body uses it. There are macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that are needed in large amounts, and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals that are needed in small amounts. Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy and can be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides. The main carbohydrates are glucose, fructose, galactose, sucrose, lactose, maltose, starch, and cellulose. Carbohydrates serve important functions like providing energy, sparing protein, fueling the brain and nervous system, regulating fat and cholesterol levels, and storing energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
15 vistas4 páginasReviewer in Nutri: Functions
Cargado por
Beverly ManaloNutrition involves the study of food and how the body uses it. There are macronutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that are needed in large amounts, and micronutrients like vitamins and minerals that are needed in small amounts. Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy and can be classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides, or polysaccharides. The main carbohydrates are glucose, fructose, galactose, sucrose, lactose, maltose, starch, and cellulose. Carbohydrates serve important functions like providing energy, sparing protein, fueling the brain and nervous system, regulating fat and cholesterol levels, and storing energy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 4
REVIEWER IN NUTRI According to Concentration –
termed as the macronutrients
Nutrition – study of food and how the [present in large amounts in the
body makes use of it body (ex. Water, fats, protein and
- Process of receiving and carbs)] and micronutrients [small
utilizing for the growth and amount (vits and trace minerals)]
renewal of the body
- Maintenance of the different QUALITIES OF GOOD FOOD
body functions Nourishes or nutritious
Functions: It has satiety value
Prevent from diseases and Prepared under sanitary
illnesses conditions, aesthetically, and
Adapting food patterns of individual scientifically
to their cultural, economic and Free from toxic agents
psychological situations and styles Palatability satisfies the
Awareness of the need in specific consumer
disease states to modify nutritional Defers variety and planned w/in
factors for therapeutic purpose socio economic context
MACRONUTRIENTS
Nutrients – chemical substances found in I. CARBOHYDRATES – organic
food compounds (saccharides-starches
Classified according to: and sugars) composed of C, H, O
According to Function Classifications of CHO
a) Body building – structural A. Monosaccharides – known as
components of the body, simple sugars, the simplest
forms tissue. (includes form of carbohydrates. Sweet
water, protein, fat, carbs and require no digestion, can
and minerals) absorbed directly into the
b) Furnish energy – yielding bloodstream from the small
energy, carbs, fats and intestine.
proteins Glucose – (dextrose)
c) Regulate body processes – blood sugar is the
all six major group of principle form in w/c
nutrients (carbohydrates, carbs is used by the
fats, protein – major organic body. Only glucose can
nutrients w/c are broken provide energy for the
down to supply energy; brain, other nerve cells
Vitamins, Minerals & water) and developing red
According to chemical nature – blood cells.
organic (CHON, water & lipid) and Gluconeogenesis
inorganic (vits and minerals) process in which protein
According to essentiality – is converted to glucose.
physiological role in the body Fructose – (levulose) is
- Concentration of a nutrient the sweetest of simple
is not related to its sugar. Found in honey,
importance (ex. 5 mg is as most fruits and some
important as 50 mg of vegies. Converted into
vitamins or 59 mg of protein) glucose in the body.
a) Dietary essentials – Galactose – not found
essentials or free in foods; produced
indispensable nutrients from lactose(milk sugar)
should supplied in the by digestion and
diet, body does not converted into glucose
synthesize these in the body.
nutrients Galactosemia infants
b) Semi essentials – that are born with an
reduces the need for a inability to metabolize
particular nutrient or galactose.
particularly spares it (e.g B. Disaccharides – or double
Cystine can reduce the sugars are made up of a
need for methionine but monosaccharides; sweet; they
it cannot completely changed to simple sugars by
replace it biochemically) hydrolysis before they can be
c) Non – dietary Essentials absorbed.
– non essential
Sucrose – (ordinary lower blood
table sugar-granulated, cholesterol
powdered, or brown) Insoluble – found
process from cane and in wheat brans,
beet sugar; found in corn brans,
fruits, vegies, syrups whole grain
and sweet food breads, and
production; composed of vegies w/c
glucose and fructose accelerate GI
Lactose – (milk sugar) transit, increase
found in milk and milk fecal weight, slow
products except cheese. down starch
Less soluble and less hydrolysis and
sweet than sucrose; delay glucose
stays longer in intestine absorption.
than other sugars; forms Pectins – non
40% of milk solids; 4.8% digestible, colloidal
lactose (cow’s milk); 7% polysaccharides having
lactose (human milk); a gel quality. Sources
favors calcium and mostly fruits and often
phosphorus use as base for jellies;
assimilation. use to treat diarrhea as
Maltose – not found free they absorb toxins and
in foods; produced by bacteria in the intestine;
hydrolysis of starch and bind cholesterol
converted into glucose reducing the amt the
in digestion; occurs in blood can absorb
malt products and in Glycogens – (animal
germinating cereal; starch) formed from
found in certain infant glucose and stored in
formulas, beer and malt liver and muscle
beverage products. tissues.
Less sweets FUNCTIONS OF CARBOHYDRATES
compared to glucose a) Chief source of energy – glucose
and sucrose. and its intermediate products,
C. Polysaccharides – composed major fuel used by muscles
of many molecules of simple b) Cheap and main energy – low cost
sugars. Commonly known as and widely distributed around the
complex sugars. world
Starch – most significant c) Protein sparer – save or spare
polysaccharides in protein for its unique function of
human nutrition; food body building
sources cereal grains, d) Sole energy source for the brain &
potatoes, and other root nerve tissue – prevent irreversible
vegies and legumes; damage of the brain
requires longer time to e) Regulator of fat metabolism –
digest prevents accumulation of flutone
Dextrins – not found free bodies and acidosis
in foods; formed as f) Storage form of energy as
intermediate products in glycogen – glycogen as immediate
the breakdown of starch source of energy
Cellulose – forms the g) Regulator of intestinal peristalsis &
framework of plants and provider of bulk
found in unrefined
grains, vegies, and II. PROTEINS – GW “protos”
fruits; non digestible meaning “primary or holding 1st
bcoz enzyme are unable place” since it is the 1st substance
to break them down. recognized as vital part of living
Soluble – found tissue
in fruits and - Organic substances that on
legumes, barley digestion yield their
and oats w/c constituent building block –
delay GI transit Amino Acids
and glucose a. Simple Proteins – those w/c yield
absorption and only amino acids upon hydrolysis
1. Albumins – soluble in water, acids that are linked in this manner
coagulated by heat are called polypeptides.
2. Globulins – insoluble in
water, soluble in dilute salt B. Essential and Non-essential Amino
solution and coagulated by Acids
heat 1. Essential amino acids cannot
3. Glutelins – insoluble in be synthesized by the body and
neutral solvents but soluble are necessary in the diet.
in weak acids and alkalis Examples: threonine, leucine,
coagulated by heat isoleucine, valine, lysine,
4. Prolamines – soluble in methionine, phenylalanine,
70% to 80% alcohol, tryptophan
insoluble in absolute 2. Non- essential amino acids –
alcohol, water and salt can be manufactured by the
solutions body. Examples: glycine,
5. Albuminoids – insoluble in alanine, aspartic acid, glutamic
all neutral solvents and in acid, proline, hydroxyproline,
dilute acids and alkalis cysteine, tyrosine, serine,
6. Histones and protamines – arginine, ristidine
soluble in water, not C. Complete and Incomplete Proteins
coagulated by heat (nuclei 1. Complete proteins – are those
of cells) that contain all the essential
b. Compound Proteins, conjugated amino acids in sufficient
proteins or Proteids quantity and ratio to supply of
1. Nucleoproteins – the body’s needs. Ex. Animal
combination of simple origin meat, milk and eggs
proteins and nucleic acid. 2. Incomplete proteins – those
(ex. DN nucleoproteins) deficient in one or more of
2. Mucoproteins and essential amino acids. Ex: plant
glycoproteins – combination origin grains, legumes seeds
of protein and large and nuts
quantities of complex
polysaccharides (ex. Mucin DIGESTION OF PROTEIN
found in secretion from A. Mouth
gastric mucos membranes) 1. Enzyme – none
3. Lipoproteins – compounds 2. Action – mechanical
of protein and a triglyceride mastication
or other lipid such as B. Stomach
phospholipids or cholesterol 1. Enzyme – pepsin, produce fist
found in cell and organelle as inactive precursor to
membranes pepsinogen, then activated by
4. Phosphoproteins – the hydrochloric acid.
compounds of phosphoric 2. Action – converts protein to
acid joined in ester linkage proteases and peptones
to protein found in casein 3. In infants, enzyme rennin
milk converts casein to coagulated
5. Chromoproteins – curd
compounds of proteins and C. Small intestine (alkaline)
nonprotein pigment found in 1. Pancreas
flavorproteins, hemoglobin, Trypsin converts
and cytochromes proteins, proteases and
6. Metalloprotein – are peptones to
compounds or metals (Cu, polypeptides and
Mg, Zn and Fe) attached to peptides
protein found in ferritin, Chrymotrypsin converts
hemosiderin, and proteases and peptones
transferrin. to polypeptides and
dipeptides, also
CHEMICAL STAGES OF A PROTEIN coagulates milk
A. An amino acid has a chemical Carboxypeptidase –
structure that combines both acid comverts polypeptides
and bases (amino) factors. This to simpler peptides,
characteristics chain structure of dipeptides and amino
amino acid is called peptide acids
linkage. Long chains of amino 2. Intestine
Aminopeptidase –
converts polypeptides to
peptides and amino
acids
Dipeptidase – converts
dipeptides to amino
acids
FUNCTIONS OF PROTEIN
1. Used in repairing worn out body
tissue proteins (anabolism)
resulting from continued wear and
tear (catabolism) going on in the
body
2. Used to build new tissue
3. Source of heat and energy
4. Contribute to numerous essential
body secretions and fluids, enzyme
and proteins (hormones, mucus,
milk, and sperm cells)
5. Important in the maintenance of
normal osmotic relations among
the various body fluids
6. Play a large role in the resistance
of then body to disease.
(antibodies – plasma globulin and
gamma globulin)
7. Dietary protein furnish the amino
acids for a variety of metabolic
functions
HEALTH EFFECTS OF PROTEINS
1. HEART DISEASE
2. CANCER
3. OSTEOPOROSIS
4. WEIGHT CONTROL
5. KIDNEY DISEASE
SOURCES OF PROTEINS
1. Meat, fish, poultry, egg, milk,
cheese
2. Legumes, nuts
3. Breads and cereals
También podría gustarte
- NCM 105 Lec 3Documento3 páginasNCM 105 Lec 3Rizaga, Carlos BenedictAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 Macronutrients CarbohydratesDocumento2 páginasChapter 2 Macronutrients Carbohydratesreajohn591Aún no hay calificaciones
- NCM105 Notes 2-CarbsDocumento3 páginasNCM105 Notes 2-CarbsPaula TalaAún no hay calificaciones
- MODULE 2 - Macronutrient (CARBOHYDRATES)Documento4 páginasMODULE 2 - Macronutrient (CARBOHYDRATES)Donna MarieAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutrition Proteins: PE 2 - MidtermDocumento4 páginasNutrition Proteins: PE 2 - Midtermgatuslao micaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 03 Essential Nutrients and Their Contribution To The Diet - Classification of NutrientsDocumento12 páginasLesson 03 Essential Nutrients and Their Contribution To The Diet - Classification of NutrientsMickey MouseAún no hay calificaciones
- CarbohydratesDocumento3 páginasCarbohydratesBianca AzoresAún no hay calificaciones
- NUTMACRODocumento9 páginasNUTMACROAliza Bea CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Documento4 páginasCHAPTER 3 - Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Ruby Jane LaquihonAún no hay calificaciones
- Macro NutrientsDocumento10 páginasMacro NutrientsClarke GriffinAún no hay calificaciones
- NDT Reviewer Carbo Lipid ProteinDocumento8 páginasNDT Reviewer Carbo Lipid ProteinMyrel Cedron TucioAún no hay calificaciones
- NDT Module 1Documento97 páginasNDT Module 1Fhei Lya Dee TioAún no hay calificaciones
- Macronutrients: Carbohydrates (CHO) Proteins (CHON) FatsDocumento32 páginasMacronutrients: Carbohydrates (CHO) Proteins (CHON) FatsGayle BocalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Animal NutritionDocumento9 páginasAnimal NutritionhopeAún no hay calificaciones
- CARBOHYDRATESDocumento5 páginasCARBOHYDRATESMicah YapAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides (Simple Sugar)Documento3 páginas1 Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides (Simple Sugar)Kara AshleighAún no hay calificaciones
- CarbohydratesDocumento16 páginasCarbohydratesUMMU MARDHIAH ABDUL HALIMAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 1 NutriDietDocumento11 páginasModule 1 NutriDietKilla BischeAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 3 CarbohydratesDocumento4 páginasUnit 3 CarbohydratesRamkrishna JanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Macronutirents CPF With Prelim ProjectDocumento78 páginasMacronutirents CPF With Prelim ProjectMONICA AGUIRREAún no hay calificaciones
- CN Unit-IiDocumento25 páginasCN Unit-IiJohn Benedict Suiza VillaruelAún no hay calificaciones
- CARBOHYDRATESDocumento3 páginasCARBOHYDRATESjaizamaeenriquez59Aún no hay calificaciones
- CarbohydratesDocumento33 páginasCarbohydratesDeboo X Xavier100% (1)
- GIT كتيب الطبعة الثانيةDocumento56 páginasGIT كتيب الطبعة الثانيةdijla51Aún no hay calificaciones
- المحاضرة الرابعة تغذية CarbohydrateDocumento30 páginasالمحاضرة الرابعة تغذية Carbohydratedeminavictor8Aún no hay calificaciones
- 6 BASIC NUTRIENTS NDT Lec Sep15Documento7 páginas6 BASIC NUTRIENTS NDT Lec Sep15Jay EstrellaAún no hay calificaciones
- MacronurientsDocumento11 páginasMacronurientsDanah Grace SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- MacronurientsDocumento11 páginasMacronurientsDanah Grace SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- CarbohydratesDocumento7 páginasCarbohydratesYo1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 MACRONUTRIENTSDocumento11 páginasChapter 3 MACRONUTRIENTSSami InglesAún no hay calificaciones
- CarbohydratesDocumento6 páginasCarbohydratesAlfred ManuelAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutrition Nursing: CarbohydratesDocumento36 páginasNutrition Nursing: CarbohydratesAngelyka Nicole Bengco DavidAún no hay calificaciones
- Macronutrients - CARBOHYDRATES Are Organic Compounds (Saccharides-Starches and Sugars) Composed ofDocumento3 páginasMacronutrients - CARBOHYDRATES Are Organic Compounds (Saccharides-Starches and Sugars) Composed ofPatriciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutrition NotesDocumento61 páginasNutrition NotesHarbrinder GurmAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutritiondiettherapy Lectureprelimstomidterm 191112061026Documento138 páginasNutritiondiettherapy Lectureprelimstomidterm 191112061026Augustine chandigaAún no hay calificaciones
- 134 Digestible and Nondigestible CarbohydratesDocumento5 páginas134 Digestible and Nondigestible CarbohydratesUmar BajwaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 4 - CarbohydratesDocumento2 páginasChapter 4 - CarbohydratesIce Cream C0neAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Long TestDocumento7 páginasBiology Long TestMarjorie AballaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 10 BiomoleculesDocumento58 páginasGrade 10 BiomoleculesBainalyn P. AragasiAún no hay calificaciones
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced STUDIES StudiesDocumento14 páginasAsia Pacific College of Advanced STUDIES StudiesJake LaylaAún no hay calificaciones
- Week 4: October 4 - 9: MC 2: BiochemistryDocumento5 páginasWeek 4: October 4 - 9: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio MoleculesDocumento15 páginasBio MoleculessofiajanineganalAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbohydrates - Revised NotesDocumento1 páginaCarbohydrates - Revised NotesJohn Nielson Baling-oayAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochem NotesDocumento17 páginasBiochem NotesKate strangeAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutrition in PeriodonticsDocumento81 páginasNutrition in PeriodonticsAtul KoundelAún no hay calificaciones
- BDA CarbsDocumento2 páginasBDA CarbslyshantahlynahAún no hay calificaciones
- M2 Lesson 1Documento10 páginasM2 Lesson 1Catherine Sinen ObinqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 MacronutrientsDocumento3 páginasChapter 3 MacronutrientsMaxdjye EyjdxamAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbs Notes (Lab)Documento4 páginasCarbs Notes (Lab)Patricia EspirituAún no hay calificaciones
- CarbohydratesDocumento33 páginasCarbohydratesCris PorlasAún no hay calificaciones
- Print Lecture 1 - Nutrition Overview - QuizletDocumento6 páginasPrint Lecture 1 - Nutrition Overview - QuizletelanineAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andDocumento12 páginasLesson 4: Biomolecules: Major Types of Biomolecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Nucleic Acids, andJuselle Faith AtaAún no hay calificaciones
- Charbohydrate: Unit - IiDocumento8 páginasCharbohydrate: Unit - IiHemant SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fructose - Fruit Sugar, HexoseDocumento11 páginasFructose - Fruit Sugar, HexoseQuinscy MadoAún no hay calificaciones
- MARIANO, Marian KylaDocumento3 páginasMARIANO, Marian KylaMarian Kyla MarianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic2 - MacronutrientsDocumento28 páginasTopic2 - MacronutrientsBea Santos BarrozoAún no hay calificaciones
- CarboDocumento22 páginasCarbopinkish7_preciousAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology in EnglishDocumento19 páginasBiology in EnglishRameshAún no hay calificaciones
- Energy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)Documento6 páginasEnergy Giving Food - Carbohydrates (CHO)camille εϊзAún no hay calificaciones
- 11th Biology-Botany English Medium TextDocumento320 páginas11th Biology-Botany English Medium Textmadhusudhanan.scholarAún no hay calificaciones
- High Sensitivity CRP - IMMULITE and IMMULITE 1000 - Rev 06 DXDCM 09017fe980297730-1538194293759Documento36 páginasHigh Sensitivity CRP - IMMULITE and IMMULITE 1000 - Rev 06 DXDCM 09017fe980297730-1538194293759Deqsa Corporativo0% (1)
- Dna Extraction Experiment by George Luck: College of DupageDocumento1 páginaDna Extraction Experiment by George Luck: College of DupageamienxzoneAún no hay calificaciones
- PH Optimo de InvertasaDocumento11 páginasPH Optimo de InvertasapsykhodelykAún no hay calificaciones
- Four Types of CreutzfeldtDocumento1 páginaFour Types of Creutzfeldtkarenkaren09Aún no hay calificaciones
- Science - 111120 - Reproduction in PlantsDocumento5 páginasScience - 111120 - Reproduction in PlantsDeepak KansalAún no hay calificaciones
- Real Time PCR: Pramod Bahadur K.CDocumento14 páginasReal Time PCR: Pramod Bahadur K.CPramod KcAún no hay calificaciones
- BDDCS Predictions, Self-Correcting Aspects of BDDCS Assignments, BDDCS Assignment Corrections, and Classification For More Than 175 Additional DrugsDocumento10 páginasBDDCS Predictions, Self-Correcting Aspects of BDDCS Assignments, BDDCS Assignment Corrections, and Classification For More Than 175 Additional DrugsBagoes AsAún no hay calificaciones
- Single Gene Inheritance HandoutDocumento16 páginasSingle Gene Inheritance HandoutMarel LatawanAún no hay calificaciones
- Control of Gene Expression Questions AQA OCR EdexcelDocumento5 páginasControl of Gene Expression Questions AQA OCR EdexcelMeeta DeviAún no hay calificaciones
- 456 Bio SensorsDocumento31 páginas456 Bio SensorsRam VBITAún no hay calificaciones
- Integumentary Sensory Organs in CrocodiliansDocumento10 páginasIntegumentary Sensory Organs in CrocodiliansEduardo LeónAún no hay calificaciones
- Neural Dynamics For Landmark Orientation and Angular Path Integration - Seelig2015Documento19 páginasNeural Dynamics For Landmark Orientation and Angular Path Integration - Seelig2015dagushAún no hay calificaciones
- Effectiveness of Fenbendazole and Metronidazole Against Giardia Infection in Dogs Monitored For 50-Days in Home-ConditionsDocumento7 páginasEffectiveness of Fenbendazole and Metronidazole Against Giardia Infection in Dogs Monitored For 50-Days in Home-ConditionsBrieAún no hay calificaciones
- The Importance ofDocumento2 páginasThe Importance ofMd Shohag Ali100% (1)
- ToxoplasmosisDocumento48 páginasToxoplasmosisIrahmal IrahmalAún no hay calificaciones
- Biotic Stree and Yield LossDocumento258 páginasBiotic Stree and Yield LossDhanraj KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Genetics Lab NotesDocumento4 páginasGenetics Lab NotesJayar AguilarAún no hay calificaciones
- Extra Nuclear InheritanceDocumento13 páginasExtra Nuclear InheritanceTony BernardAún no hay calificaciones
- MicroParaReviewer PDFDocumento12 páginasMicroParaReviewer PDFEinah EinahAún no hay calificaciones
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem ServicesDocumento18 páginasBiodiversity and Ecosystem Servicessameer AhadAún no hay calificaciones
- Classifying Living ThingsDocumento8 páginasClassifying Living Thingsdesco2011Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tips For BiologyDocumento15 páginasTips For BiologyMasega Daniel ManaliAún no hay calificaciones
- Mendivil-Giro 17 Is-Unive PDFDocumento25 páginasMendivil-Giro 17 Is-Unive PDFhalersAún no hay calificaciones
- Rainsure Company, Instrument and Assays Introduction CLVDocumento61 páginasRainsure Company, Instrument and Assays Introduction CLVMohammed H. KeshtaAún no hay calificaciones
- Genetic Linkage, Recombination, Mapping - BIO231-FKDocumento9 páginasGenetic Linkage, Recombination, Mapping - BIO231-FKmalik husnainAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter21 PDFDocumento25 páginasChapter21 PDFsgw67Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quizbee 2019 Nutrition Month EasyDocumento4 páginasQuizbee 2019 Nutrition Month EasyJaenicaPaulineCristobalAún no hay calificaciones
- General Zoology Module 1 Arthropoda and EchinodermataDocumento5 páginasGeneral Zoology Module 1 Arthropoda and EchinodermataPaul PanizaAún no hay calificaciones
- Supplement Black BookDocumento33 páginasSupplement Black Booktweetybyrd443013Aún no hay calificaciones