Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Xxsenxc A Sen A A Sen A A Sen A
Cargado por
Jose Ángel Mendoza PérezDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Xxsenxc A Sen A A Sen A A Sen A
Cargado por
Jose Ángel Mendoza PérezCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
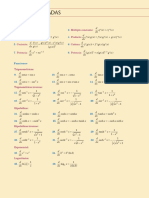
319) x x 2 senx c 0
a0 sen(0) 0
a1 cos(0) 1
a2 sen(0) 0
a3 cos(0) 1
a4 sen(0) 0
a5 cos(0) 1
1 1 1
senx ( x) ( x 3 ) ( x 5 )
1! 3! 5!
2 n 1
x
1
n
n0 (2n 1)!
luego x 1
2 n 1
x
(1) 4 n 2
x 2 1
n
1
n
n 0 (2n 1) n 0 (2n 1)
x 4n2
1
n
1
n
n0 (2n 1) (2n 1)
n 0
Convergente por el criterio de las S.A.
4n2
x
an 1
n
1 1
(2n 1) an an
2n 1 2(n 1) 1
x 4n 6
an 1 1 1
n 1
lim
(2n 3) x 2n 1
1 x 4 n6 . (2n 1)
n 1
an 1
lim lim
x an x (2n 3) 1 n x 4 n 2 x 1
(1) 4 n 2
1
4 n
x
lim n 0 (2n 1)
x (2n 3)(2n 2)
1
n
x lim
4 1 (2n 1)
x (2 n 3)(2 n 2) n 0
4 Convergente por el criterio de las S.A.
x 1
1 1
x 1 an an
2n 1 2(n 1) 1
1 x 1 1
r 1 lim
x 2n 1
R 1
IC 1,1
También podría gustarte
- Programas para Calcular Campo ElectricoDocumento4 páginasProgramas para Calcular Campo ElectricoJose Ángel Mendoza PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Anteproyecto - Mezcladora de AudioDocumento2 páginasAnteproyecto - Mezcladora de AudioJose Ángel Mendoza PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulas de MatsupDocumento2 páginasFormulas de MatsupJose Ángel Mendoza PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- INFORMEDocumento4 páginasINFORMEJose Ángel Mendoza PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocumento9 páginasEcuaciones DiferencialesJose Ángel Mendoza PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- TablasDocumento5 páginasTablasJose Ángel Mendoza PérezAún no hay calificaciones