Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Vocabulary Circles 122710
Cargado por
pfredaTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Vocabulary Circles 122710
Cargado por
pfredaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
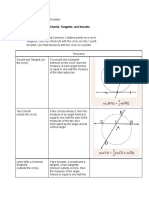
CIRCLES VOCABULARY
===================================================================================
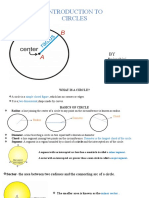
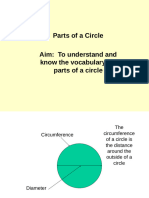
Circle Radius
The set of points some fixed distance [ = radius ] A line [or the distance] from the center of a circle to
from another point [called the center ] the circle itself
Diameter Chord
A line [or the distance] between two points on the circle A line connecting two points on a circle
which passes thru the center of the circle Secant
Tangent A line beginning external to a circle which
A line external to a circle which touches intercepts the circle at two points
the circle at ONLY one point Circumference of a Circle
Segment The measure of the length of the circle
An area internal to a circle which is formed The "perimeter" of a circle
by a chord or secant and the circle itself = 2 times Pi times the radius OR Pi times diameter
It must exclude the center of the circle Area of a Circle
Sector = Pi times radius squared
An area bounded by 2 radii and the arc between Pi = ~ 22 / 7 or 3.14159
the end points of the radii Semicircle
The arc subtended by a diameter
Central Angle Arc
Angle internal to a circle with vertex = center A part of the circumference of a circle
and end points on the circle A subset of the locus of points of the circle
An angle formed by two radii Intercepted Arc / Subtended Arc
A Central Angle = The measure the arc it subtendeds Arc cut by a central, inscribed or external angle
Inscribed Angle Major Arc
Angle internal to a circle with vertex on the circle The larger of the 2 arcs cut by chords / secants / tangents
and end points on the circle Sometimes defined as an arc > 180 degrees
An internal angle formed by 2 chords Minor Arc
with a common point The smaller of the 2 arcs cut by chords / secants / tangents
An Inscribed Angle = 1/2 the measure of the arc it subtends Sometimes defined as an arc < 180 degrees
Measure of an Arc
Complementary Angles The degree or radian measure of an arc
Angles which add to 90 degrees Equals the measure of the central angle which subtends it
Supplementary Angles Length of an Arc
Angles which add to 180 degrees The part of the circumference defined by the arc's end points
Acute Angle ; is < 90 degrees
Obtuse Angle ; is > 90 & < 180 degrees Point of Tangency
Straight Angle ; is = 180 degrees The point where a tangent and radius meet on the circle
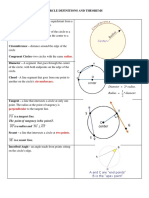
Reflex Angle ; is > 180 degrees Common Tangents
Measure of an Angle Tangents common to two different circles
The degree or radian measure of an angle There may be 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 common tangents
If the circles touch at 0, 1, or 2 points there are
Circumscribed Circle 4, 3 or 2 common tangents respectively
A circle external to a polygon passing thru the If an internal circle touches the outer circle at 1 point
vertices of the polygon there will be only 1 common tangent
Inscribed Circle If one circle is within the other circle there are
A circle internal to a polygon which is 0 common tangents
tangent to all the sides of the polygon External Tangent
Concentric Circles Common Tangent of 2 circles which does not cross
Circles with the same center but different radii the line connecting the two centers
Internal Tangent
Locus Common Tangent of 2 circles which crosses the line
A set of points satisfying some rule or condition. connecting the two centers
For example; An Ellipse is the locus of points the Vertex of an Angle
sum of whose distances to 2 other points [ Foci ] The point where the sides of an angle meet
are are equal
Unit Circle Line Segment
A circle with a radius of one unit Part of a line with end points well defined
A powerful tool of analysis in Trigonometry Example; Intersecting chords create 4 line segments
Dec 27, 2010
PFreda, Assumption College
También podría gustarte
- Introduction To CircleDocumento5 páginasIntroduction To CircleMatsuri VirusAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 - Chords Arcs Angles Tangents and SecantsDocumento9 páginas2 - Chords Arcs Angles Tangents and SecantsJoshWayne GonzagaAún no hay calificaciones
- CirclesDocumento7 páginasCirclesSrijaAún no hay calificaciones
- CirclesDocumento7 páginasCirclesSrijaAún no hay calificaciones
- Definitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryDocumento8 páginasDefinitions and Theorems For Circle GeometryPaula FanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Circle Definitions and TheoremsDocumento8 páginasCircle Definitions and TheoremsGani Almeron100% (1)
- MathDocumento10 páginasMathluisyuque102Aún no hay calificaciones
- Parts of The CircleDocumento8 páginasParts of The CircleMari CelAún no hay calificaciones
- CircleDocumento11 páginasCircleJulie Anne TolentinoAún no hay calificaciones
- MELVINDocumento16 páginasMELVINRosito BaragoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tangent and CircleDocumento1 páginaTangent and Circleaimgod100Aún no hay calificaciones
- Circles TheoryDocumento4 páginasCircles TheoryJamal AliyevAún no hay calificaciones
- Math Subject For High School - 9th Grade - Systems of Equations and Inequalities by SlidesgoDocumento24 páginasMath Subject For High School - 9th Grade - Systems of Equations and Inequalities by Slidesgolheyvin kert bautistaAún no hay calificaciones
- Math Subject For High School - 9th Grade - Systems of Equations and Inequalities by SlidesgoDocumento24 páginasMath Subject For High School - 9th Grade - Systems of Equations and Inequalities by Slidesgolheyvin kert bautistaAún no hay calificaciones
- Topik-2 Bulatan CircleDocumento36 páginasTopik-2 Bulatan Circle许如楠Aún no hay calificaciones
- CirclesDocumento8 páginasCircles246macvillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematics Reviewer For Grade 10 Q2Documento2 páginasMathematics Reviewer For Grade 10 Q2martinaloreyn.delrosarioAún no hay calificaciones
- Parts of The CircleDocumento7 páginasParts of The Circlenica monAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Parts of A CircleDocumento10 páginasBasic Parts of A CirclePrecious Kim Pascua SamboAún no hay calificaciones
- The Parts of A Circle 1Documento2 páginasThe Parts of A Circle 1Tavvia HenryAún no hay calificaciones
- Parts of A CircleDocumento33 páginasParts of A CircleMr. Rhumer LanojanAún no hay calificaciones
- Circle (Parts, Circumference, and Area)Documento12 páginasCircle (Parts, Circumference, and Area)Jerry Mae RanesAún no hay calificaciones
- Math70 F2013 Lecture Sections6 1thru6 2Documento4 páginasMath70 F2013 Lecture Sections6 1thru6 2Raiel RoaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2.1 Mom1iDocumento32 páginasChapter 2.1 Mom1iKarell Faye BatulanAún no hay calificaciones
- Everything You Need to Know About CirclesDocumento19 páginasEverything You Need to Know About CirclesAnanthuAún no hay calificaciones
- Circles Class 6Documento3 páginasCircles Class 6resmiAún no hay calificaciones
- Circle S: Circles and It's PartsDocumento6 páginasCircle S: Circles and It's PartsJohn Dale Patagan GarayAún no hay calificaciones
- Terms Realated To CirclesDocumento2 páginasTerms Realated To CirclesMilanAún no hay calificaciones
- Math Project on Circles and Their PropertiesDocumento5 páginasMath Project on Circles and Their PropertiesGeta GamingAún no hay calificaciones
- CIrclesDocumento10 páginasCIrclesMaria DzAún no hay calificaciones
- Circles: Central Angles, Arcs, Sectors, and Arc LengthDocumento1 páginaCircles: Central Angles, Arcs, Sectors, and Arc LengthTito AgooAún no hay calificaciones
- Module1 1Documento10 páginasModule1 1Jowelyn MaderalAún no hay calificaciones
- Parts of A Circle PresentationDocumento14 páginasParts of A Circle Presentationromar.allen73Aún no hay calificaciones
- Circles ModifiedDocumento134 páginasCircles ModifiedHermione ClydeAún no hay calificaciones
- CircleDocumento19 páginasCirclealexandradeleon080508Aún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER 2.1 Handout PDFDocumento5 páginasCHAPTER 2.1 Handout PDFAcuña ShineAún no hay calificaciones
- CirclesDocumento1 páginaCirclesJayczarAún no hay calificaciones
- Report On The CircleDocumento8 páginasReport On The CircleZanderAún no hay calificaciones
- Circle (Demo)Documento22 páginasCircle (Demo)Gian Carlo ClarizaAún no hay calificaciones
- Math Act1Documento2 páginasMath Act1Mel GonzalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Circle: Parts of A CircleDocumento2 páginasCircle: Parts of A CircleChristine Joy MagtibayAún no hay calificaciones
- Circle and TheoremsDocumento32 páginasCircle and Theoremsalexandradeleon080508Aún no hay calificaciones
- Circles and Related Terms ExplainedDocumento36 páginasCircles and Related Terms ExplainedPatricia CadacioAún no hay calificaciones
- CO1 CircleDocumento50 páginasCO1 CircleReinabelle Marfil Marquez100% (1)
- Circles and Its Related TermsDocumento3 páginasCircles and Its Related Termsapi-174391216Aún no hay calificaciones
- A CircleDocumento1 páginaA CircleFrenzy SenarillosAún no hay calificaciones
- CO1 CircleDocumento57 páginasCO1 CircleReinabelle Marfil MarquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Glossary Terms: R Is The Radius of The Circle and L Is The Arc LengthDocumento4 páginasGlossary Terms: R Is The Radius of The Circle and L Is The Arc LengthBonbert LascoAún no hay calificaciones
- Circles Review For Test 1 1Documento4 páginasCircles Review For Test 1 1api-256105506Aún no hay calificaciones
- Maths Project on CirclesDocumento18 páginasMaths Project on CirclesJohn Nguyen57% (42)
- Math 10 Q2W2Documento69 páginasMath 10 Q2W2Leander Kelly Transporte MarianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Circles:: Introduction To Chords, Arcs, andDocumento1 páginaCircles:: Introduction To Chords, Arcs, andPatrick PelicanoAún no hay calificaciones
- The Geometry of CirclesDocumento34 páginasThe Geometry of CirclesKhloe CeballosAún no hay calificaciones
- 01e0d1i 0Documento3 páginas01e0d1i 0Niño Enrique ManalastasAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.6 CIRCLES and Related Segments and AnglesDocumento50 páginas2.6 CIRCLES and Related Segments and AnglesJamill BalajadiaAún no hay calificaciones
- CircleDocumento11 páginasCircleKathleen Bermejo CatainAún no hay calificaciones
- Math GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerDocumento5 páginasMath GR10T3 LA2 & AU3 ReviewerGab AquinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Circle and Its PartsDocumento23 páginasCircle and Its PartsJo Ann Chrysol IringanAún no hay calificaciones
- Birds, Bees and Burgers: Puzzling Geometry from EnigMathsDe EverandBirds, Bees and Burgers: Puzzling Geometry from EnigMathsAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Fluids 110512Documento2 páginasPhysics Fluids 110512pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Thermodynamics 102612Documento2 páginasPhysics Thermodynamics 102612pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 6 Fields and Forces: Force Per Unit Mass Force Per Unit ChargeDocumento1 páginaChapter 6 Fields and Forces: Force Per Unit Mass Force Per Unit ChargepfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Simple Harmonic Motion 110512Documento2 páginasPhysics Simple Harmonic Motion 110512pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Atomic&Nuclear 102512Documento1 páginaPhysics Atomic&Nuclear 102512pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Mechanics 110512Documento3 páginasPhysics Mechanics 110512pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 6 Fields and Forces: Force Per Unit Mass Force Per Unit ChargeDocumento1 páginaChapter 6 Fields and Forces: Force Per Unit Mass Force Per Unit ChargepfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Tutoring Summary Sheet 101112Documento6 páginasPhysics Tutoring Summary Sheet 101112pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Taxonomy 100511Documento2 páginasAlgebra Taxonomy 100511pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 DVector Geometry Problems&Solutions 012612Documento4 páginas3 DVector Geometry Problems&Solutions 012612pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Astronomy 102612Documento2 páginasPhysics Astronomy 102612pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 DVector Geometry Problems 100711Documento1 página3 DVector Geometry Problems 100711pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 DVector Geometry Problems&Solutions 012612Documento4 páginas3 DVector Geometry Problems&Solutions 012612pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Taxonomy 051612Documento2 páginasAlgebra Taxonomy 051612pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 DVector Geometry Problems 100711Documento1 página3 DVector Geometry Problems 100711pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vectors Summary Sheet122211Documento2 páginasVectors Summary Sheet122211pfredaacAún no hay calificaciones
- Limits Summary Sheet 063011Documento2 páginasLimits Summary Sheet 063011pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Numerical Methods Comparison 081011Documento1 páginaNumerical Methods Comparison 081011pfredaacAún no hay calificaciones
- Vocabulary Calculus 101210Documento2 páginasVocabulary Calculus 101210pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Trig Without Tables 091611Documento1 páginaTrig Without Tables 091611pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Limits Summary Sheet 063011Documento2 páginasLimits Summary Sheet 063011pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vocabulary Sets 061408Documento1 páginaVocabulary Sets 061408pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculus Taxonomy 042411Documento1 páginaCalculus Taxonomy 042411pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 DVector Geometry Lines Planes 113011Documento2 páginas3 DVector Geometry Lines Planes 113011pfredaacAún no hay calificaciones
- Matrix Summary Sheet 122011Documento2 páginasMatrix Summary Sheet 122011pfreda100% (1)
- Mathematical & EducationalSayings 081311Documento3 páginasMathematical & EducationalSayings 081311pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculus Tables 041111Documento2 páginasCalculus Tables 041111pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vocabulary Polynomials 123010Documento1 páginaVocabulary Polynomials 123010pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vocabulary Logic 092308Documento1 páginaVocabulary Logic 092308pfredaAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Geometry - Summer of 2023 H.WDocumento11 páginasBasic Geometry - Summer of 2023 H.WFizah MAún no hay calificaciones
- Name: Name: Chapter 7 - Geometrical Construction - Checklist Chapter 7 - Geometrical Construction - ChecklistDocumento2 páginasName: Name: Chapter 7 - Geometrical Construction - Checklist Chapter 7 - Geometrical Construction - ChecklistFadlin Linsai0% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade7 MathematicsDocumento7 páginasA Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade7 MathematicsJenica KayeAún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematics - 7 Class PDFDocumento132 páginasMathematics - 7 Class PDFDhanaji WakadeAún no hay calificaciones
- SASMO 2014 Round 1 Primary 2 SolutionsDocumento6 páginasSASMO 2014 Round 1 Primary 2 Solutionsichkhuy100% (7)
- LocusDocumento6 páginasLocusZia Ul QadirAún no hay calificaciones
- KVPY SX 2019 Maths Question Answerkey SolutionsDocumento32 páginasKVPY SX 2019 Maths Question Answerkey SolutionsSatoki GintamaAún no hay calificaciones
- Math Construction ProjectDocumento24 páginasMath Construction ProjectAdyAún no hay calificaciones
- The EllipseDocumento9 páginasThe Ellipsesifogax112Aún no hay calificaciones
- Geometry Print VersionDocumento32 páginasGeometry Print VersionLina ZapataAún no hay calificaciones
- As - Q3 Math 5 Week 3 4Documento8 páginasAs - Q3 Math 5 Week 3 4Pinky SubionAún no hay calificaciones
- Geometry (PJ)Documento317 páginasGeometry (PJ)sarma e.mAún no hay calificaciones
- Extract File 20230411 141647Documento14 páginasExtract File 20230411 141647Ankit OjhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Advanced GeometryDocumento7 páginasAdvanced GeometryGenelle Mae MadrigalAún no hay calificaciones
- Q3W8-9 DLP Construction&SolvingProblemsInvolvingPolygonsDocumento15 páginasQ3W8-9 DLP Construction&SolvingProblemsInvolvingPolygonsMarjuline De GuzmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Geometry Glossary: M ABCDocumento19 páginasGeometry Glossary: M ABCfree_progAún no hay calificaciones
- Anatomy of CirclesDocumento69 páginasAnatomy of CirclesPatricia BaezaAún no hay calificaciones
- A Plane Extends Infinitely in Two DimensionsDocumento3 páginasA Plane Extends Infinitely in Two DimensionsJaime L. AustriaAún no hay calificaciones
- Add Math Coordinate GeometryDocumento14 páginasAdd Math Coordinate Geometrykamil muhammad67% (3)
- Paper-Folding Using Interactive Geometry SoftwareDocumento10 páginasPaper-Folding Using Interactive Geometry SoftwarecmcallisterAún no hay calificaciones
- Mock Exam Review Pack 1Documento13 páginasMock Exam Review Pack 1Aman WaniyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Learner's Material: We Value Your Feedback and RecommendationsDocumento56 páginasLearner's Material: We Value Your Feedback and RecommendationsBA RTAún no hay calificaciones
- Provided.: I. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Read Each Item Carefully and Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The BlankDocumento7 páginasProvided.: I. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Read Each Item Carefully and Write The Letter of The Correct Answer On The BlankRolly Dominguez Balo100% (1)
- Maths Class IV Worksheet For SeeDocumento19 páginasMaths Class IV Worksheet For SeesekharsudhansuAún no hay calificaciones
- (Monograph Book) Jacques Hadamard - Lessons in Geometry, Vol. 1 - Plane Geometry (2008, American Mathematical Society) PDFDocumento346 páginas(Monograph Book) Jacques Hadamard - Lessons in Geometry, Vol. 1 - Plane Geometry (2008, American Mathematical Society) PDFAlexandru Căliman100% (1)
- Worst-Case Optimal Algorithms For Constructing Visibility Polygon With HolesDocumento10 páginasWorst-Case Optimal Algorithms For Constructing Visibility Polygon With HolesaybelwwAún no hay calificaciones
- Isometries of The Plane - BoswellDocumento7 páginasIsometries of The Plane - BoswellGuido 125 LavespaAún no hay calificaciones
- Finding the Orientation of Points Using Cross ProductsDocumento15 páginasFinding the Orientation of Points Using Cross ProductsKawsar AhmedAún no hay calificaciones