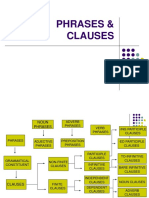
Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Basic Simple Sentence Patterns
Cargado por
ถนอมนวล ทุ่งไธสงTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Basic Simple Sentence Patterns
Cargado por
ถนอมนวล ทุ่งไธสงCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
c Simple Sentence Patterns
Sentence Subjiect Perdicate
Patterms
Nominative
Enlargement
Finite verb ID Do OC SC Extension
Adj. N
P1 Vi
PN
Adj. N Adj. N
P2 Vt
PN PN
Adj. N Adj. N Adj. N
P3 Vt
PN PN PN
Adj. N Adj. N Adj. N
P4 PN Vt PN PN
Adj.
Adj. N Adj. N
P5 PN Vl PN
Adj.
Note 1 P= Patten ID Indirect Object
S = Subject DO Diderect Object
N = Noun OC Objective Complement
PN = Pronoun SC Subjective Complement
Vi = Intransitive Verb
Vt = Transitive Verb
Vl = Linking Verb
Note 2 P51 = S+Vl+Extension
nsion
The Formation of simple sentences
The Formation of simple sentences
Parts of speech
Content word Structure word Basis Sentence Patterns (P)
1. Noun (N) 1. Proposition P1 S+Vi
2. Pronoun (PN) 2. Conjunction P2 S+Vt+DO
3.Verb (V) 3. Interjection P3 S+Vt+ID+DO
4. Adjective (Adj.) P4 S+Vt+DO+OC
Inflection
5. Adverb (Adv.) P5 S+Vl+SC
Sentence elements
Subject (S) Predicate
Nominative Enlargement Verb(v) Object Complement Extension
1. Noun (N) 1. Artuckes ca,an,the 1. Intransitive V. (V.i) 1. Direct (DO) 1. Subjective 1. Adverb (Adv.)
2. Noun phrase (Np) 2. Adijectives 2. Transitive V. (Vt) 2. Indirect (IO) 2. Objective 2. Adverb phsase (Advp)
3. Noun clavse (Nc) 3. Adhective phrase (Adjp) 3. Linking V. (Vl) 3. Adverb clause (Advc.)
4. Noun Equivalents 4. Adjective clavse (Aduc) 4. Modals V.
a Gerund 5. Woeds used as Adj. 5. Auxiliary V.
b Noun infintive a Participles
b Qualifying
infinitive
Parts of speech
Structure words
Parts speech Definition Funtion in sentence Identify parts of speech
Bu its forms By its position
1. demonstrative Adjectives 1. noun determiner 1. this, that, tehse, those
2. articles 2. noun determiner 2. a, an, the
3. indefinite adjectives 3. noun determiner 3. some, any, every, ….
4. pronouns 4. replacing a noun 4. indefinite, interrogative, demonstrative and reflexive
5. Preposition 5. indicating that a noun which is its object is coming. in, on, out, to, at, after, before.
(The phrase formed by the preposition and its object is
related to a verb, adjective, or in the sentence.
6. Connectors
a. subordinate conjections a. joining dependent and independent clauses a. when, where, if, so that,…
b. coradinate conjections b. joining words, phraes, clauses and sentence b. and, but, or, nor, for, so, as, yet
(except "for", "as", "so", "yes")
which only join two independent clauses)
c. corelatives c. joining words, phraes and clauses c. connectors that occor in pair such as both….and,
not only…but also, either…or,
d. connective adverbs or sentence conectors d. showing the relationship between clauses or sentences d. moreover, therefore, likewise
(They usually appear rithin the second independent clauses
and may be movd to various positions whthin the secound
clause.)
Parts of speech
Content words
Identify parts of speech
Part of speech Funtion of Parts of speech Function in sentence
By its form By its position
1. Noun Naming 1. Subject (S) 1. phuraliged by the addition of_s to the singular 1. precede the verb as subject
2. Object (O) Direct object (DO) countable noun
Indirect object (ID) 2. inflected by the addition of_s to show 2. follow the verb as direct object, indirect object,
3. Complement Subject complement (SC) possession object complement andobject after preposition
Object complement (OC) 3. reconiged by its ending or sufix
4. Object after preposition 3. preceded by a determiner such as articals a, an, the
5. Noun modifier
6. Noun in apposition
2. Pronoun Replace noun 1. Subject (S) 1. precede the verb as subject
1. Personal promoun mentioned before 2. Direct object and Indirect object 1. Subject : I, we, you, he, she, it, they 2. follow the verb as direct object,
2. Possessive promoun (Antecedeut) 3. Subject complement (SC) 2. Object : me, us, you, him, her, it. Them inderect object, subject complement
4. Object of preposition mine, ours, yours, his, hers, its, theirs and object after preposition
3. Verb Showing action 1. Intransitive Verb (Vi) 1. __ing 1. follow the subject of a sentence
2. Trasitive Verb (Vt) 2. __s when subject is singular 2. be introduced by verb markers
3. Linking Verb (Vl) countable noun such as auxiliary verb or modal verb,
4. Auxiliary Verb (Va) 3. __ed to from V2 and V3 which preced it
5. Mudal Verb (Vm) 4. __reconiged by its suffix
4. Adjective Modifier of Noun 1. Complement Subject complement (SC) 1. Comparative_er, superative_est or 1. precede the noun it modifies
Object complement (OC) comparative more_, superative most_ 2. between determiner and noun
2. Noun modifier (processive Adjective) 2. identify by its ending or suffix 3. predecate asject as subject complement
and object complement
5. Adverb Modifier V, Adj., or Adv.Extention 1. many adjectives plas_ly 1. before and after the sentence
2. comparative_er, superative_est or 2. between subject and verb or
comparative more_, superative most_ auxiliary verb and verb
3. placed in front of adjective or adverb--Qualifiers
Grammatical Analysis of Sentence
One Sentence of two parts :
A. Subject B. Predicate
Nominative Enlarfement
1. Nouns contable 1. Adjectives Finite Verb Object Complement Extension
uncountable 2. Adijectives 1. Intransitive Verb 1. Direct 1. Subjective 1. Adverbs
2. Noun Phrases 3. Adijective Clauses 2. Transitive Verb 2. Indeirect 2. Objective 3. Adv. Clanses
3. Noun Clauses 4. Articles (a, an, the) 3. Linking Verb (modifying
4. Noun Equivalents 5. Words or phrases 4. Auxiliary V. verbs, adverbs
(substantives) used as adj. (do, be, have, will, shall) or adjectives)
a. Gerund (Praticiples, Qualifying Infinitive) 5. Modals
b. Noun Infinitive (can, could, may, might,
c. Adj. used as a noun ought to, have to, had to)
(with article "the")
Kinds of Sentences
1. Simple 2. Compound 3. Complex 4. Compound - Complex
(one sunject + one (joined by Co-ordinate (joined by Sub+ (Mixed Sentence)
finite verb) Conj. Or ordinate Conj.) (joined by both Co-ordinate and
Conj. Adv.) a. Sub. N. CI. Sub-ordinate Conj.)
a. Cumulative b. Sub.Adj. CI. (two or more Independent CI. +
b. Alternative c. Sub.Adv. CI. one or more Dependent CI.)
c. Adversative (one Independent CI. + one
d. Illative Main or Principal CI. +
(one Independent Cl.+ one one or more Dependent CI.)
Independent Cl.)
0
También podría gustarte
- Vox Super-Mini Spanish and English Dictionary, 3rd EditionDe EverandVox Super-Mini Spanish and English Dictionary, 3rd EditionCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (4)
- Practice Makes Perfect: French Pronouns and Prepositions, Premium Third EditionDe EverandPractice Makes Perfect: French Pronouns and Prepositions, Premium Third EditionCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (8)
- LDI I Chaps 4&5 AssignmentDocumento2 páginasLDI I Chaps 4&5 AssignmentDenílsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Chinese PoSDocumento9 páginasChinese PoSpritam senseiAún no hay calificaciones
- Abbreviations: Comprehension TestDocumento1 páginaAbbreviations: Comprehension TestAditya singhAún no hay calificaciones
- 當代中文 vs. 視聽華語詞類對照 PDFDocumento2 páginas當代中文 vs. 視聽華語詞類對照 PDFlunar89Aún no hay calificaciones
- 當代中文 vs. 視聽華語詞類對照 PDFDocumento2 páginas當代中文 vs. 視聽華語詞類對照 PDFHnin Wut Yi SawAún no hay calificaciones
- I. Constituents/ Parts of Speech/ CategoriesDocumento6 páginasI. Constituents/ Parts of Speech/ CategoriesKatAún no hay calificaciones
- Key Clause Elements - Part 2Documento4 páginasKey Clause Elements - Part 2valen.martinez.aredesAún no hay calificaciones
- Structure of EnglishLETDocumento30 páginasStructure of EnglishLETAlmarie Fuentes100% (1)
- Practice l9 c2 Sentence Structure KeyDocumento5 páginasPractice l9 c2 Sentence Structure Keyapi-486816605Aún no hay calificaciones
- Phrases: Adverb Phrases (Advp) Verb Phrases (VP)Documento1 páginaPhrases: Adverb Phrases (Advp) Verb Phrases (VP)Hà Minh TrangAún no hay calificaciones
- Parts of SpeechDocumento22 páginasParts of Speechsara mohamedAún no hay calificaciones
- On Tap Ly ThuyetDocumento32 páginasOn Tap Ly ThuyetLinh NinhAún no hay calificaciones
- Infinitive Clause Syntax in The Gospels: by Edgar J. LoveladyDocumento176 páginasInfinitive Clause Syntax in The Gospels: by Edgar J. LoveladyandleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Toefl Swe DikonversiDocumento31 páginasToefl Swe DikonversiNatanael UndasAún no hay calificaciones
- JOHOR PGKT NORAINI BINTI SALLEH Sentence Patterns ProjectDocumento34 páginasJOHOR PGKT NORAINI BINTI SALLEH Sentence Patterns ProjectAin SallehAún no hay calificaciones
- Part I: Content Update: Roses Are SweetDocumento35 páginasPart I: Content Update: Roses Are SweetRommel BansaleAún no hay calificaciones
- Modal Perfect InfinitiveDocumento17 páginasModal Perfect InfinitiveLinh NinhAún no hay calificaciones
- BCS English 2023Documento111 páginasBCS English 2023Firoz MahmudAún no hay calificaciones
- Review Structure All SkillsDocumento52 páginasReview Structure All SkillsMutiara BasriAún no hay calificaciones
- 01 Overview - Syntactic StructuresDocumento3 páginas01 Overview - Syntactic StructuresvikiAún no hay calificaciones
- Grammar-Index Vol1Documento13 páginasGrammar-Index Vol1shailynAún no hay calificaciones
- LAL112 Batch 3Documento47 páginasLAL112 Batch 3Kalumßa HillaryAún no hay calificaciones
- Name: Ulum Wahyu Febri Anggraini Nim: 16110070 English English Ii Based On Your Text, Please Answer These Questions CorrectlyDocumento2 páginasName: Ulum Wahyu Febri Anggraini Nim: 16110070 English English Ii Based On Your Text, Please Answer These Questions CorrectlyhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Syntax: Categories and StructureDocumento5 páginasSyntax: Categories and Structureputri nur rahmadhani0% (1)
- Verb Complementation 1Documento2 páginasVerb Complementation 1Martiniano GarnediAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 Elements of The Sentence 2.1Documento88 páginasChapter 2 Elements of The Sentence 2.1Yousif johnAún no hay calificaciones
- Modul 2 PhrasesDocumento41 páginasModul 2 PhrasesretnoAún no hay calificaciones
- Syntax 2023 NotesDocumento33 páginasSyntax 2023 NotesBea Castañeda100% (1)
- Pharases & ClausesDocumento13 páginasPharases & ClausesNur Zara67% (3)
- Hình vị (vp)Documento38 páginasHình vị (vp)Quân TrầnAún no hay calificaciones
- Bahasa Inggris Hukum A3: Khaerul 04020220099Documento13 páginasBahasa Inggris Hukum A3: Khaerul 04020220099DiivaaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guided Reading Lesson Plan 3Documento2 páginasGuided Reading Lesson Plan 3api-432839239Aún no hay calificaciones
- Vocab A-FDocumento73 páginasVocab A-Fzeemred085Aún no hay calificaciones
- Intro DL 10 NLPDocumento99 páginasIntro DL 10 NLPNgọc Nguyễn QuýAún no hay calificaciones
- MODUL - ELEMENTARY - RevisedDocumento42 páginasMODUL - ELEMENTARY - RevisedBintang Suryadi PutraAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To English Syntax: 2 Semester 2011 by Yusep & FitriDocumento45 páginasIntroduction To English Syntax: 2 Semester 2011 by Yusep & FitriLinh HuynhAún no hay calificaciones
- Betty Schrampfer Azar BASIC ENGLISH GRAM 2 p366Documento1 páginaBetty Schrampfer Azar BASIC ENGLISH GRAM 2 p366cendol dawetAún no hay calificaciones
- Phrase Structure TreesDocumento6 páginasPhrase Structure TreesSampath Jayakody100% (1)
- EngI L6 Gram 4 Verbs CH 5Documento38 páginasEngI L6 Gram 4 Verbs CH 5Marta SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- BS English Literature Morning: Submitted By: Group 4 Sr. 1 2 3 4 5 6Documento13 páginasBS English Literature Morning: Submitted By: Group 4 Sr. 1 2 3 4 5 6Amna ShoukatAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Rules On SyntaxDocumento3 páginasBasic Rules On SyntaxElla AlmodovarAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento38 páginasUntitledQuân TrầnAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 3 - Introduction To Phrases and Clauses WBDocumento4 páginasCH 3 - Introduction To Phrases and Clauses WBkarina soledad morenoAún no hay calificaciones
- 88 Parts-of-Speech USDocumento23 páginas88 Parts-of-Speech USfredy96295Aún no hay calificaciones
- Countability: Nouns and Noun Groups: Representing ThingsDocumento8 páginasCountability: Nouns and Noun Groups: Representing ThingsPhát Tài LâmAún no hay calificaciones
- English For General Competition From Plinth To Paramount PDFDocumento424 páginasEnglish For General Competition From Plinth To Paramount PDFSamir PrasadAún no hay calificaciones
- EDSENG3: Structure of English Ms. Oharrah Mae Bernardez Officer-in-Charge, College of EducationDocumento85 páginasEDSENG3: Structure of English Ms. Oharrah Mae Bernardez Officer-in-Charge, College of EducationApenton MimiAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.structure of Englısh - DocxFilename Utf 81.structure of EnglıshDocumento19 páginas1.structure of Englısh - DocxFilename Utf 81.structure of EnglıshMarc Joshua ClareteAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 4 Engslih Sentence Pattern - CompressedDocumento11 páginasUnit 4 Engslih Sentence Pattern - CompressedGeger fiestaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mid-Term Introduction To LinguisticsDocumento4 páginasMid-Term Introduction To LinguisticsHaiqal SatriaAún no hay calificaciones
- Intelligent Thinking - Vocabulary Task - Amend Blank F21Documento2 páginasIntelligent Thinking - Vocabulary Task - Amend Blank F21avihu.purAún no hay calificaciones
- Verb PhrasesDocumento29 páginasVerb PhrasesLe Tuyet NhiAún no hay calificaciones
- Tuwali Dictionary Grammar SketchDocumento112 páginasTuwali Dictionary Grammar SketchEquinoxAún no hay calificaciones
- Tda Rubric For Grade 4 1Documento1 páginaTda Rubric For Grade 4 1api-64933074Aún no hay calificaciones
- Inisiasi 5 (Ems-2022)Documento8 páginasInisiasi 5 (Ems-2022)Hopi HopieAún no hay calificaciones
- Kuliah 1 Bahasa InggrisDocumento9 páginasKuliah 1 Bahasa InggrisAldioD.PratamaAún no hay calificaciones
- Name of Pattern Description Constituents ExamplesDocumento2 páginasName of Pattern Description Constituents ExamplesMateo IbarraAún no hay calificaciones
- Level 1: Parts of Speech: Inter Prep ConjDocumento108 páginasLevel 1: Parts of Speech: Inter Prep ConjJoselynAún no hay calificaciones
- ICT Ed 438 (21st CS) 21 Century Skill BicteDocumento4 páginasICT Ed 438 (21st CS) 21 Century Skill BicteDixit PhuyalAún no hay calificaciones
- Martha Rogers: Presented By: Lyndsi Byers, Geena Griffin, Chelsea Hoy and Mallory ShepardDocumento18 páginasMartha Rogers: Presented By: Lyndsi Byers, Geena Griffin, Chelsea Hoy and Mallory ShepardChelsea Hoy100% (2)
- اسئلة كفايات انجليزي لجميع السنواتDocumento160 páginasاسئلة كفايات انجليزي لجميع السنواتDar DoomAún no hay calificaciones
- Web-Page Recommendation Based On Web Usage and Domain KnowledgeDocumento7 páginasWeb-Page Recommendation Based On Web Usage and Domain KnowledgeGR Techno SolutionsAún no hay calificaciones
- Cinquain PoemsDocumento3 páginasCinquain Poemsapi-329472482Aún no hay calificaciones
- Self-Efficacy and Building Skills of Bachelor of Culture and Arts Education Students at Polytechnic College of BotolanDocumento15 páginasSelf-Efficacy and Building Skills of Bachelor of Culture and Arts Education Students at Polytechnic College of BotolanPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalAún no hay calificaciones
- Developing A Trauma-Informed Child Welfare SystemDocumento9 páginasDeveloping A Trauma-Informed Child Welfare SystemKeii blackhoodAún no hay calificaciones
- Ece120 Notes PDFDocumento150 páginasEce120 Notes PDFMarcus HoangAún no hay calificaciones
- COLORSDocumento4 páginasCOLORSMohit GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vila-Henninger, L. Bringing The HumanDocumento8 páginasVila-Henninger, L. Bringing The HumanCarlos Manuel Uribe GómezAún no hay calificaciones
- 3RD Quarter Grade3least Learned - MalDocumento3 páginas3RD Quarter Grade3least Learned - MalNORMAN CAMPOS JRAún no hay calificaciones
- Distillation Column Control DesignDocumento22 páginasDistillation Column Control DesignAnand Dudheliya0% (1)
- Course Syllabus LS127 PDFDocumento4 páginasCourse Syllabus LS127 PDFBlah BlamAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment Life Long October2016Documento5 páginasAssignment Life Long October2016Arvin KovanAún no hay calificaciones
- TKT Young Learners Worksheets: With Trainer NotesDocumento92 páginasTKT Young Learners Worksheets: With Trainer NotesThu NaingAún no hay calificaciones
- The Difference Between Typical and Atypical Development in ChildrenDocumento2 páginasThe Difference Between Typical and Atypical Development in ChildrenJERIC A. REBULLOSAún no hay calificaciones
- Read Unromancing The DreamDocumento5 páginasRead Unromancing The DreamJules McConnellAún no hay calificaciones
- Modul Bahasa Inggris - Kelas XIIDocumento41 páginasModul Bahasa Inggris - Kelas XIIRegina L Sihombing LumbantoruanAún no hay calificaciones
- The SAGE Handbook of Leadership PDFDocumento593 páginasThe SAGE Handbook of Leadership PDFRif'an Naufal Analis100% (8)
- Discovery Learning Edutech WikiDocumento20 páginasDiscovery Learning Edutech WikiSilil Inayrus100% (1)
- Task 1 RNWDocumento1 páginaTask 1 RNWBeyaAún no hay calificaciones
- School Climate SurveyDocumento7 páginasSchool Climate Surveywested-magnet-schools100% (1)
- Unit 3: Listening Skill Exercise 1Documento5 páginasUnit 3: Listening Skill Exercise 1Minh LêAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab Report Format (Int Sci)Documento2 páginasLab Report Format (Int Sci)Rianna SatramAún no hay calificaciones
- Certificate of Originality: Place: Place: Date: DateDocumento4 páginasCertificate of Originality: Place: Place: Date: DateSumit PandeyAún no hay calificaciones
- Round-Up 6. Teacher S GuideDocumento81 páginasRound-Up 6. Teacher S GuideМария Лошкова100% (1)
- Design Thinking Whitepaper - AlgarytmDocumento34 páginasDesign Thinking Whitepaper - AlgarytmRavi JastiAún no hay calificaciones
- Sensing Sound by Nina Sun EidsheimDocumento39 páginasSensing Sound by Nina Sun EidsheimDuke University Press100% (3)
- Essay Technology ImportanceDocumento3 páginasEssay Technology ImportanceCyrah CapiliAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 Activity - AMID, SAMUEL Jr.Documento2 páginasChapter 1 Activity - AMID, SAMUEL Jr.Belinda GeronimoAún no hay calificaciones