Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Glossary of Butterfly Terminolo
Cargado por
monarchfriend0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
721 vistas1 páginaThis is the last of the three segments (posterior) of a butterfly's body and contains the reproductive organs. This is the end of the butterfly's abdomen that contains little hooks used to attach and suspend the caterpillar from a silk pad. It is the sloughed off natural'skin' of the caterpillar or the leftover chrysalis after the butterfly has eclosed. The waste material produced by a butterfly pupa that is expelled when the
Descripción original:
Derechos de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoThis is the last of the three segments (posterior) of a butterfly's body and contains the reproductive organs. This is the end of the butterfly's abdomen that contains little hooks used to attach and suspend the caterpillar from a silk pad. It is the sloughed off natural'skin' of the caterpillar or the leftover chrysalis after the butterfly has eclosed. The waste material produced by a butterfly pupa that is expelled when the
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
721 vistas1 páginaGlossary of Butterfly Terminolo
Cargado por
monarchfriendThis is the last of the three segments (posterior) of a butterfly's body and contains the reproductive organs. This is the end of the butterfly's abdomen that contains little hooks used to attach and suspend the caterpillar from a silk pad. It is the sloughed off natural'skin' of the caterpillar or the leftover chrysalis after the butterfly has eclosed. The waste material produced by a butterfly pupa that is expelled when the
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 1
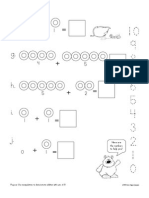
Butterfly Terminology
Here is a glossary of terms used in butterfly science.
Abdomen This is the last of the three segments (posterior) of a butterfly’s body and
contains the reproductive organs.
Antenna (singular) On a butterfly, these are usually club-shaped appendages that serve as
Antennae (plural) sensory organs. On Skipper butterflies, they are hooked as well.
Caterpillar This is a butterfly’s larval stage or the 2nd stage in the butterfly life-cycle.
Chrysalis (singular) This is the hard case of a pupa or the 3rd stage in the butterfly life-cycle
Chrysalides (plural) where complete metamorphosis takes place.
Compound eyes These are the large eyes of a butterfly and are made up of many
separate visual receptors.
Cremaster This is the end of the butterfly’s abdomen that contains little hooks used
to attach and suspend the caterpillar from a silk pad.
Diapause This is a period of time often termed ‘overwintering’ when a butterfly’s
development has been suspended and can be in any stage
depending upon the butterfly.
Eclose/Eclosion When the butterfly emerges from the chrysalis it is said to eclose.
Egg (Ova) This is the 1st stage in the butterfly life-cycle.
Exuviae The sloughed off natural ‘skin’ of the caterpillar or the leftover chrysalis
*Exo-skeleton after the butterfly has eclosed. Sometimes termed as the exo-skeleton—
Frass This is what the excrement or poop from a larva is called
(Note: if the frass is runny or diarrhea-like, then it is called scree)
Instar There are stages of molting/shedding as a caterpillar outgrows its
exo-skeleton. Butterfly larvae usually go through four to five instars.
Larva (singular) This is the caterpillar or the 2nd stage in the butterfly’s life-cycle.
Larvae (plural)
Mandibles This is the caterpillar’s specialized jaw structure that enables it to eat
leaves.
Meconium This is the waste material produced by a butterfly pupa that is expelled
when the butterfly ecloses. It is often a red colour but is not blood.
Oviposit This is the term to indicate the laying of eggs.
Proboscis This is the straw-like feeding mouthpart of a butterfly that is coiled when
not in use. Butterflies often ingest nectar using their proboscis but can
also ingest minerals from mud puddles or animal feces.
Proleg A fleshy false leg that occurs on the abdominal section of the larva that
is not found on the adult butterfly. Butterfly larva have five pairs.
Spiracles These are tiny holes in the sides of the butterfly’s and caterpillar’s body
that allow oxygen to enter its respiratory system.
Thorax This is the muscular middle segment of a butterfly’s body where the
wings and legs are attached and located.
©2008 The Butterfly Guide
monarchfriend@yahoo.com
También podría gustarte
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2102)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Method Statement For Cable Trays & Cable Ladders InstallationDocumento7 páginasMethod Statement For Cable Trays & Cable Ladders InstallationJamal Budeiri0% (1)
- Cheerios Addition ADocumento1 páginaCheerios Addition Amonarchfriend100% (12)
- Cheerios Subt IntroDocumento1 páginaCheerios Subt IntromonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- 09 Passport 7K 15K Performance Guidelines PCR 3 0Documento44 páginas09 Passport 7K 15K Performance Guidelines PCR 3 0thed719Aún no hay calificaciones
- Prawn ProcessingDocumento21 páginasPrawn ProcessingKrishnaAún no hay calificaciones
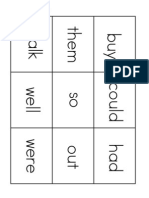
- HFW Set #13Documento1 páginaHFW Set #13monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
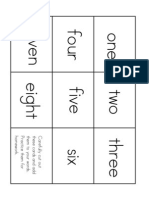
- Jelly Bean GraphDocumento1 páginaJelly Bean Graphmonarchfriend100% (4)
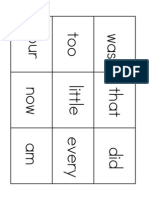
- Kindergarten High Frequency Sight WordsDocumento1 páginaKindergarten High Frequency Sight Wordsmonarchfriend100% (1)
- HFW Set 11Documento1 páginaHFW Set 11monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- HFW Set 10Documento1 páginaHFW Set 10monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- HFW Set #12Documento1 páginaHFW Set #12monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Short Phrase ListDocumento1 páginaShort Phrase ListmonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- 'Zebra' Larvae Article From MLMPDocumento1 página'Zebra' Larvae Article From MLMPmonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- HFW Set #7Documento1 páginaHFW Set #7monarchfriend100% (1)
- HFW Set #8Documento1 páginaHFW Set #8monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Kindergarten Vertical Writing PaperDocumento1 páginaKindergarten Vertical Writing Papermonarchfriend100% (2)
- HFW Set #9Documento1 páginaHFW Set #9monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Kindergarten Horizontal Writing PaperDocumento1 páginaKindergarten Horizontal Writing Papermonarchfriend100% (2)
- HFW Set #5Documento1 páginaHFW Set #5monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Kindergarten Letter Writing PaperDocumento1 páginaKindergarten Letter Writing Papermonarchfriend100% (2)
- HFW Set #6Documento1 páginaHFW Set #6monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- HFW Set #3Documento1 páginaHFW Set #3monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- HFW Set #2Documento1 páginaHFW Set #2monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Can Math FactsDocumento1 páginaCan Math FactsmonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- HFW Set #4Documento1 páginaHFW Set #4monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Let's SubtractDocumento1 páginaLet's SubtractmonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Farm Flashcards p2Documento1 páginaFarm Flashcards p2monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Thank You Note - GiftDocumento1 páginaThank You Note - GiftmonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Hundreds ChartDocumento1 páginaHundreds Chartmonarchfriend100% (10)
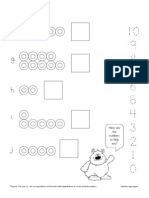
- Cereal Number BDocumento1 páginaCereal Number BmonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Cereal Number ADocumento1 páginaCereal Number AmonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Cheerios Addition BDocumento1 páginaCheerios Addition BmonarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- HFW Set 3Documento1 páginaHFW Set 3monarchfriendAún no hay calificaciones
- Product Recommendation Hyster Forklift Trucks, Electric J1.60XMTDocumento1 páginaProduct Recommendation Hyster Forklift Trucks, Electric J1.60XMTNelson ConselhoAún no hay calificaciones
- Microbiology Part 3Documento74 páginasMicrobiology Part 3Authentic IdiotAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Choice Enzymes Plant and Animal NutritionDocumento44 páginasMultiple Choice Enzymes Plant and Animal Nutritionliufanjing07Aún no hay calificaciones
- American University of BeirutDocumento21 páginasAmerican University of BeirutWomens Program AssosciationAún no hay calificaciones
- CE Review GEOMETRY 2Documento6 páginasCE Review GEOMETRY 2Paul Gerard AguilarAún no hay calificaciones
- LJ-V7080 DatasheetDocumento2 páginasLJ-V7080 DatasheetOrhan DenizliAún no hay calificaciones
- LPG GasDocumento39 páginasLPG Gasv prasanthAún no hay calificaciones
- By This Axe I Rule!Documento15 páginasBy This Axe I Rule!storm0% (1)
- Angewandte: ChemieDocumento13 páginasAngewandte: ChemiemilicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Generative Shape DesignDocumento195 páginasGenerative Shape DesignAdi Fiera100% (1)
- Eating With Chloe Lets EatDocumento150 páginasEating With Chloe Lets Eatemily.jarrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Tuesday, 16 November 2021 - Afternoon Discovering ElectronicsDocumento20 páginasTuesday, 16 November 2021 - Afternoon Discovering Electronicsnvmalt070Aún no hay calificaciones
- Opex and CapexDocumento5 páginasOpex and CapexATM Shafiq Ul AlamAún no hay calificaciones
- ODA X9 2SL DatasheetDocumento8 páginasODA X9 2SL DatasheetYudy UtamaAún no hay calificaciones
- S590 Machine SpecsDocumento6 páginasS590 Machine SpecsdilanAún no hay calificaciones
- A Tired BrainDocumento3 páginasA Tired BrainSivasonAún no hay calificaciones
- Salapare Et Al 2015 ZambalesDocumento12 páginasSalapare Et Al 2015 ZambalesTiqfar AhmadjayadiAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 SAMSS 005 Check ValvesDocumento9 páginas04 SAMSS 005 Check ValvesShino UlahannanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Bonds WorksheetDocumento2 páginasChemical Bonds WorksheetJewel Mae MercadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Pre RmoDocumento4 páginasPre RmoSangeeta Mishra100% (1)
- Calibration of Force ReductionDocumento36 páginasCalibration of Force Reductionvincenzo_12613735Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Unofficial Aterlife GuideDocumento33 páginasThe Unofficial Aterlife GuideIsrael Teixeira de AndradeAún no hay calificaciones
- Marketing Management 4th Edition Winer Test BankDocumento35 páginasMarketing Management 4th Edition Winer Test Bankapneaocheryzxs3ua100% (24)
- Mini-Case 1 Ppe AnswerDocumento11 páginasMini-Case 1 Ppe Answeryu choong100% (2)
- Pref - 2 - Grammar 1.2 - Revisión Del IntentoDocumento2 páginasPref - 2 - Grammar 1.2 - Revisión Del IntentoJuan M. Suarez ArevaloAún no hay calificaciones
- Active Faults in MalaysiaDocumento52 páginasActive Faults in MalaysiaHazim HaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nicholas Hudson - From Nation To Race: The Origin of Racial Classification in Eighteenth-CenturyDocumento19 páginasNicholas Hudson - From Nation To Race: The Origin of Racial Classification in Eighteenth-CenturyPedro IIAún no hay calificaciones