Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Introduccion A Las Fallas de Sistemas de Potencia
Cargado por
Mario Sánchez0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
12 vistas1 páginaIntroduccion a Las Fallas de Sistemas de Potencia cap 1
Título original
Introduccion a Las Fallas de Sistemas de Potencia
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoIntroduccion a Las Fallas de Sistemas de Potencia cap 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
12 vistas1 páginaIntroduccion A Las Fallas de Sistemas de Potencia
Cargado por
Mario SánchezIntroduccion a Las Fallas de Sistemas de Potencia cap 1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 1
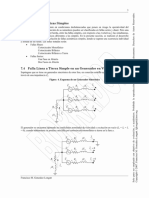
Introduction to power
system faults
Inthis introductory chapter, we introduce the important terminology of fault current
‘waveform, discuss the need for power system fault analysis and the effects of fault
‘currents in power systems. Per-unit analysis concept of single-phase and three-
‘phase power systems is presented including the base and per-unit equations of self
‘and mutual impedances and admittances
Electrical ac power systems consist of three-phase generation systems, transmis
sion and distribution networks, and loads. The networks supply large three-phase
industrial loads at various distribution and transmission voltages as wel as single-
pphase residential and commercial loads. In some countries, e.g. North America,
‘the term subtransmission is used to denote networks with voltage classes between
transmission and distribution, Distribution voltages are typically 10-60 kV, sub-
transmission voltages are typically 66-138kV and transmission voltages are
typically above 138kV. Generated voltages are up to 35kV for generators used
in large electrical power stations. Power station auxiliary supply systems and
industrial power systems supply @ significant amount of induction motor load,
Residential and commercial loads include a significant amount of single-phase
induction motor loads
For over a century, electric power systems used synchronous machines for the
‘generation of electricity, However, in the twenty-first century, the generation of
electricity from renewable energy sources such as wind has begun to expand at
4 lange pace. Generally, such generation systems use a variety of asynchronous
También podría gustarte
- Corto Circuito Parte 9Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 9Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 14Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 14Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 11Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 11Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 12Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 12Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 10Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 10Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 12Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 12Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 3Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 3Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 7Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 7Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 9Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 9Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 5Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 5Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 6Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 6Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p1Documento1 páginaCapitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p1Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 8Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 8Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 4Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 4Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p4Documento1 páginaCapitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p4Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 1Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 1Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Corto Circuito Parte 2Documento1 páginaCorto Circuito Parte 2Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Estudio de Corto Circuito SiemensDocumento2 páginasEstudio de Corto Circuito SiemensMario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cortos Circuitos en Las Instalaciones Electricas Part1Documento1 páginaCortos Circuitos en Las Instalaciones Electricas Part1Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cortos Circuitos en Las Instalaciones Electricas Part2Documento1 páginaCortos Circuitos en Las Instalaciones Electricas Part2Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p3Documento1 páginaCapitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p3Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p2Documento1 páginaCapitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p2Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p5Documento1 páginaCapitulo 1 Sistemas Electricos de Potencia p5Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia ArcoDocumento27 páginasGuia ArcoMario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fallas Asimetricas p7Documento1 páginaFallas Asimetricas p7Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fallas Asimetricas p6Documento1 páginaFallas Asimetricas p6Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fallas Asimetricas p5Documento1 páginaFallas Asimetricas p5Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fallas Asimetricas p3Documento1 páginaFallas Asimetricas p3Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fallas Asimetricas p4Documento1 páginaFallas Asimetricas p4Mario SánchezAún no hay calificaciones