Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Fluorescein Archvdatei
Cargado por
Lurthu PushparajDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Fluorescein Archvdatei
Cargado por
Lurthu PushparajCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
DaMocles SS 2011 – Jonas von Irmer, Jhilmil Hossain, Sebastian Dewald & Maximilian Gatterdam
Fluorescein
Fluorescein is a fluorescent dye, which is 3. Synthesis 4
mostly used as a chemical indicator in
many applications. Its disodium salt is a
red crystalline (chinoid form) or yellow
(lactoide form) powder called uranine,
soluble in water and alcohol, and belongs
to the group of xanthene dyes.
13
+H+
1. General data 1, 2
-H2O
IUPAC-name: 2-(6-Hydroxy-3-
oxo-3H-xanthen-9-
yl)-benzoic-acid
CAS-No.: 2321-07-5
Molecular Formula: C20H12O5
Molecular Weight: 332,32 g/mol
Melting point: 314 – 316 °C
-H+
Excitation max.: 494 nm
Emission max.: 521 nm
Lifetime: 3-4 ns
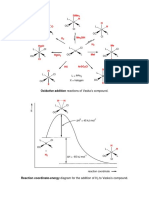
2. History 3
Fluoresceine was discovered by Adolf von
Baeyer in 1871 while experimenting with
the analogous phenolphthalein which is
synthesized from Phenol and phthalic
-H2O
anhydride. In comparison fluorescein
(earlier called Resorcinphthalein) is
synthesized by condensation of Resorcinol
and phthalic anhydride as shown in the
mechanism.
DaMocles SS 2011 – Jonas von Irmer, Jhilmil Hossain, Sebastian Dewald & Maximilian Gatterdam
4. Fluorescence 5 5. Derivatives
Fluorescence is a special type of Not only fluorescein, but also its
luminescence. It describes the absorption derivatives are needed in different fields.
of light or other electromagnetic radiation Just to mention a few of them:
and following emission of light of a
5.1 Eosin B
different wavelength.
As shown in the Jablonski diagram the
absorbed electromagnetic radiation
excites an electron from the ground state
S0 to the excited state S1. This electron can
relax to its ground state by “non-radiative
relaxation” in which the excitation energy
is transformed into vibration (heat) or by 5.2 Eosin Y
emitting radiation (fluorescence). The
absorption and emission wavelength are
specific for every fluorescent substance.
Commonly the lifetime of the excited state
is a few nanoseconds.
An explanation of phosphorescence will
not be given here because it is not
relevant for fluorescein.
Both forms of eosin are used for
14
histological compounds, indicators, to
dye tissues and cells, and to dye paper
and textiles 6.
5.3 Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)
Carboxyfluorescein*
*uses in chapter 6.4
DaMocles SS 2011 – Jonas von Irmer, Jhilmil Hossain, Sebastian Dewald & Maximilian Gatterdam
6. Applications
6.1 Uses in Water systems 1, 7: 6.3 Uses in analytic chemistry:
Fluorescein is used for dyeing A method to detect bromides is to
rivers and springs to trace their oxidize them with K2Cr2O7 and
stream course also the concentrated sulfuric acid so
subterranean ones. gaseous bromine is produced. The
It can also be applied to visualize bromine reacts with a filter paper
water leaks. drenched in a solution of 0,2g
It was also used for dyeing the uranine in 100ml ethanol and a
Chicago River green on St. Patrick`s drop of ammoniac solution (10%)
Day from 1962-1966. coloring it pink 2.
Shipwrecked crews can deploy Fluorescein (or eosin) can also be
fluorescein packages to color the used as indicator in the
sea to augment the chances of argentometry (Fajans method)9, 10.
being rescued. 500g of uranine can
dye up to 4000 m² 6.4 Fluorescence labeling:
Using this technique antibodies,
6.2 Uses in Angiography 1, 8: proteins, amino acids and peptides
Fluorescein angiography is a are labeled attaching a reactive
visualization of vasculature by derivate of a fluorophore (in this
injection of an uranine solution. case fluorescein). These can then
The now fluorescing veins can be be detected by a fluorescence
detected with a specific camera to microscope.
observe retinal diseases (macular
FITC conjugates primary amines
degeneration, inflammatory
reacting to thiourea. This method
intraocular conditions, diabetic
is applied to visualize antibodies 11.
retinopathy, and intraocular
Carboxyfluorescein can be
tumors). A new application is to
incorporated into liposomes which
show brain tumors during brain
can then be tracked passing the
surgeries.
body 12.
15
Fluorescing tissue (angiography)
DaMocles SS 2011 – Jonas von Irmer, Jhilmil Hossain, Sebastian Dewald & Maximilian Gatterdam
7. Sources
1
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fluorescein
(7.7.2011 11:24)
2
http://www.omikron-
online.de/cyberchem/cheminfo/0221-
lex.htm (8.7.2011 14:32)
3
http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fluorescein
(8.7.2011 14:26)
4
http://www.mgh.schulnetz.hamm.de/fae
cher/chemie/farbstoffe/Fluorescein.doc
(8.7.2011 14:29)
5
http://www.zoologie-
skript.de/methoden/fluo/fluo1l.htm
(8.7.2011 14:35)
6
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eosin
(8.7.2011 14:25)
7
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dye_tracing
(8.7.2011 14:17)
8
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fluorescent_
angiography (8.7.2011 14:21)
9
http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Titration_na
ch_Fajans (8.7.2011 13:39)
10
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Argentometr
y#Fajans_method (8.7.2011 13:40)
11
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fluorescein_
isothiocyanate (8.7.2011 14:10)
12
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carboxyfluor
escein (8.7.2011 14:08)
13
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/co
mmons/d/d3/Fluorescein-sample.jpg
(8.7.2011 14:43)
14
http://www.zoologie-
skript.de/methoden/fluo/jablonl.jpg
(8.7.2011 14:37)
15
http://www.optos.com/Global/images/pr
of_genophth_case_retdetach_large.jpg
(8.7.2011 14:39)
All Lewis structures are self-made with
ChemSketch.
También podría gustarte
- Words Their Way Blue SortsDocumento60 páginasWords Their Way Blue SortsSophie Lee75% (8)
- Clinical Laboratory LawDocumento26 páginasClinical Laboratory Lawlwlski71% (7)
- TSSM Unit Two Exam 2017Documento19 páginasTSSM Unit Two Exam 2017nisulAún no hay calificaciones
- Agentes Diagnósticos en OftalmologíaDocumento16 páginasAgentes Diagnósticos en OftalmologíaJosé Eduardo Zaragoza LópezAún no hay calificaciones
- Study of Kinetic, Isothermal, and Sorption Characteristics of Some Dyes Using Novel Lupine Peel PowderDocumento18 páginasStudy of Kinetic, Isothermal, and Sorption Characteristics of Some Dyes Using Novel Lupine Peel PowderIJAR JOURNALAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluorescein Dye PDFDocumento7 páginasFluorescein Dye PDFLaura FajardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluorescein Based Fluorescence Sensors For The Selective Sensing of Various AnalytesDocumento26 páginasFluorescein Based Fluorescence Sensors For The Selective Sensing of Various AnalytesJose Fernando Bastos ZayasAún no hay calificaciones
- FEBS Letters - 1997 - Ferrali - Protection Against Oxidative Damage of Erythrocyte Membrane by The Flavonoid Quercetin andDocumento7 páginasFEBS Letters - 1997 - Ferrali - Protection Against Oxidative Damage of Erythrocyte Membrane by The Flavonoid Quercetin andDea IftitahAún no hay calificaciones
- Sarkany 2008Documento7 páginasSarkany 2008Kolbert RascalAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 s2.0 S0012160621000543 MainDocumento11 páginas1 s2.0 S0012160621000543 Mainbossdesign.ifAún no hay calificaciones
- Rastogi and Pospisil 2010Documento7 páginasRastogi and Pospisil 2010anshuslsAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 16 - Dyes - 2008 - Clinical Ocular PharmacologyDocumento12 páginasChapter 16 - Dyes - 2008 - Clinical Ocular PharmacologysAún no hay calificaciones
- Synthesis of Fluorinated FluoresceinsDocumento7 páginasSynthesis of Fluorinated FluoresceinsLaura Gomez AnzaldoAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrochemical Synthesis of Erythrosin From Uorescein: Journal of Applied Electrochemistry November 1994Documento4 páginasElectrochemical Synthesis of Erythrosin From Uorescein: Journal of Applied Electrochemistry November 1994Que Verbo BataAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical Applications of Fundus Autofluorescence in Retinal DiseaseDocumento25 páginasClinical Applications of Fundus Autofluorescence in Retinal Diseasepooja barakAún no hay calificaciones
- Ojsadmin, 123 PDFDocumento4 páginasOjsadmin, 123 PDFnoor noorAún no hay calificaciones
- Multicomponent Syntheses of FluorophoresDocumento35 páginasMulticomponent Syntheses of Fluorophoresreddyraj036Aún no hay calificaciones
- Organic Photochemistry 2004 - FultonDocumento154 páginasOrganic Photochemistry 2004 - FultonVioleta GrigorasAún no hay calificaciones
- Oxidation of Avonols With Cu, Fe and Fe in Aqueous MediaDocumento7 páginasOxidation of Avonols With Cu, Fe and Fe in Aqueous MediaKatrinaAún no hay calificaciones
- FluorescenceDocumento2 páginasFluorescenceRaazia MirAún no hay calificaciones
- Membrane Interactions and Surface Hydrophobicity of Bacillus Thuringiensis S-Endotoxin CryICDocumento4 páginasMembrane Interactions and Surface Hydrophobicity of Bacillus Thuringiensis S-Endotoxin CryICme_dayakarAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Stabilize Phospholipid Liposomes (Using Nanoparticles)Documento5 páginasHow To Stabilize Phospholipid Liposomes (Using Nanoparticles)verawaty watyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 11 BPPDocumento20 páginasLesson 11 BPPMa LeslynneAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 2 - PhotosynthesisDocumento12 páginasCH 2 - PhotosynthesisnawarakanAún no hay calificaciones
- Class - Xi - Biology: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Module - 1Documento20 páginasClass - Xi - Biology: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Module - 1priyam dasAún no hay calificaciones
- 22 Photosynthesis 1Documento44 páginas22 Photosynthesis 1黄心怡Aún no hay calificaciones
- Extraction of Chlorophyll Using Dimethylsulfoxide and AcetoneDocumento23 páginasExtraction of Chlorophyll Using Dimethylsulfoxide and Acetoneاحمد الدلالAún no hay calificaciones
- PhotopsinDocumento3 páginasPhotopsinandrej.gregorcicAún no hay calificaciones
- Reaction Of S O Ion And Μ-Oxo-Tetrakis (1, 10- Phenanthroline) Diiron (Iii) Complex Ion In Aqueous Phenanthrolinium Buffer: A Kinetic StudyDocumento6 páginasReaction Of S O Ion And Μ-Oxo-Tetrakis (1, 10- Phenanthroline) Diiron (Iii) Complex Ion In Aqueous Phenanthrolinium Buffer: A Kinetic Studyibro4khadAún no hay calificaciones
- Hui Gnard 2000Documento5 páginasHui Gnard 2000Rebeca Cristina Costa de SaAún no hay calificaciones
- SR AIIMS Supe-60 MT-6 - (27-12-2022) - Key & Solution - FinalDocumento15 páginasSR AIIMS Supe-60 MT-6 - (27-12-2022) - Key & Solution - FinalAdithya BharadwajAún no hay calificaciones
- 12 - Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsDocumento5 páginas12 - Photosynthesis in Higher PlantsShruti KaleAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 s2.0 S0143720821005593 MainextDocumento9 páginas1 s2.0 S0143720821005593 MainextMoromi NathAún no hay calificaciones
- 4.monodansylpentane As A Blue-Fluorescent Lipid-Droplet Marker For Multi-Color Live-Cell ImagingDocumento8 páginas4.monodansylpentane As A Blue-Fluorescent Lipid-Droplet Marker For Multi-Color Live-Cell ImagingShalika AbeysingheAún no hay calificaciones
- Synthesis of Conformationally Locked - Deoxythreosyl Phosphonate Nucleosides Built On A Bicyclo (3.1.0) Hexane TemplateDocumento11 páginasSynthesis of Conformationally Locked - Deoxythreosyl Phosphonate Nucleosides Built On A Bicyclo (3.1.0) Hexane TemplateDiogomussumAún no hay calificaciones
- ANNINE-6plus, A Voltage-Sensitive Dye With Good Solubility, Strong Membrane Binding and High SensitivityDocumento6 páginasANNINE-6plus, A Voltage-Sensitive Dye With Good Solubility, Strong Membrane Binding and High SensitivityFrontiersAún no hay calificaciones
- Ent Ke: Lipofuscin: The "Wear and Tear" PigmentDocumento3 páginasEnt Ke: Lipofuscin: The "Wear and Tear" PigmentDileep DileepAún no hay calificaciones
- L5 Diag Dyes TextDocumento6 páginasL5 Diag Dyes TexthanifyassirAún no hay calificaciones
- Anexo 1-PaperDocumento7 páginasAnexo 1-PaperMichael CrowAún no hay calificaciones
- Jurol Fenol Ing 1Documento7 páginasJurol Fenol Ing 1milktea segerrAún no hay calificaciones
- Use of Dyes in OphthalmologyDocumento4 páginasUse of Dyes in OphthalmologyMaulana MalikAún no hay calificaciones
- Iodination of Humic Acid Samples From Different or PDFDocumento8 páginasIodination of Humic Acid Samples From Different or PDFBob RoonyAún no hay calificaciones
- The Utility of Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Neuro-OphthalmologyDocumento19 páginasThe Utility of Fundus Fluorescein Angiography in Neuro-OphthalmologyA. JumeauAún no hay calificaciones
- The Fluorosolvatochromism of Brooker's MerocyanineDocumento10 páginasThe Fluorosolvatochromism of Brooker's MerocyanineDomingas Bia SilvaAún no hay calificaciones
- 13 Photosynthesis-NotesDocumento6 páginas13 Photosynthesis-NotesDe DasAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 - Zhu - Chemcomm - Colorimetric Fluoride Pyrrole-HemiquinoneDocumento3 páginas10 - Zhu - Chemcomm - Colorimetric Fluoride Pyrrole-Hemiquinonelenggah purwandariAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluorescnec 1Documento21 páginasFluorescnec 1vscdAún no hay calificaciones
- A Method For Localizing Embryonal Laticifers by CombinedDocumento5 páginasA Method For Localizing Embryonal Laticifers by CombinedCrisMayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fing 1Documento17 páginasFing 1Hadjer Nouara Ait-KaciAún no hay calificaciones
- Synthesis of Fluorescein Dye UsingDocumento6 páginasSynthesis of Fluorescein Dye UsingMoises BarraganAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 s2.0 S0040402013009824 MainDocumento5 páginas1 s2.0 S0040402013009824 MainLizhy PedrazaAún no hay calificaciones
- Hall CyanelaDocumento13 páginasHall CyanelaGabyAún no hay calificaciones
- Histology - Lesson 1 - IntroDocumento5 páginasHistology - Lesson 1 - IntroAngelina AquinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chromophore - WikipediaDocumento4 páginasChromophore - WikipediaRizwan ShahidAún no hay calificaciones
- Vold A6TORONTO,: 1attt 3hrnruuDocumento6 páginasVold A6TORONTO,: 1attt 3hrnruuagiekAún no hay calificaciones
- FQ Phototoxicity - Martinez - Et - Al-1998-Photochemistry - and - PhotobiologyDocumento5 páginasFQ Phototoxicity - Martinez - Et - Al-1998-Photochemistry - and - PhotobiologyAndy KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Hackenberger2012 PDFDocumento7 páginasHackenberger2012 PDFWahyu FathurrachmanAún no hay calificaciones
- PhotosynthesisDocumento19 páginasPhotosynthesisthushyanthAún no hay calificaciones
- Application of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass SpeDocumento6 páginasApplication of Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass SpeĐăng LưuAún no hay calificaciones
- Staining of Cell OrganellesDocumento3 páginasStaining of Cell OrganellesDr Sanjeeb Kumar Dey BaidyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluorimetry Definition/Background: FluorescenceDocumento3 páginasFluorimetry Definition/Background: FluorescenceleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Histology NotesDocumento54 páginasHistology NotesShienila Penuela100% (1)
- Synthesis of 2-methyl-4-selenoquinazolone, 2-phenylbenzoselenazole, and its derivativesDe EverandSynthesis of 2-methyl-4-selenoquinazolone, 2-phenylbenzoselenazole, and its derivativesAún no hay calificaciones
- Nano MaterialDocumento5 páginasNano MaterialLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- Nano SynDocumento4 páginasNano SynLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- Metallostar Assemblies Based On Dithiocarbamates For Use As MRI Contrast AgentsDocumento11 páginasMetallostar Assemblies Based On Dithiocarbamates For Use As MRI Contrast AgentsLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- 12.ashnil KumaDocumento9 páginas12.ashnil KumaLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- Organic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 14 - : Aromatic CompoundsDocumento28 páginasOrganic Chemistry II / CHEM 252 Chapter 14 - : Aromatic CompoundsLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- NanoDocumento6 páginasNanoLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- 16.yong LuoDocumento14 páginas16.yong LuoLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- CNHN PDFDocumento1 páginaCNHN PDFLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- Reactivity at Different Sites On Metal-Arene Complexes A Classic Example of UmpolungDocumento1 páginaReactivity at Different Sites On Metal-Arene Complexes A Classic Example of UmpolungLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- Catcycle PDFDocumento1 páginaCatcycle PDFLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- MO diagram for MO diagram for: σ-donor ligand system, octahedral complex π-acceptor ligand system, octahedral complexDocumento1 páginaMO diagram for MO diagram for: σ-donor ligand system, octahedral complex π-acceptor ligand system, octahedral complexLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- of Mo (η -C H) (η -CH Chchch) (η -C H) .: StructureDocumento1 páginaof Mo (η -C H) (η -CH Chchch) (η -C H) .: StructureLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- OAREDocumento2 páginasOARELurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- D3o - WikipediaDocumento3 páginasD3o - WikipediaLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- Lva1 App6892Documento5 páginasLva1 App6892Lurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- ERRB-09-DRDO-Conference FormDocumento2 páginasERRB-09-DRDO-Conference FormLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- 8 M. Sc. II Inorganic ChemistryDocumento16 páginas8 M. Sc. II Inorganic ChemistryLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- Proforma - V Department of BiotechnologyDocumento5 páginasProforma - V Department of BiotechnologyLurthu PushparajAún no hay calificaciones
- Khan Academy Cellular Division QuestionsDocumento3 páginasKhan Academy Cellular Division QuestionsLoraAún no hay calificaciones
- Science NotesDocumento10 páginasScience NotesLiezel BrillantesAún no hay calificaciones
- Biomechanics, Prosthetic & Orthotics BME 2205: Anatomical MovementDocumento33 páginasBiomechanics, Prosthetic & Orthotics BME 2205: Anatomical Movementmorris loguyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Normal Hemodynamic Parameters and Lab Values - Reference CardDocumento4 páginasNormal Hemodynamic Parameters and Lab Values - Reference Cardblanquishem100% (1)
- Book JewsDocumento230 páginasBook JewsFred Duarte CaldeiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Pierluigi IghinaDocumento38 páginasPierluigi Ighinaemmepicsd100% (2)
- SynapseDocumento7 páginasSynapseNadzierah RazakAún no hay calificaciones
- Intro To Stat (STAT 111) by EwensDocumento113 páginasIntro To Stat (STAT 111) by EwensIris ZhangAún no hay calificaciones
- Placenta Extract & Castor Oil (Next Generation Wound Healer)Documento11 páginasPlacenta Extract & Castor Oil (Next Generation Wound Healer)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAún no hay calificaciones
- Regio Abdomen II.2020Documento72 páginasRegio Abdomen II.2020Anonymous 7rQI2K9deAún no hay calificaciones
- Kami Export - Exercise Lab - Mini-2Documento3 páginasKami Export - Exercise Lab - Mini-2Ryan FungAún no hay calificaciones
- J Esthet Restor Dent - 2024 - Esquivel - Timing Implant Provisionalization Decision Making and Systematic WorkflowDocumento10 páginasJ Esthet Restor Dent - 2024 - Esquivel - Timing Implant Provisionalization Decision Making and Systematic WorkflowDANTE DELEGUERYAún no hay calificaciones
- Application of Artificial Intelligence in Medical FieldDocumento8 páginasApplication of Artificial Intelligence in Medical FieldShree krishana ShresthaAún no hay calificaciones
- Human Philo IntroductionDocumento20 páginasHuman Philo Introductionshimeath delrosarioAún no hay calificaciones
- 127-Article Text-817-6-10-20180329Documento4 páginas127-Article Text-817-6-10-20180329Riri Andriani MinHoAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment - 506Documento4 páginasAssignment - 506tariq mashalAún no hay calificaciones
- Nabl 100Documento46 páginasNabl 100Mayur JadhavAún no hay calificaciones
- B K - Chapter 5 Guided ReadingDocumento8 páginasB K - Chapter 5 Guided Readingapi-235658421Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiac L4Documento19 páginasCardiac L4Qutaybah JahmanyAún no hay calificaciones
- 6000+ GK NTPCDocumento206 páginas6000+ GK NTPCPrakash PandaAún no hay calificaciones
- CSIR-NET Life Science - Notes On PhytochromesDocumento6 páginasCSIR-NET Life Science - Notes On Phytochromeskay dayAún no hay calificaciones
- 24 - Origin of SpeciesDocumento31 páginas24 - Origin of SpeciesTazneen Hossain TaniAún no hay calificaciones
- ChucrutDocumento6 páginasChucrutPAOLAAún no hay calificaciones
- Hemoglobin - Buffering CapacityDocumento22 páginasHemoglobin - Buffering CapacityPapadoveAún no hay calificaciones
- Cat Aliza Mehbin BioDocumento1 páginaCat Aliza Mehbin BioKirti DoshiAún no hay calificaciones
- Lyoplant Onlay: AesculapDocumento6 páginasLyoplant Onlay: Aesculap林金鋒Aún no hay calificaciones
- Alagappa University: Karaikudi - 630 003, Tamilnadu, IndiaDocumento17 páginasAlagappa University: Karaikudi - 630 003, Tamilnadu, IndiaVeanganAún no hay calificaciones