Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Quiz 1
Cargado por
Gideon Salino Gasulas Buniel0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
13 vistas1 páginaSAMPLE
Título original
QUIZ-1
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoSAMPLE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
13 vistas1 páginaQuiz 1
Cargado por
Gideon Salino Gasulas BunielSAMPLE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 1
1. One purpose of culture method is to ISOLATE bacteria in pure culture.
2. Type isolates by methods such as _______. BACTERIOPHAGE
3. BACTERIOCIN SUSCEPTIBILITY
4. A type of culture method which one loopful of culture is made as a primary inoculum and is then
distributed thinly over the plate. STREAK METHOD
5. It provides a uniform growth of a bacterium. Also called a carpet method. LAWN CULTURE
6. This method is employed for providing a pure growth of the bacterium for slide agglutination and other
diagnostic tests. STROKE CULTURE
7. This method is prepared by puncturing with a long straight, charged wire in a suitable medium. STAB
CULTURE
8. The suitable medium could be NUTRIENT GELATIN / GLUCOSE AGAR
9. This method gives an estimate of the viable bacterial count in a suspension. POUR PLATE CULTURE
10. What is the name of the device used in enumerating the number of colonies in pour plate culture. COLONY
COUNTER
11. This method is preferably used when large yields are desired. LIQUID CULTURE
12. CELL STAINING is a technique used for the main purpose of increasing contrast through changing the colour
of some of the parts of the structure being observed.
13. IN-VIVO STAINING - refers to the staining of a biological matter while it is still alive
14. IN-VITRO STAINING - refers to a staining technique where the biological matter is non-living.
15. The actual cells are colored and appeaar in a clear background. POSITIVE STAINING
16. It involves only one stain. You may choose from methylene blue, Gram safranin, and Gram crystal violet.
SIMPLE STAINING
17. It is a staining process which uses more than one chemical stain. DIFFERENTIAL STAINING
18. Gram staining uses two dyes: CRYSTAL VIOLET and
19. FUCHSIN OR SAFRANIN
20. The actual cells remain clear (uncolored) and the background is colored to create a contrast to aid in the
better visualization of the image. NEGATIVE STAINING
21. GRAM STAINING is used to determine gram status to classify bacteria broadly. It is based on the
composition of their cell wall.
22. Gram staining uses CRYSTAL VIOLET to stain cell walls
23. Gram staining uses a FUCHSIN OR SAFRANIN counterstain to mark all bacteria
24. GRAM-POSITIVE BACTERIA stain dark blue or violet. Their cell wall is typically rich with peptidoglycan and
lacks the secondary membrane and lipopolysaccharide layer found in Gram-negative bacteria.
25. GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA do not retain the crystal violet stain because of its physical makeup and will
stain pink
26. The name comes from its discoverer and inventor, HAN CHRISTIAN GRAM (Gram, 1884)
27. NEGATIVE STAINING is a mild technique that may not destroy the microorganisms, and is therefore
unsuitable for studying pathogens.
28-30. DRAW THE STRUCTURE OF EITHER A GRAM POSITIVE OR GRAM NEGATIVE BACTERIA
También podría gustarte
- English LetterDocumento2 páginasEnglish LetterGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Court - GonzDocumento4 páginasPractice Court - GonzGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- RULE 130 Rules of AdmissibilityDocumento134 páginasRULE 130 Rules of AdmissibilityGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- 131 EditedDocumento20 páginas131 EditedGideon Salino Gasulas Buniel100% (1)
- Individual Plan For Prof Devpt TEACHINGDocumento1 páginaIndividual Plan For Prof Devpt TEACHINGGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Minutes of Preliminary ConferenceDocumento3 páginasMinutes of Preliminary ConferenceGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Dream Jobs and Résumé FormatsDocumento13 páginasDream Jobs and Résumé FormatsGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Closing Prog ScriptDocumento2 páginasClosing Prog ScriptGideon Salino Gasulas Buniel100% (1)
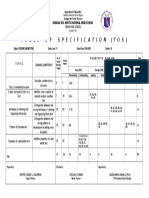
- TOS Senior High - 3QRWDocumento1 páginaTOS Senior High - 3QRWGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- History of Repair CostDocumento1 páginaHistory of Repair CostGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- BKD ScriptDocumento2 páginasBKD ScriptGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Development Plan Rpms Sy 2018 2019Documento8 páginasDevelopment Plan Rpms Sy 2018 2019Gideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd Periodical Exam - RW2018-2019Documento4 páginas3rd Periodical Exam - RW2018-2019Gideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Written Exam of Defendant DriverDocumento3 páginasWritten Exam of Defendant DriverGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Tos ElsDocumento1 páginaTos ElsSj Miasco-MejongAún no hay calificaciones
- Sadjaw SurigaoDocumento1 páginaSadjaw SurigaoGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- 2ND Acquaintance Party 2019 EMCEE SCRIPTDocumento3 páginas2ND Acquaintance Party 2019 EMCEE SCRIPTGideon Salino Gasulas Buniel79% (14)
- Teacher's Portfolio Sy 2018-2019 HeadingsDocumento18 páginasTeacher's Portfolio Sy 2018-2019 HeadingsGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Closing Remarks Madam CindyDocumento1 páginaClosing Remarks Madam CindyGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Collective Bargaining CasesDocumento394 páginasCollective Bargaining CasesGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Court 1 Script.Documento9 páginasPractice Court 1 Script.Gideon Salino Gasulas Buniel100% (1)
- ACQUAINTANCE FireDocumento2 páginasACQUAINTANCE FireGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- 12 Strategies for Overcoming Communication ProblemsDocumento26 páginas12 Strategies for Overcoming Communication ProblemsGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- TOS Senior High OCDocumento1 páginaTOS Senior High OCGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Pledge Contract EssentialsDocumento14 páginasPledge Contract EssentialsGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Consti Review DigestsDocumento15 páginasConsti Review DigestsGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- TOS Senior High OCDocumento1 páginaTOS Senior High OCGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Graduation RitesDocumento82 páginasGraduation RitesGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- BOOKMARK EngDocumento10 páginasBOOKMARK EngGideon Salino Gasulas BunielAún no hay calificaciones
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
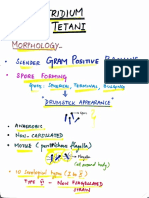
- Clostridium Tetani NotesDocumento10 páginasClostridium Tetani NotesGame GameAún no hay calificaciones
- Differentiating Staphylococcus and Micrococcus with BacitracinDocumento13 páginasDifferentiating Staphylococcus and Micrococcus with BacitracinPau SorianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Binax Product InsertDocumento96 páginasBinax Product Insertuber6791Aún no hay calificaciones
- Structure: of Bacterial CellDocumento25 páginasStructure: of Bacterial CellManila BhatiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Baileys 13th Ed Chapter QuestionsDocumento79 páginasBaileys 13th Ed Chapter QuestionsrhymeAún no hay calificaciones
- 6.1 MicrobiologyDocumento32 páginas6.1 MicrobiologyYsabelle BautistaAún no hay calificaciones
- Blue Print of Test Questions Department of Microbiology and ParasitologyDocumento5 páginasBlue Print of Test Questions Department of Microbiology and ParasitologyRosel Ann BontiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mcrobio Cell MembraneDocumento8 páginasMcrobio Cell MembraneResty De Guzman SoteloAún no hay calificaciones
- Stafilococcus (Coccus Gram Positif)Documento39 páginasStafilococcus (Coccus Gram Positif)arisita firmanAún no hay calificaciones
- 8-Kefpod 06Documento35 páginas8-Kefpod 06kurutalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Murray: Medical Microbiology, 6 Edition: Chapter 02: Bacterial Classification, Structure, and Replication Test BankDocumento3 páginasMurray: Medical Microbiology, 6 Edition: Chapter 02: Bacterial Classification, Structure, and Replication Test Bankاحمد كرمAún no hay calificaciones
- Gram Stain Kit Methylene Blue Solution Gram Stain Kit by Scytek LaboratoriesDocumento2 páginasGram Stain Kit Methylene Blue Solution Gram Stain Kit by Scytek LaboratoriesScytek Laboratories IncAún no hay calificaciones
- Microbial Staining TechniquesDocumento10 páginasMicrobial Staining TechniquesJohn Emmanuel TayagAún no hay calificaciones
- Bacterial Cell Presentation2Documento57 páginasBacterial Cell Presentation2rehanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 Microbiology QuizDocumento15 páginasChapter 1 Microbiology Quizbevqns6512Aún no hay calificaciones
- (Compre - 3itransteam) Mt6320 - Bacte Lec Unit 1.1-11Documento244 páginas(Compre - 3itransteam) Mt6320 - Bacte Lec Unit 1.1-11Ylia MastarsAún no hay calificaciones
- Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology and Determinative BacteriologyDocumento2 páginasBergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology and Determinative BacteriologyGeetha Anjali0% (1)
- Microbiological Aspects of Ozone Applications in Food: A ReviewDocumento11 páginasMicrobiological Aspects of Ozone Applications in Food: A ReviewNanda Dwi WigrhianaAún no hay calificaciones
- Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Cranberry Juice and Lemon Essential OilDocumento12 páginasAntioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Cranberry Juice and Lemon Essential OilMamta AgarwalAún no hay calificaciones
- 96D26EB60535Documento13 páginas96D26EB60535Johnson JulietAún no hay calificaciones
- Multicenter Study On Incubation Conditions For Environmental Monitoring and Aseptic Process SimulationDocumento9 páginasMulticenter Study On Incubation Conditions For Environmental Monitoring and Aseptic Process SimulationBLUEPRINT Integrated Engineering ServicesAún no hay calificaciones
- IVMS Pharmacology Flash FactsDocumento8250 páginasIVMS Pharmacology Flash FactsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Aún no hay calificaciones
- START-HERE Ch11 LectureDocumento84 páginasSTART-HERE Ch11 LecturePraveen VootlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Antimicrobial Resistance Trends in Bacterial Keratitis Over 5 Years in Sydney, AustraliaDocumento9 páginasAntimicrobial Resistance Trends in Bacterial Keratitis Over 5 Years in Sydney, AustraliaBima RizkiAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab Technologist-3Documento92 páginasLab Technologist-3AHAMED SHIFAAN100% (1)
- Chemical Science: Edge ArticleDocumento13 páginasChemical Science: Edge Articledark cocAún no hay calificaciones
- Bacteriology MCQsDocumento25 páginasBacteriology MCQshassan qureshi100% (1)
- F, MF, SeminarskiDocumento21 páginasF, MF, SeminarskiFatimaAún no hay calificaciones
- 10-Taxonomy and Major Groups of BacteriaDocumento84 páginas10-Taxonomy and Major Groups of BacteriaDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (7)
- John L. Ingraham - March of The Microbes - Sighting The Unseen-Harvard University Press (2012)Documento337 páginasJohn L. Ingraham - March of The Microbes - Sighting The Unseen-Harvard University Press (2012)Raúl Ernando Blanco UsecheAún no hay calificaciones