Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Cobb County School District 2019-2020 8 Grade Physical Science Teaching & Learning Framework Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Test Prep Extension
Cargado por
api-268569185Descripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Cobb County School District 2019-2020 8 Grade Physical Science Teaching & Learning Framework Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Test Prep Extension
Cargado por
api-268569185Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
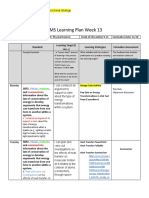
Cobb County School District 2019-2020
8th Grade Physical Science Teaching & Learning Framework
Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4
Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Test Prep Extension
9 weeks 3 weeks 3 weeks 5 weeks 9 weeks 3 weeks 4 weeks
Nature of Matter Forms and Electricity and Magnetism Nature of Waves Forces and Motion Test Prep Extension
Transformations of Energy
S8P1. Obtain, evaluate, and S8P2. Obtain, evaluate, and S8P5. Obtain, evaluate, and S8P4. Obtain, evaluate, and S8P3. Obtain, evaluate, and communicate
communicate information about communicate information about communicate information about communicate information to support the information about cause and effect relationships
the structure and properties of the law of conservation of energy gravity, electricity, and magnetism claim that electromagnetic (light) waves between force, mass, and the motion of objects.
matter. to develop arguments that energy as major forces acting in nature. behave differently than mechanical
a. Develop and use a model to can transform from one form to a. Construct an argument using (sound) waves. a. Analyze and interpret data to identify patterns
compare and contrast pure in the relationships between speed and distance,
another within a system. evidence to support the claim that a. Ask questions to develop explanations
substances (elements and and velocity and acceleration. (Clarification
a. Analyze and interpret data to fields (i.e., magnetic fields, about the similarities and differences
compounds) and mixtures.
create graphical displays that gravitational fields, and electric between electromagnetic and mechanical statement: Students should be able to analyze
b. Develop and use models to
illustrate the relationships of fields) exist between objects waves. motion graphs, but students should not be
describe the movement of particles
kinetic energy to mass and speed, exerting forces on each other even b. Construct an explanation using data to expected to calculate velocity or acceleration.)
in solids, liquids, gases, and plasma
states when thermal energy is added and potential energy to mass and when the objects are not in illustrate the relationship between the b. Construct an explanation using Newton’s Laws
or removed. height of an object. contact. electromagnetic spectrum and energy. of Motion to describe the effects of balanced and
c. Plan and carry out investigations b. Plan and carry out an b. Plan and carry out investigations c. Design a device to illustrate practical unbalanced forces on the motion of an object.
to compare and contrast chemical investigation to explain the to demonstrate the distribution of applications of the electromagnetic c. Construct an argument from evidence to
(i.e., reactivity, combustibility) and transformation between kinetic charge in conductors and spectrum (e.g., communication, medical, support the claim that the amount of force needed
physical (i.e., density, melting point, and potential energy within a insulators. military). d. Develop and use a model to to accelerate an object is proportional to its mass
boiling point) properties of matter. system (e.g., roller coasters, c. Plan and carry out investigations compare and contrast how light and sound (inertia).
d. Construct an argument based on pendulums, rubber bands, etc.). c. to identify the factors (e.g., waves are reflected, refracted, absorbed,
observational evidence to support
Construct an argument to support distance between objects, diffracted or transmitted through various
the claim that when a change in a
a claim about the type of energy magnetic force produced by an materials.
substance occurs, it can be classified
transformations within a system electromagnet with varying e. Analyze and interpret data to predict
as either chemical or physical.
e. Develop models (e.g., atomic-level [e.g., lighting a match (light to number of wire turns, varying patterns in the relationship between
models, including drawings, and heat), turning on a light (electrical number or size of dry cells, and density of media and wave behavior (i.e.,
computer representations) by to light)]. varying size of iron core) that affect speed).
analyzing patterns within the d. Plan and carry out investigations the strength of electric and f. Develop and use a model (e.g.,
periodic table that illustrate the on the effects of heat transfer on magnetic forces. simulations, graphs, illustrations) to predict
structure, composition, and molecular motion as it relates to and describe the relationships between
characteristics of atoms (protons, the collision of atoms (conduction), wave properties (e.g., frequency,
neutrons, and electrons) and simple through space (radiation), or in amplitude, and wavelength) and energy.
molecules. currents in a liquid or a gas g. Develop and use models to demonstrate
f. Construct an explanation based on (convection). the effects that lenses have on light (i.e.,
evidence to describe conservation of
formation an image) and their possible
matter in a chemical reaction
technological applications.
including the resulting differences
between products and reactants.
AC Extension: Obtain, evaluate, and AC Extension: Obtain, evaluate, AC Extension: Obtain, evaluate, AC Extension: Obtain, evaluate, and AC Extension: Obtain, evaluate, and communicate
communicate information from the and communicate information to and communicate information to communicate information to explain the information to explain the relationships among
Periodic Table to explain the explain transformations and flow explain the properties of and properties of waves. e. Develop and use force, mass, and motion. a. Plan and carry out an
relative properties of elements of energy within a system c. relationships between electricity models to explain the changes in sound investigation and analyze the motion of an object
based on patterns of atomic Analyze and interpret specific heat and magnetism. c. Plan and carry waves associated with the Doppler Effect. using mathematical and graphical models (SPS8)
structure. a. Develop and use
data to justify the selection of a out investigations to determine the (SPS9)
models to compare and contrast the
material for a practical application relationship between magnetism
structure of atoms, ions and
(e.g., insulators and cooking and the movement of electrical
isotopes. (SPS1)
vessels). (SPS7) charge.
(Clarification statement:
Investigations could include
electromagnets, simple motors,
and generators.) (SPS10)
También podría gustarte
- Electrical System A40F Copy Prosis - 3.4.0.12Documento857 páginasElectrical System A40F Copy Prosis - 3.4.0.12Bontor Tua100% (3)
- Unit Plan Science Unit Plan 5thDocumento14 páginasUnit Plan Science Unit Plan 5thapi-371640211100% (2)
- The Ocean Floor Foldable NotesDocumento22 páginasThe Ocean Floor Foldable Notesapi-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamental Concepts in Substation Design PDFDocumento26 páginasFundamental Concepts in Substation Design PDFvishalkumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Online Course Syllabus-Sherell JamesDocumento9 páginasOnline Course Syllabus-Sherell Jamesapi-665021925Aún no hay calificaciones
- Utilizing Hands-On RoboticsDocumento134 páginasUtilizing Hands-On RoboticsFaique Hussain UmraniAún no hay calificaciones
- HS PS4 3 PDFDocumento2 páginasHS PS4 3 PDFalvinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Syllabus VR 19-20Documento7 páginasPhysics Syllabus VR 19-20api-269229107Aún no hay calificaciones
- Science 8th Grade Curriculum MapDocumento1 páginaScience 8th Grade Curriculum Mapapi-298427905Aún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 4: Nuclear and Particle Physics: Number (Atomic Number)Documento1 páginaUnit 4: Nuclear and Particle Physics: Number (Atomic Number)lloyd ShawAún no hay calificaciones
- 2a Physics Syllabus VR Fall2020Documento7 páginas2a Physics Syllabus VR Fall2020api-269229107Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3a Physics Syllabus VR Fall2020Documento7 páginas3a Physics Syllabus VR Fall2020api-269229107Aún no hay calificaciones
- Syllabus Science 3BDocumento3 páginasSyllabus Science 3BxjoerenoxAún no hay calificaciones
- LOC Phy Grades9-12Documento5 páginasLOC Phy Grades9-12samanthamrwetyana03Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physical Science Lesson PlansDocumento3 páginasPhysical Science Lesson Plansapi-531774017Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry UBDFINAL2017Documento20 páginasChemistry UBDFINAL2017general1.secondaryAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Course - SyllabusDocumento15 páginasPhysics Course - SyllabusMosesAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Physical Science Georgia StandardsDocumento5 páginasScience Physical Science Georgia Standardsapi-491081853Aún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Mechanics 1Documento9 páginasBasic Mechanics 1Haxik SaeedAún no hay calificaciones
- Size-Dependent Elastic Properties of A Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Via A Molecular Mechanics Model Chang and Gao 2003 PDFDocumento16 páginasSize-Dependent Elastic Properties of A Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Via A Molecular Mechanics Model Chang and Gao 2003 PDFKishore Guru-MEAún no hay calificaciones
- 3V Physics - Lesson Plan - Nov - LopezDocumento12 páginas3V Physics - Lesson Plan - Nov - LopezMinorAún no hay calificaciones
- 41 Physics MinorDocumento27 páginas41 Physics MinorSumanth SahooAún no hay calificaciones
- Atomistic Simulation of Mechanical Properties of DDocumento18 páginasAtomistic Simulation of Mechanical Properties of Djose mauricio muñoz bolivarAún no hay calificaciones
- Multifractality of Mass Distribution in Fragmentation: Emily S.C. ChingDocumento7 páginasMultifractality of Mass Distribution in Fragmentation: Emily S.C. ChingraguerreAún no hay calificaciones
- 2009 Earth Physical ScienceDocumento5 páginas2009 Earth Physical SciencevirtualgardnerAún no hay calificaciones
- Fis 1Documento33 páginasFis 1syafrina novitaAún no hay calificaciones
- Broken Arrow Public Schools AP Physics C Objectives: # Objective 1Documento7 páginasBroken Arrow Public Schools AP Physics C Objectives: # Objective 1walyatAún no hay calificaciones
- WAEC Syllabus For PhysicsDocumento32 páginasWAEC Syllabus For Physicstrustphli73Aún no hay calificaciones
- Why Has Digital Technology Replaced Analog Technology?: HS-PS4-3Documento18 páginasWhy Has Digital Technology Replaced Analog Technology?: HS-PS4-3Reinalyn MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Course: Department Specific Elective 2-: HPHDS5021T Nuclear and Particle PhysicsDocumento3 páginasCourse: Department Specific Elective 2-: HPHDS5021T Nuclear and Particle PhysicsGrim Reaper Kuro OnihimeAún no hay calificaciones
- WAEC PHYSICS SyllabusDocumento59 páginasWAEC PHYSICS SyllabusSani MubarakAún no hay calificaciones
- Cheng 2010Documento22 páginasCheng 2010Sebastian AlvaradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Mitchell 2014Documento13 páginasMitchell 2014Kingshuk MukherjeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Prelim (2) - Physics-1 ModuleDocumento52 páginasPrelim (2) - Physics-1 ModuleHerrera, Mark NathanielAún no hay calificaciones
- Varadan1994Documento14 páginasVaradan1994Riston SinagaAún no hay calificaciones
- MS PS3 Evidence Statements June 2015 AsterisksDocumento7 páginasMS PS3 Evidence Statements June 2015 Asterisksjeache29Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 01Documento31 páginasLecture 01sivamadhaviyamAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Section: Section Topics I. Measurement Ii. Newtonian MechanicsDocumento39 páginasPhysics Section: Section Topics I. Measurement Ii. Newtonian MechanicshelloAún no hay calificaciones
- Wave-Particle Duality: Light: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIDocumento10 páginasWave-Particle Duality: Light: Project PHYSNET Physics Bldg. Michigan State University East Lansing, MIEpic WinAún no hay calificaciones
- Wave Nature of Particles: MISN-0-382Documento5 páginasWave Nature of Particles: MISN-0-382Epic WinAún no hay calificaciones
- توصيف مقررات الفيزياء الطبيةDocumento68 páginasتوصيف مقررات الفيزياء الطبيةشهد بنت علي رديفAún no hay calificaciones
- DP Unit Planner Fields and ForcesDocumento4 páginasDP Unit Planner Fields and ForcesDr-Salah JaradatAún no hay calificaciones
- Budget of Work Science 8Documento9 páginasBudget of Work Science 8Fernadez RodisonAún no hay calificaciones
- (Core Ideas of Broad Importance Across Disciplines) Core IdeasDocumento2 páginas(Core Ideas of Broad Importance Across Disciplines) Core Ideasapi-427624832Aún no hay calificaciones
- San Roque National High School Science Department Grade 8 Budget of Work S.Y 2017-2018Documento6 páginasSan Roque National High School Science Department Grade 8 Budget of Work S.Y 2017-2018Charo Nudo PongasiAún no hay calificaciones
- My ThesisDocumento10 páginasMy ThesisHundaol TesfayeAún no hay calificaciones
- 18 Effects of Mirror Symmetry On The Transmission Fingerprints of Quasiperiodic Photonic MultilayersDocumento5 páginas18 Effects of Mirror Symmetry On The Transmission Fingerprints of Quasiperiodic Photonic MultilayersCarlinhos Queda D'águaAún no hay calificaciones
- 3V Physics - Lesson Plan - Jan - LopezDocumento12 páginas3V Physics - Lesson Plan - Jan - LopezMinorAún no hay calificaciones
- Kabaldin 2008Documento9 páginasKabaldin 2008MoqaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics 1Documento24 páginasPhysics 1ZainabAún no hay calificaciones
- WAssce Physics SyllabusDocumento24 páginasWAssce Physics SyllabusIkedi UcheAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermolecular Forces Lesson PlanDocumento13 páginasIntermolecular Forces Lesson Plancheryl tayasAún no hay calificaciones
- HSC Physics The Cosmic EngineDocumento35 páginasHSC Physics The Cosmic Engineninjaassassin103Aún no hay calificaciones
- 5th U2 ElectricityMagnetism 2011-2012 GuideDocumento4 páginas5th U2 ElectricityMagnetism 2011-2012 GuideKristal Jane OjerioAún no hay calificaciones
- Dielectric Replica Measurement Revised Version CleanDocumento22 páginasDielectric Replica Measurement Revised Version CleanMatthew DaviesAún no hay calificaciones
- Syllabus For PhysicsDocumento20 páginasSyllabus For Physicsshamimshafeb2005Aún no hay calificaciones
- An Introduction To Tetryonic TheoryDocumento8 páginasAn Introduction To Tetryonic TheoryIlluminationAún no hay calificaciones
- Electron Diffraction Rapid Communication 1Documento3 páginasElectron Diffraction Rapid Communication 1api-709898488Aún no hay calificaciones
- MS Geology Performance TaskDocumento4 páginasMS Geology Performance TaskRey GoldAún no hay calificaciones
- 9th Grade CurriculaDocumento2 páginas9th Grade Curriculabugrahankilic13Aún no hay calificaciones
- My ThesisDocumento10 páginasMy ThesisHundaol TesfayeAún no hay calificaciones
- DocScanner Nov 4, 2022 9-55 AMDocumento104 páginasDocScanner Nov 4, 2022 9-55 AMChandra PrakashAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Lesson 5Documento1 páginaScience Lesson 5api-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- Science Lesson Week 3 Cross CurricularDocumento1 páginaScience Lesson Week 3 Cross Curricularapi-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- Student Check-Out ProceduresDocumento2 páginasStudent Check-Out Proceduresapi-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- Math Week 2Documento1 páginaMath Week 2api-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- 6th Grade Choice Board Week April 20-24Documento2 páginas6th Grade Choice Board Week April 20-24api-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- 8th Grade Choice Board OptionsDocumento2 páginas8th Grade Choice Board Optionsapi-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- AtmospherewebquestsDocumento4 páginasAtmospherewebquestsapi-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- Water Cycle Webquest 1Documento2 páginasWater Cycle Webquest 1api-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- Waves Web Quest 2017 - 2018 v2Documento2 páginasWaves Web Quest 2017 - 2018 v2api-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- Gravity Webquest TwoDocumento2 páginasGravity Webquest Twoapi-268569185Aún no hay calificaciones
- Bahagian A: Kertas 2Documento17 páginasBahagian A: Kertas 2wahidms84Aún no hay calificaciones
- Design of Reliable High Voltage Avalanche Transistor PulsersDocumento3 páginasDesign of Reliable High Voltage Avalanche Transistor Pulsersapchar1Aún no hay calificaciones
- API GravityDocumento4 páginasAPI GravitySridaar KanaiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 Exercises Part2Documento2 páginasChapter 2 Exercises Part2Cedric MunlawinAún no hay calificaciones
- Uppen 12000 Power Amplifier SpecificationDocumento2 páginasUppen 12000 Power Amplifier SpecificationAlexandra SanduAún no hay calificaciones
- Ac Drive: User ManualDocumento53 páginasAc Drive: User ManualJOHNATAN MARINAún no hay calificaciones
- Resonant Induction Heater PDFDocumento225 páginasResonant Induction Heater PDFBoodyBedaiweAún no hay calificaciones
- AccelerometerDocumento2 páginasAccelerometerlasky11Aún no hay calificaciones
- Essentials of Thermoelectric CoolingDocumento68 páginasEssentials of Thermoelectric Coolingvenkatesan appuAún no hay calificaciones
- Hall Effect and Hall VoltageDocumento2 páginasHall Effect and Hall VoltageHimanshu TyagiAún no hay calificaciones
- Total Power Int'L: S2A00R Series 3 Watt Low Cost DIP DC/DC Converters Single & Dual OutputDocumento4 páginasTotal Power Int'L: S2A00R Series 3 Watt Low Cost DIP DC/DC Converters Single & Dual OutputsaberAún no hay calificaciones
- Ece III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesDocumento111 páginasEce III Network Analysis (10es34) NotesGautam Sharma80% (10)
- STK0380P: PreliminaryDocumento4 páginasSTK0380P: PreliminaryHaider AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Miniaturization of A Microstrip Antenna Using A Compact and Thin Magneto-Dielectric SubstrateDocumento3 páginasMiniaturization of A Microstrip Antenna Using A Compact and Thin Magneto-Dielectric SubstrateaparnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC ChoppersDocumento55 páginasChapter Four: DC-DC Conversion: DC Choppersfor lifeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ib Physics DefinitionsDocumento20 páginasIb Physics DefinitionsJohnny HongAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 - Losses in Piping SystemsDocumento30 páginasChapter 2 - Losses in Piping SystemsNicholas EmildasAún no hay calificaciones
- TN17-1003 Pruebas de NucleoDocumento6 páginasTN17-1003 Pruebas de NucleoAlonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2010 HSC Term4 Theory PhysicsDocumento9 páginas2010 HSC Term4 Theory PhysicsSandy WongAún no hay calificaciones
- 2176 - Multi Layer Insulation (MLI)Documento10 páginas2176 - Multi Layer Insulation (MLI)mohamedAún no hay calificaciones
- Eddy PiezoDocumento19 páginasEddy Piezoshrish ukhalkarAún no hay calificaciones
- Solar EnergyDocumento8 páginasSolar EnergyftahAún no hay calificaciones
- Tle/Epas: Quarter 1 - Module 2Documento27 páginasTle/Epas: Quarter 1 - Module 2Doone Heart Santander Cabuguas83% (6)
- PKA-RP2.5FAL Pka-Rp3Fal Pka-Rp4Fal: Technical & Service ManualDocumento56 páginasPKA-RP2.5FAL Pka-Rp3Fal Pka-Rp4Fal: Technical & Service ManualMihaela CaciumarciucAún no hay calificaciones
- CRKTCT - 19. A Capacitor With Capacitance 0.1F in An RC Circuit Is Initially Charged Up ToDocumento5 páginasCRKTCT - 19. A Capacitor With Capacitance 0.1F in An RC Circuit Is Initially Charged Up ToWilburAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics Fundamentals and Applications D Chattopadhyay and P C RakshitDocumento152 páginasElectronics Fundamentals and Applications D Chattopadhyay and P C RakshitBidyut RoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Aits 1819 FT Ix Jeea Paper 1 PCM SolnsDocumento14 páginasAits 1819 FT Ix Jeea Paper 1 PCM SolnsKartik Gupta100% (1)
- SR Inter IPE Question Bank Chapter-XII (DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER)Documento1 páginaSR Inter IPE Question Bank Chapter-XII (DUAL NATURE OF RADIATION AND MATTER)sojakoj867Aún no hay calificaciones