Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Dimaampao: Doctrine of Symbiotic Relationship: Taxes Are
Cargado por
Celestino Law0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
337 vistas3 páginasThis document discusses the key differences between various types of governmental exactions including taxes, special assessments, licenses, tolls, penalties, and debts. It covers the purposes, authorities, and limitations of taxation powers. Some key points include:
- Taxes are enforced contributions levied by sovereign authority to support the government and are proportional in character. Special assessments provide benefits to specific properties.
- The power to tax is inherent in sovereignty but is subject to limitations like being for a public purpose, uniformity, and due process.
- Theories of taxation include the necessity theory based on preserving state sovereignty and the benefits protection theory tying taxes to reciprocal duties of government support and protection.
- Taxation powers
Descripción original:
summary
Título original
Tax Principles
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoThis document discusses the key differences between various types of governmental exactions including taxes, special assessments, licenses, tolls, penalties, and debts. It covers the purposes, authorities, and limitations of taxation powers. Some key points include:
- Taxes are enforced contributions levied by sovereign authority to support the government and are proportional in character. Special assessments provide benefits to specific properties.
- The power to tax is inherent in sovereignty but is subject to limitations like being for a public purpose, uniformity, and due process.
- Theories of taxation include the necessity theory based on preserving state sovereignty and the benefits protection theory tying taxes to reciprocal duties of government support and protection.
- Taxation powers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
337 vistas3 páginasDimaampao: Doctrine of Symbiotic Relationship: Taxes Are
Cargado por
Celestino LawThis document discusses the key differences between various types of governmental exactions including taxes, special assessments, licenses, tolls, penalties, and debts. It covers the purposes, authorities, and limitations of taxation powers. Some key points include:
- Taxes are enforced contributions levied by sovereign authority to support the government and are proportional in character. Special assessments provide benefits to specific properties.
- The power to tax is inherent in sovereignty but is subject to limitations like being for a public purpose, uniformity, and due process.
- Theories of taxation include the necessity theory based on preserving state sovereignty and the benefits protection theory tying taxes to reciprocal duties of government support and protection.
- Taxation powers
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 3
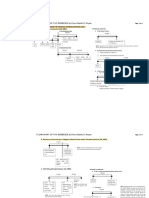
Taxation vs Police Power: purpose, amount of exaction, benefits
received, superiority of contracts, transfer of property rights
DIMAAMPAO Taxation vs ED: purpose, compensation, persons affected
TAXES SPECIAL ASSESSMENTS
*is in the nature of a tax upon
Chapter 1: General Principles property levied according to
benefits conferred upon the
Taxation property
Taxes 1. Levied on property, r or p 1. Levied on land only
1. Enforced contributions 2. A is not necessarily a tax 2. Exercise of taxing power
2. Proportional in character 3. Taxed all areas 3. Exceptional both in time
3. Levied by authority of law and locality
4. For the support of the government and public needs TAXES LICENSE
Nature of Taxation 1. Exercise of Taxing power 1. Emanates from PP
1. Inherent in sovereignty 2. Generate revenues 2. Regulatory purpose
2. Legislative Power 3. Unlimited 3. Sufficient amount of LF
3. Subject to constitutional limitations 4. Primary: raise revenue, 4. Primary: regulation,
Basis of Taxation regulation is merely incidental revenue does
1. Lifeblood Doctrine incidental not make it a tax
- Lifeblood of the government and their prompt and TAXES TOLL
certain availability is an imperious need 1. Demand of sovereignty 1. Demand of proprietorship
- Taxes are what we pay for a civilized society 2. Raising of revenues 2. Charged for the cost and
- Taxes are the lifeblood of the government and maintenance of the
should be collected without unnecessary hindrance property used
Theories in Taxation TAXES PENALTY
1. Necessity Theory 1. Civil liability 1. Punishment for the
- Necessary burden to preserve State’s sovereignty commission of a crime
and as a means to give the citizenry an anc pubp TAXES DEBT
2. Benefits Protection Theory 1. Not a debt
- Bases the power of the State to demand and receive 2. Not contract between LAHAT NG NOT SA TAXES
taxes on the reciprocal duties of support and parties AY ALISIN, DEBTS NA YUN
protection 3. Cannot be assigned as
- Doctrine of Symbiotic Relationship: Taxes are debts
what we pay for a civilized society 4. Not subject of a set-off
Liabilities Involved – personal 5. Do not draw interest
a) Civil
b) Criminal Doctrine of Equitable Recoupment: not applicable in PH
Aspects, Processes and Phases of Taxation - When the refund of a tax illegally or erroneously collected
1. Levy or overpaid by a taxpayer is barred by the statute of
2. Assessment and Collection limitations, and a tax is being assessed against taxpayer,
3. Payment said present tax may be recouped or set-off against the
Is the power to tax a power to destroy? tax, the refund of which has been barred
- The power to tax is the power to destroy if it is used - TP is allowed to credit a refund to his existing tax liability
validly as implement of police power in discouraging Inherent Limitations on the Power to Tax
and in effect, ultimately prohibiting certain things or 1. Public Purpose – embraces both direct and indirect
interests inimical to the public welfare. But, if it is public benefits ; legislative prerogative
used solely for the purpose of raising revenue, the 2. International Comity – Art. 2, Art. II; Sovereign Equality
modern view is, it cannot be allowed to confiscate or Among States
destroy (J. Cruz) 3. Territoriality – jurisdiction
- The power of taxation is sometimes called the power 4. Non Delegation of Taxing Power – legislative
to destroy. Therefore, it should be exercised with Exceptions:
caution to minimize injury to the propriety rights of a a) President may impose tariff rates, import and export
taxpayer. It must be exercised fairly, equally, quotas, custom duties, as may be authorized by
uniformly, lest the collector kill the ‘hen that lays the Congress, by law
golden egg (Roxas vs CA) b) LGUs have the power to create its own sources of
Purposes of Taxation revenue, fees, charges, subject to guidelines and
1. Primary Purpose: To raise revenues limitations as Congress may provide
2. Secondary Purposes 5. Exemption from Taxation of Government
a) Reduction of Social Inequality – progressive Agencies/Instrumentalities
b) Encourage the growth of local industries – a) Agencies performing propriety functions – T
exemptions and tax reliefs b) GOCC – T
c) Protect our local industry against unfair competition c) Exempted – GSIS, SSS, PHIC, PCSO
d) As an implement power of the State (regulatory d) Exempted from RPT – MIAA, PH Reclamation
measure) Authority
Extent of Taxing Power – CUPS Constitutional Limitations
Principles of a Sound Tax System – FAT 1. Due Process of Law – confiscation, outside J, not for
- A violation hereof may or may not invalidate a law, public p, retroactively imposes unjust taxes, violation of
except when it runs counter to theoretical justice inherent limitations
2. Equal Protection – valid classification: 1) substantial Kinds of Taxes
distinction 2) apply to both present and future conditions; 1. As to Incidence
3) germane to the purposes of law; 4) apply equally to all a) Direct
members of the same class b) Indirect – tax is primarily paid by persons who can
- Falls equally and impartially upon the person and shift the burden to someone else
properties subject to taxation Forward: transferred from a factor of
3. Uniformity in Taxation – All taxable articles or kinds of production through the factors of
property of the same class shall be taxed at the same distribution until it finally settles on the
rate ultimate purchaser or consumer. Price
4. Progressive Taxation – rate goes up depending on the increases.
resources of persons affected; taxpayers ability to pay Backward: transferred from the consumer
5. Non-Impairment Clause or purchaser through the factors of
Is Tax Exemption Revocable? It depends distribution to the factors of production.
- If the grant of exemption does not constitute a Price decreases.
contrac, but is merely a spontaneous concession by Onward: tax is shifted two or more times,
the legislature, not connected with any service or either forward or backward
duty imposed”, the State at its pleasure may revoke 2. As to Tax Rates
the exemption a) Specific – imposed based on weight or volume
- If the tax exemption constitutes a binding contract capacity or any other physical unit of measurement
and for valuable consideration, the government b) Ad Valorem – tax is based on GSP or other specified
cannot unilaterally revoke such. value of the goods
- A franchise partakes the nature of a grant which is 3. As to purpose
beyond the purview of the non-impairment clause a) General – raise revenue for the government
6. Non-Imprisonment for Non-Payment of a Poll Tax b) Special – to achieve a particular legitimate object of
7. Bills to Originate from the House of Representatives – the government
exclusively, but the Senate may propose or concur with 4. As to Scope or Authority Imposed
amendments a) National
8. Veto Power of the President – items vetoed -> returned b) Local
to lower house with objections -> 2/3 consideration of the 5. As to Object
House, if agreed to pass such, the bill will become a law a) Personal
9. President’s Power to Tax – fix tariff rates, import or b) Property
export quotas, and tonnage or wharfage dues 6. As to Graduation
10. Taxation and Freedom of the Press a) Progressive – rate increases as the base increases
11. Taxation and Freedom of Religion b) Regressive – tax rate decreases as the tax base
12. Tax Exemption of Properties actually, directly and increases
exclusively used for religious, charitable and Double Taxation – means taxing the same property twice when
educational purposes – exempt from taxation as to RPT, it should be taxed only once; that is, x x x taxing the same person
provided that the land was used for the purpose it is twice by the same jurisdiction for the same thing.
intended 1. Strict Sense (Direct) – violates the uniformity and equal
13. Tax Exemption granted to Non-Stock Non-Profit protection clause, as well as the principle that tax must
Educational Institutions – exempt from all taxes, import not be excessive, unreasonable and inequitable
duties, assessments and other charges imposed by the Requisites:
Government on all income derived from property used a) The same property is taxed twice when it should
exclusively for educational activities only be taxed once
- Subject to donor’s tax, estate tax, VAT b) Both taxes are impose on the same property
14. Appropriation of Public Money – c) Imposed by the same taxing authority
- Gen. Rule: No public money or money shall be d) Within the same jurisdiction
appropriated, applied, paid or employed directly or e) During the same period
indirectly for the use, benefit or support of any sect, f) Covering the same kind or character of tax
church, denomination, sectarian institution, or 2. Broad Sense (Indirect) – taxes are not of the same kind,
system of religion etc or the imposition are imposed for different taxing
- Exception: when said priest, minister or dignitary is authority and this involve the same subject matter
assigned to the armed forces, or to any penal Tax Treaty as a Mode of Eliminating Double Taxation
institutions or government orphanage or leposarium 1. Exemption Method – the income or capital which is
15. Grant of Tax Exemption – may be created by the taxable in the State or its source or situs is exempted in
Constitution or by an act of the legislature (e.g: tax the state of residence, although in some instances it may
amnesties, tax condonations, tax refunds) be taken into account in determining the rate of tax
Tax Amnesty: immunity from all the criminal and applicable to the taxpayer’s income or capital
civil obligations arising from non-payment of taxes; 2. Credit Method – tax paid in the State of source is
general pardon; absolute waiver; start with a clean credited against the tax levied in the state of residence
slate; applies to past tax periods 3. Reciprocity – You do not tax my citizen, I will not also
Tax Exemption: immunity from the civil liability only; tax your citizen
freedom from any charge or burden 4. Tax Treaty
16. Local Taxation – LGUs; most effective instrument to
raise revenues
17. Special Fund – tax levied for special purpose shall be
treated as SF, and paid out for such purpose only
18. SC’s jurisdiction over tax cases – BIR->CTA->CA->SC
Tax Evasion Tax Avoidance
1. Connotes fraud through 1. Legal means used by TP
the use of pretenses and to reduce taxes
forbidden devices to
lessen or defeat taxes
2. Scheme outside of lawful 2. Tax saving device
means
3. Tax Dodging – unlawful 3. Tax Minimization –
means to lessen or to get happens when TP
away with his tax minimizes his tax
liabilities by taking
Elements: advantage of legally
a) Ends to be achieved, i.e available tax planning
payment of less than that opportubities
known by the TP to be
legally due, or non-
payment of tax
b) Accompanying state of
mind which is described
as being evil, in bad faith,
wilful deliberate and not
accidental
Doctrine of Imprescriptibility
Gen. Rule: Taxes do not prescribe
Exc: Under NIRC, Tariff Codes and LGC (WAG NA TO)
Taxpayer Suit – TP is deemed to have legal standing to raise
constitutional issues when it is established that public funds from
taxation have been disbursed in alleged contravention of the law
or Constitution
Nature of Tax Laws: not political, civil, and not penal in character
Construction
1. Tax Laws – strictly against the TP, in favor of the
government
2. Tax Exemptions – strictly against the grantee
Exceptions:
a) S expressly provides for a liberal interpretation
b) Exemptions of public property
c) Those granted to traditional exemptees
d) Exemption in favour of the government
e) E by clear legislative intent
f) In case of special taxes
3. Penal Provisions of Tax Laws – strict construction
También podría gustarte
- Customer Satisfaction in The Indian Banking SectorDocumento70 páginasCustomer Satisfaction in The Indian Banking SectorAbhishek Singh82% (22)
- An Appraisal of Banker Customer Relationship in NigeriaDocumento60 páginasAn Appraisal of Banker Customer Relationship in NigeriaAkin Olawale Oluwadayisi87% (15)
- Greek CrisisDocumento7 páginasGreek CrisisFilip NikolicAún no hay calificaciones
- Constitutional LimitationsDocumento66 páginasConstitutional LimitationsDev LitaAún no hay calificaciones
- Estate Tax and Some Exempt TransfersDocumento3 páginasEstate Tax and Some Exempt TransfersfcnrrsAún no hay calificaciones
- Memory Aid TAXATIONDocumento35 páginasMemory Aid TAXATIONMary Christine Formiloza MacalinaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Airline Operating CostsDocumento27 páginasAirline Operating Costsawahab100% (7)
- Syndicate 6 - Gainesboro Machine Tools CorporationDocumento12 páginasSyndicate 6 - Gainesboro Machine Tools CorporationSimon ErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Inherent Limitations On The Taxing PowerDocumento8 páginasInherent Limitations On The Taxing PowerFranco David BaratetaAún no hay calificaciones
- A Review of The General Principles of TaxationDocumento10 páginasA Review of The General Principles of TaxationRommel Mirasol100% (1)
- Summary NIRCDocumento44 páginasSummary NIRCbebs CachoAún no hay calificaciones
- Midterm Q and ADocumento33 páginasMidterm Q and ACloieRjAún no hay calificaciones
- Handouts Gross EstateDocumento2 páginasHandouts Gross Estateonlineonrandomdays100% (1)
- Module 8 - Deductions From Gross IncomeDocumento12 páginasModule 8 - Deductions From Gross IncomeJimbo ManalastasAún no hay calificaciones
- General Principles: Taxation LawDocumento17 páginasGeneral Principles: Taxation LawB-an Javelosa100% (1)
- Lecture 5 - Donor - S TaxDocumento4 páginasLecture 5 - Donor - S TaxBhosx KimAún no hay calificaciones
- Taxation VATDocumento22 páginasTaxation VATB-an JavelosaAún no hay calificaciones
- De Facto CorporationDocumento1 páginaDe Facto CorporationKrisha Marie Carlos0% (1)
- Business Law IncorporatorsDocumento9 páginasBusiness Law IncorporatorsAsdfghjkl qwertyuiopAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 4 - Value Added TaxDocumento16 páginasModule 4 - Value Added Taxanon_455551365Aún no hay calificaciones
- NIRC - Allowable DeductionsDocumento46 páginasNIRC - Allowable DeductionsJeff Sarabusing100% (1)
- Tax 1 Quizz 02Documento4 páginasTax 1 Quizz 02Don BaylaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1401 To 1410Documento6 páginas1401 To 1410Rubz JeanAún no hay calificaciones
- Tax Reviewer (Mfp-2)Documento13 páginasTax Reviewer (Mfp-2)Mikaela Pamatmat100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Nature and Form of The Contract: 1459, However, Does Not Require That The Vendor Must Have TheDocumento10 páginasChapter 1: Nature and Form of The Contract: 1459, However, Does Not Require That The Vendor Must Have TheMarlon Amiel SungaAún no hay calificaciones
- Powers of The BIRDocumento11 páginasPowers of The BIRmartina lopez100% (1)
- Sale Report - Articles 1489-1518Documento10 páginasSale Report - Articles 1489-1518Mark Joseph DelimaAún no hay calificaciones
- TAX SITUS-It Is The Place or Authority That Has The Right To Impose and Collect TaxesDocumento58 páginasTAX SITUS-It Is The Place or Authority That Has The Right To Impose and Collect TaxesTJ Julian BaltazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Requirements For An IncorporatorDocumento2 páginasRequirements For An IncorporatorMikMik UyAún no hay calificaciones
- General Principles: Answer: CDocumento13 páginasGeneral Principles: Answer: CReno PhillipAún no hay calificaciones
- Answers 5Documento5 páginasAnswers 5Xiv NixAún no hay calificaciones
- Income Taxation ReviewerDocumento84 páginasIncome Taxation ReviewerCharmaine Mejia100% (1)
- Sarah ReviewerDocumento20 páginasSarah ReviewerdoraemoanAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporation Code Revised Corporation CodeDocumento4 páginasCorporation Code Revised Corporation Codestella marizAún no hay calificaciones
- Jimenez Vs Jimenez & Quezon City Register of Deeds, G.R. No. 228011, February 10, 2021Documento2 páginasJimenez Vs Jimenez & Quezon City Register of Deeds, G.R. No. 228011, February 10, 2021Gi NoAún no hay calificaciones
- Classification of Contracts According To Importance or Dependence of One Upon AnotherDocumento2 páginasClassification of Contracts According To Importance or Dependence of One Upon AnotherOliverMastileroAún no hay calificaciones
- Saludo vs. PNBDocumento8 páginasSaludo vs. PNBGLORILYN MONTEJOAún no hay calificaciones
- Guide Notes On Donor'S Tax Donor'S TaxDocumento10 páginasGuide Notes On Donor'S Tax Donor'S TaxNori LolaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bank Secrecy ReviewerDocumento5 páginasBank Secrecy ReviewerRizellLoey ParkAún no hay calificaciones
- TAXATIONDocumento9 páginasTAXATIONkekadiegoAún no hay calificaciones
- Deutsche Bank Ag Manila Branch Vs Commissioner of Internal Revenue (CIR) SUMMARYDocumento4 páginasDeutsche Bank Ag Manila Branch Vs Commissioner of Internal Revenue (CIR) SUMMARYTinersAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 General Principles of Income TaxationDocumento9 páginas2 General Principles of Income TaxationDenise ZurbanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture Notes Labor LawDocumento3 páginasLecture Notes Labor LawMaphile Mae CanenciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Transfer TaxesDocumento3 páginasTransfer TaxesbeverlyrtanAún no hay calificaciones
- Pactum Commissorium Can Be Found in Article 2088 of The Civil Code Which ProvidesDocumento1 páginaPactum Commissorium Can Be Found in Article 2088 of The Civil Code Which ProvidesKryzzle Martin BoriAún no hay calificaciones
- Value Added Tax Ust PDFDocumento23 páginasValue Added Tax Ust PDFcalliemozartAún no hay calificaciones
- Llamado - Income Taxation - ExpandedDocumento14 páginasLlamado - Income Taxation - ExpandedTtlrpq0% (1)
- Tax Ii: Syllabus - Value-Added Tax Atty. Ma. Victoria A. Villaluz I. Nature of The VAT and Underlying LawsDocumento12 páginasTax Ii: Syllabus - Value-Added Tax Atty. Ma. Victoria A. Villaluz I. Nature of The VAT and Underlying LawsChaAún no hay calificaciones
- New Central Bank ActDocumento16 páginasNew Central Bank ActNic NalpenAún no hay calificaciones
- Revised Corporation CodeDocumento16 páginasRevised Corporation CodeLielet MatutinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taxation Law ReviewerDocumento6 páginasTaxation Law ReviewerAlex RabanesAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 11 PledgeDocumento7 páginasCH 11 PledgecrisAún no hay calificaciones
- Important Provisions Under RA 9139Documento2 páginasImportant Provisions Under RA 9139Myn Mirafuentes Sta Ana0% (1)
- U4.3 Optional Standard Deduction (Presentation Slides)Documento4 páginasU4.3 Optional Standard Deduction (Presentation Slides)Marc Geoffrey HababAún no hay calificaciones
- Vat-Exempt Transactions (Under TRAIN Law)Documento2 páginasVat-Exempt Transactions (Under TRAIN Law)Fabiano JoeyAún no hay calificaciones
- Tax Judicial RemediesDocumento10 páginasTax Judicial RemediesSCYLLAAún no hay calificaciones
- Fair Value (Pfrs 13) :: PAS 41: AgricultureDocumento2 páginasFair Value (Pfrs 13) :: PAS 41: AgricultureCzar RabayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cir vs. Pineda, 21 Scra 105Documento1 páginaCir vs. Pineda, 21 Scra 105Jo DevisAún no hay calificaciones
- Article 962Documento31 páginasArticle 962russell apura galvezAún no hay calificaciones
- M2u Classification Individual Taxation P1Documento30 páginasM2u Classification Individual Taxation P1Xehdrickke FernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Questions (Edited)Documento8 páginasQuestions (Edited)Madelle PinedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Income Tax 01 General Principles of TaxationDocumento11 páginasIncome Tax 01 General Principles of TaxationJade Ivy GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tax 2 Notes Finals 4Documento36 páginasTax 2 Notes Finals 4Boom ManuelAún no hay calificaciones
- Income Taxation 01 Chapter 1 Summary - CompressDocumento7 páginasIncome Taxation 01 Chapter 1 Summary - CompressALTHEA REN'EE LIMPAOAún no hay calificaciones
- Income Taxation01Documento7 páginasIncome Taxation01Ailene MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- LegWri DecisionDocumento12 páginasLegWri DecisionCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Studying 04 Flowchart of Tax Remedies 2019 Update TR (1) WithMarginNotesDocumento11 páginasStudying 04 Flowchart of Tax Remedies 2019 Update TR (1) WithMarginNotesCelestino Law100% (1)
- Arts 835-885Documento6 páginasArts 835-885Celestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Secs 51 Onwards-NegoDocumento3 páginasSecs 51 Onwards-NegoCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Items of InclusionsDocumento1 páginaItems of InclusionsCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- RA 9344 - Juvenile Justice LawDocumento21 páginasRA 9344 - Juvenile Justice LawArnold OniaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ra 9048Documento4 páginasRa 9048Jm OlfindoAún no hay calificaciones
- PersonsDocumento8 páginasPersonsMa. Cariza AlmoradieAún no hay calificaciones
- Tax Finals ReviewerDocumento51 páginasTax Finals ReviewerCelestino Law100% (2)
- Comparative Study: Negotiable Intruments Law of The Philippines (R.A Act No. 2031) and New Zealand (Bills of Exchange Act of 1908)Documento9 páginasComparative Study: Negotiable Intruments Law of The Philippines (R.A Act No. 2031) and New Zealand (Bills of Exchange Act of 1908)Celestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Secs 51 Onwards-NegoDocumento3 páginasSecs 51 Onwards-NegoCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Nego FinalsDocumento5 páginasNego FinalsCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Sales-De LeonDocumento7 páginasSales-De LeonCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- IndexDocumento2 páginasIndexCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Sample ExamDocumento3 páginasSample ExamCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter Xvii Examination of WitnessesDocumento3 páginasChapter Xvii Examination of WitnessesCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Ra 9048Documento4 páginasRa 9048Jm OlfindoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2019 Edition of Handbook On Workers Statutory Monetary BenefitsDocumento78 páginas2019 Edition of Handbook On Workers Statutory Monetary BenefitsAlvin ComilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Land RegistrationDocumento5 páginasLand RegistrationCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- ProcessDocumento3 páginasProcessElaine Dianne Laig Samonte100% (1)
- Appellant Brief - LegwriDocumento21 páginasAppellant Brief - LegwriCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Items of InclusionsDocumento1 páginaItems of InclusionsCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Evidence - Outline - FranciscoDocumento35 páginasEvidence - Outline - FranciscoCelestino Law100% (1)
- Chapter Xvii Examination of WitnessesDocumento3 páginasChapter Xvii Examination of WitnessesCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- List of RequirementsDocumento1 páginaList of RequirementsCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Arts 835-885Documento6 páginasArts 835-885Celestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Corpo Law - SummarizedDocumento119 páginasCorpo Law - SummarizedCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Secs 51 Onwards-NegoDocumento3 páginasSecs 51 Onwards-NegoCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Crimes and ElementsDocumento9 páginasCrimes and ElementsCelestino LawAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter - General Journal 4Documento32 páginasChapter - General Journal 4Israr AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 7 Risk and Return Question and Answer From TitmanDocumento2 páginasChapter 7 Risk and Return Question and Answer From TitmanMd Jahid HossainAún no hay calificaciones
- Data ": Overview: Purchasing (Big)Documento3 páginasData ": Overview: Purchasing (Big)preeti singhAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 6 Fiscal Policy in Keynesian Model: 6.0 ObjectivesDocumento24 páginasUnit 6 Fiscal Policy in Keynesian Model: 6.0 ObjectivesnavneetAún no hay calificaciones
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential LW/OCT2010/LAW585Documento4 páginasUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential LW/OCT2010/LAW585AliceAinaaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nealon, Inc. Solutions (All Questions Answered + Step by Step)Documento7 páginasNealon, Inc. Solutions (All Questions Answered + Step by Step)AndrewVazAún no hay calificaciones
- TRAVELERS INDEMNITY COMPANY OF ILLINOIS Et Al v. CLARENDON AMERICAN INSURANCE COMPANY Et Al ComplaintDocumento41 páginasTRAVELERS INDEMNITY COMPANY OF ILLINOIS Et Al v. CLARENDON AMERICAN INSURANCE COMPANY Et Al ComplaintACELitigationWatchAún no hay calificaciones
- Consumer Durable LoansDocumento10 páginasConsumer Durable LoansdevrajkinjalAún no hay calificaciones
- Ubte 2013 Entrepreneurship: Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (Utar)Documento18 páginasUbte 2013 Entrepreneurship: Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman (Utar)Jyiou YimushiAún no hay calificaciones
- RSK CVDocumento2 páginasRSK CVRanveer Singh KissoondoyalAún no hay calificaciones
- Difference Between Ind As 16, As 10Documento6 páginasDifference Between Ind As 16, As 10VivekAún no hay calificaciones
- ESG Brochure March 2020Documento16 páginasESG Brochure March 2020glenlcyAún no hay calificaciones
- SubPrime Crisis and 911Documento55 páginasSubPrime Crisis and 911Eye ON CitrusAún no hay calificaciones
- PDFDocumento52 páginasPDFnaveen mamidiAún no hay calificaciones
- Redemption Application Form: Day Year MonthDocumento2 páginasRedemption Application Form: Day Year MonthSyed Mustafa Ali Zaidi (IA-Fact)Aún no hay calificaciones
- Week 4 Solutions To ExercisesDocumento5 páginasWeek 4 Solutions To ExercisesBerend van RoozendaalAún no hay calificaciones
- Monthly GK Digest June PDFDocumento26 páginasMonthly GK Digest June PDFakshaykumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Bidding Doucments: Government of BalochistanDocumento17 páginasBidding Doucments: Government of BalochistanKhan FahadAún no hay calificaciones
- Ind Nifty Divid Opp50Documento2 páginasInd Nifty Divid Opp50santosh kumarAún no hay calificaciones
- International Business: Gaurav DawarDocumento22 páginasInternational Business: Gaurav Dawarsarathnair26Aún no hay calificaciones
- A Design Measurement and Management Model: The DMI Design Value ScorecardDocumento7 páginasA Design Measurement and Management Model: The DMI Design Value ScorecardDaz ArunabhAún no hay calificaciones
- 201120020118700048000000Documento3 páginas201120020118700048000000shubhamAún no hay calificaciones
- Feasibility Study-Rimrock Kayak Rentals and MoreDocumento20 páginasFeasibility Study-Rimrock Kayak Rentals and Moreapi-335709436Aún no hay calificaciones
- CashflowDocumento3 páginasCashflowsikandar aAún no hay calificaciones
- Difference Between Accounts & FinanceDocumento4 páginasDifference Between Accounts & Financesameer amjadAún no hay calificaciones