Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
3rd-Trial 15-16
Cargado por
api-253679034Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
3rd-Trial 15-16
Cargado por
api-253679034Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
6102 - 6102 التجربة الثالثة لعام الشهادة المتوسطة ليسه دي زار
: الرقم : اإلسم ساعتان: المدة
ّ مسابقة في الرياضيات اإلنكليزي
:إ رشادات عامة
يسمح بإستعمال ألة حاسبة غير قابلة للبرمجة للتأكد من االجابة فقط-
يمكن اإلجابة على ألمسائل بالترتيب االذي تريد-
يرجى اإلجابة بخط واضح ومرتب-
01 العالمة القصوى من-
1st exercise: (7 ½ pts)
The adjacent figure represents the triangle ABC such that:
BAC 750 , ABC 450 and ACB 600 .
We suppose that: a cos A, b cos B, c cos C and cos 750 x .
We admit that a, b and c verify the relation : a 2 b 2 c 2 2abc 1 .
1) Use the above given relation and the table of particular angles,
show that: 4 x
2
2 x 2 1 0 . (1pt)
6 2 6 2
2) Consider the real numbers: U and V .
4 4
a) Verify that U and V are two solutions of the equation: 4 x 2 2 x 2 1 0 .(1½pts)
b) Deduce the exact value of cos 750 x and then deduce sin(750) and sin(150). (¾pt,1pt, ½ pt)
6 2 2 3
3) a) Compare the numbers: and .(1pt)
4 2
b) Deduce that tan( 75 0 ) 2 3 , and then calculate cot(750 ) .(1pt,¾pt )
2nd exercise: (12 pts)
In an orthonormal system of axes x Ox, y Oy , where the unit is cm, consider the points A(0;2), B(-2,;0),
C(4;-2) and D(4m- 2; 4m), where m is a real number.
(d) is the straight line of equation: y = -3x – 8.
1) a) Place the points A, B, C and draw (d) in the orthonormal system. (¾pt, ½pt)
b) Show that the straight line (AB) is defined by the equation: y = x +2. (¾pt)
2) Let I be the midpoint of [BC].
Calculate AI and BC then deduce that ABC is right at A.(1¾pts)
3) a) Show that as m varies, the point D describes the fixed straight line (AB).(¾pt)
b) Calculate m so that [CA) is the angle bisector of BCD .(1pt)
4) Calculate the area of (C), the circle circumscribed about the right triangle ABC. (¾pt)
5) (d) is tangent to (C) at a point E(a ; b).
a) Calculate, in terms of a and b, the slope of the straight line (EI).(¾pt)
a 3b 4
b) Show that the coordinates of the point E, verify the following system: .(1½pts)
3a b 8
c) Solve the system then deduce the coordinates of E. (1pt)
6) H is the point such that: CB CD CH . In this question take m = 1.
a) Calculate the coordinates of H and determine the nature of the quadrilateral BCDH.(1½pts)
b) Determine the coordinates of J, the center of the circle (C’), the image of the circle(C) by the translation
of vector CA .(1pt)
3/1 الصف التاسع – رياضيات إنكليزي- امتحان التجربة الثالثة- – أيار6102
3rd exercise: (6 ½ pts)
In a clothes store, a study was conducted about the types of 20 pieces of clothes. The following table shows
the obtained data.
Clothes Pants Sweater T-shirt Jackets Total
Frequencies 20
Part A :
The adjacent semi-circular diagram gives the distribution of the
above modalities.
1) For the above study, precise the population, the statistical unit,
the character and its nature. (1pt)
2) a) Explain how the following equations: x y 3 and
2x y 5 were obtained. (1½pts)
b) Calculate the numerical values of x and y. (¾pt)
3) Construct the bar diagram of frequencies. (¾pt)
Part B:
Now, we want to study the shoe size of the shoes bought by 80 customers.
For this, we consider the following incomplete table.
Shoe size 37 38 41 42 Total
Frequency 5 17
Increasing Cumulative Frequencies in % 33.75%
1) a) Interpret the ICF % of the shoe size 38. (¼pt)
b) Reproduce the above table and complete the missing numbers. (1½pts)
2) Calculate the mean shoe size. (¾pt)
4th exercise: (6pts)
(S) is a semi-circle of center O and radius “r ” where [AB] is a diameter. Let C be the point on (S) such that
BC 2 AC . The perpendicular to (OC) at O cuts (S) at D.
1) a) Show that AC 60 0 , then draw the semi-circle(S) and place the point C.(¾pt, ½pt)
b) Calculate the measure of the arc BD and show that triangle ABC is semi equilateral. (¾pt,¾pt)
c) Use trigonometric ratios (Sine, cosine or Tangent) to calculate, in terms of r , AD and BD. (1½pts)
2) The straight-lines (BC) and (AD) intersect at I.
a) Show that the triangles ACI and BDI are similar.(1pt)
b) Deduce that: AC BI AI BD . (¾pt)
5th exercise: (4¼ pts)
During the holidays in the Greek islands, a man wants to rent a scooter. The owner offered him the following
two options:
* Option I: Pay 3 € for every traveled kilometer (km).
* Option II: Pay a fixed price of 10 € and then obtain a reduction of 30% on the charge for every traveled
Kilometer in option I.
Designate by:
x the number of traveled kilometers.
f (x) and g (x) the sum of money paid for option I and option II, respectively.
1) a) Express f (x) in terms of x and show that g (x) = 2.1x + 10.(¾pt, 1pt)
b) Which option is more advantageous for a man who is aiming to run the scooter for 13 km? Justify.(1pt)
2) Study algebraically, according to the values of x, the most advantageous option.
(Note: two cases should be studied) (1½pts)
3/2 الصف التاسع – رياضيات إنكليزي- امتحان التجربة الثالثة- – أيار6102
6th exercise: (3¾ pts)
In the following table, only one of the proposed answers to each question is correct. Write the number of
each question and the corresponding answer, with justification.
Answers
No. Questions
A B C
x 2 4 x x 4
The system 2 , is true for all values
1. x 1 ] ;[ ] ;1[ ] ;1]
of x that belongs to the interval….. (1½pts)
The measure of the acute angle that the straight
2. line (d) of equation 3 y x 3 makes with 60o 30o 120o
x'Ox is equal to …… (1¼pts)
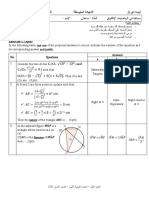
In the right triangle ABC
of hypotenuse [BC]
3. and height [AH], we have 5 3 3 5 15
BH = 3 and BC =15cm
then BA ............. (1pt)
3/3 الصف التاسع – رياضيات إنكليزي- امتحان التجربة الثالثة- – أيار6102
También podría gustarte
- Microsoft Word For The Strad Part 1 8 SeptDocumento10 páginasMicrosoft Word For The Strad Part 1 8 Septnostromo1979100% (1)
- Trigonometry For DummiesDocumento5 páginasTrigonometry For DummiesMelissa Ubando100% (2)
- (Maths) (Chung Cheng High School (Yishun) ) (4E5N) (Preliminary Examination 2) (2012) (Paper 1 Original)Documento17 páginas(Maths) (Chung Cheng High School (Yishun) ) (4E5N) (Preliminary Examination 2) (2012) (Paper 1 Original)linnbrownie100% (1)
- Romanian Problem BookDocumento19 páginasRomanian Problem BookSM200100% (2)
- Latihan Matematik Tingkatan 2 Chap02 Square, Square Root, Cube and Cube RootDocumento3 páginasLatihan Matematik Tingkatan 2 Chap02 Square, Square Root, Cube and Cube RootEzra Loganathan MuniandiAún no hay calificaciones
- Solution 2005Documento12 páginasSolution 2005BHAAJI0001Aún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometry Test ADocumento1 páginaTrigonometry Test AFatmawati AtibyAún no hay calificaciones
- 9 Sa1 Maths Sample Paper1Documento22 páginas9 Sa1 Maths Sample Paper1empty_shake5319Aún no hay calificaciones
- Calculate Horizon DistanceDocumento40 páginasCalculate Horizon DistanceSecond Subscriber80% (10)
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary CheckpointDocumento15 páginasCambridge International Examinations Cambridge Primary CheckpointAhmed MasoudAún no hay calificaciones
- Sine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Documento22 páginasSine and Cosine Rule Problems (SL)Rudi Berlian100% (2)
- Triangulation and Trilateration TechniquesDocumento38 páginasTriangulation and Trilateration TechniquesMilind Gupta71% (7)
- Triangles Lesson PlanDocumento3 páginasTriangles Lesson Planapi-548332360Aún no hay calificaciones
- Admmodule Stem Gp12v Ia 10 11Documento25 páginasAdmmodule Stem Gp12v Ia 10 11Diana Silva HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- IB Math SL Review Worksheet Packet 14Documento10 páginasIB Math SL Review Worksheet Packet 14Rebe SerranoAún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd-Trial 16-17Documento2 páginas3rd-Trial 16-17api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd-Trial 17-18Documento2 páginas3rd-Trial 17-18api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd-Trial 07-08Documento2 páginas3rd-Trial 07-08api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd-Trial 11-12Documento2 páginas3rd-Trial 11-12api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 8 THDocumento3 páginas8 THapi-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 8th Final 2010Documento2 páginas8th Final 2010api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 11-12Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 11-12api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd-Trial 10-11Documento2 páginas3rd-Trial 10-11api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- PT3 Trial MathematicsDocumento21 páginasPT3 Trial MathematicsPrakash Arumugam100% (5)
- Ib1 Math Studies 2nd Term Paper 1Documento4 páginasIb1 Math Studies 2nd Term Paper 1Jun MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- 8th Final 2014Documento3 páginas8th Final 2014api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 8th Final 2012Documento2 páginas8th Final 2012api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 12-13Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 12-13api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 8th Final 2011Documento3 páginas8th Final 2011api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd-Trial 12-13Documento3 páginas3rd-Trial 12-13api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- QB Version 3 Circular Functions and TrigDocumento21 páginasQB Version 3 Circular Functions and TrigRowanberry11Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 14-15Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 14-15api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematics PP2Documento15 páginasMathematics PP2Rainbow ICTAún no hay calificaciones
- 10icse Prelim PaperDocumento7 páginas10icse Prelim PapertraderprabhakarAún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 15-16Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 15-16api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd-Trial 14-15Documento2 páginas3rd-Trial 14-15api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- CharuDocumento7 páginasCharuK. Sai Krishna Dora Class 8 E. Roll 37Aún no hay calificaciones
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 13 For Board Exam 2024Documento6 páginasMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 13 For Board Exam 2024Mamta shettyAún no hay calificaciones
- 2011 Mock Paper BythemathscafeDocumento6 páginas2011 Mock Paper BythemathscafefardeenAún no hay calificaciones
- Class 10 Math Sample Paper 1Documento8 páginasClass 10 Math Sample Paper 1Bharath RajAún no hay calificaciones
- Instructions: This Question Paper Consist of Two Sections. Section A and Section B. AnswerallDocumento16 páginasInstructions: This Question Paper Consist of Two Sections. Section A and Section B. AnswerallSiti Suriani Mohd YusofAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 10 Maths CBSE MOCK TEST 1 pdfDocumento8 páginasGrade 10 Maths CBSE MOCK TEST 1 pdfhardik.g1209Aún no hay calificaciones
- Screenshot 2023-11-08 at 08.35.27Documento5 páginasScreenshot 2023-11-08 at 08.35.27alicejessicapreesAún no hay calificaciones
- Kcse 2010 Mathematics Paper 2Documento6 páginasKcse 2010 Mathematics Paper 2isaacAún no hay calificaciones
- Maths Paper 2 November 2005Documento10 páginasMaths Paper 2 November 2005sandieletasAún no hay calificaciones
- Maths EnglishDocumento32 páginasMaths EnglishBhaskar BhaskiAún no hay calificaciones
- ICSE Math 2Documento6 páginasICSE Math 2Sanjay SuryadevraAún no hay calificaciones
- 2001 Jun - P1qpDocumento6 páginas2001 Jun - P1qpabdee95Aún no hay calificaciones
- Value of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseDocumento11 páginasValue of (256) X (256) Is (A) 4 (B) 16 (C) 64 (D) 256.25 2. Form of 0.1 Is (A) (B) (C) (D) None of TheseAkshita KambojAún no hay calificaciones
- The Heritage-10 Question Paper (Math)Documento7 páginasThe Heritage-10 Question Paper (Math)jasmanjyotsAún no hay calificaciones
- Untitled Document-2Documento2 páginasUntitled Document-2thisuserisdead131Aún no hay calificaciones
- ICSE IX | MATHEMATICS Sample PaperDocumento5 páginasICSE IX | MATHEMATICS Sample PaperAvinash Dubey100% (1)
- Mathematics QuestionsDocumento5 páginasMathematics QuestionsSanjay AdakAún no hay calificaciones
- North Point Maths PrelimDocumento4 páginasNorth Point Maths PrelimcrimsonleafwindAún no hay calificaciones
- Chog Murugi Maths pp2Documento15 páginasChog Murugi Maths pp2ianmutwiriAún no hay calificaciones
- STD 10 Math (STD) - QP&MSDocumento19 páginasSTD 10 Math (STD) - QP&MSnamithapillai5Aún no hay calificaciones
- Al Mansoura School Math. Final Exam. Date: / / Grade: ADocumento3 páginasAl Mansoura School Math. Final Exam. Date: / / Grade: ASaid AdelAún no hay calificaciones
- Part A.: Objective Questions. Answer All QuestionsDocumento8 páginasPart A.: Objective Questions. Answer All QuestionsShafira AzmiAún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd-Trial 08-09Documento2 páginas3rd-Trial 08-09api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Adv Ex 08 EquationsDocumento4 páginasAdv Ex 08 EquationsLeroy ChengAún no hay calificaciones
- Math exam questionsDocumento1 páginaMath exam questionsmohamad edlbiAún no hay calificaciones
- 13412cbse 10th 2023 Question PaperDocumento6 páginas13412cbse 10th 2023 Question Papershahana KAún no hay calificaciones
- KV Class 10 Pre Board Mock Question Paper MATHS (STD)Documento7 páginasKV Class 10 Pre Board Mock Question Paper MATHS (STD)sreejaps45Aún no hay calificaciones
- KVS Lucknow X MATH STD (041) QP & MS (1st PB) (23-24)Documento17 páginasKVS Lucknow X MATH STD (041) QP & MS (1st PB) (23-24)x.makiyana.xAún no hay calificaciones
- 81E Maths Model - QP - 23 24Documento16 páginas81E Maths Model - QP - 23 24ianaarondosuza1230% (1)
- Form 5 Mathematics Midterm Exam Questions and Answers 2022Documento5 páginasForm 5 Mathematics Midterm Exam Questions and Answers 2022Sand FossohAún no hay calificaciones
- UCE Mathematics Paper 1 exam with 17 questionsDocumento4 páginasUCE Mathematics Paper 1 exam with 17 questionsAthiyo Martin100% (1)
- Lycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade. Name: - . - . - . - . - " " E.S-5Documento1 páginaLycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade. Name: - . - . - . - . - " " E.S-5api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . - . "Overview About Special Quadrilaterals"Documento4 páginasLycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . - . "Overview About Special Quadrilaterals"api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lycée Des Arts: ConclusionDocumento2 páginasLycée Des Arts: Conclusionapi-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade. Name: - . - . - . - . - "Factorizing Techniques" E.S-8Documento3 páginasLycée Des Arts: Mathematics 9 - Grade. Name: - . - . - . - . - "Factorizing Techniques" E.S-8api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 2nd-Trial 18-19Documento2 páginas2nd-Trial 18-19api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 11-12Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 11-12api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 08-09Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 08-09api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 21-22Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 21-22api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 12-13Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 12-13api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lycée Des Arts: Areas & Perimeters of Plane FiguresDocumento2 páginasLycée Des Arts: Areas & Perimeters of Plane Figuresapi-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 10-11Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 10-11api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 09-10Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 09-10api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 13-14Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 13-14api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 19-20Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 19-20api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 16-17Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 16-17api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 15-16Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 15-16api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1st-Trial 14-15Documento2 páginas1st-Trial 14-15api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Midyear 19-20Documento2 páginasMidyear 19-20api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Correction-Standards For Midterm 19-20Documento2 páginasCorrection-Standards For Midterm 19-20api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Midterm 19-20Documento2 páginasMidterm 19-20api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Midterm 19-20Documento2 páginasMidterm 19-20api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Midyear 19-20Documento2 páginasMidyear 19-20api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Midyear 19-20Documento2 páginasMidyear 19-20api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Correction of Midyear 19-20Documento1 páginaCorrection of Midyear 19-20api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematics - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . " Statistics" W.S-14Documento2 páginasMathematics - Grade Name: - . - . - . - . " Statistics" W.S-14api-253679034Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematics Olympiad Problems With Solution - Class 8Documento24 páginasMathematics Olympiad Problems With Solution - Class 8Balaadithya P GAún no hay calificaciones
- AIEEE 2002 Question PaperDocumento18 páginasAIEEE 2002 Question PaperHimkar SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- NMOS 2018 Preliminary RoundDocumento11 páginasNMOS 2018 Preliminary Roundyijie li0% (1)
- Forma Trougla U Arhitekturi Fasada Savremenih Objekata PrevodDocumento12 páginasForma Trougla U Arhitekturi Fasada Savremenih Objekata PrevodHadži Olivera NikolićAún no hay calificaciones
- QuadrilateralsDocumento7 páginasQuadrilateralsTrisha DasAún no hay calificaciones
- Math Virtual Learning: Grade 7 / Volume of Triangular PrismDocumento11 páginasMath Virtual Learning: Grade 7 / Volume of Triangular PrismTru ManAún no hay calificaciones
- Blockly Turtle Level TenDocumento4 páginasBlockly Turtle Level TenMunia MasumaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab ManualDocumento75 páginasLab ManualMohammed AadamAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3 Plane and Spherical TrigonometryDocumento2 páginasChapter 3 Plane and Spherical Trigonometryrex tanong100% (1)
- GR 9-IG Maths Syllabus Overview 2020-21Documento7 páginasGR 9-IG Maths Syllabus Overview 2020-21George JeniferAún no hay calificaciones
- Cavalieri Principle (Kin Y. Li)Documento4 páginasCavalieri Principle (Kin Y. Li)Hicham ElyassamiAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometry Problem Set (Math HLDocumento2 páginasTrigonometry Problem Set (Math HLABC123Aún no hay calificaciones
- 06a Practice Test Set 1 - Paper 3HDocumento20 páginas06a Practice Test Set 1 - Paper 3Hnaz2you50% (2)
- Performing Mensuration and Calculations Common PDFDocumento89 páginasPerforming Mensuration and Calculations Common PDFgerwinAún no hay calificaciones
- CBSE Class X Maths Practice PaperDocumento65 páginasCBSE Class X Maths Practice PaperSanjay SrinivasanAún no hay calificaciones
- PMO24 Qualifying StageDocumento6 páginasPMO24 Qualifying StageLei Andrique MorbosAún no hay calificaciones
- Pre-Test - Mathematics 6Documento7 páginasPre-Test - Mathematics 6Genesis San AndresAún no hay calificaciones
- Question Database For Exams Problems OnlyDocumento41 páginasQuestion Database For Exams Problems OnlyLooser PakerAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter Four Forces On Submerged Surfaces in Static FluidsDocumento24 páginasChapter Four Forces On Submerged Surfaces in Static FluidsŚæd ÖsmąņAún no hay calificaciones
- 5-2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities PDFDocumento25 páginas5-2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities PDFseniorss17100% (2)