Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
A Novel Triband Mobilephone PCB Antenna PDF
Cargado por
AguekeTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
A Novel Triband Mobilephone PCB Antenna PDF
Cargado por
AguekeCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
A novel tri-band mobile-phone PCB antenna
Xuedong Wang
School of Communication and Information Engineering, Shanghai University, shanghai, 200072, China
Yingfan Ni
Shanghai Detian Display Expo co., Ltd. Shanghai, 200062, China
Abstract: A novel external PCB (print circuit board)
antenna suitable for applications in GSM/DCS/PCS
tri-band mobile phones is presented. A microstrip
resonator with stubs is introduced to this antenna. This
structure can decrease camera’s influence on antenna’s
electrical performance. The experimental results of this
antenna are presented.
I INTRODUCTION
With the development of wireless communication,
antennas [1-4] for dual-or triple-band operation in the
extended global system for mobile communication (EGSM,
880-960MHz), the digital communication system (DCS,
1710-1880MHz) and personal communication system (PCS, (a) meander line and pad
1850-2990MHz) are being used in more and more fields. (b) rectangular microstrip with stubs
For external mobile phone antennas, helical ones are mature. Figure 1 The proposed PCB antenna. (the unit is millimeter)
There is a main drawback about this kind of antenna: the side of the PCB is meander line and pad which is connected
electrical performance is not stead in mass production. The to mobile phone’s feed point; on the other side of the PCB is
PCB (print circuit board) antenna has two advantages over rectangular microstrip resonator with stubs [5] as figure1(b)
usual helical antenna. 1 there is more scope to designing a shows. Meander line resonants on low frequency. Changing
more fashionable, sleeker looking phone. 2 the RF the length can change low resonant frequency.
performance is very robust because everything is fixed.
In this paper, we propose another novel PCB antenna for
application as a mobile-phone antenna. A microstrip
resonator [5] with stubs is introduced to this antenna. The
proposed antenna has wide impedance bandwidths for
EGSM, DCS and PCS. The main advantage of this antenna
is that this antenna decreases the influence of the camera on
electrical performance. Details of the proposed antenna are
described, and the experimental results of this constructed a Capacitive loading
prototype are presented. b Inductive loading
Figure 2 Equivalent transmission line models
II ANTENNA DESIGN Figure2 shows the equivalent transmission line models for
Figure1 shows the geometry of the proposed antenna the rectangular resonator with stubs. Rectangular microstrip
mounted on the two sides of a Nelco4000-12 substrate. The resonants on high frequency. Changing the number and size
unit is millimeter in figure1. The PCB size is only about of the stub can change high resonant frequency.
19.8mm × 5.4mm × 1.6mm. On one
0-7803-9433-X/05/$20.00 ©2005 IEEE. APMC2005 Proceedings
19 May 2004 13:56:44
is better about 1.5dBi than usual PCB antenna in the case of
CH1 S 11 log MAG 10 dB/ REF 0 dB 4_:-11.659 dB
1 850.000 000 MHz camera’s influence.
PRm
1_:-9.9187 dB
880 MHz
Cor
MARKER 4 2_:-7.8784 dB
960 MHz
1.85 GHz
IV CONCLUSION
Del
3_:-6.8706 dB
1.71 GHz
5_:-12.647 dB
1.99 GHz
A novel low-profile PCB antenna suitable for mobile
communications has been proposed. The antenna covers
4
1
2 3
GSM/DCS/PCS triple band. A microstrip resonator with
5
stubs is introduced to this antenna which decreased the
influence of mobile phone camera.
START 600.000 000 MHz STOP 2 200.000 000 MHz
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors would like to thank Ping Chen and Li Chen of
Figure 3 measured return loss for the proposed antenna
Skycross for useful help and support on this paper.
1. 5
1
0. 5 REFERENCES
0
- 0. 5
1 R. Johnson., Antenna engineering handbook,
-1
McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York, 1998.
- 1. 5
peak gai n aver age gai n
-2 2 K.L.Wong, Planar antennas for wireless communications,
- 2. 5
870 890 910 930 950 970 Willey, New York, 2003.
3 P.L.Teng and K.L.Wong, Planar monopole folded into a
Figure 4 Measured antenna gain across the EGSM (880-960 compact structure for very low-profile multi-band mobile
MHz) phone antenna, Microwave Opt Technol Lett 33 (2002),
22-25.
4 H.C.Tung, C.Y.Fang, and K.L.Wong, An inverted-L
monopole antenna loaded with a meander wire for
GSM/DCS dual-band mobile phones, Microwave Opt
Technol Lett 33 (2002), 212-214.
5 Karto Q. da Costa and Victor Dmitriev, A simple
theoretical model for rectangular microstrip resonator with
stubs, Microwave Opt Technol Lett 41 (2004), 119-123
Figure 5 Picture of the designed antenna.
III EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
A prototype of the proposed antenna was constructed and
tested on one mobile phone fixture. In fact, the PCB is put
into an interface, installed a sheath and then assembled to
the mobile phone. Figure3 shows the measured return loss. It
is -9.9dB at 880MHz, -7.9dB at 960MHz, -6.9dB at
1710MHz and -12.6dB at 1990MHz. The two
wide-impedance bandwidths obtained cover the operating
bandwidths of the GSM/DCS/PCS bands. Figure 4
presented the measured antenna peak and average gain
against frequency in GSM band. Figure 5 shows a picture of
the designed antenna. The antenna peak gain is about
0.3-0.9dBi and the average gain is about -1.9-0.3dBi which
También podría gustarte
- Análisis Mascara Espectral MATLABDocumento2 páginasAnálisis Mascara Espectral MATLABAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
- Technology in education opportunities and challengesDocumento3 páginasTechnology in education opportunities and challengesAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
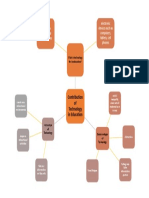
- Mapamental ContribuciondetecnologiaDocumento1 páginaMapamental ContribuciondetecnologiaAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
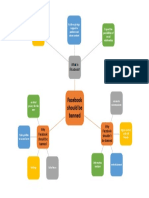
- What is Facebook and how it connects peopleDocumento1 páginaWhat is Facebook and how it connects peopleAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
- Selling Tobacco Should Be Banned: Tobacco Is A Product of Agriculture Originating in AmericaDocumento1 páginaSelling Tobacco Should Be Banned: Tobacco Is A Product of Agriculture Originating in AmericaAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
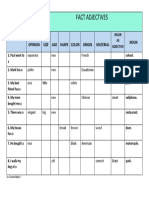
- Adjective Fill in ChartDocumento1 páginaAdjective Fill in ChartAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
- Description Topics ListDocumento1 páginaDescription Topics ListAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
- A Coupled-Fed PIFA Antenna For 4G Mobile Phone Application: @eecs - Stut.edu - TWDocumento5 páginasA Coupled-Fed PIFA Antenna For 4G Mobile Phone Application: @eecs - Stut.edu - TWAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
- A Novel Triband Mobilephone PCB AntennaDocumento2 páginasA Novel Triband Mobilephone PCB AntennaAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
- Multi-Band Hybrid Mobile Phone Antenna Based On Electromagnetic CouplingDocumento5 páginasMulti-Band Hybrid Mobile Phone Antenna Based On Electromagnetic CouplingAguekeAún no hay calificaciones
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- Microstrip Low Pass Filter DesignDocumento22 páginasMicrostrip Low Pass Filter DesignSakshiKoul100% (1)
- Pat Tapu 2018Documento8 páginasPat Tapu 2018husam hamidAún no hay calificaciones
- Design of A Multiband Quasi-Yagi-Type Antenna With CPW-to-CPS TransitionDocumento4 páginasDesign of A Multiband Quasi-Yagi-Type Antenna With CPW-to-CPS TransitionTâm Trần ĐứcAún no hay calificaciones
- Multi-Band Printed Metamaterial Inverted-F Antenna (IFA) For USB ApplicationsDocumento4 páginasMulti-Band Printed Metamaterial Inverted-F Antenna (IFA) For USB ApplicationsPhạm GiangAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Choice Ques Ec-505Documento11 páginasMultiple Choice Ques Ec-505ManishSharanAún no hay calificaciones
- M13 CAD Study Guide Radio Frequency SummaryDocumento19 páginasM13 CAD Study Guide Radio Frequency SummaryJuan NightstandAún no hay calificaciones
- Emtl Chap 4-5Documento53 páginasEmtl Chap 4-5Outfit BSAún no hay calificaciones
- Finals Comm3 Question BankDocumento28 páginasFinals Comm3 Question BankShayneBumatayAún no hay calificaciones
- Anna University Exams Nov/Dec 2018 - Transmission Lines & Wave Guides QuestionsDocumento2 páginasAnna University Exams Nov/Dec 2018 - Transmission Lines & Wave Guides QuestionsAngelinAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic 3 Transmission Lines Part II PDFDocumento50 páginasTopic 3 Transmission Lines Part II PDFArash ZikryAún no hay calificaciones
- Sources and remedies for high-frequency piping vibrationDocumento24 páginasSources and remedies for high-frequency piping vibrationSmith780512Aún no hay calificaciones
- TLWG 2marksDocumento10 páginasTLWG 2marksElakya PrabhuAún no hay calificaciones
- AN010 Bias Web PubDocumento7 páginasAN010 Bias Web PubGs SrikanthAún no hay calificaciones
- 10-RF Electronics Kikkert Ch7 RFFiltersPart2Documento27 páginas10-RF Electronics Kikkert Ch7 RFFiltersPart2AliOucharAún no hay calificaciones
- ADS Momentum Tutorial HL KY Final W09Documento18 páginasADS Momentum Tutorial HL KY Final W09Pragash SangaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Design of Ultra Wide Band Bandpass FiltersDocumento37 páginasDesign of Ultra Wide Band Bandpass Filtersnikhil_bangarAún no hay calificaciones
- Distributed ComponentsDocumento486 páginasDistributed ComponentsKyusang Park0% (1)
- Trans PDF 2Documento117 páginasTrans PDF 2Briely BrizAún no hay calificaciones
- The Gamma Match: 1 Equal Size ElementsDocumento7 páginasThe Gamma Match: 1 Equal Size ElementsOreolAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminar Report: Microstrip Patch Antenna and Its ApplicationsDocumento26 páginasSeminar Report: Microstrip Patch Antenna and Its ApplicationsDebdeep Sarkar100% (1)
- Microwave CommunicationsDocumento6 páginasMicrowave CommunicationsAkhil AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- A Filter For The Dual-Band 10 & 24 GHZ Feedhorn For Offset DishesDocumento4 páginasA Filter For The Dual-Band 10 & 24 GHZ Feedhorn For Offset DishesAmador Garcia IIIAún no hay calificaciones
- A New Spin On The Big Wheel - Popular 2 Meter Antenna - L B Cebik W4RNL - Bob Cerreto WA1FXT - 2008Documento7 páginasA New Spin On The Big Wheel - Popular 2 Meter Antenna - L B Cebik W4RNL - Bob Cerreto WA1FXT - 2008vreaucartiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Transmission-Line Modeling (TLM) Method in ElectromagneticsDocumento132 páginasThe Transmission-Line Modeling (TLM) Method in ElectromagneticsFabio Hugo Souza MatosAún no hay calificaciones
- Harmonised Amateur Radio Exam GuideDocumento40 páginasHarmonised Amateur Radio Exam GuideserepezAún no hay calificaciones
- Stub Matching Techniques ExplainedDocumento19 páginasStub Matching Techniques ExplainedJirah GicangaoAún no hay calificaciones
- RF Transmission Line Design and AnalysisDocumento7 páginasRF Transmission Line Design and AnalysisiaessackjeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics and Communication Subjects GuideDocumento45 páginasElectronics and Communication Subjects GuideAmrityam RoutAún no hay calificaciones
- 100 RFME 2 MarksDocumento11 páginas100 RFME 2 MarksdhanarajAún no hay calificaciones
- Transmission Lines & E M. Waves Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 12Documento22 páginasTransmission Lines & E M. Waves Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 12mrd9991Aún no hay calificaciones