Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Quiz 2
Cargado por
Shara Maica Sincioco SalvadorDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Quiz 2
Cargado por
Shara Maica Sincioco SalvadorCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
1.
It utilizes current transformers (CTs) at each terminal of the equipment under protection, thus,
the two currents either in magnitude or in phase or both and issue a trip output if the difference
exceeds a predetermined set value.
a. Fuse c. Differential Protection
b. Circuit Breaker d. None of the above
2. Differential protection is not effective when used in
a. Generators c. Transmission Line
b. Bus Bars d. Transformer
3. What is the most commonly used protection system of alternator against stator winding fault?
a. Earth Leakage Protection c. Differential Current Protection System
b. Merz-Price Scheme d. Both A and B
4. Fault outside the protective zone is called __________.
a. External Fault c. Through Fault
b. Internal Fault d. Both A and C
5. These are subjected to very high external fault currents.
a. Generators c. Transformer
b. Bus Bars d. None of the Above
6. What transformer is the most commonly used in differential protection?
a. Autotransformer c. Three Phase Transformer
b. Voltage Transformer d. Current Transformer
7. This is adjusted by changing the tension of the restraining spring.
a. Minimum pick-up Setting c. Plug Setting
b. Relay Setting d. Slope Setting
8. This is adjusted by changing the tapping on the restraining coil.
a. Minimum pick-up Setting c. Plug Setting
b. Relay Setting d. Slope Setting
9. During external faults in simple differential protection, there is _______________________.
a. Current in the spill path and the scheme remains stable
b. Current in the spill path and the scheme remains unstable
c. No current in the spill path and the scheme remains stable
d. No current in the spill path and the scheme remains unstable
10. In the figure below, what does the coil C represents?
a. Relay Coil c. Zone of Protection
b. Pickup Coil d. Restraining Coil
11. If currents are made to enter dot marked terminals on two or more coupled coils, the fluxes
produced by these currents are ________.
a. Addititive c. Unequal
b. Subtractive d. Equal
12. What is the “through fault stability limit”?
a. . The minimum 'through fault' current beyond which the scheme loses stability
b. The maximum 'through fault' current beyond which the scheme loses stability
c. The minimum 'through fault' current beyond which the scheme gains stability
d. The maximum 'through fault' current beyond which the scheme gains stability
13. During double end fed internal fault, the internal fault current is equal to __________.
a. I1-I2 b. I1+I2
b. I2-I1 c. (I1*I2)/ I2
También podría gustarte
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- WESMDocumento181 páginasWESMberto_diegoAún no hay calificaciones
- 20180321-ForMS-Declaration of Surviving SpouseDocumento1 página20180321-ForMS-Declaration of Surviving SpouseShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- IEEE C37guide For Power SystemDocumento124 páginasIEEE C37guide For Power SystemJohn Bihag100% (2)
- ACSR AluminumConductorSteelReinforcedDocumento3 páginasACSR AluminumConductorSteelReinforcedkkn1234Aún no hay calificaciones
- Notes For Transient Stability Analysis PDFDocumento18 páginasNotes For Transient Stability Analysis PDFAnurag PugaliaAún no hay calificaciones
- WSG01 01 CapacityDocumento3 páginasWSG01 01 CapacityjannumitsAún no hay calificaciones
- Solar Power FactorDocumento4 páginasSolar Power FactorrjayashanthaAún no hay calificaciones
- SAS Nov Seminar Part1Revg1Documento62 páginasSAS Nov Seminar Part1Revg1amolkajalednyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Transimission Line Cost Calculation PDFDocumento72 páginasTransimission Line Cost Calculation PDFjuanperezpintoAún no hay calificaciones
- DSOAR Main Text Final VersionDocumento72 páginasDSOAR Main Text Final VersionMerlie Oyad LandocanAún no hay calificaciones
- Changes Philippine Distribution Code 2017 EditionDocumento42 páginasChanges Philippine Distribution Code 2017 EditionShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- J 03325760Documento4 páginasJ 03325760IOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalAún no hay calificaciones
- FuseologyDocumento127 páginasFuseologyDao Ming ElijordeAún no hay calificaciones
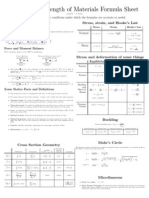
- Statics and Strength FormulasDocumento1 páginaStatics and Strength FormulasRichard TsengAún no hay calificaciones
- Orlando - Logistics 2019Documento3 páginasOrlando - Logistics 2019Shara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Cpe102L Final Report: AnalysisDocumento2 páginasCpe102L Final Report: AnalysisShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- PARALLEL AND SERIES CONNECTION OF LINEAR RESISTORS ExperimentDocumento9 páginasPARALLEL AND SERIES CONNECTION OF LINEAR RESISTORS ExperimentShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- ClaimForm2 2018Documento2 páginasClaimForm2 2018Geraldine100% (1)
- ECE Experiment 7Documento6 páginasECE Experiment 7Shara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Epira Law 2001Documento35 páginasEpira Law 2001euroaccessAún no hay calificaciones
- Epira Law 2001Documento35 páginasEpira Law 2001euroaccessAún no hay calificaciones
- Safety Requirement For The CourseDocumento2 páginasSafety Requirement For The CourseShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment SuperpositionDocumento6 páginasExperiment SuperpositionShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- TransientsDocumento14 páginasTransientsShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Design ExperimentDocumento4 páginasDesign ExperimentShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 3 Basic Circuit LawsDocumento27 páginasLesson 3 Basic Circuit LawsShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 2 Basic Circuit LawsDocumento21 páginasLesson 2 Basic Circuit LawsShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment SuperpositionDocumento6 páginasExperiment SuperpositionShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- DC Circuit Power MeasurementsDocumento13 páginasDC Circuit Power MeasurementsShara Maica Sincioco SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- VRV A 12 PDFDocumento1 páginaVRV A 12 PDFMoe Thiri ZunAún no hay calificaciones
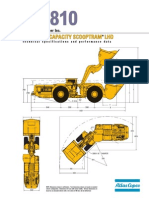
- Scoop Atlas Wagner ST1810Documento4 páginasScoop Atlas Wagner ST1810Juan Manuel PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- GL Setup ListDocumento88 páginasGL Setup ListSundaroraclefinAún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematics of Finance: Simple and Compound Interest FormulasDocumento11 páginasMathematics of Finance: Simple and Compound Interest FormulasAshekin MahadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 1Documento24 páginasLesson 1Jayzelle100% (1)
- Reference Mil-Aero Guide ConnectorDocumento80 páginasReference Mil-Aero Guide ConnectorjamesclhAún no hay calificaciones
- Climate Change: The Fork at The End of NowDocumento28 páginasClimate Change: The Fork at The End of NowMomentum Press100% (1)
- USB GPW CB03 MT02 - EngDocumento21 páginasUSB GPW CB03 MT02 - EngRafael BispoAún no hay calificaciones
- Python - How To Compute Jaccard Similarity From A Pandas Dataframe - Stack OverflowDocumento4 páginasPython - How To Compute Jaccard Similarity From A Pandas Dataframe - Stack OverflowJession DiwanganAún no hay calificaciones
- c1Documento19 páginasc1vgnagaAún no hay calificaciones
- How Dna Controls The Workings of The CellDocumento2 páginasHow Dna Controls The Workings of The Cellapi-238397369Aún no hay calificaciones
- Employee performance factors analysis electronic companyDocumento10 páginasEmployee performance factors analysis electronic companyAmrithaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction - Week 2Documento37 páginasIntroduction - Week 2Tayyab AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Reboilers and VaporizersDocumento20 páginasReboilers and Vaporizers58 - Darshan ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- Pipeline Corrosion Assessment MethodsDocumento21 páginasPipeline Corrosion Assessment MethodsGilletAún no hay calificaciones
- dp0 PDFDocumento4 páginasdp0 PDFSimonAún no hay calificaciones
- SRM Institute of Science and Technology Department of Mathematics Probability and Queueing Theory Tutorial Sheet I2Documento1 páginaSRM Institute of Science and Technology Department of Mathematics Probability and Queueing Theory Tutorial Sheet I2Cooldude 69Aún no hay calificaciones
- Submittal Chiller COP 6.02Documento3 páginasSubmittal Chiller COP 6.02juan yenqueAún no hay calificaciones
- ISCOM HT803 DatasheetDocumento2 páginasISCOM HT803 Datasheetnmc79Aún no hay calificaciones
- Canalis KDP-KBA-KBB-KNA-KSA-20-1000A-2014Documento324 páginasCanalis KDP-KBA-KBB-KNA-KSA-20-1000A-2014Rubén González CabreraAún no hay calificaciones
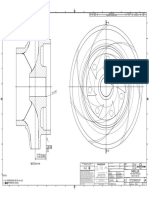
- Impeller: REV Rev by Description PCN / Ecn Date CHK'D A JMM Released For Production N/A 18/11/2019 PDLDocumento1 páginaImpeller: REV Rev by Description PCN / Ecn Date CHK'D A JMM Released For Production N/A 18/11/2019 PDLSenthilkumar RamalingamAún no hay calificaciones
- Blowfish Encryption AlgorithmDocumento3 páginasBlowfish Encryption AlgorithmParkerAllisonAún no hay calificaciones
- Reliability EngineeringDocumento9 páginasReliability Engineeringnvaradharajan1971Aún no hay calificaciones
- Indian Standards List As On Jan2009Documento216 páginasIndian Standards List As On Jan2009Vasudeva Pavan VemuriAún no hay calificaciones
- Craig Vaughan CHPTR 07Documento44 páginasCraig Vaughan CHPTR 07Jorge CananeaAún no hay calificaciones
- Probability Statistics and Random Processes Third Edition T Veerarajan PDFDocumento3 páginasProbability Statistics and Random Processes Third Edition T Veerarajan PDFbhavyamAún no hay calificaciones
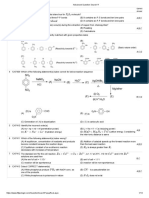
- Pragathi Full Test-6, Paper-2 (Qp+Key) - 18.07.22Documento14 páginasPragathi Full Test-6, Paper-2 (Qp+Key) - 18.07.22Ganesan MuthukrishnanAún no hay calificaciones
- Astm D5501Documento3 páginasAstm D5501mhmdgalalAún no hay calificaciones
- 3BSE079234 - en 800xa 6.0 ReleasedDocumento7 páginas3BSE079234 - en 800xa 6.0 ReleasedFormat_CAún no hay calificaciones
- WR424GB00DDocumento16 páginasWR424GB00DIgor San Martín PeñalozaAún no hay calificaciones