Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Number: 08 Ddec Vi-40 S.M. REF.: 13.2 Engine: Dd15 DATE: August 2008
Cargado por
Hamilton miranda0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
13 vistas4 páginasDDEC VI
Título original
08DDECVI32
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoDDEC VI
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
13 vistas4 páginasNumber: 08 Ddec Vi-40 S.M. REF.: 13.2 Engine: Dd15 DATE: August 2008
Cargado por
Hamilton mirandaDDEC VI
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 4
NUMBER: 08 DDEC VI–40 S.M. REF.: 13.
2 ENGINE: DD15 DATE: August 2008
SUBJECT: BELT NOISE
PUBLICATION: DDC-SVC-MAN-0029
A new section has been added to Chapter 13 “Excessive Noise.”
13.2 BELT NOISE
Excessive belt noise can be caused by damaged or worn belts, pulleys or a failed accessory. First
inspect the belt drive tensioner system for wear and tear.
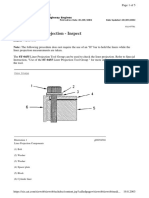
INSPECTION OF THE BELT DRIVE TENSIONER SYSTEM
Check as follows:
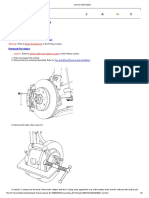
1. Inspect the belt contact surface for chips, flaking, cracks and discoloration.
ABRASION CHUNK-OUT
IMPROPER INSTALL CRACKING
PILLING UNEVEN RIB WEAR
MISALIGNMENT GRAVEL PENETRATION
2. Inspect the bearings in the idler pulleys and accessories by rotating the pulleys to look for
bearing slop or choppy feeling bearings.
3. Inspect the springs on the tensioner. If the rubber is damaged or if the spring is damaged,
change the assembly.
4. Inspect the pulleys for damage and excessive wear. If pulleys or the belts are damaged, change
the damaged pulley and the belt.
5. Check the belt wear pattern on all idler pulleys.
[a] If the belt wear pattern is incorrect (A), change the pulley and bracket assembly.
[b] If the belt wear pattern is correct (B), the idler and bracket can be reused.
ADDITIONAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Additional service information is available in the DD15 Troubleshooting Guide
(DDC-SVC-MAN-0029).
Detroit Diesel®, DDC®, Series 60® and the spinning arrows design are registered trademarks of Detroit Diesel Corporation.
© Copyright 2008 Detroit Diesel Corporation. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A.
También podría gustarte
- Engine Brake DD15Documento7 páginasEngine Brake DD15Hamilton miranda100% (1)
- D13F Viscoso Fan ChekDocumento2 páginasD13F Viscoso Fan ChekHamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Plymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceDe EverandPlymouth and Chrysler-built cars Complete Owner's Handbook of Repair and MaintenanceAún no hay calificaciones
- A Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesDe EverandA Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- SV250 Case Skid Steer Loader PDFDocumento583 páginasSV250 Case Skid Steer Loader PDFKEIZI ALENCARAún no hay calificaciones
- Repair Instructions - Off Vehicle Aveo 1.6Documento32 páginasRepair Instructions - Off Vehicle Aveo 1.6rectificamos100% (1)
- Boat Mechanical Systems Handbook (PB): How to Design, Install, and Recognize Proper Systems in BoatsDe EverandBoat Mechanical Systems Handbook (PB): How to Design, Install, and Recognize Proper Systems in BoatsAún no hay calificaciones
- 008 - Automatic Transmission - 6T40 (MH8 MHH) - Repair Instructions - Off VehicleDocumento82 páginas008 - Automatic Transmission - 6T40 (MH8 MHH) - Repair Instructions - Off VehicleGedas GvildysAún no hay calificaciones
- Rboat Davit MAINTENANCE MANUAL PDFDocumento14 páginasRboat Davit MAINTENANCE MANUAL PDFAnoop AnupAún no hay calificaciones
- Section 4 - Basic Hydraulics PDFDocumento25 páginasSection 4 - Basic Hydraulics PDFKhalid ZaeemAún no hay calificaciones
- Dry Screw Compressor General Arangement Drawings - RedactedDocumento1 páginaDry Screw Compressor General Arangement Drawings - Redactedvomawew647Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cummin KTA50-G3 Main Bearing Installation ManualDocumento15 páginasCummin KTA50-G3 Main Bearing Installation ManualRey Anthony Pole100% (2)
- Cat Hose & Connector Installation Guide PDFDocumento35 páginasCat Hose & Connector Installation Guide PDFKeron TrotzAún no hay calificaciones
- Kawasaki ZX9R 98-99Documento307 páginasKawasaki ZX9R 98-99motomech100% (3)
- 4th Computer Hardware ServicingDocumento25 páginas4th Computer Hardware ServicingShabby Gay Malala TroganiAún no hay calificaciones
- Prolog Testing A003Documento51 páginasProlog Testing A003pablo elias perez ortegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Reuse and Salvage Guidelines - Specifications For Crankshafts in 3000 To 3400 and D-Series EnginesDocumento38 páginasReuse and Salvage Guidelines - Specifications For Crankshafts in 3000 To 3400 and D-Series EnginesJuan Pujol100% (2)
- Amboid Rear Differential Carrier: Rear/Rear Carrier On MT-40-143MA-N Tandem Drive AxlesDocumento55 páginasAmboid Rear Differential Carrier: Rear/Rear Carrier On MT-40-143MA-N Tandem Drive AxlesCosmicdancer RudraAún no hay calificaciones
- sebf 8264толкатели и ролики 3116Documento9 páginassebf 8264толкатели и ролики 3116Jone BaneAún no hay calificaciones
- Cf625 3, Cf500 6, Cf625 6 Service Manual v1Documento266 páginasCf625 3, Cf500 6, Cf625 6 Service Manual v1NAUTI SUR100% (1)
- Flexible CouplingDocumento21 páginasFlexible CouplingDildeep PallipadAún no hay calificaciones
- SEBF8301 ADocumento9 páginasSEBF8301 AnopainmadafakaAún no hay calificaciones
- 3226 Fmi 13Documento6 páginas3226 Fmi 13Hamilton miranda100% (2)
- Meritor Axle MT 40 143MA NDocumento55 páginasMeritor Axle MT 40 143MA Nford62bAún no hay calificaciones
- 6761200en FDDocumento64 páginas6761200en FDWilliam moreAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamentals of Safety Relief Valves in Ammonia Refrigeration SystemsDocumento3 páginasFundamentals of Safety Relief Valves in Ammonia Refrigeration SystemsBehnam AshouriAún no hay calificaciones
- SEBF8043 Crankshaft Visual InspectionDocumento49 páginasSEBF8043 Crankshaft Visual InspectionpramAún no hay calificaciones
- John Deere 450CLC Excavator Service Repair Technical Manual (TM1925)Documento14 páginasJohn Deere 450CLC Excavator Service Repair Technical Manual (TM1925)laopaodunAún no hay calificaciones
- All Models and Model Years (Except Xdiavel) Service Repair Bulletin Srv-Srb-18-030Documento21 páginasAll Models and Model Years (Except Xdiavel) Service Repair Bulletin Srv-Srb-18-030demoracingeduAún no hay calificaciones
- John Deere CT322 Compact Track Loader Service Repair Manual (TM2152)Documento17 páginasJohn Deere CT322 Compact Track Loader Service Repair Manual (TM2152)laopaodunAún no hay calificaciones
- Section 4 - Cam Followers/Tappets - Group 04Documento9 páginasSection 4 - Cam Followers/Tappets - Group 04Miodrag HuberAún no hay calificaciones
- Number: 08 Ddec Vi-48 S.M. REF.: 72.5 Engine: Dd15 DATE: September 2008Documento2 páginasNumber: 08 Ddec Vi-48 S.M. REF.: 72.5 Engine: Dd15 DATE: September 2008Hamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- BrakesDocumento180 páginasBrakesAdam BonsallAún no hay calificaciones
- AC 43.13-1B Chapter 08Documento42 páginasAC 43.13-1B Chapter 08Vorrataa KulkeitpravatAún no hay calificaciones
- C6.6 Cam Shaft InstallDocumento5 páginasC6.6 Cam Shaft InstallsenAún no hay calificaciones
- Rear Drum Brakes: Section: 4E2Documento12 páginasRear Drum Brakes: Section: 4E2Rafael HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- 016 - Automatic Transmission - 6T70 (M7U M7W) - Repair Instructions - Off VehicleDocumento106 páginas016 - Automatic Transmission - 6T70 (M7U M7W) - Repair Instructions - Off VehicleGedas GvildysAún no hay calificaciones
- LevasDocumento15 páginasLevase7424410Aún no hay calificaciones
- Appendix A - Torque Specs Torque Charts: Standard Bolt Torque Metric Bolt TorqueDocumento6 páginasAppendix A - Torque Specs Torque Charts: Standard Bolt Torque Metric Bolt TorquejlfyAún no hay calificaciones
- REVE Dorado Service ManualDocumento32 páginasREVE Dorado Service ManualHéctor Alberto LaioloAún no hay calificaciones
- D-Elsa 2 Reaction Beam Air Disc Brake: Maintenance Manual No. MM-1130Documento56 páginasD-Elsa 2 Reaction Beam Air Disc Brake: Maintenance Manual No. MM-1130LUKASAún no hay calificaciones
- C32 BeltsDocumento2 páginasC32 Beltskrlose.g.eAún no hay calificaciones
- sebf 8067 -толкателиDocumento17 páginassebf 8067 -толкателиJone BaneAún no hay calificaciones
- Track Shop Manual 2011 Lynx XU - ACE 600 - 1200 4-TEC enDocumento2 páginasTrack Shop Manual 2011 Lynx XU - ACE 600 - 1200 4-TEC enSkorost SkorostAún no hay calificaciones
- 2012 Dorado Pro Service ManualDocumento29 páginas2012 Dorado Pro Service ManualSea RidersAún no hay calificaciones
- Specifications: Application Specification Metric EnglishDocumento21 páginasSpecifications: Application Specification Metric Englishjhon greigAún no hay calificaciones
- 4346 InstructionsDocumento5 páginas4346 Instructions薛泽绵Aún no hay calificaciones
- Roatary Actuators - Micromatic Repair Manual - 26R-2 Thru 26R-124Documento14 páginasRoatary Actuators - Micromatic Repair Manual - 26R-2 Thru 26R-124tungAún no hay calificaciones
- Number: 08 Ddec Vi-36 S.M. REF.: 38.2 Engine: Dd15 DATE: July 2008Documento2 páginasNumber: 08 Ddec Vi-36 S.M. REF.: 38.2 Engine: Dd15 DATE: July 2008Hamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- 800 Series Service ManualDocumento48 páginas800 Series Service ManualCarlos AnticonaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bearing Clearance CheckDocumento3 páginasBearing Clearance ChecksxturboAún no hay calificaciones
- Repair Instructions - Off VehicleDocumento90 páginasRepair Instructions - Off Vehiclenghia phanAún no hay calificaciones
- Crankshaft - InstallDocumento5 páginasCrankshaft - InstallalonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- Replacement of Rear DOJ and BJ Boots: A: RemovalDocumento2 páginasReplacement of Rear DOJ and BJ Boots: A: RemovalmiguelAún no hay calificaciones
- 216B 226B 232B 242B Skid Steer Loader BXM00001-04224 (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3024C Engine (SEBP3770 - 65) - Systems & Components 1 UBADocumento4 páginas216B 226B 232B 242B Skid Steer Loader BXM00001-04224 (MACHINE) POWERED BY 3024C Engine (SEBP3770 - 65) - Systems & Components 1 UBAubaldo caraballoAún no hay calificaciones
- Front Brake Disc Replacement PDFDocumento3 páginasFront Brake Disc Replacement PDFY. VásquezAún no hay calificaciones
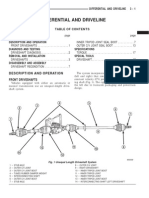
- Differential and Driveline: Description and Operation Front DriveshaftsDocumento0 páginasDifferential and Driveline: Description and Operation Front DriveshaftsLuis Alberto OrtegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Slewing Drives Installation & Maintenance ManualDocumento14 páginasSlewing Drives Installation & Maintenance ManualRamesh YadlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Hose and Connector Installation Guide: 1 Edition Created: October 2012Documento35 páginasHose and Connector Installation Guide: 1 Edition Created: October 2012Keron TrotzAún no hay calificaciones
- Front Disc BrakesDocumento13 páginasFront Disc BrakesCarlos VelázquezAún no hay calificaciones
- AVID Service Manual BB7 BB5Documento13 páginasAVID Service Manual BB7 BB5bakster67Aún no hay calificaciones
- Clutch Release System Wear Damage Endurant and Paccaar Trans Taib0889Documento5 páginasClutch Release System Wear Damage Endurant and Paccaar Trans Taib0889rpmjasa0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cylinder Line Projection - SMCS - 1216 - 040Documento5 páginasCylinder Line Projection - SMCS - 1216 - 040ToispuoliAún no hay calificaciones
- Section 34 Abrasive Wheels: RequirementsDocumento11 páginasSection 34 Abrasive Wheels: RequirementsnagaAún no hay calificaciones
- SRBF8091 ролики 3500Documento20 páginasSRBF8091 ролики 3500mohamed hamedAún no hay calificaciones
- TRNG rprt3Documento17 páginasTRNG rprt3Fahim AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Mccauley Propeller Systems Owner Operator Information ManualDocumento6 páginasMccauley Propeller Systems Owner Operator Information ManualElLoko MartinesAún no hay calificaciones
- Cleveland PDFDocumento111 páginasCleveland PDFJuan Eduardo Salazar Zambrana100% (1)
- Crankshaft Front Seal InstallSMCS - 1160 - 012Documento4 páginasCrankshaft Front Seal InstallSMCS - 1160 - 012Tawanda Tradyboy MorgansAún no hay calificaciones
- 3013C Pistons and Connecting Rods - Install - PDF Version 1 PDFDocumento4 páginas3013C Pistons and Connecting Rods - Install - PDF Version 1 PDFJaime Herrera LaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Caterpillar Cat M322D Wheeled Excavator (Prefix W2S) Service Repair Manual (W2S00001 and Up) PDFDocumento22 páginasCaterpillar Cat M322D Wheeled Excavator (Prefix W2S) Service Repair Manual (W2S00001 and Up) PDFfkdmma100% (1)
- QuickServe en Línea - (4310736) ISX15 CM2250 SN Manual de Servicio PDFDocumento3 páginasQuickServe en Línea - (4310736) ISX15 CM2250 SN Manual de Servicio PDFHamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- QuickServe en Línea - (4310736) ISX15 CM2250 SN Manual de ServicioDocumento14 páginasQuickServe en Línea - (4310736) ISX15 CM2250 SN Manual de ServicioHamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- QuickServe en Línea - (4310736) ISX15 CM2250 SN Manual de ServicioDocumento4 páginasQuickServe en Línea - (4310736) ISX15 CM2250 SN Manual de ServicioHamilton miranda100% (1)
- QuickServe en Línea - (4310736) ISX15 CM2250 SN Manual de ServicioDocumento14 páginasQuickServe en Línea - (4310736) ISX15 CM2250 SN Manual de ServicioHamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Service Bulletin Trucks: SB730005, Adaptive Cruise With Braking, TroubleshootingDocumento21 páginasService Bulletin Trucks: SB730005, Adaptive Cruise With Braking, TroubleshootingHamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- QSK45-60G 4021359 GDocumento6 páginasQSK45-60G 4021359 GHamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- NUMBER: 8 04-10 S.M. REF.: Listed in Table ENGINE: EPA07/10 DD Platform DateDocumento4 páginasNUMBER: 8 04-10 S.M. REF.: Listed in Table ENGINE: EPA07/10 DD Platform DateHamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cam Timing DDEC S50Documento4 páginasCam Timing DDEC S50Hamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- DDC War Man 0014Documento12 páginasDDC War Man 0014Hamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- RR Trmt0952Documento6 páginasRR Trmt0952Hamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- 876 MC 5 X 5 TWDocumento29 páginas876 MC 5 X 5 TWHamilton mirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- E6K WiringDocumento1 páginaE6K Wiringjo_falconAún no hay calificaciones
- Hayabusa Turbo Stage Kit CarDocumento1 páginaHayabusa Turbo Stage Kit Carha5611Aún no hay calificaciones
- Schedul Main OdooDocumento59 páginasSchedul Main OdooM MiftakhAún no hay calificaciones
- Auma GSTI 25.1-40.1 Multi-Turn Gearboxes Technical Data - ENDocumento2 páginasAuma GSTI 25.1-40.1 Multi-Turn Gearboxes Technical Data - ENGyörgy KollárAún no hay calificaciones
- Rockstar WDocumento24 páginasRockstar Wangeljavier9Aún no hay calificaciones
- Optibelt TH V Belt Drives PDFDocumento188 páginasOptibelt TH V Belt Drives PDFPaula FerreiraAún no hay calificaciones
- 2022 Nissan Pathfinder Brochure enDocumento9 páginas2022 Nissan Pathfinder Brochure enYudyChenAún no hay calificaciones
- Bahria Town LHR Electric Fencing With Wifi EnergizerDocumento3 páginasBahria Town LHR Electric Fencing With Wifi EnergizerTicketKataaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Implementation of Automatic Color Mixing and Filling Using PLC & SCADADocumento6 páginasImplementation of Automatic Color Mixing and Filling Using PLC & SCADAJaya ShreeAún no hay calificaciones
- TECHNICAL FehlmannDocumento5 páginasTECHNICAL FehlmannSahrul RomadonAún no hay calificaciones
- SP FLX SGT 50.v3Documento2 páginasSP FLX SGT 50.v3sungkarsAún no hay calificaciones
- LV100 3000Documento3 páginasLV100 3000Tibi IonAún no hay calificaciones
- Cat c27c32Documento3 páginasCat c27c32Catalina HuenumanAún no hay calificaciones
- LG Digital SignageDocumento21 páginasLG Digital SignageYazan RamezAún no hay calificaciones
- Sym Joyride Servicemanual PDFDocumento203 páginasSym Joyride Servicemanual PDFkamal ishakAún no hay calificaciones
- Hybrid Grounding in Off-Shore Utility Plant: August 2014Documento9 páginasHybrid Grounding in Off-Shore Utility Plant: August 2014AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Section 1720 Data - 2Documento10 páginasSection 1720 Data - 2Andri AjaAún no hay calificaciones
- Power Supply System Guardian Access 3U Instruction ManualDocumento54 páginasPower Supply System Guardian Access 3U Instruction ManualMohammad KilaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Intercom PDFDocumento2 páginasIntercom PDFganda irvanAún no hay calificaciones
- Levante Sistemas de Automatización y Control S.L.: CatálogosDocumento437 páginasLevante Sistemas de Automatización y Control S.L.: CatálogosHoa DuongAún no hay calificaciones
- Spec 315 MV 105 PowerGuard-XL 35KVDocumento2 páginasSpec 315 MV 105 PowerGuard-XL 35KVSarah PinkAún no hay calificaciones
- Escobillon para Tubos Centrifugos VWR 149-0219Documento1 páginaEscobillon para Tubos Centrifugos VWR 149-0219luis hernandezAún no hay calificaciones