Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
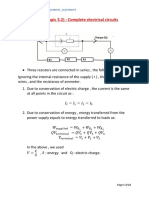
Power in Electric Circuits
Cargado por
DanKimberleyTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Power in Electric Circuits
Cargado por
DanKimberleyCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Power in electric circuits
When voltage is measured in a circuit, it is measuring the conversion of electrical energy to other
forms. As energy is conserved, the component can be said to be doing work, as this is defined as a
transfer of energy.
Electrical work
As the equation defining potential difference includes a term for the amount of energy transferred,
E, W = E. Therefore: 𝑊 = 𝑉 × 𝑄. The definition of current, in rearranged form, is 𝑄 = 𝐼𝑡. Combining
these equations gives us:
𝑊 = 𝑉𝐼𝑡
Electrical power
Power, P, is the rate of transfer of energy i.e. the rate of doing work. In a circuit, the energy is
𝐸 𝑊
dissipated by a component. The mathematical definition for this is 𝑃 = 𝑡
𝑜𝑟 𝑃 = 𝑡
.
Incorporating the equation above:
𝑉𝐼𝑡
𝑃= = 𝑉𝐼
𝑡
Power dissipated by resistors
Variations of the electrical power equation can be formed by substituting in terms from Ohm’s law.
Therefore, if we only know current and resistance:
𝑃 = 𝑉𝐼 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑉 = 𝐼𝑅 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑃 = 𝐼 2 𝑅
If we only known pd and resistance:
𝑉 𝑉2
𝑃=𝑉 × =
𝑅 𝑅
Efficiency
The equations above can be used to calculate the work and power of an electrical device, however
to be useful, we must consider the purpose of the device. Therefore, efficiency = useful energy
output / total energy input or / total power input.
También podría gustarte
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsDe EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsAún no hay calificaciones
- Phys502 Lect 4Documento7 páginasPhys502 Lect 4MaissaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 DielectricsDocumento12 páginasChapter 8 DielectricsnAún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureDe EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureAún no hay calificaciones
- Natural Units and Electromagnetic UnitsDocumento11 páginasNatural Units and Electromagnetic UnitsMaxImus AlphAAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 1. Electric Charges and FieldDocumento55 páginasCH 1. Electric Charges and FieldAnila PadinjarayilAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Energy Storage ElementsDocumento13 páginasIntroduction To Energy Storage ElementspaulamarieestrellalengascoAún no hay calificaciones
- Three Vector Relation Converted1Documento5 páginasThree Vector Relation Converted1Mahmudur Rahman AdilAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit WorkBook 1 3 HN U21 Electric MachinesDocumento23 páginasUnit WorkBook 1 3 HN U21 Electric MachineswizairdAún no hay calificaciones
- S PDFDocumento90 páginasS PDFAmritha V100% (1)
- 3rd WeekDocumento6 páginas3rd WeekNanzkie Andrei SamanAún no hay calificaciones
- Power in Ac Circuits: Resistive LoadDocumento8 páginasPower in Ac Circuits: Resistive LoadMunyaradzi zonkeAún no hay calificaciones
- 2021 - JNRSE - High Efficient Boost Energizing and Transferring Circuit Concept For Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting - 04Documento3 páginas2021 - JNRSE - High Efficient Boost Energizing and Transferring Circuit Concept For Electromagnetic Energy Harvesting - 04Bobby SluddsAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivation of Gravitational Potential Energy Using Calculus2Documento7 páginasDerivation of Gravitational Potential Energy Using Calculus2W-d DomAún no hay calificaciones
- Electric Potential and Capacitors 16: Senior Secondary Course Learner's Guide, PhysicsDocumento4 páginasElectric Potential and Capacitors 16: Senior Secondary Course Learner's Guide, PhysicsFatuhu Abba dandagoAún no hay calificaciones
- GP2 - Q3 - Week 3Documento14 páginasGP2 - Q3 - Week 3Kyla EsmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Class Act Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocumento8 páginasClass Act Electromechanical Energy ConversionsfasdfAún no hay calificaciones
- EEE241L - Lab 7 - AC PowerDocumento7 páginasEEE241L - Lab 7 - AC PowerMd. Imdadul Haque Nayan 2222846643Aún no hay calificaciones
- DC Load Flow Method: I J Ij Ij Ij IjDocumento3 páginasDC Load Flow Method: I J Ij Ij Ij Ijhemang patelAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter TwoDocumento12 páginasChapter TwoBediria MohamadAún no hay calificaciones
- Electric Charges and Fields IPE 4M QuestionsDocumento11 páginasElectric Charges and Fields IPE 4M Questionsbhanu010420Aún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetically Coupled Circuits-Lecture 2Documento16 páginasMagnetically Coupled Circuits-Lecture 2YousefAún no hay calificaciones
- The Watt: Grade 11 - General Physics 2 Week 3 and 4Documento6 páginasThe Watt: Grade 11 - General Physics 2 Week 3 and 4Kevin AlibongAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 24Documento59 páginasChapter 24Prosonjit Chandra DashAún no hay calificaciones
- Test6 v0Documento8 páginasTest6 v0Marcus PoonAún no hay calificaciones
- MODULE 3 Electric PotentialDocumento9 páginasMODULE 3 Electric PotentialVenus CaringalAún no hay calificaciones
- Work Energy and PowerDocumento5 páginasWork Energy and PowerjunquelalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Electromagnetics-Lec8-Divergence Theorem, Energy and Electric PotentialDocumento15 páginasElectromagnetics-Lec8-Divergence Theorem, Energy and Electric PotentialNerlisa NadadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 - Modulation - Problems and SolutionsDocumento15 páginasChapter 1 - Modulation - Problems and Solutionsmandy aninagyeiAún no hay calificaciones
- End SEM SyllabusDocumento45 páginasEnd SEM SyllabusShreyans KothariAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapt 2 Electric Circuits-1Documento40 páginasChapt 2 Electric Circuits-1Blessed RazimosAún no hay calificaciones
- Capacitive Sensors ActuatorsDocumento55 páginasCapacitive Sensors ActuatorsVenkateshwaran AAún no hay calificaciones
- General Physics 2Documento5 páginasGeneral Physics 2Nanzkie Andrei SamanAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 1 (Part 1) Improved Teaching-Learning Delivery MethodsDocumento12 páginasUnit 1 (Part 1) Improved Teaching-Learning Delivery Methods1NT20EE021 AKANKSHAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 11 Electrostatics Genius Series Formula SheetDocumento52 páginasChapter 11 Electrostatics Genius Series Formula SheetHaseebShahAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 5-Capacitance and Inductance of DC CircuitsDocumento24 páginasChapter 5-Capacitance and Inductance of DC CircuitsDouglas OngomAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 4Documento23 páginasChapter 4amanuelfitsum589Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mathematics of Electric PowerDocumento2 páginasMathematics of Electric PowerVidulaAún no hay calificaciones
- Capacitors: Mitul M. Modi, Asst ProfDocumento35 páginasCapacitors: Mitul M. Modi, Asst ProfJay SathvaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Transition State With Catalyst G Activation Free Energy G Driving Force GDocumento10 páginasTransition State With Catalyst G Activation Free Energy G Driving Force GMir RafsanAún no hay calificaciones
- 8 Power Considerations and The Poynting VectorDocumento10 páginas8 Power Considerations and The Poynting VectorMuhammad SaadAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 - Principles of Electromechanical Energy ConversionDocumento22 páginasChapter 2 - Principles of Electromechanical Energy Conversionchibssa alemayehuAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 Electric FieldDocumento30 páginasChapter 2 Electric Fieldofcp52Aún no hay calificaciones
- Unit Checklist - Topic A.3Documento2 páginasUnit Checklist - Topic A.3haydnlucawhyteAún no hay calificaciones
- SY - Electric Potential EnergyDocumento3 páginasSY - Electric Potential EnergyNeelam KapoorAún no hay calificaciones
- Energy MethodsDocumento15 páginasEnergy MethodsgalehAún no hay calificaciones
- Sanad ElectricityDocumento13 páginasSanad ElectricityAli SalamehAún no hay calificaciones
- OCR A Physics A-Level: Topic 6.1: CapacitorsDocumento9 páginasOCR A Physics A-Level: Topic 6.1: CapacitorsjmsonlAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 7 - Chapter 23 Part 3Documento18 páginasLecture 7 - Chapter 23 Part 3Mircea PanteaAún no hay calificaciones
- Electric Charge and Coulombs LawDocumento14 páginasElectric Charge and Coulombs LawFiaz HusainAún no hay calificaciones
- ACTIVITY 2 - Verification of VDT and CDTDocumento5 páginasACTIVITY 2 - Verification of VDT and CDTNeszel Jean Japus SaplotAún no hay calificaciones
- Critical Power Revisited: An Alternate Interpretation of Physiology Based On ObservationDocumento17 páginasCritical Power Revisited: An Alternate Interpretation of Physiology Based On ObservationNursahanizaAún no hay calificaciones
- Work Energy Power PDFDocumento4 páginasWork Energy Power PDFTahmeed AzizAún no hay calificaciones
- ECEN 214 Lab 9Documento9 páginasECEN 214 Lab 9Shoaib AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Potential Energy and Conservation of EnergyDocumento39 páginasPotential Energy and Conservation of Energy張耀恩Aún no hay calificaciones
- PHYS 122 (Electrostatics)Documento14 páginasPHYS 122 (Electrostatics)Yusuf ZaynabAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment No: Experiment Name: Capacitance of Metal Spheres and of A Spherical Capacitor ObjectiveDocumento14 páginasExperiment No: Experiment Name: Capacitance of Metal Spheres and of A Spherical Capacitor ObjectiveRana RashidAún no hay calificaciones
- Electricity - Part 2Documento22 páginasElectricity - Part 2Anonymous CommentatorAún no hay calificaciones
- Problems in Electrostatics, Current ElectricityDocumento14 páginasProblems in Electrostatics, Current ElectricityThayumanavar SachithananthamAún no hay calificaciones
- StamitzDocumento2 páginasStamitzDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Waking Up: Author Finished? TopicsDocumento2 páginasWaking Up: Author Finished? TopicsDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lord of The Flies: Author Date Read Fiction / Non-Fiction Rating /10 TopicsDocumento1 páginaLord of The Flies: Author Date Read Fiction / Non-Fiction Rating /10 TopicsDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Gcse WavesDocumento1 páginaGcse WavesDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Core Practical 11 - Dan KimberleyDocumento1 páginaCore Practical 11 - Dan KimberleyDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Force Against Velocity: Circular MotionDocumento1 páginaForce Against Velocity: Circular MotionDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Waves 2Documento1 páginaWaves 2DanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Core Practical 9Documento4 páginasCore Practical 9DanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Paper 3 Things: Means Add Raw Uncertainty, Multiply or Divide Means Add Percentage UncertaintyDocumento1 páginaPaper 3 Things: Means Add Raw Uncertainty, Multiply or Divide Means Add Percentage UncertaintyDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Practical 9 Take 2Documento3 páginasPractical 9 Take 2DanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Core Practical 4Documento4 páginasCore Practical 4DanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Practical 9Documento2 páginasPractical 9DanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Spreadsheet 5Documento3 páginasSpreadsheet 5DanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Core Practical 5Documento3 páginasCore Practical 5DanKimberley100% (1)
- DragDocumento1 páginaDragDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Semiconductors: Semiconductors Are Generally Solid Materials With Small Numbers of Delocalised Electrons Free ToDocumento2 páginasSemiconductors: Semiconductors Are Generally Solid Materials With Small Numbers of Delocalised Electrons Free ToDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Fluid Movement: Laminar FlowDocumento2 páginasFluid Movement: Laminar FlowDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Core Practical 2: Measuring Resistivity: 1 PreparationDocumento3 páginasCore Practical 2: Measuring Resistivity: 1 PreparationDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical Energy Transfer: Voltage Is A Measure of The Amount of Energy Per Unit Charge, ThereforeDocumento2 páginasElectrical Energy Transfer: Voltage Is A Measure of The Amount of Energy Per Unit Charge, ThereforeDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Power in Electric CircuitsDocumento4 páginasPower in Electric CircuitsDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- What Makes This Scene Dramatic and SignificantDocumento2 páginasWhat Makes This Scene Dramatic and SignificantDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Gravitational and Kinetic EnergiesDocumento1 páginaGravitational and Kinetic EnergiesDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Piano PiecesDocumento1 páginaPiano PiecesDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Macbeth Quotations For LearningDocumento4 páginasMacbeth Quotations For LearningDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Collection: Populations and SamplesDocumento3 páginasData Collection: Populations and SamplesDanKimberleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDe EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (10)
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsDe EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (3)
- Flow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringDe EverandFlow Analysis for Hydrocarbon Pipeline EngineeringAún no hay calificaciones
- Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsDe EverandAsphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsAún no hay calificaciones
- A Practical Handbook for Drilling Fluids ProcessingDe EverandA Practical Handbook for Drilling Fluids ProcessingAún no hay calificaciones
- Casing and Liners for Drilling and Completion: Design and ApplicationDe EverandCasing and Liners for Drilling and Completion: Design and ApplicationCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (3)
- Machinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideDe EverandMachinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideCalificación: 2 de 5 estrellas2/5 (1)
- Internal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesDe EverandInternal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Subverted the AlternativesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (2)
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresDe EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresAún no hay calificaciones
- Enhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingDe EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery Handout: A Focus on WaterfloodingAún no hay calificaciones
- Advanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationDe EverandAdvanced Production Decline Analysis and ApplicationCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (4)
- An Operations Guide to Safety and Environmental Management Systems (SEMS): Making Sense of BSEE SEMS RegulationsDe EverandAn Operations Guide to Safety and Environmental Management Systems (SEMS): Making Sense of BSEE SEMS RegulationsAún no hay calificaciones
- Hybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart WaterfloodingDe EverandHybrid Enhanced Oil Recovery Using Smart WaterfloodingAún no hay calificaciones
- Case Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesDe EverandCase Studies of Material Corrosion Prevention for Oil and Gas ValvesAún no hay calificaciones
- Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic DataDe EverandAcquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic DataCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (4)
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationDe EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (3)
- Abrasive Water Jet Perforation and Multi-Stage FracturingDe EverandAbrasive Water Jet Perforation and Multi-Stage FracturingAún no hay calificaciones
- Guide to the Practical Use of Chemicals in Refineries and PipelinesDe EverandGuide to the Practical Use of Chemicals in Refineries and PipelinesCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- The Petroleum Engineering Handbook: Sustainable OperationsDe EverandThe Petroleum Engineering Handbook: Sustainable OperationsCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (5)
- 100 AI Use Cases in the Upstream Industry: A Comprehensive Guide for Professionals and Researchers to Overcome Industry Challenges Using AI and PythonDe Everand100 AI Use Cases in the Upstream Industry: A Comprehensive Guide for Professionals and Researchers to Overcome Industry Challenges Using AI and PythonAún no hay calificaciones