Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Active and Passive Tenses Chart Explained
Cargado por
Manivannan Ssn0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
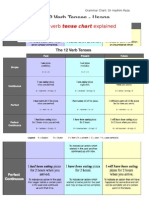
81 vistas5 páginasThe document provides a chart comparing active and passive tenses in English. It lists various tenses such as simple present and past, present and past continuous, present perfect and past perfect. For each active tense, it gives the corresponding passive form by changing the verb pattern and making the object of the active sentence the subject of the passive sentence.
Descripción original:
Título original
Active Passive Tenses
Derechos de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoThe document provides a chart comparing active and passive tenses in English. It lists various tenses such as simple present and past, present and past continuous, present perfect and past perfect. For each active tense, it gives the corresponding passive form by changing the verb pattern and making the object of the active sentence the subject of the passive sentence.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
81 vistas5 páginasActive and Passive Tenses Chart Explained
Cargado por
Manivannan SsnThe document provides a chart comparing active and passive tenses in English. It lists various tenses such as simple present and past, present and past continuous, present perfect and past perfect. For each active tense, it gives the corresponding passive form by changing the verb pattern and making the object of the active sentence the subject of the passive sentence.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 5
ACTIVE AND PASSIVE TENSES CHART
SIMPLE PRESENT and SIMPLE PAST
The active object becomes the passive subject.
am/is/are + past participle
was/were + past participle
Active: Simple Present Passive: Simple Present
The movie fascinates me. I am fascinated by the movie.
The movie bores Jack. Jack is bored by the movie.
The movie surprises them. They are surprised by the movie.
Active: Simple Past Passive: Simple Past
The movie bored me. I was bored by the movie.
The movie fascinated Jack. Jack was fascinated by the movie.
The movie surprised them. They were surprised by the movie.
PRESENT and PAST CONTINUOUS (PROGRESSIVE)
Passive form:
am/is/are + being + past participle
was/were + being + past participle
Passive: Present Continuous
Active: Present Continuous
Shannon is being helped by me.
I am helping Shannon.
Su and Ling are being helped by
June is helping Su and Ling.
June.
Passive: Past Continuous
Active: Past Continuous The bathroom was being cleaned
I was cleaning the bathroom. by me.
They were cleaning the bedroom. The bedroom was being cleaned
Susan was cleaning the kitchen by them.
and courtyard. The kitchen and courtyard were
being cleaned by Susan.
PRESENT PERFECT, PAST PERFECT and FUTURE PERFECT
Passive form:
have/has been + past participle
had been + past participle
Passive: Present Perfect
Active: Present Perfect
The gift has been mailed by me.
I have mailed the gift.
The gifts have been mailed by
Jack has mailed the gifts.
Jack.
Active: Past Perfect Passive: Past Perfect
Steven Spielberg had directed the The movie had been directed by
movie. Steven Spielberg.
Penny Marshall had directed those The movies had been directed by
movies. Penny Marshall.
Active: Future Perfect Passive: Future Perfect
John will have finished the project The project will have been finished
next month. by next month.
They will have finished the projects The projects will have been
before then. finished before then.
FUTURE TENSES
Passive forms: will + be + past participle
is/are going to be + past participle
Active: Future with WILL Passive: Future with WILL
I will mail the gift. The gift will be mailed by me.
Jack will mail the gifts. The gifts will be mailed by Jack.
Passive: Future with GOING TO
Active: Future with GOING TO The cake is going to be made by
I am going to make the cake. me.
Sue is going to make two cakes. Two cakes are going to be made
by Sue.
PRESENT / FUTURE MODALS
The passive form follows this pattern:
modal + be + past participle
Passive: WILL / WON'T (WILL
Active: WILL / WON'T (WILL
NOT)
NOT)
Tom will be invited to the party by
Sharon will invite Tom to the party.
Sharon.
Sharon won't invite Jeff to the
Jeff won't be invited to the party by
party.
Sharon.
(Sharon will not invite Jeff to the
(Jeff will not be invited to the party
party.)
by Sharon.)
Passive: CAN / CAN'T (CAN
NOT)
Active: CAN / CAN'T (CAN NOT)
The future can be foretold by Mai.
Mai can foretell the future.
The future can't be foretold by
Terry can't foretell the future.
Terry.
(Terry can not foretell the future.)
(The future can not be foretold by
Terry.)
Active: MAY / MAY NOT Passive: MAY / MAY NOT
Her company may give Katya a Katya may be given a new office
new office. by her company.
The lazy students may not do the The homework may not be done by
homework. the lazy students.
MIGHT / MIGHT NOT MIGHT / MIGHT NOT
Her company might give Katya a Katya might be given a new office
new office. by her company.
The lazy students might not do the The homework might not be done
homework. by the lazy students.
Active: SHOULD / SHOULDN'T Passive: SHOULD / SHOULDN'T
Students should memorize English English verbs should be
verbs. memorized by students.
Children shouldn't smoke Cigarettes shouldn't be smoked by
cigarettes. children.
Active: OUGHT TO Passive: OUGHT TO
Students ought to learn English English verbs ought to be
verbs. memorized by students.
(negative ought to is rarely used)
Active: HAD BETTER / HAD Passive: HAD BETTER / HAD
BETTER NOT BETTER NOT
Students had better practice English had better be practiced
English every day. every day by students.
Children had better not drink Whiskey had better not be drunk
whiskey. by children.
Passive: MUST / MUST NOT
Active: MUST / MUST NOT
A passport to travel abroad must
Tourists must apply for a passport
be applied for.
to travel abroad.
That door must not be used by
Customers must not use that door.
customers.
Active: HAS TO / HAVE TO Passive: HAS TO / HAVE TO
She has to practice English every English has to be practiced every
day. day.
Sara and Miho have to wash the The dishes have to be washed by
dishes every day. them every day.
DOESN'T HAVE TO/ DON'T DOESN'T HAVE TO/ DON'T
HAVE TO HAVE TO
Maria doesn't have to clean her Her bedroom doesn't have to be
bedroom every day. cleaned every day.
The children don't have to clean Their bedrooms don't have to be
their bedrooms every day. cleaned every day.
Active: BE SUPPOSED TO Passive: BE SUPPOSED TO
I am supposed to type the The composition is supposed to be
composition. typed by me.
I am not supposed to copy the The stories in the book are not
stories in the book. supposed to be copied.
Janet is supposed to clean the The living room is supposed to be
living room. cleaned by Janet.
She isn't supposed to eat candy Candy and gum aren't supposed to
and gum. be eaten by her.
They are supposed to make dinner Dinner for the family is supposed to
for the family. be made by them.
They aren't supposed to make Dessert isn't supposed to be made
dessert. by them.
PAST MODALS
The past passive form follows this pattern:
modal + have been + past participle
Active: SHOULD HAVE / Passive: SHOULD HAVE /
SHOULDN'T HAVE SHOULDN'T HAVE
The students should have learned The verbs should have been
the verbs. learned by the students.
The children shouldn't have The window shouldn't have been
broken the window. broken by the children.
Active: OUGHT TO Passive: OUGHT TO
Students ought to have learned The verbs ought to have been
the verbs. learned by the students.
(negative ought to is rarely used)
Active: BE SUPPOSED TO Passive: BE SUPPOSED TO
(past time) (past time)
I was supposed to type the The composition was supposed
composition. to be typed by me.
I wasn't supposed to copy the The story in the book wasn't
story in the book. supposed to be copied.
Janet was supposed to clean the The living room was supposed to
living room. be cleaned by Janet.
She wasn't supposed to eat Candy and gum weren't
candy and gum. supposed to be eaten by her.
Frank and Jane were supposed Dinner was supposed to be made
to make dinner. by them.
They weren't supposed to make Dessert wasn't supposed to be
dessert. made by them.
Active: MAY / MAY NOT Passive: MAY / MAY NOT
That firm may have offered Katya Katya may have been offered a
a new job. new job by that firm.
The students may not have The paper may not have been
written the paper. written by the students.
MIGHT / MIGHT NOT MIGHT / MIGHT NOT
That firm might have offered Katya might have been offered a
Katya a new job. new job by that firm.
The students might not have The paper might not have been
written the paper. written by the students.
También podría gustarte
- Passive & Verb Tenses PDFDocumento8 páginasPassive & Verb Tenses PDFlovely callsAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocumento5 páginasActive and Passive Tenses ChartvenkteshAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Voice Chart 11Documento3 páginasActive and Passive Voice Chart 11Inmaculada SenovillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocumento3 páginasActive and Passive Tenses Chartabida jamaliAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocumento3 páginasActive and Passive Tenses Chartrondick93% (29)
- Passive Voice ChartsDocumento5 páginasPassive Voice ChartsnenoulaAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 7. Passives. Tenses ChartDocumento0 páginasUnit 7. Passives. Tenses ChartunidienteAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Voice Chart 11Documento3 páginasActive and Passive Voice Chart 11Ryan Yudhistyanto PutroAún no hay calificaciones
- The Passive Voice. Tenses ChartDocumento5 páginasThe Passive Voice. Tenses Chartlondonfaidel6511Aún no hay calificaciones
- English Active Passive Tenses ChartDocumento7 páginasEnglish Active Passive Tenses ChartSanjay TiwariAún no hay calificaciones
- 8242 Active and Passive Voice ChartDocumento3 páginas8242 Active and Passive Voice ChartGabriela GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Passive Sentences: Ajvilches. 6/ 2009Documento7 páginasPassive Sentences: Ajvilches. 6/ 2009abingvAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocumento4 páginasActive and Passive Tenses ChartchandraAún no hay calificaciones
- ACTIVE AND PASSIVE TENSESDocumento5 páginasACTIVE AND PASSIVE TENSESAishhwarya PriyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Simple Present and Simple PastDocumento5 páginasSimple Present and Simple PastRaymond Sabanal BanquirigoAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Voice ChartDocumento3 páginasActive and Passive Voice ChartDea ZarynaAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Voice ChartDocumento15 páginasActive and Passive Voice ChartYoussef BoulaghlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grammar ChartsDocumento7 páginasGrammar ChartsHashim Raza Siyal100% (2)
- An English-Zone - Com Chart: Active and Passive VoiceDocumento4 páginasAn English-Zone - Com Chart: Active and Passive VoiceAra CMAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Voice Tenses ChartDocumento11 páginasActive and Passive Voice Tenses ChartMarco GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- RUmus Passive VoiceDocumento4 páginasRUmus Passive VoiceElma JelenatorAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive VoiceDocumento7 páginasActive and Passive Voiceazadali735323Aún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Voice Chart PDFDocumento1 páginaActive and Passive Voice Chart PDFcastillo ceciliaAún no hay calificaciones
- GrammarguideDocumento2 páginasGrammarguideAlexandraAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Tense ChartDocumento4 páginasActive and Passive Tense ChartAna Paula MedinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Passivization Elt3Documento5 páginasPassivization Elt3Kerwin Gener GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana7 Inglestecnico2Documento5 páginasSemana7 Inglestecnico2Javiera AzuaAún no hay calificaciones
- Passive Voice 2Documento2 páginasPassive Voice 2ClaudioAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Tenses ChartDocumento5 páginasActive and Passive Tenses ChartaresAún no hay calificaciones
- Present Continuous TenseDocumento2 páginasPresent Continuous TenseIoana MariaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grammar: PresentDocumento36 páginasGrammar: PresentEva Trinidad Vera GómezAún no hay calificaciones
- The Tense SystemDocumento3 páginasThe Tense SystemAdriana KarvaiováAún no hay calificaciones
- English Lessons Summary for Baccalaureate StudentsDocumento11 páginasEnglish Lessons Summary for Baccalaureate StudentsElisa GerAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 - Tenses ReviewDocumento24 páginas1 - Tenses ReviewDenis Bozo ZavallaAún no hay calificaciones
- Without Electrical EnergyDocumento7 páginasWithout Electrical EnergypaolaAún no hay calificaciones
- Blue & Pink Present Tenses Presentation (1) (1)Documento14 páginasBlue & Pink Present Tenses Presentation (1) (1)Gisela Cruz RiosAún no hay calificaciones
- Active and Passive Voice Lecture 7Documento38 páginasActive and Passive Voice Lecture 7maheenshaikh119Aún no hay calificaciones
- Am/is/are + Being + Past Participle Q Was/were + Being + Past ParticipleDocumento3 páginasAm/is/are + Being + Past Participle Q Was/were + Being + Past ParticipleBen HussaAún no hay calificaciones
- ملخص شامل لدروس bac PDFDocumento11 páginasملخص شامل لدروس bac PDFAnonymous wwD1u4TmGh100% (5)
- Apunts Anglès 2n BatxilleratDocumento9 páginasApunts Anglès 2n BatxilleratNoèlia Vallverdú BarberàAún no hay calificaciones
- Grammar: PresentDocumento37 páginasGrammar: PresentJavi DiAún no hay calificaciones
- Active Voice and Passive VoiceDocumento16 páginasActive Voice and Passive VoiceYabinda B SaadAún no hay calificaciones
- b21 DexwayDocumento25 páginasb21 DexwayJacqueline Prieto GarayAún no hay calificaciones
- Voices of VerbsDocumento34 páginasVoices of VerbsKwatro KantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Universidad Tecnica de ManabíDocumento4 páginasUniversidad Tecnica de ManabíMaria Patricia CedeñoAún no hay calificaciones
- Passive VoiceDocumento5 páginasPassive VoiceViktóóriaa TóthAún no hay calificaciones
- Tense Subject Auxiliary Past Participle Singular Plural: Passive Verb FormationDocumento7 páginasTense Subject Auxiliary Past Participle Singular Plural: Passive Verb FormationMarloAún no hay calificaciones
- Present Tenses: Present Simple Present Continuous Present PerfectDocumento22 páginasPresent Tenses: Present Simple Present Continuous Present PerfectFedelis RemmiAún no hay calificaciones
- Modal Verbs & Narrative Tenses. (Apuntes)Documento23 páginasModal Verbs & Narrative Tenses. (Apuntes)Luis MiguelAún no hay calificaciones
- Week 13 - PPT - 2024-1Documento18 páginasWeek 13 - PPT - 2024-1josebtafurvAún no hay calificaciones
- ملخص شامل لدروس BacDocumento6 páginasملخص شامل لدروس Bacعبد العزيز تقية100% (3)
- Present Tenses ExplainedDocumento5 páginasPresent Tenses ExplainedElenaGalánAún no hay calificaciones
- Oxford Discover Grammar 5Documento114 páginasOxford Discover Grammar 5Joyce WangAún no hay calificaciones
- Active Passive Extensive Conversion Practice Sheet Answer KeyDocumento5 páginasActive Passive Extensive Conversion Practice Sheet Answer KeyMaha AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Present Tenses: Present Simple Present Continuous Present PerfectDocumento22 páginasPresent Tenses: Present Simple Present Continuous Present Perfectsaharsh yadavAún no hay calificaciones
- The Present Perfect Is Used To Talk About An Event That Began in The Past and Continues Up To The PresentDocumento17 páginasThe Present Perfect Is Used To Talk About An Event That Began in The Past and Continues Up To The PresentRodinei VieiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Questions & Answers: Positive & Negative SentencesDocumento8 páginasQuestions & Answers: Positive & Negative SentencesARHAún no hay calificaciones
- Serbian: Vocabulary Practice A1 to the Book “Idemo dalje 1” - Latin Script: Serbian ReaderDe EverandSerbian: Vocabulary Practice A1 to the Book “Idemo dalje 1” - Latin Script: Serbian ReaderAún no hay calificaciones
- Spanish for English Speakers: Dictionary English - Spanish: 700+ of the Most Important Words / Vocabulary for Beginners with Useful Phrases to Improve Learning - Level A1 - A2De EverandSpanish for English Speakers: Dictionary English - Spanish: 700+ of the Most Important Words / Vocabulary for Beginners with Useful Phrases to Improve Learning - Level A1 - A2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Types of VerbsDocumento4 páginasTypes of Verbstadashii0% (1)
- Bahasa Inggris SDDocumento19 páginasBahasa Inggris SDNyoman SinduyasaAún no hay calificaciones
- Eastern New England Phonology in The Bonin IslandsDocumento12 páginasEastern New England Phonology in The Bonin IslandsJoaquin ReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- List Prefix Sufix StudentsDocumento5 páginasList Prefix Sufix StudentschascarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Kel 3Documento2 páginasTugas Bahasa Inggris Kel 3delsa alifahAún no hay calificaciones
- Compound-Adjectives-Activity AnswersDocumento3 páginasCompound-Adjectives-Activity AnswersRosana Echavez100% (1)
- Jas KulaDocumento243 páginasJas KulaFabian Gonzalez RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- Part of Speech - SoalDocumento3 páginasPart of Speech - SoalHasbiallah AnsorAún no hay calificaciones
- Class XII Sample Question 2018-2019 Tangkhul (MILDocumento3 páginasClass XII Sample Question 2018-2019 Tangkhul (MILParth ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- © David RickertDocumento3 páginas© David Rickertapi-394733232Aún no hay calificaciones
- Time: Connecting Words and Expressions: One Thing Before AnotherDocumento4 páginasTime: Connecting Words and Expressions: One Thing Before AnotherJuan Francisco Amand de MendietaAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Pronounce 'Ed' at The End of A VerbDocumento1 páginaHow To Pronounce 'Ed' at The End of A VerbRonaldo Sá GuimarãesAún no hay calificaciones
- CONFUSING ENGLISH WORDS EXPLAINEDDocumento3 páginasCONFUSING ENGLISH WORDS EXPLAINEDXiao LinhAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 Susanta KR Bardhan - 20-29 - Jan 2013 - Vol 1 Issue 1 PDFDocumento10 páginas04 Susanta KR Bardhan - 20-29 - Jan 2013 - Vol 1 Issue 1 PDFglobaljournalellAún no hay calificaciones
- Language LimitationDocumento5 páginasLanguage LimitationRahul KejriwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Hamza (H) : I. OrthographyDocumento3 páginasHamza (H) : I. OrthographyZeeya HussAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjectives PDFDocumento3 páginasAdjectives PDFRitikaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lexurgy LSCDocumento3 páginasLexurgy LSCÆk y ÉrøsAún no hay calificaciones
- NounsDocumento11 páginasNounsrawaa FathiAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Noun Phrase - Adverb PhraseDocumento41 páginas1 Noun Phrase - Adverb PhrasePaolo JamerAún no hay calificaciones
- Reported SpeechDocumento14 páginasReported Speechapi-237574246Aún no hay calificaciones
- Past perfect tense guideDocumento3 páginasPast perfect tense guideAfroditi PolAún no hay calificaciones
- English Tenses Timeline GuideDocumento3 páginasEnglish Tenses Timeline GuideqkhaiproAún no hay calificaciones
- DolchDocumento6 páginasDolchJeffrey EstacioAún no hay calificaciones
- Reported Questions SummarizedDocumento29 páginasReported Questions SummarizedCarolina MarinAún no hay calificaciones
- Passive Voice Dan ComparisonDocumento27 páginasPassive Voice Dan ComparisonAnindya BhaswaraAún no hay calificaciones
- New American Inside Out Elementary Unit 2 Test: Part ADocumento4 páginasNew American Inside Out Elementary Unit 2 Test: Part ATonatiuhAún no hay calificaciones
- Plural Possessive Nouns 6th Grade WorksheetDocumento2 páginasPlural Possessive Nouns 6th Grade WorksheetGel OrdanzaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Simple Past Tense 5-6th GradeDocumento2 páginasThe Simple Past Tense 5-6th GradeAlexandra Eva75% (4)
- Grammar Reference GuideDocumento6 páginasGrammar Reference GuideBort FortAún no hay calificaciones