Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
2014 DAY4 Ankle Joint Bulleted
Cargado por
azuma12345Descripción original:
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
2014 DAY4 Ankle Joint Bulleted
Cargado por
azuma12345Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Musculoskeletal Week Day 4
The Ankle Joint
The cadaver should be supine.
You will find it to be helpful if you can position the cadaver so that its foot is facing
anteriorly in anatomical position and not turned laterally due to hip external rotation.
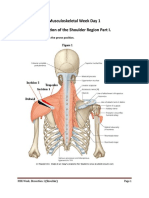
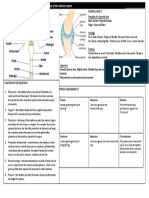
Define the tibialis anterior
tendon and the tip of the medial
malleolus (Figure 1).
Observe that the tibialis anterior
is the medial-most tendon in
the anterior compartment of
the leg.
Release this tendon from the
surrounding connective tissue
as far distally as its attachment
to the medial cuneiform bone.
Cut the tendon close to its distal
attachment and reflect it
proximally.
Identify the extensor hallucis
longus muscle (EHL). Note the
neurovascular bundle traveling
between extensor hallucis
longus and tibialis anterior.
Release the tendon of the EHL
distal to the ankle, transect it,
and reflect it proximally (Figures
1, 2).
MSK Week, Dissection 4 (Ankle) Page 1
Identify the extensor digitorum longus.
Cut its tendon proximal to where it divides, and reflect it in order to expose the
structures associated with the ankle joint.
MSK Week, Dissection 4 (Ankle) Page 2
Identify the fibrous capsule of the ankle joint.
Clean and observe it. Make an “H”- shaped cut in the capsule oriented so that the
horizontal bar of the “H” courses from medial to lateral over the joint cavity and the
medially located longitudinal bar courses over the tibia and talus.
On the medial aspect reflect the capsule as far as the tendon of the tibialis posterior
muscle; this tendon hugs the posteromedial aspect of the medial malleolus. You should
be exposing the joint cavity as you proceed (Figure 3).
Clean and observe the large deltoid (also –medial or tibial collateral) ligament (Figure 4).
MSK Week, Dissection 4 (Ankle) Page 3
Now begin reflecting the capsule laterally.
Continue reflecting until you completely expose the distal fibula.
Clean, observe, and palpate the distal tibiofibular joint (a syndesmosis).
The anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) is a capsular reflection that is delicate and
difficult to distinguish. Using the pulp of your index finger, try to palpate a band of tissue
running anteriorly from the tip of the fibula to the neck of the talus (Figures 3,6).
Identify and clean the tendon of fibularis (peroneus) brevis that passes posterior to the
lateral malleolus.
Release the tendon, following it to its distal attachment on the base of the 5 th metatarsal
bone.
Release the tendon of fibularis longus to approximately the same point. Place a probe
deep to these tendons near the tip of the fibula and transect them. Reflect the cut
tendons (Figure 5).
MSK Week, Dissection 4 (Ankle) Page 4
The calcaneofibular ligament (CFL) is a relatively large, distinct band of tissue running
between the distal fibula and the calcaneus.
To better view this structure, try to invert the foot at the subtalar joint; using your probe,
try to define this ligament. Note: there is an angle of approximately 135 o between the
ATFL and the CFL (Figure 6).
MSK Week, Dissection 4 (Ankle) Page 5
CHECKLIST OF STRUCTURES NOT PREVIOUSLY
ENCOUNTERED IN THE LAB
(Remember – in general, bones are not included on the check lists)
deltoid (medial, tibial collateral) ligament
distal tibiofibular joint (a syndesmosis).
anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL)
calcaneofibular ligament (CFL)
MSK Week, Dissection 4 (Ankle) Page 6
También podría gustarte
- Lectura Previ2 - U1-M6-T4-CAPITULO LESIONES DE PIE 2Documento13 páginasLectura Previ2 - U1-M6-T4-CAPITULO LESIONES DE PIE 2Maria De Los Angeles Vitteri EdenAún no hay calificaciones
- 20-Hip, Knee & Ankle JointsDocumento9 páginas20-Hip, Knee & Ankle JointsKainat LatifAún no hay calificaciones
- General Zoology Muscular System of The Frog - NotesDocumento15 páginasGeneral Zoology Muscular System of The Frog - NotesMarian CordanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Managementofelbow Trauma:: Anatomy and ExposuresDocumento11 páginasManagementofelbow Trauma:: Anatomy and ExposuresMishael Diaz PoncecaAún no hay calificaciones
- Thorax Region & Abdominal WallDocumento10 páginasThorax Region & Abdominal WallKaiAún no hay calificaciones
- MUSCLEDocumento5 páginasMUSCLEFadhlina OmarAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 11 Biology Week 2 Lesson 2Documento5 páginasGrade 11 Biology Week 2 Lesson 2NesiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Act09 Muscular System DiscussionDocumento10 páginasAct09 Muscular System DiscussionSofia A.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Jathtrain00002 0050Documento11 páginasJathtrain00002 0050NeerajAún no hay calificaciones
- Knee 05102018Documento24 páginasKnee 05102018Dk KAún no hay calificaciones
- Relations of Knee Joint: AnteriorlyDocumento100 páginasRelations of Knee Joint: AnteriorlysrisakthiAún no hay calificaciones
- ARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemDocumento7 páginasARMONIA ALEXA JOIE C. BSN 1B Manual Skeletal SystemJohanna Marie GantalaoAún no hay calificaciones
- The Infrapatellar Fat Pad in The KneeDocumento10 páginasThe Infrapatellar Fat Pad in The KneeDeogracias S. Espiritu IIAún no hay calificaciones
- Accessory LigamentsDocumento10 páginasAccessory LigamentsWidy AnniAún no hay calificaciones
- Anatomy 2019 1Documento6 páginasAnatomy 2019 1YMORAún no hay calificaciones
- Elzatona Anatomy 2023Documento9 páginasElzatona Anatomy 2023mahmoud ezzeldeenAún no hay calificaciones
- The Skeletal SystemDocumento25 páginasThe Skeletal SystemEyda CartagenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Biomechanics of Mallet Finger A Case ReportDocumento4 páginasBiomechanics of Mallet Finger A Case ReportAkbar GazaliAún no hay calificaciones
- The Ultimate Sports Health and Exercise Science GuideDocumento27 páginasThe Ultimate Sports Health and Exercise Science GuideTiago José ReisAún no hay calificaciones
- The Skeletal SystemDocumento6 páginasThe Skeletal Systemstar fireAún no hay calificaciones
- Dynamic Ligaments The Revolutionary Re-Vision of Jaap Van Der Wal 2011 EN Article PDFDocumento6 páginasDynamic Ligaments The Revolutionary Re-Vision of Jaap Van Der Wal 2011 EN Article PDFJorge Flores TorresAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter III SkeletalDocumento26 páginasChapter III SkeletalTitoMacoyTVAún no hay calificaciones
- 11.2 Movement: 11.2 Movement AHL Animal PhysiologyDocumento14 páginas11.2 Movement: 11.2 Movement AHL Animal PhysiologyReshma DookarranAún no hay calificaciones
- Politeus Msl.Documento6 páginasPoliteus Msl.Ajay Pal NattAún no hay calificaciones
- Common Pathological Conditions Affecting Movement System Function - HadleyDocumento40 páginasCommon Pathological Conditions Affecting Movement System Function - HadleywilliamadiwinataAún no hay calificaciones
- Principles of Occlusion: Key TermsDocumento35 páginasPrinciples of Occlusion: Key TermsStef AleAún no hay calificaciones
- Correctly Label The Bones On The Skeleton Below: Clavicle Scapula Mandible CraniumDocumento5 páginasCorrectly Label The Bones On The Skeleton Below: Clavicle Scapula Mandible CraniumMurphy MurphyAún no hay calificaciones
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Documento6 páginasI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipAún no hay calificaciones
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Documento6 páginasI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipAún no hay calificaciones
- General AnatomyDocumento17 páginasGeneral AnatomyAbubakar Umar GaladanchiAún no hay calificaciones
- Block 1 Essay Question and Answers (MBBS)Documento188 páginasBlock 1 Essay Question and Answers (MBBS)jdfAún no hay calificaciones
- Sport Science NotesDocumento5 páginasSport Science NotesSpicyChildrenAún no hay calificaciones
- JointsDocumento5 páginasJointsSEAN JODI M. COSEPEAún no hay calificaciones
- Elbow and Antebrachium NotesDocumento8 páginasElbow and Antebrachium NoteschadAún no hay calificaciones
- Myology Refleks & Arcus RefleksDocumento30 páginasMyology Refleks & Arcus RefleksHIDAYATUL RAHMIAún no hay calificaciones
- Elbow Anatomy & Biomechanics (Fornalski,)Documento11 páginasElbow Anatomy & Biomechanics (Fornalski,)Gloria Pg MontzeAún no hay calificaciones
- Gross Anatomy Learning Objectives - LimbsDocumento8 páginasGross Anatomy Learning Objectives - Limbskep1313Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ankle & Foot Complex: Proximal Tibiofibular JointDocumento3 páginasAnkle & Foot Complex: Proximal Tibiofibular JointJackielyn C. AportaderaAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment Skeletal Tabalba DoneDocumento4 páginasAssignment Skeletal Tabalba DoneShane V. TabalbaAún no hay calificaciones
- Working With Ankle Mobility, Part II (Myofascial Techniques)Documento5 páginasWorking With Ankle Mobility, Part II (Myofascial Techniques)Advanced-Trainings.com100% (2)
- Foot and Ankle Bones and JointsDocumento43 páginasFoot and Ankle Bones and Jointshannah murphyAún no hay calificaciones
- The Skeletal SystemDocumento24 páginasThe Skeletal SystemAlexa100% (1)
- Lesson 11: Skeletal Muscle Lesson ObjectivesDocumento6 páginasLesson 11: Skeletal Muscle Lesson ObjectivesRichee LunnayAún no hay calificaciones
- 2014 DAY1 Shoulder BulletsDocumento8 páginas2014 DAY1 Shoulder Bulletsazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- 0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSDocumento24 páginas0.5x ANATOMY LOWER LIMBSArijeet77Aún no hay calificaciones
- Biosci Chap6 (Muscular System Notes)Documento3 páginasBiosci Chap6 (Muscular System Notes)Man DejeloAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic 4 The Foot and Ankle 16th JulyDocumento39 páginasTopic 4 The Foot and Ankle 16th JulyTom Myhill-JonesAún no hay calificaciones
- Rehabilitation Guidelines For Hip Arthroscopy Procedures: Figure 1 Hip Joint (Opened) Lateral ViewDocumento8 páginasRehabilitation Guidelines For Hip Arthroscopy Procedures: Figure 1 Hip Joint (Opened) Lateral ViewDevi MigiekaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 MariebDocumento5 páginasChapter 8 MariebmjhenkeAún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER 2 Thoracic LimbDocumento32 páginasCHAPTER 2 Thoracic LimbChristine Joyce NavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Gen Ana Assignment 1 2Documento2 páginasGen Ana Assignment 1 2Jei SanAún no hay calificaciones
- The Axial JointsDocumento45 páginasThe Axial JointsZaid HamdanAún no hay calificaciones
- Fibrous Joint: Types: 1. Sutures 2. Syndesmoses 3. Gomphoses 4. SchindylesisDocumento9 páginasFibrous Joint: Types: 1. Sutures 2. Syndesmoses 3. Gomphoses 4. SchindylesisNu Ri LeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Skeletal System - KODocumento1 páginaSkeletal System - KOGift Munyinda (G-Man)Aún no hay calificaciones
- LAB Gluteal Region & Posterior ThighDocumento8 páginasLAB Gluteal Region & Posterior ThighnanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Anatomical Planes of The BodyDocumento8 páginasAnatomical Planes of The Bodyjainsumit3Aún no hay calificaciones
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyDocumento4 páginasSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: AnatomyMavic VillanuevaAún no hay calificaciones
- 21-Knee JointDocumento61 páginas21-Knee JointRamesh KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Neurorad Fellowship Pathways - RVSDDocumento1 páginaNeurorad Fellowship Pathways - RVSDazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Year of On-Demand Access!Documento32 páginas1 Year of On-Demand Access!azuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Complete Street Epistemology Guide 1st EdDocumento31 páginasThe Complete Street Epistemology Guide 1st Edazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- RRUMC Valet Parking Instructions For UCLA Medical Residents & FellowsDocumento1 páginaRRUMC Valet Parking Instructions For UCLA Medical Residents & Fellowsazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ucla DgsomDocumento26 páginasUcla Dgsomazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- ARRS Sample 5 Slide PowerPoint PresentationDocumento6 páginasARRS Sample 5 Slide PowerPoint Presentationazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ucsf Neuroradiology Fellowship Programs: Pathway First Year Second YearDocumento1 páginaUcsf Neuroradiology Fellowship Programs: Pathway First Year Second Yearazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- 2014.MSG - Card Muscle Contr - Student QuestDocumento2 páginas2014.MSG - Card Muscle Contr - Student Questazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Meal PlanningDocumento1 páginaMeal Planningazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Eras Faqs - 2012/2013Documento4 páginasEras Faqs - 2012/2013azuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Atrophy of The Superior Oblique MuscleDocumento2 páginasAtrophy of The Superior Oblique Muscleazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- 2014 DAY1 Shoulder BulletsDocumento8 páginas2014 DAY1 Shoulder Bulletsazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Empiric Antibiotic Therapy For Selected Infectious SyndromesDocumento2 páginasEmpiric Antibiotic Therapy For Selected Infectious Syndromesazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Clerkship Grading Criteria 2015-16 - CorrectedDocumento1 páginaClerkship Grading Criteria 2015-16 - Correctedazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Appendix 8 Normal Urine OutputDocumento1 páginaAppendix 8 Normal Urine Outputazuma12345Aún no hay calificaciones
- Anatomy of Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento6 páginasAnatomy of Musculoskeletal SystemDevi AswandiAún no hay calificaciones
- Sciatic Nerve - IipptDocumento21 páginasSciatic Nerve - IipptPraneetha NouduriAún no hay calificaciones
- Alternative Activity 1 Month Plan Core and Butt Work Out (DONATO)Documento32 páginasAlternative Activity 1 Month Plan Core and Butt Work Out (DONATO)Jhasmina DonatoAún no hay calificaciones
- Mod 1 Pe 3 1Documento3 páginasMod 1 Pe 3 1Garvilles Belle AngelieAún no hay calificaciones
- Blue Stripe Syllabus - Taranaki ITF TaekwondoDocumento7 páginasBlue Stripe Syllabus - Taranaki ITF TaekwondoMaria Elisa MonclusAún no hay calificaciones
- European Stroke ScaleDocumento3 páginasEuropean Stroke ScaleAbdur RasyidAún no hay calificaciones
- Prosedur Tindakan Yang Sering Dilakukan Sesuai ICD9CMDocumento13 páginasProsedur Tindakan Yang Sering Dilakukan Sesuai ICD9CMadefcesyoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ligaments of The AnkleDocumento11 páginasLigaments of The AnklePrasidha PrabhuAún no hay calificaciones
- Workbook - Tactical Baton September 2023Documento15 páginasWorkbook - Tactical Baton September 2023bilalchoudary4Aún no hay calificaciones
- Four Directions Tai-Chi Form Aka Five Elements Tai-ChiDocumento21 páginasFour Directions Tai-Chi Form Aka Five Elements Tai-ChiDiana IleaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physica Educatio Reviewer: Line DanceDocumento7 páginasPhysica Educatio Reviewer: Line DanceJuno Merdien GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Knee Meniscus InjuryDocumento6 páginasKnee Meniscus InjuryHazel Aikulola GriffithAún no hay calificaciones
- Frog's AnatomyDocumento13 páginasFrog's AnatomyMark Tolentino100% (1)
- Learn To Skate v5Documento6 páginasLearn To Skate v5The BuddhaAún no hay calificaciones
- PPPPPDocumento5 páginasPPPPPksheckelAún no hay calificaciones
- Sit and Be Fit Neuropathy Exercise GuideDocumento8 páginasSit and Be Fit Neuropathy Exercise Guidefitnesadvice11 blogspot comAún no hay calificaciones
- FR Coaching Cues Cheat Sheets 070512 2Documento4 páginasFR Coaching Cues Cheat Sheets 070512 2api-30886506Aún no hay calificaciones
- Comfort DevicesDocumento42 páginasComfort DevicesPreeti ChouhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Disease of VeinDocumento6 páginasDisease of Veinadriana aisyaAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Minutes of Yoga: To Jump Start Your Work DayDocumento11 páginas10 Minutes of Yoga: To Jump Start Your Work DayrameshAún no hay calificaciones
- Giles - A2 ReviewerDocumento27 páginasGiles - A2 ReviewerCatrina TanAún no hay calificaciones
- Crutch Instructions: Before You Get StartedDocumento4 páginasCrutch Instructions: Before You Get StartedjulanneAún no hay calificaciones
- Cotton OsteotomyDocumento16 páginasCotton OsteotomybaoAún no hay calificaciones
- TRX Six Procedures PDFDocumento8 páginasTRX Six Procedures PDFBabis XAún no hay calificaciones
- Module in Individual StuntsDocumento8 páginasModule in Individual StuntsKARL MICHAEL NAVARETTEAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamental Gymnastics PositionDocumento3 páginasFundamental Gymnastics PositionApple LanonAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Newborn Assessment 93667Documento122 páginas2 Newborn Assessment 93667Izziddin YassineAún no hay calificaciones
- The Skeleton: Chapter 7 Part CDocumento73 páginasThe Skeleton: Chapter 7 Part CDon KeyAún no hay calificaciones
- Jospt 2006 2265Documento14 páginasJospt 2006 2265dvenumohanAún no hay calificaciones
- Ankle ExaminationDocumento16 páginasAnkle Examinationbjpalmer100% (2)