Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Calculo de Vigas
Cargado por
Giselle DelgadoDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Calculo de Vigas
Cargado por
Giselle DelgadoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
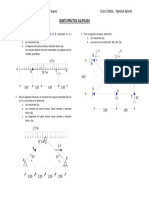
CALCULO DE VIGAS.
Viga de Piso #1
Carga Mayorada.
Pu = 1,2 (748,17) + 1,6 (200) = 1217,804
𝑊 𝐿2 (3,5)2
Momento = M = P x = 1217,80 𝑥 = 1,86
8 8
Viga según su dirección: eje “y”
Como son vigas perdidas en losa; altura de viga = H = 20 cm
V = 3 cm; según tabla 20.6.1.3.3
𝑓𝑦
2 𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105 𝑤=𝜌
𝑏𝑑 = 𝑓 ′𝑐
𝜙 𝑥 𝑓′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1−0.59(0.318))
𝒘 = 𝟎. 𝟑𝟏𝟖
𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105
𝑏=
𝑑 2 𝑥 𝜙 𝑥 𝑓 ′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
1,86 𝑥 105
𝑏= = 13.21
172 𝑥 0,9 𝑥 210 𝑥 318 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
𝑏 = 13.21
𝑏 = 13,21 𝑐𝑚 ≈ 25𝑐𝑚
Acero de viga 1, dirección “y”
As= 𝜌 𝑥 𝑏 𝑥 𝑑
As= 0.159*(25)*(17)
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎 ∗ 4
√ = 1,46 𝑚 ≈ 16 𝑚𝑚
𝜋
As= 6.7575 𝑐𝑚2 = 1.46 4 varillas de 14mm 𝜙
Viga de piso # 1; en dirección “x”
Pu = 1,2 (748,17) + 1,6 (200) = 1217,804
𝑊 𝐿2 (3,65)2
Momento = M = P x = 1217,80 𝑥 = 2,03
8 8
Viga según su dirección: eje “x”
Como son vigas perdidas en losa; altura de viga = H = 20 cm
V = 3 cm; según tabla 20.6.1.3.3
𝑓𝑦
2 𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105 𝑤=𝜌
𝑏𝑑 = 𝑓 ′𝑐
𝜙 𝑥 𝑓′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1−0.59(0.318))
𝒘 = 𝟎. 𝟑𝟏𝟖
𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105
𝑏=
𝑑 2 𝑥 𝜙 𝑥 𝑓 ′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
2,03 𝑥 105
𝑏= = 14,37
172 𝑥 0,9 𝑥 210 𝑥 318 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
𝑏 = 14,37
𝑏 = 14,37 𝑐𝑚 ≈ 25𝑐𝑚
Acero de viga 1, dirección “x”
As= 𝜌 𝑥 𝑏 𝑥 𝑑
As= 0.159*(25)*(17)
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎 ∗ 4
√ = 1,46 𝑚 ≈ 16 𝑚𝑚
𝜋
As= 6.7575 𝑐𝑚2 = 1.46 4 varillas de 14mm 𝜙
Viga de Piso #2
Carga Mayorada.
Pu = 1,2 (820,57) + 1,6 (200) = 1304,684
𝑊 𝐿2 (3,65)2
Momento = M = P x = 1304,684 𝑥 = 4,08
8 8
Viga según su dirección: eje “y”
Como son vigas perdidas en losa; altura de viga = H = 20 cm
V = 3 cm; según tabla 20.6.1.3.3
𝑓𝑦
2 𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105 𝑤=𝜌
𝑏𝑑 = 𝑓 ′𝑐
𝜙 𝑥 𝑓′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1−0.59(0.318))
𝒘 = 𝟎. 𝟑𝟏𝟖
𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105
𝑏=
𝑑 2 𝑥 𝜙 𝑥 𝑓 ′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
4,08 𝑥 105
𝑏= = 28,89
172 𝑥 0,9 𝑥 210 𝑥 318 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
𝑏 = 28,89
𝑏 = 28,89 𝑐𝑚 ≈ 30𝑐𝑚
Acero de viga 2, dirección “y”
As= 𝜌 𝑥 𝑏 𝑥 𝑑
As= 0.159*(30)*(17) = 8,109
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎 ∗ 4
√ = 1,311 𝑚 ≈ 14 𝑚𝑚
𝜋
As= 6.7575 𝑐𝑚2 = 1.46 4 varillas de 14mm 𝜙
Viga de piso # 2; en dirección “x”
Pu = 1,2 (748,17) + 1,6 (200) = 1217,804
𝑊 𝐿2 (4,1)2
Momento = M = P x = 1304,684 𝑥 = 2,74
8 8
Viga según su dirección: eje “x”
Como son vigas perdidas en losa; altura de viga = H = 20 cm
V = 3 cm; según tabla 20.6.1.3.3
𝑓𝑦
2 𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105 𝑤=𝜌
𝑏𝑑 = 𝑓 ′𝑐
𝜙 𝑥 𝑓′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1−0.59(0.318))
𝒘 = 𝟎. 𝟑𝟏𝟖
𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105
𝑏=
𝑑 2 𝑥 𝜙 𝑥 𝑓 ′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
2,74 𝑥 105
𝑏= = 19,43
172 𝑥 0,9 𝑥 210 𝑥 318 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
𝑏 = 19,43
𝑏 = 19,43 𝑐𝑚 ≈ 25𝑐𝑚
Acero de viga 2, dirección “x”
As= 𝜌 𝑥 𝑏 𝑥 𝑑
As= 0.159*(25)*(17) = 6,7575
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎 ∗ 4
√ = 1,46 𝑚 ≈ 16 𝑚𝑚
𝜋
As= 6.7575 𝑐𝑚2 = 1.46 4 varillas de 14mm 𝜙
Viga de Piso #3 (cubierta)
Carga Mayorada.
Pu = 1,2 (511,27) + 1,6 (70) = 725,524
𝑊 𝐿2 (4,6)2
Momento = M = P x = 725,52 𝑥 = 1,92
8 8
Viga según su dirección: eje “y”
Como son vigas perdidas en losa; altura de viga = H = 20 cm
V = 3 cm; según tabla 20.6.1.3.3
𝑓𝑦
2 𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105 𝑤=𝜌
𝑏𝑑 = 𝑓 ′𝑐
𝜙 𝑥 𝑓′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1−0.59(0.318))
𝒘 = 𝟎. 𝟑𝟏𝟖
𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105
𝑏=
𝑑 2 𝑥 𝜙 𝑥 𝑓 ′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
1,92 𝑥 105
𝑏= = 13,60
172 𝑥 0,9 𝑥 210 𝑥 318 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
𝑏 = 13.60
𝑏 = 13,60 𝑐𝑚 ≈ 25𝑐𝑚
Acero de viga 3 (cubierta), dirección “y”
As= 𝜌 𝑥 𝑏 𝑥 𝑑
As= 0.159*(25)*(17) = 6,7575
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎 ∗ 4
√ = 1,46 𝑚 ≈ 16 𝑚𝑚
𝜋
As= 6.7575 𝑐𝑚2 = 1.46 4 varillas de 14mm 𝜙
Viga de piso # 3 (Cubierta); en dirección “x”
Pu = 1,2 (511,27) + 1,6 (70) = 725,524
𝑊 𝐿2 (4,1)2
Momento = M = P x = 725,52 𝑥 = 1,52
8 8
Viga según su dirección: eje “x”
Como son vigas perdidas en losa; altura de viga = H = 20 cm
V = 3 cm; según tabla 20.6.1.3.3
𝑓𝑦
2 𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105 𝑤=𝜌
𝑏𝑑 = 𝑓 ′𝑐
𝜙 𝑥 𝑓′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1−0.59(0.318))
𝒘 = 𝟎. 𝟑𝟏𝟖
𝑀𝑢 𝑥 105
𝑏=
𝑑 2 𝑥 𝜙 𝑥 𝑓 ′ 𝑐𝑥 𝑊 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
1,52 𝑥 105
𝑏= = 10,805
172 𝑥 0,9 𝑥 210 𝑥 318 (1 − 0.59(0.318))
𝑏 = 10,805
𝑏 = 10,805 𝑐𝑚 ≈ 25𝑐𝑚
Acero de viga 3 (cubierta), dirección “x”
As= 𝜌 𝑥 𝑏 𝑥 𝑑
As= 0.159*(25)*(17) = 6,7575
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑢𝑛𝑖𝑡𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎 ∗ 4
√ = 1,46 𝑚 ≈ 16 𝑚𝑚
𝜋
As= 6.7575 𝑐𝑚2 = 1.46 4 varillas de 14mm 𝜙
También podría gustarte
- Viga HormigonDocumento7 páginasViga HormigoncheliquebarcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Enunciados 20 A 25Documento7 páginasEnunciados 20 A 25Katy SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño Puente Viga LosaDocumento10 páginasDiseño Puente Viga LosaMichael Martínez BelliAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Ponton de 10.67 M (Autoguardado)Documento32 páginasDiseño de Ponton de 10.67 M (Autoguardado)Walter Nilo Avelino GiraldoAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo Estructuras Final Ok OkDocumento12 páginasCalculo Estructuras Final Ok OkjudithsoleAún no hay calificaciones
- Presupuesto de Planta de Tratamiento de Aguas Residuales PDFDocumento4 páginasPresupuesto de Planta de Tratamiento de Aguas Residuales PDFsolangel rodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tipos de Cubiertas y CelosíasDocumento21 páginasTipos de Cubiertas y CelosíasAlvaro Pazmiño RomanAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Reservorio de 12 m3Documento22 páginasDiseño de Reservorio de 12 m3Christian Villena FernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica 5Documento1 páginaPráctica 5bernabe rosado reyesAún no hay calificaciones
- Memoria Cal Culo Steel FramingDocumento11 páginasMemoria Cal Culo Steel FramingDavid SilvaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea Grupal EstructurasDocumento29 páginasTarea Grupal EstructurasNaomi OchanteAún no hay calificaciones
- Muro de Contención 01Documento15 páginasMuro de Contención 01Amado Miguel Barandiaran MeoñoAún no hay calificaciones
- Flexion Simple 1Documento14 páginasFlexion Simple 1Jose Alfredo RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Tenson Limite Flexion PDFDocumento9 páginasTenson Limite Flexion PDFBautista RdgoAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de Esfuerzos Por Cortante en VigasDocumento18 páginasProblemas de Esfuerzos Por Cortante en VigasMarco Tapia ChávezAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseno de Vigas Postensadas de Un Puente CortoDocumento44 páginasDiseno de Vigas Postensadas de Un Puente CortoRaul Bedoya HerediaAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 9 Diseño Sismorresistente de VigasDocumento71 páginasSemana 9 Diseño Sismorresistente de VigasMadyori FGAún no hay calificaciones
- Presupuesto Paseo Peatonal FinalDocumento9 páginasPresupuesto Paseo Peatonal FinalJuan Carlos PaucarAún no hay calificaciones
- Alternativa Analisis Estructural Tanque 50,000 Galones Cristo de Esquipulas IIDocumento19 páginasAlternativa Analisis Estructural Tanque 50,000 Galones Cristo de Esquipulas IIAnis Maher KafatiAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplo de Diseño Flexion Segun AASHTO LRFDDocumento6 páginasEjemplo de Diseño Flexion Segun AASHTO LRFDVladimirAún no hay calificaciones
- CubiertaDocumento8 páginasCubiertaVivi NavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Estructura de GradasDocumento14 páginasEstructura de GradasJosue Pilco PezoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica de Estructuras MetalicasDocumento7 páginasPractica de Estructuras MetalicasbetoporcelAún no hay calificaciones
- Apuntes de Clase Concreto ArmadoDocumento19 páginasApuntes de Clase Concreto ArmadoDanicko Ocko100% (1)
- Ejercicios Individuales Resistencia IIDocumento43 páginasEjercicios Individuales Resistencia IIronald ccama chura100% (1)
- Memoria de Calculo Pte SenzanoDocumento42 páginasMemoria de Calculo Pte SenzanoRoberto TórrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cargas de Gravedad - Semana 3Documento5 páginasCargas de Gravedad - Semana 3CM JesusAún no hay calificaciones
- CLASE 2. Sección Transformada PDFDocumento2 páginasCLASE 2. Sección Transformada PDFMARLENE ROJAS MEDINAAún no hay calificaciones
- Planilla Mayores MetradosDocumento20 páginasPlanilla Mayores MetradosJubert Jara PachecoAún no hay calificaciones
- Memoria de Cálculo de Plataforma Metálica - Indal 1Documento19 páginasMemoria de Cálculo de Plataforma Metálica - Indal 1firstmechsacAún no hay calificaciones