Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Tgas Statistik
Cargado por
Yanti RambeDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Tgas Statistik
Cargado por
Yanti RambeCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
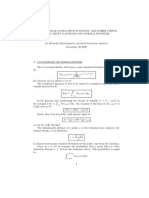
Distribution Sampling Correlation Coefficient
A description of the correlation coefficient r in the parts and then fully applies to
the relationship between X and Y and does not depend on the assumptions that apply to
the variables X and Y. Where now for the X and Y there are certain patterns, such as
how X and Y are distributed, then the correlation analysis could go further, among others,
determine the interval estimation and hypothesis testing. For this, assumed that X and Y
are normally combined distributed with two variables in which among others contains the
parameter ρ (read: rho) as a correlation coefficient.
From the normal population this that has two variables take all random samples of
size n and then calculate the correlation coefficients of r with the formula that has been
described above. Then obtained a set of correlation coefficient, r, r 2, r 3,. . . . . . . . . From
this collection we can form the sampling distribution of correlation coefficients and
subsequently the average and standard deviation can be calculated. The Average and
standard deviation for the sampling distribution of correlation coefficients will be given
the symbol µ r and σ r.
It is distinguished to two things:
A. Its population has ρ = 0
If all that random samples from normal populations with variable two ρ = 0, then
the sampling distribution of correlation coefficients be symmetric with µ r = 0. if it is
formed statistics:
r n-2
t =
1- r2
then we will get student distribution t with dk = (n – 2)
B. The population has ρ ≠ 0 ≠ 0
If the population from which random samples were taken have ρ = ρ 0 ≠ 0, then the
sampling distribution of correlation coefficients are not symmetric. In this case, using a
transformation will not cause a symmetric distribution that approaches a normal
distribution. Transformation that is used is Fisher's transformation:
1 1 + r
Z = ln
2 1- r
with In is the original logarithms, the logarithm with the base e.
In the ordinary logarithm, this transformation can also be written as:
1 + r
Z = (1,1513 ) log
1- r
With this transformation, the normal distribution that occurred (a form of approach) has
an average and standard deviation:
1 + ρ0
µz = 1 2 ln
1 - ρ0
1
σ =
n -3
µ z formula can also be written in this form:
1 + ρ0
µ z = (1,1513 ) log
1 − ρ0
También podría gustarte
- Homework 3Documento3 páginasHomework 3TeoTheSpazAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Artificial Intelligence PDFDocumento8 páginasIntroduction To Artificial Intelligence PDFAndre SetiawanAún no hay calificaciones
- CURRICULUM MANAGEMENT (BM Purwanto)Documento65 páginasCURRICULUM MANAGEMENT (BM Purwanto)Wiyah SalwiyahAún no hay calificaciones
- Use Case DiagramDocumento17 páginasUse Case DiagramKosar Abdulla100% (1)
- CHM 577 Exp 8Documento7 páginasCHM 577 Exp 8Amirah AhmadAún no hay calificaciones
- Qualitative Data Analysis An Expanded Sourcebook 2nd EditionDocumento352 páginasQualitative Data Analysis An Expanded Sourcebook 2nd Editionconnadoz4518100% (2)
- Correlation 23Documento1 páginaCorrelation 23Chipo ChipAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec12 CorrelationDocumento6 páginasLec12 Correlationsyedhafza4Aún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics and Probability: Maryjoyce I. Palma STAT 12 InstructorDocumento19 páginasStatistics and Probability: Maryjoyce I. Palma STAT 12 InstructorDanilyn Coquilla CadizAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Linear Transformations and Their Matrix Repre-SentationsDocumento9 páginas1 Linear Transformations and Their Matrix Repre-SentationsStelios KondosAún no hay calificaciones
- Simple Linear Regression and Correlation Analysis: Chapter FiveDocumento5 páginasSimple Linear Regression and Correlation Analysis: Chapter FiveAmsalu WalelignAún no hay calificaciones
- Correlation & Regression AnalysisDocumento39 páginasCorrelation & Regression AnalysisAbhipreeth Mehra100% (1)
- SS y Y: Explained Variance Is SimilarlyDocumento2 páginasSS y Y: Explained Variance Is SimilarlyOkanÜnlüAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Calculate A CorrelationDocumento5 páginasHow To Calculate A CorrelationAireeseAún no hay calificaciones
- Regression and CorrelationDocumento9 páginasRegression and CorrelationVivay Salazar100% (1)
- Chapter 3 NotesDocumento5 páginasChapter 3 NotesPete Jacopo Belbo CayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Correlation 1Documento57 páginasCorrelation 1mikhil.murali100% (1)
- Standard ErrorDocumento3 páginasStandard ErrorUmar FarooqAún no hay calificaciones
- Correlation and RegressionDocumento7 páginasCorrelation and Regressionmr haldarAún no hay calificaciones
- CorrelationDocumento39 páginasCorrelationLokesh Jain100% (1)
- Difference Between (Median, Mean, Mode, Range, Midrange) (Descriptive Statistics)Documento11 páginasDifference Between (Median, Mean, Mode, Range, Midrange) (Descriptive Statistics)mahmoudAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT-3: Correlation and Regression AnalysisDocumento3 páginasUNIT-3: Correlation and Regression AnalysisArkhitekton DesignAún no hay calificaciones
- Examining Relationships Scatterplot Analysis.: R N 1 Xi X SX Yi y SyDocumento3 páginasExamining Relationships Scatterplot Analysis.: R N 1 Xi X SX Yi y SyJaico DictaanAún no hay calificaciones
- Formula StablesDocumento29 páginasFormula StablesRobert ChapmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson Plan PPT (Ict in Math)Documento23 páginasLesson Plan PPT (Ict in Math)Jennifer EugenioAún no hay calificaciones
- W10 - Module 008 Linear Regression and CorrelationDocumento6 páginasW10 - Module 008 Linear Regression and CorrelationCiajoy KimAún no hay calificaciones
- Correlation and RegressionDocumento9 páginasCorrelation and RegressionMd Ibrahim MollaAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear Regression Analysis For STARDEX: Trend CalculationDocumento6 páginasLinear Regression Analysis For STARDEX: Trend CalculationSrinivasu UpparapalliAún no hay calificaciones
- M/M/1 Queueing ModelDocumento12 páginasM/M/1 Queueing ModelSparrowGospleGilbertAún no hay calificaciones
- FormulasDocumento12 páginasFormulaspsm1991Aún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics Economics - CorrelationDocumento5 páginasStatistics Economics - CorrelationsamirAún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics ReviewDocumento16 páginasStatistics ReviewAlan BatschauerAún no hay calificaciones
- Rank CorrelationDocumento34 páginasRank CorrelationBrindha SAún no hay calificaciones
- Introductory of Statistics - Chapter 4Documento5 páginasIntroductory of Statistics - Chapter 4Riezel PepitoAún no hay calificaciones
- Subjective QuestionsDocumento8 páginasSubjective QuestionsKeerthan kAún no hay calificaciones
- Module - 2 Correlation Analysis: Contents: 2.2 Types of CorrelationDocumento7 páginasModule - 2 Correlation Analysis: Contents: 2.2 Types of Correlationakj1992Aún no hay calificaciones
- CorrelationDocumento22 páginasCorrelationanupamkher0% (1)
- 7 Measure of RelationshipDocumento6 páginas7 Measure of RelationshipRonald LanotAún no hay calificaciones
- 9correlation and RegressionDocumento41 páginas9correlation and Regressionyadavaryan2004ccAún no hay calificaciones
- Introductory of Statistics - Chapter 4Documento5 páginasIntroductory of Statistics - Chapter 4Riezel PepitoAún no hay calificaciones
- Z-Transform Representation of Discrete-Time Signals and SystemsDocumento40 páginasZ-Transform Representation of Discrete-Time Signals and SystemsFreddy PesantezAún no hay calificaciones
- 009 D 1 CorrelationDocumento29 páginas009 D 1 Correlationlittle2102Aún no hay calificaciones
- Coursera Statistics One - Notes and FormulasDocumento48 páginasCoursera Statistics One - Notes and FormulasLuisSanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Czekanowski Index-Based Similarity As Alternative Correlation Measure in N-Asset Portfolio AnalysisDocumento1 páginaCzekanowski Index-Based Similarity As Alternative Correlation Measure in N-Asset Portfolio AnalysisKonrad KonefałAún no hay calificaciones
- 15 Profile AnalysisDocumento41 páginas15 Profile AnalysismesutAún no hay calificaciones
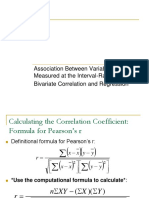
- Association Between Variables Measured at The Interval-Ratio Level: Bivariate Correlation and RegressionDocumento26 páginasAssociation Between Variables Measured at The Interval-Ratio Level: Bivariate Correlation and RegressionBonie Jay Mateo DacotAún no hay calificaciones
- Statistical ToolsDocumento17 páginasStatistical ToolsKlaus AlmesAún no hay calificaciones
- Cumulative Function N Dimensional Gaussians 12.2013Documento8 páginasCumulative Function N Dimensional Gaussians 12.2013msayalaAún no hay calificaciones
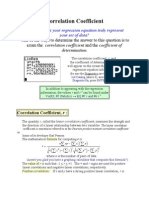
- Correlation CoefficientDocumento3 páginasCorrelation CoefficientbalubalubaluAún no hay calificaciones
- FM Project REPORT - Group3Documento24 páginasFM Project REPORT - Group3Jagmohan SainiAún no hay calificaciones
- Bivariate Statistics: by The End of This Sub-Topic, Learners Should Be Able ToDocumento7 páginasBivariate Statistics: by The End of This Sub-Topic, Learners Should Be Able ToPrince MpofuAún no hay calificaciones
- Bias in Estimation and Hypothesis Testing of Correlation: Psicológica (2003), 24, 133-158Documento26 páginasBias in Estimation and Hypothesis Testing of Correlation: Psicológica (2003), 24, 133-158Abishanka SahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Arteco Nr. 4Documento107 páginasArteco Nr. 4Deea MelisseAún no hay calificaciones
- Bsa Unit 3Documento12 páginasBsa Unit 3Predator Helios 300Aún no hay calificaciones
- Forecasting Lec 6Documento13 páginasForecasting Lec 6Jungle DiffAún no hay calificaciones
- Correlation NotesDocumento15 páginasCorrelation NotesGAYATHRI NATESHAún no hay calificaciones
- StatestsDocumento20 páginasStatestskebakaone marumoAún no hay calificaciones
- 9.1 Simple Linear Regression AnalysisDocumento8 páginas9.1 Simple Linear Regression AnalysisBekele GebreamanuleAún no hay calificaciones
- Correlation and RegressionDocumento44 páginasCorrelation and RegressionAmanAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 BMGT 220 Normal DistributionDocumento10 páginas5 BMGT 220 Normal DistributionPamela Chimwani100% (1)
- High-Dimensional Linear Discriminant Analysis: Optimality, Adaptive Algorithm, and Missing DataDocumento32 páginasHigh-Dimensional Linear Discriminant Analysis: Optimality, Adaptive Algorithm, and Missing DataSamson Ikinimore MaxAún no hay calificaciones
- Inference For RegressionDocumento24 páginasInference For RegressionJosh PotashAún no hay calificaciones
- MAE 300 TextbookDocumento95 páginasMAE 300 Textbookmgerges15Aún no hay calificaciones
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (8)
- Harmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)De EverandHarmonic Maps and Minimal Immersions with Symmetries (AM-130), Volume 130: Methods of Ordinary Differential Equations Applied to Elliptic Variational Problems. (AM-130)Aún no hay calificaciones
- Petra Storjohann - Lexical-Semantic Relations - Theoretical and Practical Perspectives (Lingvisticæ Investigationes Supplementa) - John Benjamins Publishing Company (2010) PDFDocumento197 páginasPetra Storjohann - Lexical-Semantic Relations - Theoretical and Practical Perspectives (Lingvisticæ Investigationes Supplementa) - John Benjamins Publishing Company (2010) PDFHello BeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Anselm and The Ontological Argument For The Existence of GodDocumento3 páginasAnselm and The Ontological Argument For The Existence of GodAbhinav Anand100% (1)
- Relationships Between Leadership, Motivation and Employee-Level Innovation: Evidence From IndiaDocumento17 páginasRelationships Between Leadership, Motivation and Employee-Level Innovation: Evidence From IndiaIonut-Catalin StanoiuAún no hay calificaciones
- Revised eDocumento23 páginasRevised esidrence bajentingAún no hay calificaciones
- With Sample On Activities of TBL PDFDocumento145 páginasWith Sample On Activities of TBL PDFHaya MonaAún no hay calificaciones
- Beyond Boredom and Anxiety Csikszentmihalyi en 1518Documento5 páginasBeyond Boredom and Anxiety Csikszentmihalyi en 1518Bassem KamelAún no hay calificaciones
- Teaching PreffesionDocumento5 páginasTeaching Preffesionregine alcaydeAún no hay calificaciones
- Second Language AcquistionDocumento19 páginasSecond Language AcquistionJenylen Tajanlangit-CabisoAún no hay calificaciones
- (GoT3) To Rule The Realm - Leadership & MotivationDocumento8 páginas(GoT3) To Rule The Realm - Leadership & Motivationenisa21Aún no hay calificaciones
- Archives in Liquid Times PDFDocumento332 páginasArchives in Liquid Times PDFVaniaMontgomery100% (1)
- Studies The Interaction Between Language and SocietyDocumento2 páginasStudies The Interaction Between Language and SocietyКларибэль Цветок ГутьерресAún no hay calificaciones
- Gravitational SingularityDocumento13 páginasGravitational Singularityperception888Aún no hay calificaciones
- A Comparison of Prediction Accuracy, Complexity, and Training Time of Thirty-Three Old and New Classification AlgorithmsDocumento27 páginasA Comparison of Prediction Accuracy, Complexity, and Training Time of Thirty-Three Old and New Classification Algorithmsrmov 002Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Potentials of Psychological Approaches To Literature: Philobiblon January 2016Documento17 páginasThe Potentials of Psychological Approaches To Literature: Philobiblon January 2016Nica KimAún no hay calificaciones
- Eye Movement and PersuasionDocumento2 páginasEye Movement and PersuasionecartetescuissesAún no hay calificaciones
- Language Ideologies: Practice and TheoryDocumento21 páginasLanguage Ideologies: Practice and TheorycaroldiasdsAún no hay calificaciones
- Titchener. The Problems of Experimental Psychology.Documento14 páginasTitchener. The Problems of Experimental Psychology.Juliana Gutiérrez ValderramaAún no hay calificaciones
- Honey Mumford - Learning Styles QuizDocumento7 páginasHoney Mumford - Learning Styles QuizMuhammad EzzatAún no hay calificaciones
- Just-In-Time and Performance Measurement Systems: David UptonDocumento10 páginasJust-In-Time and Performance Measurement Systems: David UptondengkulAún no hay calificaciones
- A Theory of ' Psychological Scaling: Clyde H. CoombsDocumento107 páginasA Theory of ' Psychological Scaling: Clyde H. CoombsionutAún no hay calificaciones
- The Art of Asking Powerful Questions in The World of SystemsDocumento9 páginasThe Art of Asking Powerful Questions in The World of Systemsrobrussell6097Aún no hay calificaciones
- Occupy Fuck YouDocumento7 páginasOccupy Fuck YouKeeKee Of The NorthAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 - EthicsDocumento7 páginasChapter 1 - EthicsEzekylah AlbaAún no hay calificaciones
- Uncertainty and Making MeasurmentsDocumento8 páginasUncertainty and Making MeasurmentsTheo Clark75% (4)