Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Chap 02 Set 1 Answer
Cargado por
Khor Han YiDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Chap 02 Set 1 Answer
Cargado por
Khor Han YiCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
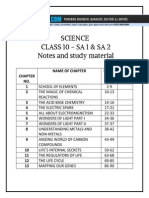
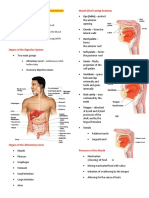
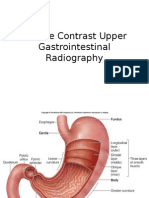
Science Form 2
Chapter 1 ₪ The World Through Our Senses ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
S
R
Q
P
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the areas of taste on the human tongue. Which part of
the following is sensitive to sweet?
* A P
B Q
C R
D S
Q
S
R
Figure 2
2 Figure 2 shows the cross section of human skin. Q, R and S represent
the different receptors of the skin. What is the function of receptor Q?
A To detect hot or cold object
* B To detect pain from cut, bite or pinch
C To detect smooth or rough object
D To detect heavy or light object
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 1 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
O
N
P
M
Figure 3
3 Figure 3 shows the cross section of the human ear. Which part of the ear
collects sound waves and directs them into the auditory cochlea?
* A M
B N
C O
D P
4 What is the function of ear?
A To detect touch
B To detect light
* C To detect sound
D To detect smell
5 Which of the following is true about the blind spot?
A Sensitive to light
* B Not sensitive to light
C Can not see distant objects clearly
D Can not see near objects clearly
Figure 4
6 What is the function of the part labeled P?
A Is found in the bottom of the nose cavity
B Is evaluates the smell
C Is to clean the air that enters to lung
* D Is to smell and sends impulses to the brain through nerve cells
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 2 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 5
7 What is the function of the part labeled R?
A Absorb light ray and prevents reflection of light ray
B Stimulates light sensitive cell so that the eye can see
* C Controls the amount of light that entering the eye
D Change the direction of the light ray
P - Ossicles
Q - Eardrum
R - Auditory canal
S - Cochlea
8 P, Q, R and S are the various parts of the ear. Which of the following
shows the correct path way of the sound waves that is collected by the
ear pinna?
A S, P, R and Q
* B R, Q, P and S
C P, Q, R and S
D P, R, S and Q
9 Which of the following shows the correct light ray?
A
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 3 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* D
10 Which of the following lenses is most suitable for the correction of
long-sightedness?
* D
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 4 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 6
11 Figure 6 shows the structure of the human ear. The parts that labeled by
P is use to
A transforms vibrations into impulses
* B amplify sound waves
C control balance of the body
D channels vibrations to the ear drum
Figure 7
12 Figure 7 shows the apparatus used to study the responses of plants
towards a certain stimulus. Which of the following conclusion can be
made regarding the experiment shown above?
A Positive geotropism
B Negative geotropism
* C Positive phototropism
D Negative phototropism
Figure 8
13 Figure 8 shows a mimosa plant. This plant responds to the following
stimuli except
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 5 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
A light
B touch
C water
* D sound
Figure 9
14 Figure 9 shows a plant has leaves which are sensitive to touch. By
closing its leaves, this plant will be able to
A retain water which falls onto its leaves
B absorb carbon dioxide that is necessary for photosynthesis
* C trap any insects that touch it leaves
D reduce the loss of water through its leaves
15 Which of the following are human sensory organs?
I Skin
II Tongue
III Hair
IV Eyes
A I, II and III only
* B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV.
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 6 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
P
R
Q
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the cross section of the human ear.
(a) Name the structures labeled P, Q and R.
P : Ear ossicles
Q : Eardrum
R : Cochlea
(b) Which part of the ear carries sound waves to the R?
Ear ossicles
(c) Name the part of the ear that help to amplify sound waves.
Ear ossicles
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which sensory organ is correctly matched with the stimulus?
Sensory organ Stimulus
* A Skin Pain
B Nose Pressure
C Eye Heat
D Ear Light
2 Which of the following sequences show the correct flow of nerve
impulses?
* A stimulus → sensory organs → nerves → brain → nerves → response
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 7 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B stimulus → nerves → response → brain → nerves →
sensory organs
C stimulus → sensory organs → brain → nerves → response → nerves
D stimulus → response → nerves → brain → nerves →
sensory organs
3 The brain is linked to all parts of the body by
A veins
B muscles
* C nerves
D organs
Figure 1
4 Figure 1 shows a children holding some flowers on his hand. What are
the senses involved in the process above?
A Smell only
B Smell and sight only
C Touch, sight and taste only
* D Smell, touch and sight only
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 8 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the area of taste on our tongue.
(a) State the taste that can be detected by the taste receptors labeled
as P and Q.
P : Bitter taste
Q : Sweet taste
[2 marks]
(b) How many types of taste receptors that are available on our
tongue?
Four types
[1 mark]
(c) What do you call the little bumps that are found on the surface of
the tongue?
Taste buds
[1 mark]
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 1 9 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 1 ₪ The World Through Our Senses ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Receptor R Receptor Q
Receptor S
Receptor P
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the cross section of the human skin. P , Q , R and S
represent the different receptors of skin. What is the function of the
receptor Q?
A To detect temperature changes
B To detect heavy or light objects
* C To detect smooth or rough surfaces
D To detect hot or cold
2 The brain is linked to all party of the body by
A muscles
B veins
C arteries
* D nerves
3 The skin can detect all of the following stimuli, except
A pain
* B light
C pressure
D heat
4 The ear cannot detect following stimuli, except
A pain
B taste
* C hearing
D light
5 What is function of the nose?
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 2 10 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
A Light
* B Smell
C Heat
D Pain
Z
X
Y
Figure 2
6 What is the sense of taste X and Y shows in Figure 2?
A Bitter , salty
B Sour, sweet
C Sweet , bitter
* D Salty , sweet
7 Figure 2 shows the top surface area of the tongue that is sensitive to
specific tastes . Which part of the tongue is sensitive to balsam pear?
* A W
B X
C Y
D Z
R
P
Q
S
Figure 3
8 Which part of the eye carries light impulses to the brain?
A P
B Q
C R
* D S
9 Sound cannot travel through which of the following medium?
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 2 11 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* A Vacuum
B Metal
C Water
D Air
Light
Soap tray
Germinating seed Soil + water
Dry air
Box
Silica gel
Figure 4
10 The Figure 4 , after few days what do you notice about the seedlings ?
I The root curve up
II The shoots grow upright
III The shoots bend towards the light
A I and II only
B I only
* C I and III only
D I, II and III
11 Why does the mimosa plant close its leaves when touched?
A It is shy
B It responds to geotropism
C It responds to thigmotropism
* D It responds to nastic movement
12 The stimuli of tongue is
* A chemical substances
B sound
C light
D pressure
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 2 12 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 6
13 A cat stands beside a pool of water. Which of the following show his
image in the water?
* A
14 Which of the following instruments help us to overcome the limitations of
sight?
I Telescope
II Stethoscope
III Microscope
A I and II only
* B I and III only
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 2 13 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C II and III only
D I , II and III only
Figure 7
15 A bat can fly freely at night without knocking itself against the walls of a
cave or trees around it as shown in Figure 7. This is brought about by it
acute sense of
A Taste
* B Hearing
C Touch
D Sight
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Q S
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the pathway from stimulus to response in your nervous
system.
(a) The tongue is the organ of
Taste.
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 2 14 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(b) State the tastes that can be detected by the taste receptors
labeled as P and Q.
P : Bitter taste
Q : Sweet taste
(c) What is name and the function of the part labeled R?
Pupil. It allows light to enter the eye.
(d) Which part of the eye is most sensitive to light?
The retina.
(e) (i) Name the organ indicated by X.
Brain
(ii) What does it do?
Interprets impulses.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Y
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the sense of hearing. What is Y?
A Ear canal
B Anvil
C Ear drum
* D Ear lobe
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 2 15 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
1 2 3 4
Figure 2
2 Which the Figure 2 show the correct path taken by light through a glass
prism?
A 1
B 2
* C 3
D 4
P - Cochlea
Q - Ossicles
R - Auditory canal
S - Auditory nerve
T - Eardrum
3 P, Q, R, S and T are the various parts of the ear. Which of the following
represents the correct path way of the sound waves that is collected by
the ear pinna?
* A R→T→Q→P→S
B T→R→S→Q→P
C S→T→R→P→Q
D Q→R→P→T→S
Figure 3
4 Figure 3 shows a plant that has leaves which are sensitive to touch by
closing its leave, this plant will be able to
* A trap any insects that touch its leaves
B retain water which falls into its leaves
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 2 16 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C absord carbon dioxide that is necessary for photosynthesis
D reduce the lose of water through its leaves
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Air entering
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the cross section of human nose
(a) Name the function of the nose labeled P and Q.
P : Nostril
Q : Smell receptors
[2 marks]
(b) What is the function of the mucus that is secreted by the glands in
the nasal cavity?
To keep the smell receptors moist.
[1 mark]
(c) How do we detect the smell of certain objects?
Chemical from the objects dissolve in the mucus that coats the
smell receptors. The information produced is then sent to the
brain to be interpreted as the smell of the objects.
[2 marks]
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 2 17 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 1 ₪ The World Through Our Senses ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which part of the body have thin epidermis and many receptors sensitive
to touch?
A Elbow
* B Fingertips
C Knee
D Buttocks
Questions 2 and 3 are based on Figure 1.
P
Q
S
Figure 1
2 Which one of the following is sensitive to cold?
A P
* B Q
C R
D S
3 Which one of the following is sensitive to pressure?
A P
B Q
C R
* D S
Question 4 are based on Figure 2.
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 3 18 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
P
Q
R
S
Figure 2
4 Which part of tongue can detects taste of lemon?
A P
* B Q
C R
D S
5 Which parts of ear is not involved in the hearing mechanism?
A Auditory canal
B Cochlea
* C Semicircular canal
D Ear ossicles
Figure 3
6 What is the function of X?
* A Controls size of the pupils
B Hold the eye lens in position
C Detects the light stimulus
D Protects the eye
7 The function of Y is
A Detect the light stimulus
B carries nerve impulses from the retina to the brain
* C Refracts and focuses light onto the retina
D Supplies food and oxygen to the eye tissues
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 3 19 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
8 When a student moves from a bright area into a dark area, what
happened to the student is eye?
A The pupil of eye become smaller
* B The pupil of eye become enlarges
C Less light enter the eye
D The eye is not 'blinded' by excess light
9 A long-sighted person
A can be corrected by cylindrical lens
B can see near objects clearly
* C can see distant objects clearly
D can be corrected by concave lens
10 Short-sightedness maybe caused by
* A abnormally long eyeballs
B abnormally short eyeballs
C eye lens that are abnormally thin
D too strong the ciliary muscles
11 Which one of the following do not has stereoscopic vision?
A Dog
B Tiger
C Human
* D Mouse
Figure 4
12 Which one of the following is a response shown by the plant?
A Geotropism
* B Phototropism
C Hydrotropism
D Thigmotropism
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 3 20 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
13 A doctor use a ________ to listen to the heartbeat.
A loud speaker
B hearing aid
* C stethoscope
D microscope
14 Sound is caused by
A energy
* B vibrations
C light
D touches
15 What type of tropism respond to stimulus of gravity?
* A Geotropism
B Hydrotropism
C Phototropism
D Thigmotropism
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Tuning fork
Beaker containing
water
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows an experiment carried out by a group of students in a
science lab.
(a) What will happen when the vibrates tuning fork was put in the
beaker that containing water?
The water in the beaker splashes up when the vibrating tuning
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 3 21 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
fork is put into it.
(b) How does sound produces?
During vibrations, kinetic energy is converted into sound energy.
(c) Sound travels fastest in what medium?
Solid medium
(d) Can sound travels through a vacuum? Why?
No. Because there are no molecules to pass on the vibrations.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
P - Lips
Q - Palm of the hand
R - Buttocks
S - Elbow
1 P, Q, R and S represent part of the body. Which of the following more
sensitive to touch?
* A P only
B P and Q only
C Q and S only
D Q and R only
Eardrum → ossicles → oval window → X → auditory nerve
2 What is X?
A Ear pinna
* B Cochlea
C Brain
D Auditory canal
3 Which one of the following is false?
Structure Function
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 3 22 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Cornea Refracts light entering the eye and helps to
A focus the light onto the retina
B Pupil Controls the amount of light entering the eye
* C Central fovea Send nerve impulses from the retina to the brain
D Iris Control the size of the pupil
4 To correct astigmatism, the optician recommends
A convex lenses
B any lenses
C concave lenses
* D cylindrical lenses
5 All of following are several devices are made to overcome our limitations
of sight, except
A magnifying
B microscope
C binocular
* D stethoscope
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
R
S
Figure 1
1 Name of P, Q, R and S
(i) P : Pressure receptor
(ii) Q : Pain receptor
(iii) R : Heat receptor
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 3 23 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(iv) S : Cold receptor
[4 marks]
2 Sensitivity of skin depends on the
(i) thickness of the epidermis
(ii) number of receptor present
[2 marks]
3 Name two parts of the body that are not so sensitive to touch.
(i) Elbow
(ii) Knee
[2 marks]
Chapter 1_The World Through Our Senses_Set 3 24 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 2 ₪ Nutrition ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a class of food. These class of foods are rich in
A fats
● For healthy reproductive system
● Difficulty at conceiving
2 The information above describes the functions of a certain vitamin. This
particular vitamin is
B vitamin E
Carbohydrates
Protein
Fat
Figure 2
3 A certain food has the composition show above, the food probably
B butter
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 25 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Q
R
S
Figure 3
4 A section of the human digestive system is show in Figure 3. In which
part does the food passes through by peristalsis?
A P
Figure 4
5 Figure 4 shows a human digestive system. What is a function of X?
C Secretes pancreatic juice
6 Which one of the following minerals help with forming new cells?
B Potassium
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 26 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
muscle contracts
muscular wall food
Figure 5
7 The process that help to push food along the alimentary canal by the
contraction of muscular walls is known as
D peristalsis
8 Food is needed to
I make new cells
II repair damaged tissues
III provide energy for daily activities
IV protect the body from diseases
D I, II, III and IV
9 What happen to children if they lack of protein?
C Kwashiorkor
10 Carbohydrates include following, except
D glycerol
11 Which of the following is correct?
Sugars Sources
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 27 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B Fructose Common in plants, but rarely found in animals
Fat 18g
Protein 28g
Carbohydrates 11g
Table 1
12 Table 1 states the amount of fat, protein and carbohydrates in 100 grams
of food X. What is the calorific value of 100 grams of food X ? (Given that
the energy released per gram are fats = 42 kj, protein = 25 kj,
carbohydrate = 22 kj)
A 1 698 kj
13 Below is the functions of fats except
C to build new cells
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Visking tube
Distilled water
Glucose solution
Boiling tube
Figure 1
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 28 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows an experiment carried out by a group of students.
(a) What is the main aim of the experiment above?
To study the process of absorption of glucose using the
Visking tube
(b) Fill in the blanks below if glucose solution replace with starch
solution.
(i) What is the solution to test the present of starch and glucose.
Iodine solution to test starch and Benedict's solution to test
glucose.
(ii) What is the observation and inference at the end of the
experiment?
Boiling Food test Observation Inference
tube
Iodine test Brown solution Starch absent
With
starch Glucose
solution Benedict's test Blue solution absent
Iodine test Brown solution Starch absent
With
glucose Glucose
Benedict's test Brick-red precipitated
solution present
(c) What is the conclusion of the experiment above?
Glucose can diffuse through a Visking tube.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The function of liver is
B secretes bile
2 What is the final product of digestion for protein?
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 29 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C Amino acid
3 The function of vitamin A is
A maintain good eyesight
Figure 1
4 A bit of corn flour is added to a test tube half filled with distilled water. A
few drops of iodine solution are then added to the mixture as shown in
Figure 1. What happens to the solution after the iodine is added to it?
D The solution turns dark blue
Butter
Figure 2
5 Figure 2 shows what classes of food?
B Fats
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 30 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows various types of food that we consume daily
(a) Name the parts labeled A,B and C.
(i) Duodenum
(ii) Ileum
(iii) Large intestine
[3 marks]
(b) What is the function of the stomach?
Produces gastric juices which contain hydrochloric acid and
enzymes (rennin and pepsin).
[1 mark]
(c) Name organ in digestion system involve in the process of
peristalsis.
Oesophagus
[1 mark]
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 31 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 2 ₪ Nutrition ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a class of food. These class of foods are rich in
* A fats
B vitamins
C protein
D carbohydrates
● For healthy reproductive system
● Difficulty at conceiving
2 The information above describes the functions of a certain vitamin. This
particular vitamin is
A vitamin K
* B vitamin E
C vitamin B
D vitamin C
Carbohydrates
Protein
Fat
Figure 2
3 A certain food has the composition show above, the food probably
A potatoes
* B butter
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 32 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C vegetable
D apple
Q
R
S
Figure 3
4 A section of the human digestive system is show in Figure 3. In which
part does the food passes through by peristalsis?
* A P
B Q
C R
D S
Figure 4
5 Figure 4 shows a human digestive system. What is a function of X?
A Digests proteins
B Stores bile temporarily
* C Secretes pancreatic juice
D Transports the food to the stomach
6 Which one of the following minerals help with forming new cells?
A Iron
* B Potassium
C Sodium
D Iodine
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 33 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
muscle contracts
muscular wall food
Figure 5
7 The process that help to push food along the alimentary canal by the
contraction of muscular walls is known as
A transpiration
B absorption
C emulsification
* D peristalsis
8 Food is needed to
I make new cells
II repair damaged tissues
III provide energy for daily activities
IV protect the body from diseases
A I, II and III only
B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
9 What happen to children if they lack of protein?
A Beri-beri
B Anaemia
* C Kwashiorkor
D Goiter
10 How many types of carbohydrates are there?
A 2
* B 3
C 4
D 5
11 Which of the following is correct?
Sugars Sources
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 34 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
A Glucose Malted cereals and sprouting grains
* B Fructose Common in plants, but rarely found in animals
C Maltose Milk of all mammals, including humans
D Galactose Found at least in small quantities in all animals
Fat 18g
Protein 28g
Carbohydrates 11g
Table 1
12 Table 1 states the amount of fat, protein and carbohydrates in 100 grams
of food X. What is the calorific value of 100 grams of food X ? (Given that
the energy released per gram are fats = 42 kj, protein = 25 kj,
carbohydrate = 22 kj)
* A 1 698 kj
B 1 320 kj
C 1 460 kj
D 146 kj
13 Below is the functions of fats except
A supplying energy
B to protect internal organs
* C to build new cells
D as a solvent
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Visking tube
Distilled water
Glucose solution
Boiling tube
Figure 1
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 35 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows an experiment carried out by a group of students.
(a) What is the main aim of the experiment above?
To study the process of absorption of glucose using the
Visking tube
(b) Fill in the blanks below if glucose solution replace with starch
solution.
(i) What is the solution to test the present of starch and glucose.
Iodine solution to test starch and Benedict's solution to test
glucose.
(ii) What is the observation and inference at the end of the
experiment?
(c) What is the conclusion of the experiment above?
The simple digested food molecules diffuse through the small
intestine walls into the bloodstream.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The function of liver is
A secrets pancreatic juice
* B secretes bile
C completes digestion
D stores faeces
2 What is the final product of digestion for protein?
A Glucose
B Fatty acids
* C Amino acid
D glycerol
3 The function of vitamin A is
* A maintain good eyesight
B involves in the formation of red blood cells
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 36 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C maintains healthy skin
D helps in the absorption of iron
Figure 1
4 A bit of corn flour is added to a test tube half filled with distilled water. A
few drops of iodine solution are then added to the mixture as shown in
Figure 1. What happens to the solution after the iodine is added to it?
A The solution turns dark
B There is no change in the colour of the solution
C The solution turns brown
* D The solution turns dark blue
Figure 2
5 Figure 2 shows what classes of food?
A Protein
* B Fats
C Carbohydrate
D Vitamin
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 37 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows various types of food that we consume daily
(a) Name the parts labeled A,B and C.
(i) Duodenum
(ii) Ileum
(iii) Large intestine
[3 marks]
(b) What is the function of the stomach?
Produces gastric juices which contain hydrochloric acid and
enzymes.
[1 mark]
(c) Name organ in digestion system involve in the process of
peristalsis.
Oesophagus
[1 mark]
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 1 38 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 2 ₪ Nutrition ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The elements founds in carbohydrates are
I carbon
II hydrogen
III oxygen
IV nitrogen
A II and III only
B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II and III only
Q R
Figure 1
2 A section of the human digestive system is shown in Figure1. In which
part does the digestion of protein begin?
A P
B Q
* C R
D S
3 Absorption of most of the remaining water and the formation of faeces
are carried out in the
A rectum
B duodenum
* C large intestine
D small intestine
Question 4 and 5 is based on Figure 2.
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 2 39 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Visking tube
Water at 37°C
Starch solution + amylase
Figure 2
4 At the end of 30 minutes, what is found in the water outside the visking
tube?
A Water only
B Starch solution
C Amylase solution
* D Sugar solution
5 Which one of these reagents will give a positive result when it is heated
with the water outside the Visking tube at the end of 30 minutes?
* A Iodine solution
B Millon's reagent
C Benedict's solution
D Starch solution
6 Which of the following classes of food is most important for growing
children?
A Fats
B Vitamin
C Carbohydrate
* D Protein
7 Which part of the alimentary canal keeps the faeces for a while before it
is defaecated?
A Anus
B Appendix
* C Rectum
D Large intestine
8 Where is water reabsorbed into the body?
* A Large intestine
B Small intestine
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 2 40 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C Mouth
D Oesophagus
9 Which of the following classes of food does not contain carbohydrate?
A Rice
B Potato
C Noodles
* D Butter
10 Which structure in the alimentary canal helps to absorb digested food?
A Rectum
B Gall bladder
C Liver
* D Villi
11 Which of the following is the correct path taken by food through the
alimentary canal?
* A Mouth → oesophagus → stomach → small intestine → large
intestine → anus
B Mouth → Stomach → Small intestine → Oesophagus →
Large intestine → anus
C Anus → mouth → stomach → small intestine → large intestine →
oesophagus
D Oesophagus → mouth → anus → stomach → small intestine →
large intestine
12 Which of these helps to determine a person's balanced diet?
I Size
II Age
III Type of job
A I and III only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III
13 Liver is produce X. What does X contains?
A oil droplets
* B pigments and salts
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 2 41 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C pepsin and rennin
D lipases
14 A type of food has the following characteristics
● It provides energy
● It contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen elements
● It turns blue when tested with iodine
The food is?
A Egg
* B Rice
C Meat
D Butter
15 The path that the undigested food passes to become faeces is
* A Colon → rectum → anus
B Anus → rectum → colon
C Rectum → colon → anus
D Rectum → anus → colon
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Visking tube Beaker
Starch solution
Distilled water + amylase
at 37°C
Figure 1
1 The experiment is set up as shown in the figure 1. At the end of 30
minutes, the water in the beaker is tested for starch and sugar.
(a) (i) How do you test for starch?
Starch gives a blue-black colour with iodine solution.
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 2 42 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(ii) Is there starch in the water? Why?
No. Starch molecules are big. They cannot go through the
Visking tube.
(b) (i) How do you test for sugar?
When sugar solution is heated with Benedict's solution,
a brick-red colour is seen.
(ii) Is there sugar in the water? Why?
Yes. Sugar molecules are smaller. They can diffuse
through a Visking tube.
(c) Name the processes that take place in the
(i) Visking tube : Digestion
(ii) Visking tube wall : Diffusion
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a few types of food. These foods are rich in
A Fats
B Proteins
C Carbohydrates
* D Vitamins
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 2 43 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 2
2 Figure 2 shows a few types of food. These foods are rich in
A Vitamins
B Carbohydrates
* C Protein
D Fats
3 Why is water important to the body?
I Digest food
II Keep a constant body temperature
III Get rid of waste substances
A I and III only
* B I, II and III
C I and II only
D II and III only
4 Which of the following do not contain fat?
A Margarine
B Butter
C Meet
* D Rice
Y
Figure 3
5 What is the name for figure 3 of X and Y?
X Y
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 2 44 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* A Small intestine Rectum
B Large intestine Pancreas
C Liver Stomach
D Anus Rectum
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Small intestine
wall
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows cross section of the small intestine.
(a) What is the function of part labeled X?
To absorb a digested food by the villi on the small intestine
wall.
[2 marks]
(b) What name of part labeled X ?
Villus
[1 mark]
Give two characteristics of the part labeled X which helps it to
(c)
absorb digested food.
(i) Thin walled
(ii) Richly supplied with blood vessels / capillaries
[2 marks]
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 2 45 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 2 ₪ Nutrition ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 All of the following are example of sugars, except
A lactose
B glucose
C sucrose
* D lipase
2 Lack of ____________ will cause a Paralysis.
A iron
B calcium
C phosphorus
* D potassium
3 All of the following are functions of fat, except
A supplying energy
* B for growth
C insulator of heat
D protecting the internal organs
4 Which one of the following function is necessary for the clotting of blood?
A Vitamin E
* B Vitamin K
C Vitamin D
D Vitamin C
5 Deficiency in ____________ can causes rickets.
A vitamin K
B vitamin C
* C vitamin D
D vitamin E
6 Lack ____________ will cause anaemia.
* A iron
B sodium
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 3 46 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C calcium
D iodine
7 Phosphorus necessary for
A builds haemoglobin of the blood cells
B the functioning of the thyroid gland
C constituent of blood plasma
* D the formation of strong bones and teeth
8 All of the following are the functions of hydrochloric acid, except
* A preparation of an alkaline medium for enzymic action
B providing an acidic medium for enzymic action
C killing bacteria found in food
D neutralising the alkaline property of saliva and stopping the action of
salivary amylase enzymes
9 All of the following are the enzymes of pancreatic juice, except
A pancreatic amylase
B protease
C lipase
* D bile
pancreatic protease
Peptones K
10 What is K?
A Maltose
* B Amino acids
C Fatty acids
D Glycerol
11 Which one of the following is not true?
Structure Function
A Mouth Food is broken down to small parts
B Oesophagus Sends food to the stomach
C Stomach Digestion of protein begins
* D Duodenum Secretes bile
Question 12 and 13 are based on Figure 1.
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 3 47 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
S Q
R
Figure 1
12 What is the function of X?
A Secrets saliva that is alkaline and contains salivary amylase
* enzymes
B Sends food to the stomach
C Digestion of fat protein and starch
D Food is broken down to small part
13 Which of the following is not true?
Part Structure
A P Oesophagus
B Q Stomach
C R Pancreas
* D S Bile duct
14 Excessive nutrient of salt will cause
* A kidney damage
B tooth decay
C obesity
D diabetes
15 Final product of digestion of carbohydrate is
* A glucose
B amino acid
C fatty acids
D glycerol
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 3 48 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the cross-section of the human small intestine.
(a) Name the part labeled X and Y.
(i) X : Villus layer
(ii) Y : Circular muscles
(b) Process M is the process when the end products of digestion
enter the blood stream through the small intestine walls. What is
process M?
Absorption
(c) The efficiency of absorption of digested food in the small intestine
can be increased by
(i) more villi to increase surface area.
(ii) villus with very thin walls.
(d) State three examples of digested food that diffuse through the
walls of the small intestine.
(i) Glucose
(ii) Amino acids
(iii) Glycerol / fatty acids
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 3 49 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
1 The pancreatic amylase digest starch into __________.
A amino acids
B fatty acids
* C maltose
D glycerol
Figure 1
2 Figure 1 shows the food items are sources for a class of food. What
function does this class of food play?
A Supplying energy
* B To replace damaged tissue
C Protect the body from various types of diseases
D Maintain body's health
3 X is a green-coloured liquid. It has no enzymes. It is alkaline and made
up of almost 90% water. It also gives colour to our faeces. What is X?
A water
B protease
* C bile
D glycerol
4 Junk food with high contents of sugar will result in the following disease
except
A tooth decay
B obesity
* C high blood pressure
D diabetes
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 3 50 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Q
R
S
Figure 5
5 Figure 2 shows digestive system, water is reabsorbed in
A P
B Q
C R
* D S
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Dietary finder Fat Mineral salts
Classes of food
X Water Vitamin Y
Figure 1
1 What is X and Y if the food rich in Y include rice, potato, sugar, bread,
banana and the food rich in X include fish, milk, meat, egg white and
nuts?
(a) (i) X : Protein
(ii) Y : Carbohydrate
[2 marks]
(b) Roughage helps to stimulate _____________ and the muscle
movement of the small and big intestines.
Peristalsis
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 3 51 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
[1 mark]
(c) State three functions of water.
(i) Controlling the concentration of blood
(ii) Transporting food during digestion
(iii) As a lubricant
[3 marks]
Chapter 2_Nutrition_Set 3 52 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 3 ₪ Variety of Living Things ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 Which of the following are characteristics of the animal shown in Figure
1?
I Warm blooded
II Fur or hair
III Lays eggs
* A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and III only
D I, II and III
Figure 2
2 This animal lives on
* A land
B water
C tree
D house
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 53 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Vertebrates
Amphibians Fish Bird
X Y
Figure 3
3 Figure 3 show the classification of animals what are probably the animal
labeled as X and Y
X Y
A Monkey Snake
* B Glows Eagles
C Cats Camel
D Rabbit Crocodile
Figure 4
4 Animal can be classified into two main group as vertebrates and
invertebrates. The animal shown in Figure 4 is a vertebrate because
A it has a long stick tongue
B it has two sensitive eye
C it has a strong back leg
* D it has a strong back bone
5 What is the similarly between a frog and a crocodile?
* A Habitat
B Breathing organs
C Characteristic of body
D Type of fertilisation
Question 6 and 7 are based on Table 1.
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 54 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Characteristics Monocotyledons Dicotyledons
Type of roots Fibrous root system Tap root system
Type of stem Fibrous root system Tap root system
Number of cotyledons One cotyledon Two cotyledon
in seeds
Type of veins found Leaves have parallel Leaves have network
on leaves veins veins
Table 1
6 Which of the following is an example of dicotyledons?
A Maize plant
B Coconut plant
* C Mango plant
D Paddy plant
7 The correct type of stem above is
Monocotyledons Dicotyledons
A Woody stem Woody stem
* B Soft stem Woody stem
C Woody stem Soft stem
D Soft stem Soft stem
Figure 5
8 Figure 8 shows a cat. Which of the following is true?
A Breathing organs − Gills
B Method of reproduction − Lay eggs
C Type of fertilisation − External fertilisation
* D Type of blood − Warm blooded
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 55 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Group of animals
Without wings With wings
With legs No legs
Hard shell No shell
Example: Example:
Snail X
Figure 6
9 The chart above shows the identification keys used to classify animals.
Which of the following is an example of X?
A Bat
B Eagle
* C Snake
D Snail
Fern Moss
Figure 7
10 Based on Figure 7, which of the following is true?
* A The two living organisms live in moist places
B Fern possess chlorophyll for manufacturing food
C Moss possess real leaves, stems and roots
D The two living organisms live as parasite or saprohyte
11 Which of the following are characteristics of Fungus?
I Possess leaves, stems and roots
II Do not have chlorophyll
III Majority live on land
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 56 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
IV Live as parasite or saprohyte
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C I, III and IV only
* D II, III and IV only
12 Which of the following is not flowerings plant?
A Rose
B Orchid
C Coconut
* D Seaweed
Figure 8
13 This animal is classified as
* A mammal
B amphibian
C fish
D bird
Figure 9
14 This above animal is classified as
A fish
B bird
* C mammal
D reptile
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 57 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
● Has leaves have parallel veins
● Soft stem
15 The diagram above shows two characteristics of a plant. The plant is
A Mango tree
B Maize plant
* C Hibiscus plant
D Durian tree
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a durian tree.
(a) Find the characteristics of the durian tree.
(i) Leaves have network veins
(ii) Tap root system
(iii) Two cotyledons
(iv) Woody stem
(b) State another plants that have same characteristics with durian
tree.
(i) Mango tree
(ii) Rubber tree
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 58 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Non-flowering plants can be divided into four groups. Which of the
following plants can make its own food?
I Algae
II Fungus
III Ferns
IV Moss
A I, II and III only
B II and III only
* C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
M N
Figure 1
2 The diagram above shows M and N are two characteristic of two plants.
Which of the following pair is true?
M N
A Rubber tree Maize plant
B Grass Hibiscus plant
C Maize plant Grass
* D Durian tree Mango tree
Snake
Chicken
Figure 2
3 The diagram above shows two animals. What is the difference between
these two animals?
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 59 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* A Type of blood
B Type of fertilisation
C Breathing organ
D Method of reproduction
4 How can an invertebrates support its body?
A A hard internal skeleton
B Use their legs
* C By using their body fluids
D Backbones
5 Which of the following non-flowering plants have chlorophyll?
I Seaweed
II Ferns
III Spirogyra
IV Yeast
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
* C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows two types of non-flowering plants.
(a) Name the plants shows in Figure 1.
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 60 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(i) P : Mushroom
(ii) Q : Moss
[2 marks]
(b) Which of the plants makes its own food?
Plant Q
[1 marks]
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 1 61 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 3 ₪ Variety of Living Things ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 Some animals are warm-blooded and some are cold-blooded. The
animal shown in the Figure 1 can be classified as warm-blooded because
* A It has mammary glands to feed milk to its young
B It can easily float and swim in very cold water
C It uses gills to breath
D Its body temperature is higher than the water around it
2 Which of the following animals are correctly classified?
Amphibians Reptiles Mammals
A Snake Bat Snake
* B Salamander Lizard Bat
C Duck Newt Tortoise
D Porcupine Duck Sea horse
3 Non-flowering plants are divided ito ________ group.
A one
B two
C three
* D four
4 Which of the following is a monocotyledonous plants?
A Balsam
B Groundnut
* C Banana
D Hibiscus
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 2 62 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
5 Vertebrates are classified into ________ classes.
A two
B three
* C four
D five
6 What are the similarities between fish and reptiles?
A They breathe with lungs
B They give birth to their young
* C They are cold-blooded
D Ther body is not covered with scales
Invertebrates
Animal with jointed legs
Three pairs of legs Four pairs of legs
P Q
Figure 3
7 Figure 3 shows the classification of animals based on the number of legs.
P and Q are the animals that process the features shown. Which of the
following could most likely be P and Q?
P Q
A Millipede Centipede
B Dragon fly Pawn
* C Beetle Spider
D Scorpion Wasp
Figure 4
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 2 63 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
8 Which of the following are characteristics of the plants shown in figure
4?
I Live on land in moist and shady places
II Have stems and true roots
III Reproduce from spores
IV Make their own food
A I and II only
* B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
9 A dicotyledonous plant is different from a monocotyledonous plant
because it
A bears flowers
* B has leaves with network veins
C lives on land
D has fibrous roots
Figure 5
10 Which of the following is the characteristics of the organisms shown
above?
A Live in moist habitats
* B Majority live on land
C Possess chlorophyll
D Possess vascular system
● Millepede
● Scorpion
● Cookcroach
11 Which of the following are the characteristic of the animal list shown
above?
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 2 64 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
A Warm-blooded
B Carry out external fertilisation
* C Do not have backbones
D Have an external hard shell
12 Which of the following is able to maintain its body temperature?
A Frog
B Fish
* C Sparrow
D Lizard
13 A dicotyledon plant has how many petals?
A 2 to 4
B 3 to 6
* C 4 to 5
D 6 to 8
Figure 6
14 The following are characteristics of the animal shown in Figure 6, except
A Lays eggs
B Body is covered with moist skin
C Cold-blooded
* D Breathes through lungs
15 Which of the following is not a flowering plant?
A Coconut
B Rose
* C Liverwort
D Orchid
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 2 65 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Vertebrates
Fish X Birds
Amphibian Y
Figure 3
1 Figure 1shows the classification of vertebrates.
(a) What vertebrates are classified as X and Y?
Reptiles, mammals
(b) Give one difference and one similarity between vertebrate X and
vertebrate Y.
(i) Difference : Y are warm-blooded while X are
cold-blooded.
(ii) Similarity : Y and X breathe through lungs.
(c) Give two similarity between amphibians and the animals classified
as X
Both amphibians and the animals X are cold-blooded and can
live on land and in water
(d) Give two examples of animals classified as X
Crocodiles and tortoises
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 2 66 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Non-flowering plants
Fern X Moss Fungi
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the classification of non-flowering plants. What are
probably the plants labelled as X?
A Mushroom
* B Algae
C Monocotyledon
D Dicotyledon
Figure 2
2 The animal shows in Figure 2 can be classified as fish because they
* A Are cold-blooded
B Are hot-blooded
C Have claws
D Have teeth
Figure 3
3 The plants that bears the flowers shown in Figure 3 has
A fibrous roots
B leaves with parallel veins
* C seed with two cotylodens
D fibrous roots
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 2 67 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 4
4 The following plants have the root pattern shown in the Figure 4 except
A tomato
B groundnut
C hibiscus
* D orchid
5 Which of the following is not true about flowering plants?
* A They have spores growing in capsules
B They produse seeds and fruits
C They have flowers with reproductive organs
D Their seeds have one or two seed leaves
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
P Q R S
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 show the pictures of plants P, Q, R and S found in a scrap books
of a pupil.
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 2 68 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(a) Classify plants P, Q, R and S based on the common
characteristics that can be observed. Give two examples of plants
with these common characteristics.
Vertebrates
● Has fibrous roots ● Has fibrous roots
● Leaf has paralled ● Leaf has paralled
veins veins
Example Example
Mango and balsom Sugarcane and maize
[4 marks]
(b) State two characteristics that can be observed to classify plants P,
Q, R and S.
(i) Has tap roots
(ii) Has fibrous roots
[2 marks]
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 2 69 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 3 ₪ Variety of Living Things ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 All of the following are invertebrate animals except
* A snake
B squid
C centipede
D caterpillar
Vertebrates
M N O P Q
Example of P → Cat, Rabbit, Goat
Figure 1
2 Based of Figure 1, what is P?
A Fish
B Amphibians
C Reptilec
* D Mamals
● Cold blooded
● Covered with dry scales
3 Which of the following have the above characteristics?
A Frog
* B Snake
C Anteater
D Toad
● Snake
● Owl
● Goat
4 Which of the following is a common characteristic among all the
vertebrates listed above?
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 3 70 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
A Give birth to young
* B Internal fertilisation
C Warn blooded
D Cold blooded
5 Which of the following is true?
A Reptiles → anteaters
* B Mamals → dolphin
C Birds→ bats
D Amphibians → porcupines
● Leaf with network vein
● Has tap root system
6 Which of the following have the above characteristics?
A Paddy plant
B Coconut tree
* C Hibiscus plant
D Maize plant
● Ferns
● Mushrooms
● Moss
7 Which of the following is a common characteristic among all the non-
flowering plants listed above?
A Present chlowphyll
B Makes its own food
C Does not have real stem
* D Produces spores
Questions 8 and 9 based on Figure 2.
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 3 71 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Animals
P Vertebrates
Fish Birds Amphibians
Q Reptiles
Figure 2
8 Figure 2 shows the classification of animals. Which of the following is
represented by P?
A Snake
* B Caterpillar
C Eel
D Toad
9 Which of the following is common charateristic of Q?
A Cold-blooded
B Breathing with gills
C Lay eggs
* D Internal fertilisation
Figure 3
10 All of the following are the common characteristic of the plants shows in
Figure 3, except
A gets food from lining things or dead organisms
* B produces spores
C does not have real stem, leaves and roots
D lives in damp places
Questions 11, 12 and 13 are based on Figure 4.
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 3 72 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Plants
Flowering plants Non-flowering plants
Ferns Y
Monocotyledons X Fungus Moss
Figure 4
11 Which of the following is the example of X?
A Coconut tree
B Paddy plant
* C Hibiscus plant
D Maize plant
12 Which of the following is not the example of Y?
A Chlamydomonas
B Seaweed
* C Mould
D Spirogyra
13 Which of the following is not true about Y?
A Lives in water or damp places on land
B Make its own food
* C Binary fission
D Has leaves but does not have reall stem and roots
Figure 5
14 The plant having a leaf as shown in Figure 5 has
I soft stem
II tap root system
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 3 73 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III two cotyledons
* A I only
B I and II only
C I, II and III only
D II and III only
Figure 6
15 This non-flowering plants
A gets food from liring thingsoro dead organisms
* B produces spores
C binary fission
D does not has stem
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Animals
Invertebrates P
Mammals Q Fish
Birds Amphibians
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows classification of animals
(a) What is P?
P : Vertebrates
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 3 74 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(b) State three example of animals have the characteristics of Q
(i) Snake
(ii) Crocodile
(iii) Lizard
(c) State three eharactenstic of mammals.
(i) Breathing with lungs
(ii) Internal fertilisation
(iii) Warm-blooded
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which one of the following is false?
Animals Habitat
A Snakes Bushes
B Amoeba Pond
* C Termite Tree
D Bird Tree
● Warm blooded
● Breathing with lungs
2 Which of the follwing have the above characteristics?
I Eel
II Bat
III Whale
IV Chicken
A I and II only
B I ,II and IV only
* C II, III and IV only
D III and IV only
3 Which of the following groups of animals are give birth to young only?
A Anteaters, rattle snakes, crocodiles
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 3 75 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B Anteaters, whale, platypus
* C Whale, bat, cow
D Platpus, crocodiks, shark
● Does not have real stem
● Lives in damp places
● Produces spores
4 Which of the following plants has the characteristics listed above?
I Moss
II Mushroom
III Mould
IV Yeast
A I and II only
* B II and III only
C III and IV only
D I and IV only
P Q
Figure 1
5 Figure 1 shows the leaf of two type of plants. Which of the following
represented by P and Q?
P Q
A Rubber tree Mango tree
* B Maize plant Hibiscus plant
C Hlibiscus plant Mango tree
D Paddy plant Coconut tree
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 3 76 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Plants
Flowering plants Non-flowering plants
Moss Y
Monocotyledons X Algae Ferns
Figure 1
1 Figure 1shows classification of plants
(a) State three charasteristic of X.
(i) Leaves have network veins
(ii) Tap root system
(iii) Woody stem
[3 marks]
(b) State three example of plant of Y.
(i) Mushrooms
(ii) Yeast
(iii) Mould
[3 marks]
(c) State four example of plant of monocotyledon.
(i) Maize plant
(ii) Coconat tree
(iii) Grass
(iv) Paddy plant
[4 marks]
Chapter 3_Variety of Living Things_Set 3 77 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
Chapter 4 ₪ Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 The diagram above shows an interaction between two organisms. The
interaction between two organisms above can be classified as
* A commensalism
B parasitism
C competition
D mutualism
2 Which of the following statements are true based on the pyramid from
top to bottom?
I The number of organisms increase
II The size of the organimsm decrease
III More energy is lost
IV The size of the organisms increase
* A I and II only
B II and III only
C III and IV only
D I and IV only
Chlorophyll
Carbon dioxide + Water Glucose + Y
Sunlight (food)
3 The equation above shows the process of photosynthesis. Y is
A hydrogen
B water
C carbon dioxide
* D oxygen
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 1 78
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
4 What is the meaning of ecosystem?
* A Living things that interact with each other and with the physical
environment
B A group of organisms of the same kind that live in a habitat
C Several animal and plant populations living together and interacting
with one another in a habit
D Natural place in which plants and animals live
Figure 2
5 What is the kinds of interaction shows in Figure 2?
* A Prey-predator
B Symbiosis
C Competition
D Commensalism
Water
leaf pieces
Figure 3
6 The diagram above shows a process in an experiment to test the
presence of starch in a leaf. Why are the leaf pieces are boiled in water?
A To remove chlorophyll
B To soften them
C To remove starch from the plant
* D To kill the cells and break the cell walls
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 1 79
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
Figure 4
7 Figure 3 shows the wood mushroom, an example of total parasite. Total
parasite such as the wood mushroom are
* A never green in colour
B sometimes green in colour
C plants which manufacture part of their own food
D plants that do not cause damage to their host
54% 31%
bird snake
Figure 5
8 In the diagram above shows the percentage of energy obtained by the
bird and the snake. However, the percentage of energy has been
decreased from the bird to the snake. It is because some energy is lost
as heat when the organism carries out its life processes such as
I reproduction
II growth
III respiration
IV excretion
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C I, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 1 80
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
P Q R S
Figure 6
9 Figure 6 shows living organisms found in the sea. Which is the correct
sequence of the organisms to from a valid food chain?
A R→Q→S→P
B P→R→S→Q
* C S→P→R→Q
D P→Q→R→S
10 Conditions necessary for photo synthesis are
I the presence of sunlight
II the presence of chlorophyll
III the presence of carbon dioxide
IV the presence of oxygen
A I and II only
B II, III and IV only
* C I, II and III only
D I, III and IV only
11 What is the meaning of parasitism?
A Relationship between two different organisms such that both benefit
from it
B Relationship between two differrent organisms living together such
that one benefits from it while the other is not significantly affected
by it
* C Relationship between two different organisms such that one
organism benefits while the other is harmed by it
D Organisms need the same resources which are in short supply
12 Which of the following processes use oxygen and release carbon
dioxide?
I Respiration
II Combustion
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 1 81
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
III Photosynthesis
IV Rusting
A I, III and IV only
B II, III and IV only
* C I, II and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
Figure 7
13 Figure 7 shows a cabbage with layers of leaves. Plant with such a
feature are
* A producers
B decomposers
C primary consumers
D secondary consumers
Questions 14 and 15 are based on Figure 8.
X Y
Bees
Eagles
Green plants
Rats
Snakes
Figure 1
14 The diagram above shows an example of food web. What could be X?
A Caterpillars
* B Lizard
C Tiger
D Birds
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 1 82
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
15 Y is a
* A tertiary consumer
B producer
C secondary consumer
D primary consumer
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
1 (a) State three kinds of interaction in nature.
(i) Prey-predator
(ii) Symbiosis
(iii) Competition
(b) State two example of animals for the each of following
(i) Commensalism : Bird's nest fern and tree;
Remora fish and shark
(ii) Parasitism : Wood mushroom and a tree;
Rafflesia and a tree
(iii) Mutualism : Sea anemone and hermit crab;
Ox peckers and buffaloes
(c) What is biological control?
Biological control is a method in which a predator, which is a
natural enemy to a certain pest, is used to control the population
of that pest in an area.
(d) State three advantages of biological control.
(i) Does not pollute the environment.
(ii) Does not kill other organisms because natural enemies
are used.
(iii) Is cheap and safe to use.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 1 83
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make use
___________ and water produce food in the presence of sunlight and
chlorophyll.
* A carbon dioxide
B energy
C carbon cycle
D reaction
2 Which of the following plants can be classified as mutualism?
I Rafflesia and a tree
II Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and leguminous plant
III Sea anemone and hermit crab
IV Remora fish and shark
A I and II only
* B II and III only
C III and IV only
D I and IV only
3 What energy will change when a plant carries out process of
photosynthesis?
A Chemical energy → Kinetic energy
B Light energy → Heat energy
* C Light energy → Chemical energy
D Kinetic energy → Heat energy
P Q R
Figure 1
4 Which of the diagram is / are parasitism?
A P only
B P and Q only
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 1 84
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
C P and R only
* D P, Q and R
5 A producers
* A are green plants that make food through photosynthesis
B are animals that eat plants or other animals
C are organisms that decompose dead organisms and change them
into simple substances
D is the main source of energy for all living organisms in a food chain
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Water
Alcohol
Leaf pieces
Figure 1
1 The diagram above shows an experiment carry out by a group of
students.
(a) What is the aim of the experiment above?
To test the presence of starch in a leaf.
[1 mark]
(b) Why alcohol is added in the experiment?
Alcohol is added in the experiment to remove chlorophyll.
[1 mark]
(c) What is X?
Wire gauze
[1 mark]
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 1 85
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
Chapter 4 ₪ Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 What is the habitat of a termite?
* A Bush
B Soil
C River
D Wood
2 The organisms in a community interact with one another to obtain
I transport
II shelter
III support
IV food
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
Snake
Frog
Caterpillar
Leaf
Figure 1
3 Based on Figure 1, what will happen if all the frogs in the area are
captured?
A The number of snakes will increase
B The number of caterpillars will decrease
* C The number of leaves will decrease
D The number of leaves will increase
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 2 86
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
Figure 2
4 The zebra in Figure 2 has body stripes that resemble its surroundings.
The purpose of having these features is to enable it to
A provide a means of self defence
* B hibernate easily
C camouflage itself
D kill its victims easily
5 What are the special characteristics that help the prey escape from the
predator?
I Live in a group to fight for survival
II Sharp sense of hearing
III Larger in size than the prey
IV Ability to run faster than the predator
A I, II and III only
* B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
6 Which of the following methods is not a good way to conserve and
preserve our living organisms?
A Encourage consumption of exotic endangered organisms
B Greating
C National parks
* D Kind of construction
Figure 3
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 2 87
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
7 Figure 4 is an example of pyramid of numbers. What orgarism best
represent M?
* A Tree
B Bird
C Caterpillar
D Eagle
Question 8 and 9 are based on Figure 4.
Kingfisher Water hyacinth
Tadpoles
Fish
Elodea
Shrimps
Figure 4
8 According to the diagram above, choose the correct food chain.
* A Elodea → Tadpoles → Fish → Kingfisher
B Tadpoles → Fish → Water hyacinth → Kingfisher
C Water hyacinth → Fish → Tadpoles → Kingfisher
D Elodea → Fish → Tadpoles → Kingfisher
9 Which of the following statement is true when the fishes in the lake
decrease?
* A Water hyacinth in the lake will increase
B The elodea inside the lake will increase
C Kingfisher will increase
D The tadpoles inside the lake will decrease
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 2 88
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
Cardboard cover Garden snail
Cardboard box
Figure 5
10 A group of students carry out an experiment shown as above. After 20
minutes, the garden snail moved into the dark area. We can conclude
that
I garden snails prefer to live in a dark environment
II sunshine can damage the garden snails
III garden snails are afraid of brightness
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
Figure 6
11 Based on the diagram above, name the organisation of the living things.
A Species
* B Population
C Ecosystem
D Community
P Q R S
Figure 7
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 2 89
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
12 Figure 7 shows an experiment to show the compensating effect of
oxygen produced from photosynthesis. The water in tubes P, Q, R and S
was tested with bikarbonate indicator at the start of the experiment. After
6 hour, the water in tubes P, Q, R and S is again tested with bicarbonate
indicator. The result are shown below:
Tubes P Q R S
At the start of the experiment Pink Pink Pink Pink
After 6 hours Purple Pink Yellow Pink
Why tube R will change from pink to yellow?
* A The fish respired giving out carbon dioxide and the gas made the
water acidic
B Oxygen produced by fish was used for respiration and carbon
dioxide given out by elodea was used for photosynthesis in elodea
C The fish producing oxygen, turning the indicator into yellow
D The fish respired giving out oxygen and the gas made the water
alkalis
Green plant Bell jar
Pot with soil Sodium hydroxide
Glass sheets solution
Figure 8
13 Figure 8 shows an experiment to test that carbon dioxide is needed for
photosynthesis. Why the sodium hudroxide solution is needed in the
experiment above?
A To remove starch from the plant
* B Absorb carbon dioxide from the air
C To remove oxygen in the bell jar
D Release carbon dioxide from the air
14 The importance and role of photosynthesis are
I supplies food to animals
II removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
III enables green plants to make their own food
IV regulates and maintain carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 2 90
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
A I, II and III only
B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV only
15 The food chain always begins with
* A producer
B tertiary consumer
C secondary consumer
D primary consumer
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 The figure above shows an experiment carried out by a group of
students.
(a) What is the main aim of the experiment above?
To show that sunlight is needed for photosynthesis.
(b) State a conclusion from the experiment above.
Sunlight is needed for photosynthesis.
(c) What does sunlight supplies to plant?
Sunlight supplies energy to the plant to break water molecules.
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 2 91
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The processes that release carbon dioxide into the air is
I respiration
II combustion
III decomposition
IV breathing
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
2 Human activities that destroy the balance of nature are
I fishing
II logging
III illegal hunting
IV agriculture
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
3 Oxygen constitutes about how many percent of the atmosphere?
A 100%
B 50%
* C 20%
D 10%
4 Plants use ________ to make food.
A oxygen
* B sunlight
C carbon dioxide
D nitrogen
5 Oxygen is returned to the atmosphere by green plants through
* A photosynthesis
B respiration
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 2 92
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
C decomposition
D combustion
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
White part (Yellow-brownish
colour)
Before After
Green plant (Dark blue colour)
Figure 1
1 The figure above shows an experiment carried out by a group of
students.
(a) What is the main aim of the experiment above?
To show that chlorophyll is needed for photosynthesis.
[1 mark]
(b) What is the equation that represents photosynthesis?
Sunlight
Carbon dioxide + water Glucose + Oxygen
Chlorophyll
[2 marks]
(c) What is needed for photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll
[1 mark]
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 2 93
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
Chapter 4 ₪ Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 __________ is a relationship between two organisms. One organisms
benefits from the other. The second organisms is not adversely affected
by the relationship.
* A Commensalisms
B Parasitism
C Mutualism
D Symbiosis
2 A __________ consists of several types of animal and plant populations
that live together and interact with one another in a habitat.
* A community
B ecosystem
C species
D population
3 Explain the interaction that takes place between a lion and a rabbit.
A Competition
* B Prey-predator
C Symbiosis
D Commensalisms
4 What is the interaction between remora fish and shark?
A Parasitism
B Mutualism
* C Commensalisms
D Symbiosis
5 All of the following are the example of prey-predator relationship except
A a tiger and a chickens
B a lizard and a mosquito
* C a sea anemone and a hermit crab
D a kingfisher and a fish
6 Which of the following is the example of commensalisms?
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 3 94
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
A Rafflesia and a tree
B Wood mushroom and tree
C Mistletoe and a tree
* D Bird's nest fern and tree
7 Which of the following is not the example of plants that live on tree to
obtain sunlight?
* A The bryonyllom plant
B The money plant
C The staghound fern
D The bird nest fern
Nodule
Roots of leguminous
plant
Figure 1
8 In Figure 1, why the nitrogen-fixing bacteria have to live under
leguminous plant?
* A To obtain sunlight
B To obtain food
C To obtain transport
D To protect the leguminous plant
Figure 2
9 Figure 2 shows a type plant that lives beside a tree. Which of the
following interaction is shared by the plant and the tree?
A Commensalisms
* B Parasitism
C Mutualism
D Competition
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 3 95
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
10 __________are animals that eat plants or other animals.
A Producers
* B Consumers
C Decomposers
D Food chain
Question 11, 12 and 13 are based on Figure 3.
R
From base to the
Q top of the pyramid
Figure 3
11 From the base of the pyramid to the top of the pyramid,
I the number of organisms decrease
II the size of organisms increase
III more energy gain
* A I and II only
B I only
C I and III only
D I, II and III only
12 What is P and Q?
A Secondary consumer, primary consumer
B Producer, tertiary consumer
* C Producer, primary consumer
D Primary consumer, secondary consumer
13 Which of the following is the example of S?
A Rat
B Frog
C Bird
* D Snake
Leaves Lady bird Frog X Eagles
Figure 4
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 3 96
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
14 Figure 4 shows a food chain. Which of the following are probably
organisms X?
A Rats
B Caterpillars
* C Snake
D Bird
15 The process that release carbon dioxide into the air include
I breathing
II photosynthesis
III decomposition
A II and III only
* B I and II only
C I and II only
D I, II and III only
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
P Q
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows two different interaction between two different organisms.
(a) Name the organisms labelled X and Y.
(i) X : Bird's nest fern
(ii) Y : Sea anemone
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 3 97
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
(b) What is the interaction between the organisms shows in P?
Commensalism
(c) What are the benefit of the interaction shown in P?
The bird's nest fern get support and is able to receive more
sunlight as it grows high up on the tree.
(d) Q shown an example of mutualism. What is mutualism?
Mutualism is the interaction between two organisms in which both
benefit.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Type of interaction Example
P Green algae and fungus
Q Remora fish and shark
R Mistletoe and a tree
Table 1
1 Based on Figure 1, what is P, Q and R?
P Q R
A Commensalism Parasitism Mutualism
* B Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism
C Mutualism Parasitism Commensalism
D Parasitism Commensalism Mutualism
2 Which of the following is false?
A Mutualism : green algat and fungus
B Parasitism : wood mushroom and tree
* C Commensalisms : mistletoe and a tree
D Prey - predator : a lion and a rabbit
3 The following organisms are classified as secondary consumers except
* A grasshopper
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 3 98
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
B bird
C frog
D chicken
4 All of the following are adverse effects on the ecosystem or environment
of logging / miming / construction, except
A soil erosion
B sedimentation in rivers which cause flooding
C disturbs the oxygen and carbon cycles
* D the excessive use of chemical pesticides and fertilizers pollutes the
environment
5 All of the following are the steps we can take to reduce environmental
pollution, except
A use unleaded petrol
B make nuclear testing illegal
* C releasing smoke, haze and acidic gases into the atmosphere
D create special places to burn rubbish
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
1 (a) State three important and role of photosynthesis.
(i) Supplies food to animals.
(ii) Removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
(iii) Enables green plants to make their own food.
[3 marks]
(b) The processes that use oxygen include
(i) respiration
(ii) combustion
(iii) rusting
(iv) decomposition
[4 marks]
(c) State three environmental issues that cause by human activities.
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 3 99
© Amazing Tunas Enterprise Science Form 2
(i) The greenhouse effect
(ii) The thinning of the ozone layer
(iii) Acid rain
[5 marks]
Chapter 4_Interdependence Among Living Organisms and the Environment_Set 3 100
Science Form 2
Chapter 5 ₪ Water and Solutions ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 What is the physical properties of water ?
I Colourless
II Odourless
III Tasteless liquid
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
2 Water exists in how many states?
A Two
* B Three
C Four
D Five
3 What is the density of water?
A 2g per cm3
* B 1g per cm3
C 1g per cm2
D 2g per cm2
4 How does the particles vibrate when we boiled the water?
* A Fast
B Slow
C Cannot move anymore
D Nothing happen
5 What is the freezing point of water?
* A 0°C
B 1°C
C −1°C
D 0.1°C
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 1 101 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
6 Which of the following is use to test the presence of water?
I Lime water
II Anhydrous cobalt chloride
III anhydrous copper sulphate
A I only
B I and III only
* C II and III only
D I, II and III only
7 What is the composition of water?
I 2 hydrogen atoms
II 1 oxygen atoms
III 1 carbon dioxide
A I only
B I and III only
* C I and II only
D I, II and III only
8 What is the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen in one molecule of water?
A 1:1
B 1:2
* C 2:1
D 3:2
9 Which of the following is use to separated hydrogen and oxygen in a
compound of water?
* A Process of electrolysis
B Process of water evaporation
C Process of evaporation and boiling
D Process of filtration
10 Which of the following is true about evaporation and boiling?
Boiling Evaporation
I Take place at any
Conditions for it
Only at boiling point temperature and
to happen
time
II The rate of
Fast Slow
process
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 1 102 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III Take place only on the Take place
How it happen
surface of water throughout the water
A III only
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
* D I and II only
11 Which of the following is the principle of water evaporation in everyday
lift?
I Drying clothes
II Cooling the body
III Producing common salt
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
12 What is solution?
A Used to dissolve a substance
B Substance that dissolves
* C Mixture that is formed from a solvent and a solute
D Liquid that has small particles
13 Which of the following are the factors that influence the solubility rate of
substances ?
I Size of the solutes
II Stirring
III Volume and temperature of solvent
IV Humidity
A I only
B I and II only
C I, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV only
14 Which of the following are the importance of water as a solvent?
I Most chemical reaction in our body need water.
II Dissolves oxygen and food so that these can be transported to body
cell
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 1 103 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III Dissolves oxygen and carbon dioxide for aquatic organisms
A I only
B I and II only
* C I, II and III only
D II and III only
15 Water cannot dissolve organic substances such as
I alcohol
II petrol
III ether
A I only
B III only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
X Y
Plastic container
Water + dilute
sulphuric acid
Carbon rod Carbon rod
(negative electrode) (positive electrode)
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the set up of an experiment to study the effect of
electrolysis on dilute sulphuric acid.
(i) What is the gas in tube Y. How do we test it?
Oxygen is released at tube Y. A glowing splinter placed into the
test tube will burst into flames.
(ii) What is the aim of the experiment?
To find the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms in water.
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 1 104 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(iii) What is the gas in negative electrode. How can we test it?
Hydrogen is releasad at the negative electrode. A glowing
splinter placed into the test tube and produce 'pop' sound.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 What is the function of alcohol?
* A To prepare a shellac solution to polish wooden furniture
B To dilute paint to make it easier to use
C To stick plastic substance like number plates on car
D To make cosmetics such as nail polish and perfumes
Acid + Carbonate X
Figure 1
2 Based on the Figure 1 , what is probably represent by X?
* A Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
B Salt + Hydrogen
C Iron nitrate + Water + Carbon dioxide
D Icon nitrate + Hydrogen
3 What are the properties of acids?
I Corrosive
II Change red litmus paper to blue colour
III Change blue litmus paper to red colour
IV Have PH values greater than 7
A I and II only
* B I and III only
C I, II and III only
D II and III only
4 Which of the following is not alkalis?
A Sodium hydroxide
B Ammonium hydroxide
* C Hydrogen chloride
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 1 105 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
D Calcium hydroxide
5 Which of the following are the acidic substances in our everyday life?
I Lemon
II Vinegar
III Yoghurt
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Red litmus paper Blue litmus paper
Evaporating dish
Citric acid crystal
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows an experiment carried out by a group of students in a
school laboratory.
(a) What effect on the blue litmus paper when it is placed in the
evaporating dish as shown in Figure 1?
No change
[1 mark]
(b) The group of students carried out another experiment with a few
drops of water are added to the citric acid crystal. What will
happen to the blue litmus paper now?
Blue litmus paper changes to red.
[1 mark]
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 1 106 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(c) In the experiment above, what is the aim of the experiment?
To study the role of water in acids.
[1 mark]
(d) What is the conclusion of the experiment above?
The function of water is to enable acids to show their properties.
[1 mark]
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 1 107 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 5 ₪ Water and Solutions ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
X Y
Ice Water Water
1 What is the process of X and Y?
X Y
A Boiling Melting
* B Melting Boiling
C Freezing Evaporation
D Condensation Melting
Temperature (°C)
S
100
R
P Q
Time (minutes)
Figure 1
2 Which letter P, Q, R or S in the graph shows the boiling point and melting
point of water?
Boiling point Melting point
A P S
* B Q P
C R Q
D S P
3 What is the boiling point of water when salt is added?
A 100°C
* B 102°C
C −2°C
D 98°C
4 What is the effect when scatter common salt is on ice?
A The melting point of ice become higher
B The freezing point of ice become lower
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 2 108 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C The melting point of ice become lower
D The freezing point of ice become higher
Gas P
Dilute hydrochloric
acid Magnesium
Figure 2
5 In this experiment, gas P was produced. What can we use to identify gas
P?
A Glowing splinter
B Hydrogen carbonate solution
* C Burning splinter
D Lime water
6 Which of the following does not show the water evaporation process?
A Drying hair
B Cooling the body
C Producing common salt
D Boiling the water
Gas X Gas Y
Anod Cathode
Figure 3
7 Figure 3 shows electrolysis process by that diluted acidified water. What
are gas X and gas Y?
Gas X Gas Y
* A Oxygen Hydrogen
B Hydrogen Oxygen
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 2 109 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C Carbon dioxide Oxygen
D Nitrogen Hydrogen
8 Which of the following methods can increase the solubility of lump of
common salt in water?
* A Breaking up the lump of common salt into small pieces and hearing
B Adding common salt
C Stirring the dilute solution
D Adding water
9 What organic solvent can clean oily and greasy floors?
A Water
B Alcohol
C Acetone
* D Kerosene
R P Q
pH
7
Figure 4
10 Figure 4 shows the pH scale for P, Q and R. Which of the following
represents P, Q and R.
P Q R
A Water Lemon Washig soda
B Lemon Tea Toothpaste
* C Distilled water Toothpaste Tea
D Milk Washing soda Apple
11 Following show several pH indicators normally used in the laboratory to
determine if a substance is acidic, neutral or alkaline. Which is true?
Indicator Acidic Neutral Alkaline
* A Litmus solution Red Purple Blue
B Methyl orange / red Pink Orange Pink
C Phendphalein Red Blue Green
D Universal indicator Red Orange Yellow
12 The methods of water purification include
I filtration
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 2 110 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
II boiling
III chlorination
IV distillation
A I and II only
B I, III and IV only
C I, II and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
13 Arrange the increasing amount of dissolved substances and dirt in order.
I River water
II Pond water
III Spring water
IV Well water
A IV, II, I, III
* B III, IV, I, II
C IV, II, III, I
D II, I, III, IV
Reservoir Sedimentation
tank
Coagulation X
tank
Chlorine
to customers
Storage tank
Figure 5
14 Figure 5 shows a water purification and supply system. What is function
X?
A Removed fine suspended particles
B Killing microorganisms
C Collect water raining
* D Being supplied to homes
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 2 111 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
15 The experiment used to determine the composition of water is called
A evaporation
* B electrolysis
C filtration
D condensation
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Sand filter
Pond water
Fine sand
Coarse sand
Pebbles
Gravel
Rubber tube
Clip
Figure 1
1 The apparatus shows in Figure 1 is set up to study the purification of
water through filtration.
(a) State 1 advantage and 1 disadvantage.
(i) Advantage : Water is clear and free from
suspended particles only.
(ii) Disadvantage : Water still has microorganisms and
dissolved substance.
(b) Suggest two other methds for purifying water.
(i) Boiling
(ii) Chlorination
(c) Is the water purified using method suitable for drinking? Give a
reason can support your answer.
The filtrate is not suitable for drinking as it contains
microorganisms that may be harmful to our health.
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 2 112 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which of the following are contain alkalis?
I Toothpaste
II Detergent
III Lemon
IV Soap
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and IV only
Acid + Alkali ____________
2 Base of the diagram above, complete the equation above.
* A Salt + water
B Magnesium chloride + hydrogen
C Carbon + water
D Zinc chloride + hydrogen
3 What are the properties of alkalis?
I Taste sour
II Feel slippery
III Have PH value more than 7
IV Corrosive
A I only
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
* D II, III and IV only
4 What function is acetic acid?
I Preserves food like pickles
II Used in fruit juices
III To make soft drinks
* A I only
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 2 113 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B I and II only
C II and III only
D I, II and III only
5 Which of the following are the methods of water purification?
I Filtration
II Chlorination
III Distllation
A II only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 The two figure above show two applying the principle of water boiling and
evaporation in everyday life.
(a) State the similarities between the two figures.
(i) Heat is absorbed
(ii) Liquids become gases
[2 marks]
(b) Based on Figure 1 and Figure 2, explain two differences between
the 2 figures.
The kettle in Figure 1 carried out the process of boiling and a boy
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 2 114 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
in Figure 2 who are cooling his body with a fan are carrying out
the process of evaporation. The differences between the 2 figures
are the rate of the process and conditions for it to happen. The
rate of the process boiling is faster than the process of
evaporation. In addition, conditions for the process boiling happen
is only at boiling point but the process of evaporation takes place
at any temperature and at any time.
[4 marks]
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 2 115 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 5 ₪ Water and Solutions ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 What is X?
A Freezing
B Melting
* C Boiling
D Condensation
2 What is the property of acids?
* A Corrosive
B Change red litmus paper to blue
C Have pH values of more than 7
D Taste bitter
3 Which type of sugar will dissolve the quickest in a liquid?
* A
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 116 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
4 The table above shows the differences between evaporation and boiling.
Which of the following are true?
A I, II and III only
* B I, II and IV only
C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
5 What is the advantages when using the methods of boiling in
purification?
A Water is free from dissolved substances
* B Water is free from dangerous microorganisms
C Water is free from suspended particles only
D Water is clear
6 Water is a compound consisting of two element's which are
I Oxygen
II Nitrogen
III Hydrogen
IV Helium
A II and IV only
B I and II only
* C II and III only
D III and IV only
7 The factors that influence the rate of water evaporation are
I surrounding temperature
II surface area
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 117 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III air movement
IV air humidity
A I and II only
B II, III and IV only
C I, II and III only
* D I, II, III and IV
Figure 2
8 What is the most probable PH value of toothpaste?
* A 9
B 7
C 8
D 6
9 What liquid can be used to remove lipstick from clothes?
A Turpentine
B Petrol
C Kerosene
* D Acetone
● Taste sour
● Corrosive
● Change blue litmus paper to red
10 Which of the following example has characteristics as shown as the
diagram above?
A Detergent
* B Tap water
C Milk of magnesium
D Toothpaste
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 118 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Water
Fine salt (100 g)
Figure 3
11 The Figure 3 shows 100 g fine salt are added to the beaker that contain
300 ml water. How to increase the solubility rate of fine salt inside the
water?
I By stirring the water
II Add some water into the beaker
III Heat up the water
IV By replacing the fine salt with bigger size one
A I, II and III only
* B I and III only
C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
Temperature
Boiling point
100°C
Time
Figure 4
12 Based on the heating graph of water above, which of the following
statement is false?
A As water boils into steam, the temperature remains constant at
100°C
B The particles move at greater speeds and further away from one
another
C The boiling point is 100°C
D The particles in the water lose their kinetic energy as the
* temperature rises
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 119 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Substance Type of gas released
P Carbon dioxide
Q Hydrogen
Table 1
13 Table above shows the gases that are released when a dilute acid reacts
with substances P and Q respectively. Which of the following are P and
Q?
P Q
A Copper sulphide Iron oxide
* B Aluminium oxide Copper
C Copper oxide Calcium
D Iron carbonate Zinc
14 A suspension will form when water is added to
A soy sauce
B salt
C sugar
* D pepper
15 Which of the following factors can affect against the solubity of a solvent?
I Nature of solvent
II Humidity
III Temperature
IV Nature of the solute
A I, II and III only
B I and IV only
* C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 120 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Thermometer
Water
out
Muddy water
Porcelain chips
Water
Bunsen burner Distilled liquid
in
Figure 1
1 Figure above shows an experiment to study the purification of water
through distillation.
(a) What is the main function of distilling sea water?
To separate dissolved and floating particles from muddy water
and to obtain pure water.
(b) Even distilled water is very clean and free from all suspended
substances, microorganisms and dissolved substances but it is
not the ideal form pf water for drinking. Why?
It is because this wter does not contain dissolved minerals which
our bodies need.
(c) Why the porcelain chips are aded to the round-bottomed flask?
To break up the air bubbles
(d) How can we realised that the experiment is successfully tested?
Taste some of the liquid that we collected and found that the
is tasteless.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which of the following statement is true about acid?
A Acid has a pH value more than 7
B Acid turn red litmus paper blue
* C Acid react with active metals to produce hydrogen gas
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 121 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
D Acid react with ammonium salts to produce ammonia gas
2 Certain materials cannot be corroded by acid. An example of these
meterials is
A skin
* B glass
C wood
D metal
3 Copper sulphate crystals can dissolve faster in 10mR water when it is
stired. This is because stiring helps to
A increase the temperature of water.
B lower their temperature of water.
C narrow the surface area.
* D increase the kinetic energy.
4 Why is distilled water not good for the body when taken for a long time?
A It has no taste
B It contains too much minerals
* C It does not contain mineral
D It still contains microorganisms
Rain water
Layers of sand and stone
Figure 2
5 What is the name of this process used for purifying water? How does it
purify the water?
Process Purification
A Chlorination Kill germs
B Distillation Remove dissolved matter
* C Filtration Remove solids
D UV treatment Kill germs
TEST IT YOURSELF
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 122 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Alum and
Reservoir slaked lime
Valve
pump
X Y Filtration tank
Chlorine
Storage tank
to customers
Valve
pump
Figure 1
1 The diagram above shows a water purification and supply system.
(a) Name the part of X and Y.
(i) X : Coagulation tank
(ii) Y : Sedimentation tank
[2 marks]
(b) What is the function of of alum and slaked lime?
Alum and slaked are added to coagulate the suspended particles
from small particles to become big particles.
[2 marks]
(c) In some places, why fluoride is added in water purification?
To reduce tooth decay.
[1 mark]
(d) State two steps to save water.
(i) Bathe by showering
(ii) Wash clothes in big quantities
(iii) Use a watering can to water plants
(iv) Turn off the tap when not in use
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 123 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(v) Wash vegetables in a basin
(vi) Repair all water pipe leaks immediately
(any two answers)
[2 marks]
Chapter 5_Water and Solutions_Set 3 124 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 6 ₪ Air Pressure ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 What energy caused by gas particles colliding with the walls of a
container?
I Heat energy
II Air pressure
III Gas pressure
A I only
B II and III only
C I and II only
* D III only
2 Which of the following needs to do if want gas turn into liquid?
I Heat it
II Compress it
III Cool it
A I only
B I and III only
* C II and III only
D I and II only
3 Why an empty bottle crushes when pressed?
A Air collide the bottle
* B The air pressure outside is lower than air pressure inside
C Heat from the hand expands the air in the bottle
D Air inside the bottle forced out
4 If a balloon goes higher up into the air, what will happen?
A The size of the balloon changes
* B The size of the ballon increases
C Water droplets are formed outside the balloon
D The wall of the balloon becomes thinner
5 Which of the following statements about air is true?
A Air has weight
B Air is a compound
* C Air is a mixture
D We can see air through our eyes
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 1 125 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
6 Air pressure can be measured by
A Tachometer
B Galvanometer
C Thermometer
* D Barometer
7 Which of the following are used to store in the aerosol cans?
I Perfumes
II Drinking water
III Hair spray
IV Paint
A I, II and III only
B II, III and IV only
C I and III only
* D I, III and IV only
Glass
Water
Thick cardboard
Figure 1
8 Why the water won't fall down from the glass although there is nobody
holding the thick cardboard?
A The air exerts pressure on the glass that supports the water in the
glass
* B The air exerts pressure on the cardboard that supports the water in
the glass
C The glass exerts pressure on the cardboard that supports the water
in the glass
D The glass exerts pressure on the air that supports the water in the
glass
9 A leak in a rubber hose connected to a gas cylinder. How can we test it?
* A Rub some soapy solution on the rubber hose
B Paint the rubber hose
C Pour some salt on the rubber hose
D Bend the rubber hose
10 What is kinetic theory of gases?
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 1 126 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* A A matter are always moving or vibrating
B A matter are always expands
C Air molecules acting on a surface
D Air particles move very fast and at random
11 What is function of syringe?
A Used to pump water
B Used to reduce liquids
* C Used to suck up liquids
D Used to sack drinks from container
12 Which of the following is safety measures when using gases under high
pressure?
I Place the gas tank down right
II Light a match first before turning on the gas
III Keep the gas tank away from heat sources or sunlight
IV Do not throw aerosol cans into a fire as they will explode
A I, II and III only
B II and III only
* C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV only
13 What are the factors that can affect air pressure?
I Volume of air
II Temperature of the air
III Air particle
A I and II only
B III only
* C I, II and III only
D II only
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 1 127 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Balloon
Flask
Water
Bunsen burner
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 set up to show the effect of air pressure.
(a) What will happen when turned on the Bunsen burner.
The ballon will expand.
(b) Give your reason for your answer in ( a ).
When the Bunsen burner is turned on, the temperature of the
water and the temperature inside the flask will increases.
The higher are pressure push the ballon and caused it expand.
(c) If uncorked, do you think the ballon will expand?Give you reason.
It will not expand. Because the air pressure inside the flask and
outside will be the same
(d) What conclusion can you make between temperature and air
pressure?
When temperature increases, its pressure also increases.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 What function of sucker hook?
A Used to suck air out of a container.
B Used to suck up liquids.
C Used to suck drinks from containers.
* D Used to hang light objects from a wall.
2 Which of the following can be used in aerosol cans?
I Cooking gas
II Oxygen tank
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 1 128 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III Cylinder gas
IV Water bottle
A I only
B II and III only
* C I, II and III only
D I and IV only
A C
C
Figure 1 B*
3 Which point shows the direction that air pressure acts to support the
water does not flow out?
Pulled
Syringge
Water
Beaker
Figure 2
4 What will happen if the syringe pulled up?
* A Water cannot sucked into the syringe.
B Water can sucked into the syringe.
C The water can full the syringe .
D Water is sucked up and the flows back to beaker.
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 1 129 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 Figure shows a suction pump.
(a) What is the used of suction pump?
It is used to remove the blockage in the pipe.
[1 mark]
(b) How to remove the blockage of this tool?
The pushing and pulling of the section pump reduces the air
pressure around the blockage. Pushes and loosen the blockage
which will then flow out with the water inside.
[2 marks]
(c) State two example used the principle of air pressure to explain.
(i) Dropper
(ii) Bunsen burner
[2 marks]
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 1 130 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 6 ₪ Air Pressure ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 We can ensure maximum grip a rubber sucker when we
I press lightly on the rubber seal.
II place the rubber seal on a smooth flat.
III moisten it.
A I only
B I and II only
* C II and III only
D I, II and III only
2 There are how many factors that affect atr pressure?
* A Two
B Three
C Four
D Five
3 What pressure produced when the air particle collide with walls of a
container?
I Air pressure
II Atmospheric pressure
III Inner pressure
A I only
B II and III only
* C I and II only
D I, II and III only
4 Which statement is not true about the pump and its function?
Instrument Function
A Rubber sucker To hang on a piece of glass
B Lift pump To draw water from pump
* C Suction pump To pump air into a balloon
D Lift pump To draw water from pump
5 Which of the following tools depend on air pressure to operate?
I Syringe
II Siphon
III Insecticide spray
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 2 131 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
IV Drinking straw
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
Air pressure
Air pressure
Figure 1
6 In figure 1 is a rubber sucker hook. Which area is low pressure?
I A
II B
III C
A I only
B II and III only
C I and II only
* D III only
Figure 2
7 The diagram above shows a glass of fruit juice. What will happened
when a man sucked the glass of fruit juice using the drinking straw
shown as above?
A When sucked, air inside the straw is removed, leaving a high-
pressure area
* B When sucked, air inside the straw is removed, leaving a low-
pressure are
C When sucked, air inside the straw is restored, leaving a low-
pressure area
D When sucked, air inside the straw is restored, leaving a high-
pressure area
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 2 132 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
8 Why should two holes be on the lid for the milk to flow out?
I Not easier to flow out
II One hold atmospheric pressure push the milk out
III One hold for the milk come out
A I only
B I and II only
* C II and III only
D I, II and III only
9 The definition of the experiment kinetic theory of gases is
I Air contain particle
II Move in all direction
III Colliding with each other
A I only
B III only
C I and II only
* D I, II and III only
10 The pressure on the earth called
I Air pressure
II Inner pressure
III Atmospheric pressure
A I only
B I and II only
* C I and III only
D II and III only
11 Air pressure is exerted in what direction?
* A All directions
B South
C East
D North
12 The random movement of air particles can be explain by
* A kinetic theory.
B theory of relativity.
C potential energy.
D gravitational theory.
13 What are the factors that affecting air pressure?
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 2 133 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
I Kinetic energy of air particles
II Volume of container
III Quantity of air particles
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a milk tin being poured into a cup. The tin has one hole
on it.
(a) How can we make the milk flow faster?
Make another hole on the lid opposite the existing hole.
(b) Why does the condensed milk flow very slow?
The air pressure inside the tin is lower than outside.
(c) Give your reason in suggestion in (b).
The another hole will let air pressure inside and push the milk out.
So that it can balance air pressure inside and outside.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The features of air pressure are
I acts in all direction.
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 2 134 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
II changes from one place to another.
III decreases the higher you go above ground lever.
A I and II only
B II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
Figure 1
2 Why the can become dented?
A Because air pressure inside and outside are same.
* B Because air pressure inside lower than outside.
C Because air pressure inside higher than outside.
D Because there are no presure inside.
3 Which of the following is the principle of air pressure?
I Piston
II Thermometer
III Spray canister
A I only
* B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II and III only
4 Which are the following is to be done gas turn to liquid?
I Compress it
II Boil it
III Heat it
* A I only
B II only
C II and III only
D III only
TEST IT YOURSELF
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 2 135 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Plunger is pulled
Lower air pressure
Higher air pressure
Liquid Liquid is sucked into the syringe
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a syringe.
(a) What is the function of a syringe?
A syringe is used to suck liquid which is then injected into an
object.
[1 mark]
(b) What will happened when a boy pulled the plunger?
When the plunger is pulled, air pressure in the syringe decreases.
[1 mark]
(c) What will happened if there is hogher air pressure outside the
syringe?
Exerts its force on the surface of the liquid.
[1 mark]
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 2 136 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 6 ₪ Air Pressure ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The increasing volume of gas in the container. It increases
I Air pressure
II Atmospheric pressure
III Inner pressure
A I only
* B I and II only
C III only
D I, II and III only
2 Which of the following is the direction that air move?
* A Randomly in all direction
B Randomly in one direction
C Randomly in two direction
D Randomly in three direction
3 How is air pressure increases?
* A When air is heated
B When air is cooled
C When air is heated and then cooled
D When air condensed
4 What factor will make gas pressure increases?
I Adding gas
II Gas is compressed
III Gas is heated
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I only
* D I, II and III only
5 Which of the following is depend on air pressure to operate?
I Syringe
II Siphon
III Insecticide spray
IV Drinking straw
A I and II only
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 3 137 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
* D I, II, III and IV only
6 How to be gas change into liquid?
I High pressure
II Cooled
III Compressed
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
7 How is petroleum gas or natural gas store in a cylinder tank?
I Compressed
II High pressure
III Cooled
IV Heated
A I and II only
B II and III only
* C I, II and III only
D I, II, III and IV only
8 Which of the following tools are depend on air pressure to operate?
I Syringe
II Siphon
III Insecticide spray
IV Drinking straw
A I, II and III only
B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
9 We can't drink through the straw if
A the length of straw have increase
* B have a hole on the straw
C we use the straw at higher places
D the drink is poison
10 What is the function of siphon?
* A Used to transfer liquids from a higher level to a lower level
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 3 138 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B Used to suck drink from containers
C Used to spray insecticide over a large area
D Used to suck up water
11 The pressure of a quantity in an enclosed container depends on the
I Volume of the air
II Temperature of the air
III Composition of the air
IV Quantity of air particles
A I, II and III only
B II and III only
C I and IV only
* D I and II only
12 The principle of air pressure can be used to solve problems in our daily
life such as
I Suction pump
II Pouring liquid from a container
III Bunsen burner
A I only
B I and III only
C I and II only
* D I, II and III
Q S
Figure 4
13 A hole pierced at which P, Q, R and S as shown in figure 4, will prevent
water from following up from the beaker?
A P and Q
B Q and R
* C R and S
D P, Q, R and S
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 3 139 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 A student drink some water from the drinking straw as shown in Figure
1.
(a) What happens to the air pressure inside the stram?
The air pressure in the straw will less.
(b) Compare the air pressure inside and outside the straw
The air pressure inside is lower than outside.
(c) What causes the water flow into the student mouth?
The air pressure outside the straw pushes the water into the
straw and up till it reaches her mouth.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Why gases want kept in liquid state in aerosall can?
* A To save space
B To easy to carry
C To easy to ramous
D For safety
2 What is the function of filter pump?
A Used to hang light objects
B Used to suck up liquid
* C Used to suck air out of a container
D Used to transfer liquid from a higher lever to lower level
3 Air has particles that are continually moving and colliding with things on
earth we produce by
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 3 140 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
I Air pressure
II Atmospheric pressure
III Inner pressure
* A I and II only
B II and III only
C I only
D I, II and III only
4 When air is compress or cooled, it will change to
A Solid
* B Liquid
C Gases
D Nothing change
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Glass
Water
Thick cardboard
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 show a activity to study air pressure.
(a) What will happen when the hand removed?
The waters are still in the tin. It does not flow out.
(b) What conclusion can you make in his activity?
Air produces pressure.
Chapter 6_Air Pressure_Set 3 141 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 7 ₪ Dynamics ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 What are the effects of forces?
I Shape
II Position
III Speed
IV Direction
A I and II only
B II and III only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV only
2 Which of the following are the types of force?
I Frictional force
II Inner force
III Magnetic force
A I only
* B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II and III only
3 What is gravitational force?
* A The force attraction that pulls objects towards the centre of the Earth
B Produced when two surfaces rub against each other
C The attractive or repulsive force exerted by magnets
D Produced when electrons move through a conductor
4 What unit is use to measured force?
A Kilogram
* B Newtons
C Kelvin
D Celcius
5 Fraction always acts in the direction that opposes the direction so it can
I Prevent a stationary object from moving
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 1 142 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
II Slow down or stop a moving object
III Make a moving object faster
A I only
* B I and II only
C II and III only
D I, II and III only
6 The magnitude of the force depends on
I the nature of the surface in contact.
II the weight of object.
III surface area.
A I only
B I and III only
C I, II and III only
* D I and II only
7 Which of the following is the advantage of friction?
I Enable a match to be lit
II Enable a ladder to lean against a wall
III Wears away materials
A I only
B II and III only
C I and II only
* D I, II and III only
8 Which of the following can be reduced friction?
I Box
II Wheels
III Grease
A I only
B I and II only
C I, II and III only
* D II and III only
9 What is the fomula of work done?
* A Work done = Force H Distance
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 1 143 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Force H Distance
B Work done = Time
C Work done = Force H Time
Force H Time
D Work done = Distance
10 Which of the following is the situation when work is done?
I Sitting on a chair
II Pushing against a wall
III Brushing teeth
A I only
B I and III only
* C III only
D I, II and III only
11 A force is a
* A pull and push
B collision
C strength
D pressure
12 A wooden block is pulled to a distance of 5m with a force of 6N.calculate
the work done
A 32 N
B 25 N
* C 30 N
D 29 N
13 Ali pushes a box with a mass of 20kg over a distance. It the work he has
done is 2000J, calculate the distance he move?
( Assume that 1kg = 10N )
A 15 m
B 10 m
* C 17 m
D 20 m
14 SI unit of power is
I Watt
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 1 144 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
II Joules
III Newton
A I only
* B I and II only
C II and III only
D I, II and III
15 6 seconds are needed to push a box. It the work done is 30 J, calculate
the power.
* A 5W
B 6W
C 3W
D 9W
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Wooden block
Spring balance
Thread
Pull
Figure 1
1 The apparatus as shown in Figure 1 is set up to study the direction and
magnitude of friction . The reading on the spring balance at very moment
the wooden blook is moved is 4 N.
(a) What is the magnitude of frictional force in this experiment?
4N
(b) What is frictional force?
Force that opposite the movement of an object.
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 1 145 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(c) What type of force is frictional force?
A pulling force.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 A student weighting 500N and carrying a weight of 200N in his hands,
climbs a flight of stairs of vertical height 3m.Calculate the work done.
A 2 200 J
B 1 900 J
* C 2 100 J
D 2 300 J
2 Ah Ming pushes a car with a force of 500 N over a distance of 2 m in
10 seconds. Calculate the power.
* A 100 W
B 110 W
C 90 W
D 200 W
3 The tiny bits of paper are attracted to the plastic. What force that
produce?
A Frictional force
B Gravitational force
* C Electrostatic force
D Magnetic force
4 What electrical force produce?
* A When electrons move through a conductor
B Attraction that pulls objects towards the Earth
C Two surface rub against each other
D Presence of static electrical change
5 Force can change all the following characteristics of an object except
A speed
B size
* C moss
D shape
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 1 146 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
3m
Figure 1
1 In Figure 1, a man carries a heavy stuff and climb up a stairs. He requires
some power.
(a) What is the general equation for the calculation power?
Work done
Power = time taken
[1 mark]
(b) What is the definition of power ?
Power is defined as the rate of energy transfer or the rate of
doing work.
[1 mark]
(c) The man in Figure 1 weights 500 N and he carries a 45 N stuff
and climb up a 3 meters high staircase in 10seconds. What is the
power generated by the boy?
(450 N + 50 N) H 3 m
Power = 10 Second = 150 N
[1 mark]
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 1 147 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 7 ₪ Dynamics ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The strength of force measured in
A watt
B joule
* C newton
D coulumb
Situation Force
A bus travelling from town P to town Q X
Satellite to move in an orbit round the Earth Y
Table 1
2 What types of force are X and Y as described in table above?
X Y
* A Frictional Gravitation
B Gravitation Frictional
C Magnetic Electrostatic
D Electrostatic Magnetic
3 Which of the following situations does not use frictional force?
* A A clerk using the computer
B A monkey climbing up a tree
C A swimmer swimming in a pool
D A person writing with a pen
4 Which of the following describe the disadvantage of frictional force?
A Friction allows things to rest on their own position
B Friction allows us to walk
* C Friction can produce noise
D Friction allows a moving car to stop
5 A force can change all of the following characteristics of an object except
A size
* B mass
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 2 148 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C shape
D speed
6 If the weight of a box is 350 N. What is its mass?
* A 35 kg
B 350 kg
C 35 000 kg
D 35 g
7 Alex climb up a mountain of 65 m high. If the weight of Alex is 500 N,
what is the work done by Alex in climbing the mountain?
A 15 602 J
B 23 220 J
* C 32 500 J
D 41 077 J
200N
Figure 1
8 Figure 2 shows a boy is pulling a card box with a force of 200 N. What is
the work done by the boy if he take 5 minutes to pull the box over
distance of 5 M?
A 40 J
B 100 J
* C 1 000 J
D 4 000 J
9 Work is not done when someone
A climbs the stairs
* B pushes a wall
C kicks a ball
D cycles bicycle
10 How much power is need for a car weighing 10 000 N to move through a
distance of 5 metres in 10 seconds?
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 2 149 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
A 500 W
* B 5 kW
C 50 kW
D 100 kW
11 What is the instrument that used to measure the magnitude of force?
* A Spring balance
B Micrometer
C Ammeter
D Voltmeter
12 What is the SI unit for power?
A N
* B Js−1
C ms−1
D Ns
13 Find the weight of the books, if a boy does 340 J of work to carry the
books to a distance of 3 m.
* A 180 N
B 220 N
C 276 N
D 342 N
14 A motor can lift a weight of 100 N object to a height of 6 m in 15 seconds.
The power of the motor is
A 20 W
* B 40 W
C 60 W
D 80 W
S Q
P
Figure 2
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 2 150 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
15 Which arrow represent the frictional force and gravitational force
respectively?
Frictional force Gravitational force
A S R
* B S P
C P S
D R Q
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
1 (a) Define force.
A force is defined as a push or a pull.
(b) Give two advantages of frictional force.
(i) Friction allows objects to slow down and stop.
(ii) Friction allows us to walk or run without slipping.
(c) Explain briefly the types of force that measured by spring balnce.
(i) Spring balance measures the gravitational force, when it
lifts a weight.
(ii) Spring balance measures the frictional force, when it
drags an object along a surface.
(d) Give two applications of increasing friction.
(i) Tyres with deep treads or grooves can give a good grip
on slippery surfaces.
(ii) Rough surfaces on floor prevent us from slipping when we
move on them.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The force that can attract small pieces of paper without touching them is
A gravitational force
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 2 151 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B frictional force
* C electrostatic force
D magnetic force
2 The magnitude of power depends on
I time used to doing work
II the magnitude of force applied
III the total distance moved in the direction of the force
IV the velocity of object
A I and III only
* B I, II and III only
C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
3 A student with a mass 45 kg climbing up the mountain with the height of
10 m in 50 seconds. Find the power.
A 80 J/s
* B 90 J/s
C 8 J/s
D 9 J/s
4 Which of the following is the advantage of frictional force?
A Produces heat which can move a machine
B Slow down or stops the moving object
* C Prevents ladders from sliding
D Produces sound
Name Weight Split time
Jojo 50 kg 18 second
Joester 45 kg 14 second
Jessica 40 kg 11 second
Table 1
5 Three students of various masses are racing against each other on a 100
metres track based on the information given in Table 1, Arrange the
student from the one who produces the most power to the one who
produces the least power.
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 2 152 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
A Joester → Jojo → Jessica
B Jessica →Jojo → Joester
C Jojo → Jessica → Joester
* D Jojo → Joester → Jessica
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
75 kg F
10 m
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a man pull the wooden box up to the lorry in 2 minutes.
The mass of wooden box is 75 kg.
[Take the force of 1 kg = 10 N]
(a) What is the work done by the man to pull the wooden box up to
the lorry?
Work done, W == Force H Distance moved
= 75 H 10 N H 2 m
= 750 N H 2 m
= 1 500 J
[2 marks]
(b) What is the power produced by man in pulling the wooden box?
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 2 153 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Work done
Power =
Time taken
1 500 J
=
2 minutes
1 500 J
=
2 H 60 s
1 500 J
=
120 s
= 12.5 Js−1
[2 marks]
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 2 154 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 7 ₪ Dynamics ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which of the following is the methods of reducing friction?
* A Wheels
B Rough surface
C Graded sand paper
D Steel wire cleaning ball
2 Which of the following machines require energy?
I Air conditioner
II Telephones
III Weighing scale
IV Windmill
A I and II only
B II and III only
* C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
3 Which of the following are the types of force?
I Frictional force
II Gravitational force
III Magnetic force
A I only
B II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
4 What can force change?
I Shape
II Position
III Size
IV Direction
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 3 155 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* D I, II, III and IV
5 What are the method that can reducing friction?
I Ball bearings
II Air cushion
III Lubrication
IV Box
A I and II only
B II, III and IV only
* C I, II and III only
D I, II, III and IV
6 What is the disadvantages of frictional force?
I Produces heat
II Wears out object or surfaces in constant
III Shows down or stop the moving object
IV Produces sound
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
* D I, II, III and IV
7 Which of the following is the magnitude of the frictional force?
I Surface
II Weight
III Surface area
* A I and II only
B III and IV only
C I and III only
D I, II and III only
8 A worker pushes a box with a mass of 25 kg over a distance. If the work
he has done is 2 500 J, calculate the distance he moves?
A 5M
B 7M
* C 10 M
D 15 M
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 3 156 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
9 Which of the following force are acting on a box so that a man is able to
move the box?
I Gravitational force
II Magnetic force
III Frictional force
IV Electrostatic force
A I and II only
B I and III only
* C II and III only
D II, III and IV only
10 Which of the following is caused the sun become hot?
A Gravitatinal force
B Electrostatic force
C Magnetic force
* D Frictional force
11 Which of the following forces act on a monkey who is climbing a tree?
I Frictional force
II Gravitational force
III Electrostatic force
* A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and III only
D I, II and III
12 Which of the following is used to reduce friction?
I Air
II Oil
III Bail bearings
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III
13 Which of the following forces enables a blunt saw to be sharpened?
A Electrostatic force
* B Frictional force
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 3 157 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C Magnetic force
D Gravitational force
14 Which of the following surfaces provides the greatest of the friction to the
movement of a wheelbarrow on it?
* A Sand
B Rood
C Tiled floor
D Germent floor
15 What is the unit for measuring power?
* A Watt
B Joule
C newton
D Metre
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
15 cm
15 cm
Figure 1
1 Diagram P shows a box pull on rough surface. When the student pull the
box, spring balance shows 6 N. Diagram Q shows a box pull on smooth
surface by a student. When the student pull the box, spring balance
shows 4 N.
(a) Why two of the spring balance shows difference magnitude?
Because rough surface will produce frictional force larger than
smooth surface.
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 3 158 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(b) Find the work done for diagram P and Q respectively.
(i) P Work = Force H distance
= 6 N H 0.15 m
= 0.9 J
(ii) Q Work = Force H distance
= 4 N H 0.15 m
= 0.6 J
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 When a plastic ruler is used to rub on a soft cloth. This is an effect of
A magnetic force
B gravitational force
* C electrostatic force
D frictional force
2 Which one of the following is advantage of frictonal force?
A Wears out objects
* B Allows a person to walk
C Produces heat
D Produces sound
3 A tight scissors can be loosen by using a
* A Lubrication
B ball bearings
C water
D Air cushion
4 SI unit of work is
A Kilometer
* B Joule
C Watt
D Kilogram
5 Which of the following are forces?
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 3 159 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
I Magnetic
II Electric
III Gravitational
A I and II only
* B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II and III
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
1 (a) Give three way to increasing friction.
(i) Wheels are used in vehicles and to move object
(ii) Rods are used to move objects.
(iii) The layer of air between the underside of a hovercraft and
the surface of water reduces friction.
[3 marks]
(b) Give two examples why friction needs to be increased.
(i) Smooth worn out tyres need to be replaced with new
ones to prevent vehicles from slidding.
(ii) Shoes with worn out soles need to be replaced with new
soles to prevent us from slipping.
[2 marks]
Chapter 7_Dynamics_Set 3 160 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 8 ₪ Support and Movement ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which one of the following animals uses exoskeleton to proted its body?
A Eagle
* B Grasshopper
C Gold fish
D Frog
2 The following are the function of endoskeleton in humans, except
A to support the weight of the body
B protect soft organs of the body
C to produce blood cells
* D to kill the virus that attack our body
3 Which of the following animals are supported by hard exoskeletons and
hydrostatic skeleton?
I Ant
II Scorpion
III Whale
IV Crab
* A I and II only
B I, II and IV only
C II and IV only
D III and IV only
Starfish Jellyfish
Figure 1
4 Figure 1 shows two animals, they are suported by
I hard exoskeletons
II exoskeletons
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 1 161 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III hydrostatic skeletons
A I and II only
B II and III only
C II only
* D III only
Figure 2
5 Figure 2 is
* A balsam plant
B rambutan tree
C durian tree
D casuarina tree
Figure 3
6 Figure 3 shows an aquatic plant. How can it suspends in water?
* A supported by buoyancy of water
B has tendrils
C uses turgor pressure in their cells
D supported by woody tissue
7 This body of an insect is supported by
A exoskeleton
B air sacs
* C endoskeleton
D hydrostatic pressure
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 1 162 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Support system in animals
Vertebrates Vertebrates
Land Aquatic
Y
Figure 1
1 The chart above shows support and movement of animals and plant.
Based on the chart above, answer the question below.
(a) What is the property of Y?
Have endoskeletons
(b) State three differences between land vertebrates and a aquatic
vertebrates.
(i) Types of support system
(ii) Size of the pectoral and pelvic girdles
(iii) Strength of the pectoral and pelvic girdles
(c) What are the functions of hard external structures in the
invertebrates animals?
(i) Maintain their shape
(ii) Supporting their bodies
(iii) Aiding movement
(iv) Protecting their internal body organs
(d) Name the part which is the exoskeleton consists of a hard
substance.
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 1 163 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chitin
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Question 1 and 2 are based on Figure 1.
R P
Figure 1
1 What is R?
* A Pelvic girdle
B Backbone
C Shoulder
D Pectoral girdle
2 What is P?
A Pelvic girdle
* B Pectoral girdle
C Bone
D Hip
3 Which of these animals uses their body fluid for support?
A Crab
B Centipede
C Beetle
* D Earthworm
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 1 164 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
P Q
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows two types invertebrates.
(a) What are the differences between P and Q?
Invertebrates P's body support by exoskeleton system and
invertebrates Q's body support by buoyancy of water.
(b) What are the similarties between P and Q?
Both have hard exoskeletons.
(c) Name two other invertebrates that use the same mechanism to
support.
(i) P : ant, spider
(ii) Q : prawn, cockle
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 1 165 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 8 ₪ Support and Movement ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 What are the function of the endoskeleton in human?
I To support the weight of the body
II To produce blood cells
III To give the body its structure and body
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and III only
* D I, II and III only
2 Humans are supported by
* A Endoskeleton
B Hydrostatic skeleton
C Exoskeleton
D Land vertebrates
3 Which of the following are hydrostatic skeleton?
I Ant
II Spider
III Rose plant
IV Tiger
* A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and IV only
D I, II and IV only
4 Which of the following are support system of land plants?
I Woody plants
II Non woody plants
III Exosteleton
A I only
B II only
* C I and II only
D I, II and III only
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 2 166 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
5 Which of the following are support by clinging onto other plants?
I Rattan
II Brugainvillea
III Rambutan tree
A I only
* B I and II only
C II and III only
D I, II and III only
6 Which of the following plants have climbing stuctures?
I Peper plant
II Cucumber plant
III Rambutan tree
A I only
B II only
* C I and II only
D I, II and III only
7 Which plant is support by woody trunk?
* A Mango tree
B Rambutan tree
C Cucumber tree
D Tomato plant
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 2 167 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
P
Q
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a human skeleton.
(a) Fill in the blanks below.
(i) P : Pectoral girdle
(ii) Q : Ribs
(iii) R : Spinal column / Spine / Backbone
(iv) S : Femur
(v) T : Fibula
(b) Which part of the human skeleton is the biggest and strongest?
Pelvic girdle
Space filled with
bone marrow
Figure 2
(c) Figure 2 shows the longitudinal section of femur of the human
skeleton.
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 2 168 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(i) Based on the figure above, state two advantages of
spongy bone.
Lighter and stronger than the solid bones with the same
length and weight.
(ii) State one animal which also has spongy bones.
Bird
Figure 3
(d) Figure 3 shows a skeleton of a horse. The horse is similar as
human which also classified as land vertebrates. State three
characteristics of land vertebrates.
(i) Give them shape.
(ii) Support their weight.
(iii) Protect their soft tissues and organs of the body.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 Refer to Figure 1, which one of the following is the plant supports itself?
* A Twining stems
B Holdfast roots
C Thorns
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 2 169 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
D Tendrils
Figure 2
2 Figure 2 shows the cross section the stem of a plant. What is the habitat
of this plant?
* A Pond
B Garden soil
C Small tree
D Forest
● Outgrowth of the epidermis
● Can be easily removed from the stem
● Used to stick to or climb other structures
3 Which of the following plant has characteristic shown as above?
* A Rose plant
B Money plant
C Bougainvilaea
D Banyan
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
1 All living things needs a support system to support soft body tissues.
(a) What are the factor that is needed by an animal?
(i) Size
(ii) Habitat
[2 marks]
(b) What are the three type supports system in animal?
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 2 170 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(i) Hydrostatic skeleton
(ii) Exoskeleton
(iii) Endoskeleton
[3 marks]
(c) Give two examples of animal that require an hydrostatic skeleton.
(i) Starfish
(ii) Caterpillar
[2 marks]
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 2 171 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 8 ₪ Support and Movement ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 The function of ribs is
* A protect the heart and lungs
B supports the head and arms
C allow movement of the arms and legs
D protects the spinal cord
2 Land plants are divided into how many groups?
* A 2
B 3
C 4
D 5
3 Which of the following shows the similarities between land and aquatic
invertebrates?
* A Hydrostatic skeletons
B Water buoyancy
C Exoskeletons
D Hydrostatic pressure
Epidermis
X
Soft tissue
Figure 1
4 What is X?
* A Air sack
B Prop roots
C Buttress roots
D Tendrill
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 3 172 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 2
5 Figure 4 shows the support feature utillized by the black pepper is
know as
A thorns
B tendrils
* C holdfast roots
D twining stems
6 Which of the following special features are used by woody plants for
support?
I Buttress roots
II Clasping roots
III Thorn
IV Drop roots
A III only
B I, II and IV only
* C I, II and III only
D I, II, III and IV only
Figure 3
7 What is X?
A Pith
* B Woody bark
C Woody tissue
D Prickle
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 3 173 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the skeleton of a whale.
(a) (i) What is X?
Pectoral gridle
(ii) What is Y?
Pelvic girdle
(b) How does the whale supported its body weight?
The body weight of aquatic vertebrates is supported by the
buoyancy of water
(c) Why the whale can grow to enormous sizes?
Aquatic vertebrates do not have to support their weight.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 3 174 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 What is X?
A Femur
B Compact
* C Hollow
D Spongy
2 Which of the following are hydrostatic skeleton?
A
*
C
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 3 175 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
3 Why is the backbone of the animal in Figure 1 curved?
A To allow the animal to stand up
B To allow the animal to walk with four feet
* C To give stronger support to muscles attached to it
D To allow the animal to move with easy flexibility
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
1 All living thing need a support system to support soft body tissues.
(a) What are the three types support systems in animal?
(i) Hydrostatic skeleton
(ii) Exoskeleton
(iii) Endoskeleton
[3 marks]
(b) Give one examples of animals that require an exoskeleton for
support.
(i) Crab
[1 mark]
Chapter 8_Support and Movement_Set 3 176 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 9 ₪ Stability ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 What is the function of plumb line?
* A Determine the centre of gravity of an irregular object
B Measure the height of an object
C Measure the base areas of an object
D Measure the weight of an object
Q
R
P
Figure 1
2 The figure shows a baseball. Which point is the most probably the centre
of gravity of the baseball?
* A P
B Q
C R
D S
J K L M
Figure 2
3 Which of the objects in figure does not have a centre of gravity located
within its own structure?
A J
B K
* C L
D M
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 1 177 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
P
S
Figure 3
4 The Figure 3 shows a star cardboard. The point of equilibrium is at
A P
B Q
C R
* D S
5 Which of the following increase the stability of a object?
I Large base areas
II Low centre gravity
III The point at which objects achieve balance
IV Decrease the height
A I, II and III only
B I, III and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
Figure 4
6 The figure above shows a car. Which one of the following improve the
stability of the car?
A Change the tyre of the car to a better quality
* B Lower the centre gravity of the car
C Upgrade the engine of the car
D Fetch lesser passengers
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 1 178 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Y
Z
Figure 5
7 The figure above shows an experiment which uses 3 wooden blocks of
the different height and base areas placed on a rough piece of board.
What is the order in which the models tapple over from the last to the first
when the board is tilted.
* A X, Y, Z
B X, Z, Y
C Y, X, Z
D Z, X, Y
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Baby Children Adult
Figure 1
1 The figure shows the growth of human.
(a) Which stage of the growth of human is the most stable?
Baby
(b) Give your reason to support your answer in 1 (a).
Because the baby has the lowest centre gravity and largest base
areas compare with other stages.
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 1 179 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Figure 1
1 The figure above shows a person standing with different posses, why
poss Q is more stable than poss P?
A Because poss Q is more cool
B Because poss Q has a lower centre of gravity and larger base than
* poss P
C Because poss P has a higher centre of gravity and larger base area
than poss Q
D Because poss Q is more confidence
Figure 2
2 Figure above shows 4 different alphabets. Arrange the wooden models in
order of decreasing stability.
A A, H, W, T
B T, A, W, H
C T, W, A, H
* D T, W, H, A
3 In Figure 3, object Q is more stable than object P because of
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 1 180 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
4 cm
2 cm
2 cm
* B
2 cm
4 cm
4 cm
5 cm
4 cm
4 cm
D
4 cm
5 cm 1 cm
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Motorcycle Car
Lorry
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows 3 types of vehicle.
(a) Which of the vehicle is the most stable.
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 1 181 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Lorry
[1 mark]
(b) Arrange the vehicles in order of increasing stability.
Motorcycle > Car > Lorry
[1 mark]
(c) Arrange the vehicles in order of increasing stability.
Because the lorry has the largest base areas compare with other
vehicles.
[1 mark]
(d) Suggest a way that can increase the stability of motorcycle.
The motorcyclist bends his body forward to lower his centre of
gravity when speeding in order to be more stable.
[1 mark]
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 1 182 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 9 ₪ Stability ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which one of the following will increase the stability of an object?
A Having a higher centre of gravity
B Having a narrower base
* C Having a lower centre of gravity
D Having the centre of gravity outside of the object
2 Centre of gravity defined as
A The position of its centre of gravity
B The position of its base area
* C The position of its centre of gravity and its base area
D The position of its centre of gravity and its mass
Q
P
R
Figure 1
3 Which of the following shows the tables in an increasing order of stability?
A P, Q, R
* B Q, P, R
C R, Q, P
D P, R, Q
E E G H
Figure 2
4 Figure 4 show four different shapes made of paper. Which one of these
shapes would be impossible to balance on a wooden stick?
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 2 183 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* A E
B F
C G
D H
P Q R S
Figure 3
5 In the Figure 3, which of the shapes is least stable?
A P
* B Q
C R
D S
Figure 4
6 The diagram shows a racing car. The racing car will become more stable
if
I the tyres are wide
II the tyres are set wide apart
III the body of the car is heavier
IV The car is built high
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
* D I, II and IV only
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 2 184 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 5
7 What happens to the cycle's centre of gravity and base area when the leg
of the cycle is shortened?
Centre of gravity Base area
A Raised Decreased
B Lowered Increased
* C Lowered Decreased
D Raised Increased
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
X Y Z
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows three types of building. The structure of building are
made by the same materials.
(a) Identify the most stable building.
Z
(b) Arrange the buildings in an increasing order of stability.
X, Y, Z
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 2 185 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(c) Explain the relationship between the height and the stability of
objects.
The shorter the object, the lower its centre of gravity. Therefor, the
object is more stable. The taller the object, the higher its centre of
gravity. Therefore, the object is less stable.
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Object Base area The shape of the object
P 45 cm2 Cube
Q 30 cm2 Cuboid
R 100 cm2 Cuboid
S 120 cm2 Cube
Figure 1
1 The diagram above shows 4 type of object with the difference of base
area. Which of the following object is most stable?
A P
B Q
C R
* D S
Figure 2
2 Refering to Figure 2, state the statement that relevant the figure above.
A A stable object should have a low centre of gravity and a large base
area
B The position of the point of equilebrium of an object depends on the
weight of the object
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 2 186 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C The stability of an object is affected by base area
* D The position of the point of equilibrium of an object depends on the
shape of the object
3 The following are the principle of stability that we apply in our daily
activities except
A weightlifer need to spreas his leg when lifting a heavy weight
B boxers stand with their feet wide apart
C usage of stick by old person
* D leaning backward when climbing a mountain
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a girl standing with his legs close together. The student is
easily pushed when shoved from behind.
(a) Suggest a way by which the student shown in the Figure 1 can
make himself more stable.
Bend his body forwards.
[1 mark]
(b) Explain the reason for your answer in (a).
Bending his body forwards will lower his centre of gravity, this will
increase his stability.
[2 marks]
(c) Suggest a way that can make a race car more stable.
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 2 187 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Lower the height of the car to lower its centre of gravity.
[1 mark]
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 2 188 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 9 ₪ Stability ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which of the following are the factors affecting the stability of an object?
I Base area
II Position of the centre of gravity
III Surface area
A I only
B II only
C II and III only
* D I and II only
2 A double decker travelling bus carries 45 adult passengers. Where do
you think the passengers should be seated to make the bus most stable?
Upper deck Lower deck
A 25 20
* B 15 30
C 40 5
D 20 25
3 The position of the centre of gravity can affects the _________ of an
object.
A height
B weight
* C stability
D strength
4 Point X in the figures below represent the point of equilibrium. Which one
of the following is the correct position of X?
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 3 189 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B
X
C
X
* D
5 Figure 2 shows a boats with a driver and a passenger on it. Why the
passenger are not allowed to stand?
* A To keep the centre of gravity low
B To increase the base area
C To increase the speed of the boat
D To avoid the passengers from falling from the boat
6 Which is the following characteristics can make the object more stable?
I A broad base of support
II A low centre of gravity
III A broad surface area
A I only
B II only
* C I, II only
D I, II and III
7 The centre of gravity of an object can be lowered by
I broad the surface area
II reducing the height of an object
III making the object heavier at the botton
A I only
B II only
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 3 190 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C I, II only
* D II and III only
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Stool
Vaulting horse
Figure 1
1 (a) How can we make this vaulting horse more stable?
By spreading its legs wide apart.
(b) Give two ways to make the stool more stable?
(i) Shorten its legs
(ii) Spread its leg wide apart
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which of the following that affecting the stability of an object?
I Surface area
II Position of the centre of gravity
III Base area
A I only
B I and II only
* C II and III only
D I, II and III
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 3 191 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
2 Which of the following are the importance of stability?
I Old people use walking sticks to increase their base area
II A person lifting weights will spread out his legs to increase the base
area
III Stand on both feet with legs apart
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and II only
* D I, II and III
P Q R S
Figure 1
3 Which of the shapes shown in Figure 1 is most stable?
A P
B Q
* C R
D S
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
X Y
Figure 1
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 3 192 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
1 Figure 1 shows 2 different leg of table.
(a) Which table is more stable? Why?
Table Y. Because it has larger base area compare with table X.
[1 mark]
(b) How to make the less stable table become more stable?
Expand the stand of the table X to broaden the base area of
table X.
[1 mark]
Chapter 9_Stability_Set 3 193 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 10 ₪ Simple Machines ₪ Set 1
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Q S
Figure 1
1 Based on Figure 1, where is fulcrum?
* A P
B Q
C R
D S
2 Which of the following are third-class lever?
I Sweeping with broom
II Scissors
III Knife
IV Nutcracker
A I and II only
B III and IV only
* C I and III only
D II and IV only
3 Which of the following is true when determine third-class lever?
I If the fulcrum lies in the centre, then the device is categorised as a
third-class lever
II If the effort lies in the centre, then the device is categorised as a
third-class lever
III If the load lies in the centre, then the device is categorised as a
third-class lever
IV If the force lies in the centre, then the device is categorised as a
third-class lever
A I
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 1 194 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* B II
C III
D IV
Effort
Fulcrum
Load
80 cm
2m
Figure 2
4 How much effort is required to lift a load of mass 40 kg?
A 180 N
B 200 N
C 220 N
* D 240 N
5 Which of the following statement is true about second-class lever?
I The effort and load act in opposite directions
II The effort is always farther from the fulcrum compared to the load
III The fulcrum is between the effort and the load
A I only
* B I and II only
C II and III only
D I, II and III
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 1 195 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 3
6 Figure 3 shows a boy pulling a box by using a pulley. Which of the
following example are similar class lever as shown as diagram above?
* A Scissors
B Nutcracker
C Bottle opener
D Broom
7 The moment of a force is measured in
A newtons
B joules per second
* C newton-methes
D kilograms
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 1 196 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
1 Figure 1 shows a boy is fishing.
(a) Based on the diagram above, answer the questions below.
(i) State the principle used by the man who is fishing.
Principle of moment
(ii) Name the class lever which is used by the man as shown
as the diagram above.
Second-class lever
(b) Based on your answer in a(i), explain the principle.
The principle of moments states that when a lever is in
equilibrium, the product of load and distance of load from the
fulcrum is equal to the product of effort and the distance of effort
from the fulcrum.
(c) Based on your answer in a(ii), simplify explain the class lever.
A large load can be overcome by using a small effort.
(d) Give two another example which are similar to the class lever as
shown as the diagram above.
(i) Bottle opener
(ii) Nutcracker
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Effort (E)
Fulcrum Load (L)
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a lever system. This system is in equilibrium if
A a+y = EHa
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 1 197 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B E H y = L H (a + a)
C LH a = EH y
* D L H (a + y) = E H a
Simple machines
example
Levers
classified as
First-class lever Second-class lever Third-class lever
Examples Examples Examples
● See-saw ● Bottle opener ● Broom
● X ● Y ● Z
Figure 2
2 The chart above shows a simple machine that can be classified into three
group. Which of the following is true?
X Y Z
A Paper cutter Crowbar Arm
Using a nail to open
B Knife Scissors
the cover of a tin
Opening the hood Nutcracker
C Ice tongs
of a car
* D Pliers Wheel barrow Fishing rod
3 Which of the following pairs of 'class of lever' and 'device' are matched
wrongly?
Device Class of lever
A Pliers First-class lever
B Knife Third-class lever
* C See-saw Second-class lever
D Scissors First-class lever
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 1 198 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 Levers are very useful in everyday life. Figure 1 is an example of a lever
used in everyday life.
(a) What is the name of the device shown in Figure 1.
Ice tongs
[1 mark]
(b) Which class of levers does this device belong to?
Third class levers
[1 mark]
(c) Where is the effort located with respect to the load and fulcrum in
this class of levers?
The effort is located between the load and the fulcrum.
[1 mark]
(d) What is the relationship between the distance moved by the effort
and that moved by the load for this class of levers?
A short distance moved by the effort makes the load moves
through a longer distance.
[1 mark]
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 1 199 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 10 ₪ Simple Machines ₪ Set 2
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which of the following has the same class of level as the stapler?
A Bottle opener
* B Hammer
C Scissors
D Pliers
Q S
P
Figure 1
2 The Figure 1 shows a stapler. The fulcrum is at
A P
B Q
C R
* D S
3 Which of the following is first-class lever?
* A
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 2 200 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 2
4 Figure 2 shows a lever is in equilibrium. What is the distance of the force
from the fulcrum?
* A 2.4
B 1.8
C 1.7
D 1.9
P Q R
Figure 3
5 Figure 3 shows a knife. Which of the points P, Q and R represent the
fulcrum, effort and load?
Fulcrum Effort Load
A P Q R
* B Q P R
C Q R P
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 2 201 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
D R P Q
Force = 75 N
4.5 m
40 N
Figure 4
6 In the Figure 4, what is the force needed to balance the load of 15 N?
A 47.83 N
B 40.01 N
C 37.98 N
* D 37.38 N
7 Which of the following examples are simple machines?
I Lever
II Wheel
III Wedge
IV Pulley
A I, II and III only
B I, II and IV only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II, III and IV
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 2 202 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Q
R
65 cm
100 cm
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a wheelbarrow.
(a) Name the parts labelled P, Q and R.
(i) P : Effort
(ii) Q : Fulcrum
(iii) R : Load
(b) How much effort is required to lift a load of mass 45 kg?
Load H Distance of load == Effort H Distance of effort
= Effort H 100 cm H 35 cm
450 N H 35 cm
Effort =
100 cm
= 157.5 N
(c) What class of lever is the wheelbarrow?
Second-class lever
(d) Name two example except this class lever.
(i) Scissors
(ii) Knife
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 2 203 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
1 Which of the following levers has the effort located between the fulcrum
and load.
* D
Effort
60 cm
90 cm
80 N
Figure 1
2 The lever in Figure 1 is in a position of equilibrium. What is the effort
need to maintain that equilibrium?
A 100 N
B 120 N
C 160 N
* D 240 N
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 2 204 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
30 cm 45 cm
Figure 2
3 Figure 2 shows a device that acts as a lever. What is the distance of the
load from the fulcrum and the distance of the effort from the fulcrum?
Distance of load from Distance of effort from
fulcrum ( cm ) fulcrum ( cm )
A 49 30
* B 30 49
C 30 79
D 79 49
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
8 cm 4 cm
12 N
Figure 1
1 (a) Name a balance that is similar in action to the lever shown Figure
1.
Beam balance
[1 mark]
(b) What class of the plate do the lever shown in Figure 1 belong to.
First-class lever
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 2 205 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
[1 mark]
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 2 206 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Chapter 10 ₪ Simple Machines ₪ Set 3
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which of the following are the simple machine in our daily life?
* A The working principle of broom and fishing rod is also based on the
lever mechanism
B Households are equipped with washing machines, refrigerators and
vacuum
C People use cars, buses, trains or even bicycles to reach certain
destinations faster without getting themselves tired
D Factories have many types of machines to manufacture their product
2 In first-class lever, the distance between the effort and the fulcrum need
* A to be greater than the distance between the load and the fulcrum
B to be farther from the fulcrum compared to the load
C a small load is lifted using a large effort
D to be farther from the load compared to the fulcrum
3 Which of the following has the same class lever as the nutcracker?
* A Bottle opener
B Tongs
C Stapler
D Pliers
4 Which of the following are involved in the moment of a force?
I Magnitude
II Weight
III Distance
A I only
B I and II only
* C I and III only
D I, II and III
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 3 207 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Force
20 cm
50 cm
10 N
Figure 1
5 The lever shows in Figure 1 is in equilibrium. Find the value of force.
A 3N
B 5N
* C 4N
D 6N
5 cm 9 cm
P 30 N
Figure 2
6 Figure 2 shows a lever in equilibrium. What is the value of P?
A 50 N
B 51 N
C 52 N
* D 54 N
P S
R
Figure 3
7 Figure 3 shows a hammer. The load is at
* A P
B Q
C R
D S
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 3 208 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
Instruction: Answer all questions.
Figure 1
1 Levers are very useful in our daily life. Figure 4 is an example of a lever.
(a) Which class of levers does this device belong to?
Third-class lever
(b) Name the device that shown in Figure 4.
Ice tongs
(c) Name two other example of levers in our daily life which belong to
same class.
(i) Broom
(ii) Fishing rod
PMR TARGET QUESTIONS
Instruction: Each question is followed by four options. Choose the best answer for each question.
1 Which of the following is / are first-class lever?
I Scissors
II Tongs
III Bottle opener
* A I only
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 3 209 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B I and III only
C II only
D I, II and III
2 Which of the following levers has the effort between the fulcrum and the
load?
* A Tongs
B Nutcracker
C Pliers
D See-saw
Effort
Y cm
30 cm
Effort
Figure 1
3 What is Y?
A 60 cm
B 70 cm
C 80 cm
* D 90 cm
TEST IT YOURSELF
Instruction: Answer all questions.
2 cm 9 cm
Figure 1
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 3 210 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
1 Figure 1 shows a bottle opener.
(a) What is P and Q?
(i) P : Load
(ii) Q : Effort
(b) Name the principle behind the operation of the opener.
Principle of movement
(c) The bottle opener shown as Figure 1 is in what class?
Second-class lever
Chapter 10_Simple Machines_Set 3 211 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
PMR Module Test Paper ₪ Set 1
PAPER 1
Time: 1 hour
Instruction: Answer all questions. Choose the best answer for each question from the four
options given.
1 What is the sensory organ of touch?
A Nose
B Tongue
C Eye
* D Skin
2 How many classes of food there are?
A 5
* B 7
C 6
D 9
3 Which of the following are the invertebrate animals?
I Prawn
II Tiger
III Deer
IV Centipede
A I only
B II and III only
C II and IV only
* D I and IV only
4 What is a community?
* A Consists of several types population that live together
B Consists of several communities that interact with one another and
with physical enviroment
C A group of organisms that have the same shape and structure and
can live together
D A natural living place for plants and animal
5 Which of the following are the properties of water?
I Colourless
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 212 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
II Odourless
III Tasteless liquid
A I only
B I and II only
C III only
* D I, II and III
6 How can natural gas change to liquid state in a gas tank?
I High pressure
II Low pressure
III Cooling
IV Boiling
A I and IV only
B II and III only
* C I and III only
D III and IV only
7 Which of the following force can change?
I Shape
II Position
III Direction
A I only
B II only
C I and III only
* D I, II and III
8 Which of the following are supported the weight of land vertebrates?
I Pectoral
II Pelvic
III Girdles
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III
9 What are the factors that can affecting the stability of an object?
I Base area
II Surface area
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 213 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III Position of the centre of gravity
A I and II only
B II and III only
* C I and III only
D I, II and III
10 Which of the following are the propertics of second class lever?
I The load is between the falcrum and the effort
II The effort and load act in the same direction
III The effort and load act in opposite direction
A I only
B II only
* C I and II only
D II and III only
11 What are the three state of water?
I Solid
II Liquid
III Element
IV Gases
A I only
B I and II only
C I, II and III only
* D I, II and IV only
12 Which of the following are not same as ths relationship between sea
anemone and hermit crab?
A Green algae and fungus
B Symbiotic bacteria and herbivorous animals
* C Stem borers and oil plam leaves
D Ox peakers and buffaloes
13 What are the example of non-flowering plant?
I Algae
II Rambutan tree
III Fungi
IV Moss
A I only
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 214 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B II only
C I, II and III only
* D I, III and IV only
14 Which of the following are the importance of food?
I Growth
II Warms the body
III Builds new cells
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and III only
* D I, II and III
15 What are the defect of long-sighted cause?
I Abnormally short eyeballs
II eye lens too thicks
III eyeballs too long
* A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and III only
D I, II and III
16 When the gas is heated the gas pressure will be
A decreases
* B increases
C increases and than decreases
D no change
17 Which one of the following are not work done?
A Pushing a wheelbarrow
B Brushing teeth
* C Pressing down on the surface of a table
D Compressing a spring
18 Which one of the following is supported the body weight of aquatic
vertebrates?
* A Buryancy of water
B Endoskeleton
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 215 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C Hydrostatic skeleton
D Exoskeleton
P Q R S
Figure
Figure11
19 Which one of the following are the most stable?
A P
B Q
* C R
D S
P
R Q
Figure 2
20 Figure 2 is showing a see-saw. Which part of the following are the load?
A P
R Q
C R
* D S
21 What is the function for vitamin A?
A Promotes the effective functioning system
* B For good vision at night
C promotes healthy skin
D Maintain a healthy reproductive system
22 What are the four types of taste buds on the tongue sensitive?
I Sour
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 216 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
II Salty
III Oval
IV Bitter
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I, II and III only
* D I, II and IV only
Figure 3
23 What is X?
* A Condensation
B Freezing
C Melting
D Boiling
caterpillar Bird
Plants bug lizard Eagle
earthworm frog
Figure 4
24 How many food chain are there in Figure 4 about?
A 3
* B 4
C 5
D 7
25 Which of the following are the characteristic of monocatyledons?
I Seed with one cotyledon
II Has tap root system
III Stem is usually woody
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 217 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
IV Leaf with parallel veins
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and III only
* D I and IV only
Load Effort
Fulcrum
Figure 5
26 Based on the Figure 5 above, which of the following can be found same
lever as Figure 5?
I Paper cutter
II Knife
III Wheelbarrow
A I only
B II only
C I and III only
* D I and III only
2m
Figure 6
27 A wooden block is pulled to a distance of 2 m with a force of 5 N.
Calculate the work done.
* A 10 N
B 15 N
C 8N
D 17 N
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 218 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 7
28 A man weight is 450 N and carrying a box with 50 N in his hand, climbs a
stairs of vertreal height 5 m. Calculate his work done.
A 1 500 J
* B 2 500 J
C 100 J
D 1 300 J
S
R
Q
P
Figure
Figure88
29 Based on the Figure above, which part is taste for sweet?
* A P
R Q
C R
D S
30 Which of the following is sensitive to skin?
I Heat
II Cold
III Pressure
A I only
B II only
C I and II only
* D I, II and III
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 219 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
● Cucumber plant
● Bitterground plant
Figure 9
31 The plant mentioned above have soft stem and climb on tree to obtain.
I Sunlight
II Mineral salt
III Water
A I only
* B II only
C I and II only
D I, II and III
32 Water is a element which consist of two elements. What are the two
elements?
I Hydrogen
II Oxygen
III Carbon dioxide
IV Helium
* A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
Plants
chicken earthworm bird
snake eagle
Figure 10
33 Based on the Figure above, which of the following is the primary
consumer?
A Bird
B Snake
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 220 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C Eagle
* D Earthworm
34 Which of the following is the methods of water purification?
I Boiling
II Chlorination
III Distillation
IV Filtration
A I and II only
B I and III only
C I, II and III only
* D I, II, III and IV
35 What is the simple explanition for third-class lever?
A Centre position is load
* B A small load is lifted using a larger effort
C No need effort
D A large load can be overcome by using a small effort
Figure 11
36 Figure 11 shows a group of fish in a pond. Such a group of animals we
call it as
A Habitat
* B Population
C Species
D Ecosystem
37 The following animals are primary consumers except
A Rat
B Earthorm
* C Snake
D Bug
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 221 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
38 Which of the following is the characteristics of fish?
I Breathing with gill
II Covered by moist skin
III External fertilisation
A I only
B II only
C I and II only
* D I and III only
39 Which of the following are the living things that are in danger of
extinction?
I Hornbill
II Tapir
III Rafflesia
A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and II only
* D I, II and III
40 Which one of the following is the types of carbohydrate?
I Cellulose
II Oxygen
III Starch
A I only
B II and III only
C I and II only
* D I and III only
PAPER 2
Section A
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Instruction: Answer all questions in this section.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 222 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Classes of food
protein water Q R
P Roughage Vitamin
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows the classes of food.
(a) Name the part labelled P, Q and R.
(i) P : Carbohydrate
(ii) Q : Fats
(iii) R : Mineral salts
(b) What are the carbohydrate make up of?
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
(c) What type of vitamin is good for vision at night?
Vitamin A
Plant
Bird
Rat
Snake
Eagle
Figure 2
2 Figure 2 shows an example of a food web.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 223 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(a) Fill in the blank.
(i) Producer : Plant
(ii) Primary consumer : Rat, Bird
(iii) Secondary consumer : Snake
(iv) Tertiary consumer : Eagle
(b) If the bird shifted to another area. What will happen to the snake
and rat population?
(i) Rat population : Increases tremendously
(ii) Snake population : Decreases slightly
Q
R
Figure
Figure 33
3 (a) Give two reason that cause the sensitivity of the skin.
(i) The concentration of receptors.
(ii) The thickness of the epidermis
(b) What is the function of the epidermic of the skin? To prevent the
entry of bacteria into the tissues of the body.
(i) P : Touch receptor
(ii) Q : Heat receptor
(iii) R : Cold receptor
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 224 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Y
X
Figure 4
4 Figure 4 shows a cross-section of the human ear.
(a) Complete the following chart below.
Ear pinna (i) auditory canal eardrum
(iii) auditory nerve cochlea (ii) ossicles
Figure 4
(b) Label the following parts in Figure 4.
(i) X : Ear Ossicles
(ii) Y : Semicircular canal
(iii) Z : Eustachian tube
Plants
Non-Flowering Flowering Plant
plant
Mosses
Monocotyledonous Decotyledonous
plants plants
X Conifers
Figure 5
5 (a) (i) What is mean by monocotyledonous plant?
Monocotyledonous are plants with one cotyledon in their
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 225 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
seed
(ii) Give two example for monocotyledonous plant?
(i) Paddy plant
(ii) Maize plant
(b) (i) What mean by non-flowering plant?
Non-flowering plants are plants that not produced flowers.
(ii) Name the group labelled X.
Fungi
(iii) How do non flowering plants produce?
Non flowering plants repraduce from spores or cones.
(iv) Where do you normally find group X plants?
In moist and shady places.
rat owl
Paddy snake
grasshopper frog
Figure 6
6 Figure 6 shows a food web in a paddy field.
(a) How many food chains are there in the food web shown in Figure
6?
(b) Which organism is called a producer?
Paddy plant
(c) Which organisms are the pests for paddy plants?
(i) Rat
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 226 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(ii) Grasshopper
(d) What will happen if the snakes reproduce very fast?
(i) The amount of rats and frogs will decrease.
(ii) The population of owl will increase.
(iii) The paddy will incrense.
Section B
Instruction: Answer all questions in this section.
Measuring
cylinders
Carbon electrode Acidified water
Anode Cathode
(positive terminal) (negative terminal)
Ammeter
Figure 7
7 Figure 7 shows the set up experiment to study the effect of electrolysis
on dilute acidified water.
(a) What is the aim of this experiment ?
To find out the particles in the water.
(b) What is the gas that is released of the negative electrode? How
can we test it?
Hydrogen gas is released at the negative electrode. We can test
it with a burning wooden splinter and it will produce a " pop
"
sound.
(c) What is the gas that is released at the positive electrode? How
can we test it?
Qxygen is released at the positive electrode. We can test it with
a glowing wooden splinter and the wooden splinter will burn.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 227 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(d) For the experiment above, what conclusion can we make
regarding the ratio of the hydrogen and oxygen in the composition
of the water molecule?
The ration of hydrogen are two time the ratio of oxygen.
water
out
Liebig condenser
River water
water Beaker
in
Figure 8
8 Figure 9 shows the appratus needed to study the purification of water by
distillation.
(a) (i) Is sea water suitable for drinking?
No, it is not suitable for drinking.
(ii) Give your reason for your answer in (a)(i).
Because sea water contion harmful bacteria.
(b) (i) Explain how distillation can purify river water.
River water change into stem when it boils. The steam
condenses into pure water and leaving behind the
impurities such as suspanded substance and dissolved
substance.
(ii) What is the meaning of "distillation" ?
Distillation is the process of changing water into steam
and condenses the steam to form pure water.
(c) (i) What is the function of the liebig condenser?
To condenser the steam that flows through it to water.
(d) (i) Is distilled water suitable for drink?
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 228 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
No.
(ii) Give your reason in (d)(i).
Because distilled water does not contain any dissolved
mineral that are need for good health.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 1 229 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
PMR Module Test Paper ₪ Set 2
PAPER 1
Time: 1 hour
Instruction: Answer all questions. Choose the best answer for each question from the four
options given.
1 Which part of the human ear magnify vibration?
A Cochlea
B Semicircular canal
C Eustachian tube
* D Pupil
2 Which of the following functions are true about phosphorus?
I Support muscle contraction
II Helps in bloodd-clotting
III Builds strong bones and teeth
IV Stores energy
A I, II and III only
* B I, III and IV only
C I, II and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
3 Which of the following statements is true about sound?
I Sound can travel through vacum
II Sort surfaces are good absorbers of sound
III Sound can be reflected with hard uniform surfaces
IV Sound travels faster through solids than liquids
A I and II only
B II and IV only
C I, II and IV only
* D II, III and IV only
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 230 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure
Figure2 1
4 Figure 1 shows the apparatus study to the responses of plants. What are
the conclusions can be made out after this experiment?
* A Shoots of plants show positive photoropism
B Shoots of plants show negative phototropism
C Shoots of plants show positive geotrapism
D Shoots of plants show negative geotrapism
Figure 2
5 Figure 2 shows a food pyramid. Which of the following food can be
considered in stage X?
A Food
B Milk
* C Apple
D Cheese
6 The enzyme that responsible for digesting and converting is…
A Lipase
B Protease
* C Amylase
D Casein
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 231 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Blue litmus paper Red litmus paper
Dilute hydrochloric
Figure 3
7 What is the conclusion you can get from the experiment above?
A Acids are corrosive
* B Acids turn blue litmus paper red
C Acids react with active metals to produce hydrogen gas
D Acids have a pH value less than 7
8 Which of the following method is used to change the gas to the liquid?
I Hot it
II Compress it
III Boil it
* A II only
B I and II only
C I and III only
D II and III only
9 What is caused by gas particles with the walk of a container?
I Heat energy
II Kinetic energy
III Gas pressure
A I only
B II only
* C III only
D II and III only
10 Which of the following enables chloride powder dissolve in a saturated
sodium chloride?
A Stiring
B Using a bigger beaker
* C Adding water to the beaker
D Adding alcohol to the beaker
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 232 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
11 The random movement of particle can be explain by…
A Theory of relativity
B Bernoulli principle
* C Kinetic theory
D Brownian movement
12 The position of the centre of gravity effects the ________ of an object.
A Height
B Strength
* C Stability
D Mass
13 Cooking gas contains gas under high pressure. Which of the following
safety measures must follow?
I Cooking gas must be kept vertical with the value facing upwards
II Cooking gas should be kept away from heat
III The valve of the gas is to be switched off after use
A I an II only
B II only
C III only
* D I, II and III
14 The force needed to loosen a nat can be reduced by using?
* A Shorter spanner
B Longer spanner
C Lighter spanner
D Heavier spanner
15 Which of the following animals are matched correctly with its support
system?
Animal System
* A Beetle Exoskeletons
B Centipede Hydrostatic skeleton
C Starfish Exockeletons
D Elephant Hydrostatic skeleton
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 233 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Ice
Lime juice
Liquid X
Figure 4
16 Figure 4 shows an expriment to study the change of state of matter.
Which of the following is characteristic of liquid X?
I It is sour
II It has a ph of 7
III It change red litmus paper to blue.
IV It boils at 100°c
A II only
* B II and IV only
C II and IV only
D I, III and IV only
17 Which of the following process takes place when the temperature of ais
cube changes from 0°C to 1°C?
A Freezing
B Boiling
* C Melting
D Evaporation
P 1
2 S
Figure 5
18 Figure 5 shows a circle of number. Which organism will be as following
for P and S?
P S
A Leaves Caterpillars
B Small birds Eagles
* C Snakes Leaver
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 234 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
D Careal Snakes
P Q R S
Figure 6
19 Which of the following objects shows in Figure 6 does not have a centre
gravity located?
A P
B R
* C Q
D S
20 The animal have a hard substance that protects their soft body.
A Bird
* B Turtle
C Dog
D Horse
21 A fruit dropping from a tree. What is the force showing on the fruit?
A Magnetic force
B Electrostatic force
* C Gravitation force
D Fractional force
22 Which of the following statements is true?
A Air has no mass
B Air is not mixture
* C Air is not compound
D Air does not ocuppies space
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 235 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Clouds Rain
Y
Vapour Water
Figure 7
23 Figure 6 shows a nature's way of recycling water. What is the process Y
in the cycle?
* A Evaporation
B Heating
C Condensation
D Boiling
24 Which of the following organisms cannormally be found in a desert
environment?
A Lion
* B Cacti
C Bird
D Horse
25 Which of the following is a flowering plant?
* A Rose
B Mushroom
C Ferns
D Seaweed
26 What are the factors that can affect the stability of an object?
I Base area
II Surface area
III Position of the centre of gravity
A I an II only
B II and III only
* C I and III only
D I, II and III
27 Which of the following figure is correct?
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 236 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
* D
Vertebrates
Birds Mamals Y Reptiles Amphibians
Figure 8
28 Figure 7 shows the classification of vertebrates. Which of the following is
the animal grouped in class Y ?
* A Shark
B Bat
C Whale
D Lizard
29 List all the food that can strengthen teeth?
I Milk
II Meat
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 237 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III Anchovies
IV Sweet
A I and II only
* B I and III only
C III and IV only
D II, III and Iv only
30 Which of the following is categorized as a cold-blooded?
A Camel
* B Lizard
C Rabbit
D Bird
31 Which of the food contain carbohydrate?
* A Bread
B Vegetable
C Fruit
D Meat
32 Which of the following solvents can remove that ball point ink stain from
the cloth?
* A Alcohol
B Turpentine
C Chloroform
D Acetone
Organism Number of organism
W 300 000
X 1 300 000
Y 25 000
Z 700
Table 1
33 Figure 8 shows some organism and their number in a area, which of the
following is a food chain formed from organism W, X, Y, Z ?
A Y→W→Z→X
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 238 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B W→X→Z→Y
C Z→Y→W→X
* D X→W→Y→Z
● Spider
● Lizard
● Turtle
34 Which of the following is a common characteristic among the vertebrates
listed?
* A Body covered with slimy scales
B Internal fertilisation
C Lay eggs
D Cold - blooded
35 Which is the function of liver?
A Completes digestion
B Digestion of protein begins
* C Secretes bile
D Stores faeces
36 Which of the following are characteristics of conifers?
I Reproduce by seeds
II Can live long
III Reproduce in water
* A I and II only
B I and III only
C II and III only
D II and IV only
● Warm blooded
● Egg - laying
● Has feather
37 An animal has the above characteristic. This animal is a
A reptile
B amphibian
C fish
* D bird
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 239 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
38 Which of the following are factors that affect the rate of dissolving?
I Size of the solute particles
II Rate of stirring
III Humidity
IV Temperature
A I, II and III only
* B I, II and IV only
C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
39 The stability of an object depends on
I the position of the centre of gravity
II the area of the base
III the weight of the object
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
40 Which of the following organism properly is a producer?
A Rat
* B Grass
C Eagle
D Snake
PAPER 2
Section A
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Instruction: Answer all questions in this section.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 240 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Figure 1
1 Figure 1 shows a simple grassland ecosystem.
(a) How does grass produce food for itself?
Grass absorb sunlight and carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
with chlorophyill.
(b) What will happen if one of the organisms in the organisms in the
ecosystem in removed?
Population of some organisms will decrease and population of
some organisms will increase.
(c) (i) Which organisms is called primary consumer?
Grasshopper
(ii) Draw a food chain based on the Figure 1 shown
Paddy plant grasshopper bird
River water
Fine sand
Coarse sand
Fine stone
Pebbles
Rubber stopper
Figure 2
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 241 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
2 (a) Is the filtereal water suitable for drink?
No
(b) Give your reason why for question (a).
Because it still contains harmful bacteria and not good for our
body.
Figure 3
3 (a) Name the parts labeled X and Y .
(i) X : Small intestine
(ii) Y : Large intestine
(b) What is the function of the rectum?
To store undigested food.
(c) What are two important organs in digestion system that food does
not pass?
(i) Pancreas
(ii) Liver
4 (a) Complete the chart 1 below to show the way from stimulus to
response.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 242 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Stimulus Effectors (i) Nerves
(ii) Brain
Response (iii) Effectors Nerves
Figure 4
(b) Complete the following table.
Sense Sensory organ
Sense of smell (i) Nose
Sense of taste (ii) Tongue
Sense of touch (iii) Skin
Sense of hearing Ear
Sense of sight Eyes
Table 1
P Q
Figure 5
5 The diagrams shown stems of two plants.
(a) Name the plant has the type of stem like P ?
Casuarina tree
(b) What is the system for plant P ?
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 243 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Woody trunk
(c) Name the plant that has the same type stem like Q ?
Yam plant
(d) What is the system for plant Q ?
Water retention stem
(e) Give two example same system as P.
(i) Rambutan tree
(ii) Durian tree
Vertebrates
Reptiles P Amphibians Q Birds
Example: Example:
Octupus Camel
Figure 6
6 (a) What are vertebrates?
Vertebrates means with backbones
(b) Name the group A and B .
(i) A : Fishs
(ii) B : Mamals
(c) What is the diffrence between animals in group while animals in
group A and B in their method of fertilisation?
Animals in group A carry out internal fertilisation while animals In
group B carry out external fertilistion.
(d) (i) Explain the meaning of "cold blooded animal"
Body temperature changes with any enviroment
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 244 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(ii) Which group of animals are cold blooded animal?
(i) Fish
(ii) Reptile
Figure 7
7 A boy left his bottle of fish in the science laboratary hear the window for
five house. His fish did not die even though the bottle was covered.
(a) Why didn't his fish die?
The water plants provide fish with oxygen.
(b) What is the process that take place and the gases that are given
off from the water plants and the fish.
(i) Water plants
Process : Photosynthesis
Gas : Oxygen
(ii) Fish
Process : Respiration
Gas : Carbon dioxide
(c) What will be the colour of the bicarbonate indicator in?
(i) Pure water pink
(ii) Alkaline water Purple
(iii) Acidic water yellow
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 245 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(d) If the boy test the water from the bottle with bicarbonate indicator,
what colour will be seen?
Pink
(e) Where is this ecosystem found?
Pond, river
R
Q
P Wooden block
Figure 8
8 Figure 8 shows three wooden block have the same weight but different
base area.
(a) (i) Which wooden block will fall first?
Block P
(ii) Give your reason for your answer (a)(i).
Block P has the smallest base area.
(b) (i) Which wooden block will fall last, if the board is slowly
tilted over?
Block R
(ii) Give your reason in (b)(i).
Block R is the langest base area.
(c) (i) What conclusion for this experiment?
A large base area is the most stability.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 2 246 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
PMR Module Test Paper ₪ Set 3
PAPER 1
Time: 1 hour
Instruction: Answer all questions. Choose the best answer for each question from the four
options given.
1 Which part of the eye carries light impulses to the brain?
A Iris
B Suspensory ligament
* C Optic nerve
D Auditory nerve
C
D B*
Figure 1
2 Which of the following part is used to detect cold?
3 What is the function of carbohydrate?
A For rebuilt new cells in the body
* B To keep our body heat and energy
C For repair of worn out tissues
D It gives twice as much energy as protein
4 Which one of the following food contain high fats?
* A Butter
B Rice
C Potato
D Jam
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 247 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Visking tube
Water at 37°C
Starch solutio and amylase
Figure 2
5 At the end of 20 minutes, what we can found in the water outside the
visking tube?
A Amylase solution
* B Sugar solution
C Water only
D Starch solution
6 Which of the following are advantages of the biological control?
I Does not pollute the environment
II Does not kill other organisms because natural enemies are used
III Increase the number of organisms
IV Is cheap and safe to use
A I, II and III only
B I, III and IV only
* C I, II and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
7 What will happened if the ozone layer has thinned?
I Skin cancer
II Cataracts
III The immune system to function improperly
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III only
* D I, II and III only
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 248 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Plants
Rats Chicken
Eagle
Figure 3
8 This food web is found in a habitat. Which organism in the food web is a
secondary consumer?
A Chicken
B Rat
* C Eagle
D Plants
9 What is the meaning of satured solution?
A A solution that has very little solute
B A solution that has a lot of solute
* C A solution that has the maximum amount of solute
D A liquid that has small particles in it
Figure 4
10 What is the process above?
* A Filtration
B Chlorination
C Distillation
D UV Treatment
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 249 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Glass
Water
Thick cardboard
Figure 5
11 What is the conclusion based on the experiment above?
A Air produces pressure
B The volume of gas and its temperature affect air pressure
C The thick cardboard has an energy to suck the glass
* D Air exerts pressure
12 The solubility rate of substances depends on the
I Size of the solutes
II Stiring
III Volume of solvent
IV Surrounding temperature
A I only
B I and II only
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II and III
13 Which of the animal below breath through lung?
* A Elephant
B Prawn
C Fish
D Eel
14 Acid + Carbonate ?
A Salt + Water
B Water + Carbon Dioxide
C Salt + Carbon Dioxide
* D Salt + Water + Carbon dioxide
15 Which of the following statement will cause water pollution?
I Domestic waste
II Carbon dioxide
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 250 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
III Industrial waste
IV Chemical substances in agriculture
A I only
B II, III and IV only
* C I, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
16 Which of our internal organ store bile?
A Small intestine
B Large intestine
C Stomach
* D Gall bladder
17 Pancreatic amylase digests peptone into ________ .
A maltose
B starch
* C amino acid
D fatty acid
18 Which sensory organ in our body detects pressure?
A Eye
* B Skin
C Ear
D Tongue
Figure 6
19 Which of the following animals has the same type of vision as the animal
shown in Figure 5?
I Elephant
II Rat
III Monkey
* A I only
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 251 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
B I and II only
C I, II and III
D II and III only
20 If a person has short-sightedness, the image of a distant object fall
________ of retina.
A up
B down
* C in front
D behind
21 Which of the following factors can increase friction in our daily life?
I Making the surface in contact rougher
II Increasing the height of the moving object
III Increasing the weight of the moving object
* A I and III only
B I and II only
C II and III only
D I, II and III
22 Which of the following is non-woody plants?
A Durian tree
* B Banana tree
C Rambutan tree
D Rose
23 How can we lowered the centre of gravity of an object?
I Using the small base area of an object
II Reducing the height of an object
III Making the object heavier at the bottom
* A I and II only
B II and III only
C I and III only
D I, II and III
24 Levers are divided into three classes based in the
A length of the lever
B distance of fulcrum from the force
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 252 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C direction of the fulcrum, force and load
* D location of the fulcrum, force and load
25 The alimentary canal is made up of
I mouth
II small intestines
III anus
IV lips
A I and II only
* B I, II and II only
C II, III and IV only
D I, II, III and IV
26 Why clorine is added to the water in a swimming pool?
* A To kill the microorganisms
B To prepare pure or distilled water
C To remove suspended substances
D To reduce tooth decay
27 Which of the following can dissolve iodine, chlorophyll and shellac?
A Amyl acetate
B Aseton
* C Alcohol
D Choroform
28 What is the value of acid in pH?
A Higher than 7
* B Below than 7
C 7
D 0
29 Fossil fuels are
I Oil
II Gas
III Coal
IV Oxygen
A I and II only
B II and III only
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 253 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C II, III and IV only
* D I, II and III only
30 A force of 5 000 N is used to move a metal block through a distance of 10
m. Find the work done.
A 500 J
* B 50 000 J
C 5 010 J
D 4 990 J
P 300 N
Figure 7
31 Figure 6 shows a lever in equilibrium. What is the value of P ?
A 800 N
* B 600 N
C 500 N
D 700 N
32 What is the freezing point of the water?
A 100°C
* B 0°C
C 50°C
D 75°C
33 Why is distilled water bad for health?
A It tasteless
B It contains minerals
C It does not contain minerals
* D It still contains microorganisms
34 What are the way to improve the stability?
I Apart the legs of the chair
II Increase the weight of the chair
III Stand on both feet with legs apart
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 254 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
IV Increase the height of the object
A I only
B I and II only
C II and III inly
* D I and III only
35 Which of the following is second class of lever?
A Scissors
* B Wheel barrow
C Ice tongs
D See-saw
36 Which of the following can be categorized as a warm-blooded animal?
A Spider
* B Rabbit
C Whale
D Snake
37 Which of the following is related to commensalism ?
I Shark and remora fish
II Woodmushroom and a tree
III Sea anemone and hermit crab
IV Mistletoe and a tree
* A I only
B II and III only
C III and IV only
D I and II only
38 A student weigt 400 N and is carrying a weight of 100 N in his hands,
climbs a flight stairs of vertical height 3 m . Find the work done.
A 3 000 J
* B 1 500 J
C 4 500 J
D 5 000 J
39 Which digestive enzyme change starch to maltose?
* A Amylase
B Lipase
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 255 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
C Gastric juice
D Protease
Figure 8
40 Figure 7 shows a pyramid of numbers. Which of the following may be
organisms R and S ?
R S
A Snake Leaves
B Small birds Caterpillars
* C Caterpillars Small birds
D Leaves Caterpillars
PAPER 2
Section A
Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
Instruction: Answer all questions in this section.
secondary consumer
(i) Frog
primary consumer
(ii) Grasshopper
(iii) Grass producer
Figure 1
1 Fill in the blanks.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 256 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
● Grass ● Grasshopper ● Frog
Organic solvent Substanus that are dissolved
(a) Acohol (i) Chlorophyll
(b) Petrol (ii) Fresh paint
(c) Ether (iii) Grease
(d) Benzene (iv) Latex
(e) Citric Acid (v) Fruit stains
Figure 2
2 Complete the above table.
● Chrorophyll ● Fresh paint ● Grease
● Latex ● Fruit stains
Classes of Food
X Vitamin Minerals Y Water
Water Fats Z
Figure 2
3 (a) Function of Y is supplies us with energy to carry out daily
activities. What is Y ?
Carbohydrate
(b) If X can get from fruits, what function of X ?
Function of X is to help stimulate peristalsis and the muscle
movement of the small and big intestines.
(c) What is Z? Write 2 food contains Z.
Z is Protein and 2 food contains Z are fish and egg
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 257 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
rat owl
Paddy snake
grasshopper frog
Figure 3
4 (a) How many food chains can be found in the food web?
5
(b) Which organism is categorized as a secondary consumer?
Frog and snake.
(c) Which organism are the predator of rats?
(i) Owl
(ii) Snake
(d) What will happen if the population of owl increase immediately?
The population of rat, snake, and frog will decrease and the
of grasshopper will increase.
5 (a) (i) State the unit of work done.
Joules
(ii) State the formula to calculate work.
Work ( J ) = Force ( N ) H distance ( M )
(b) (i) State the unit of power.
Watt
(ii) What is the meaning of the term " power " ?
Power mean the rate of doing work.
(c) (i) Osman's weight is 750 N . If he walks up the stairs 6 m
high in 12 seconds, what is Osman's power ?
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 258 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
Work = 750 H 6
= 4 500 J
Power = 4 500 J
12 s
= 375 watt
(ii) If he walks up stairs in 10 second, does he do more work?
Why?
No. Because work not effected by time.
6 (a) State three differences between acids and alkalis.
(i) Acids have sour taste and alkalis have bitter taste.
(ii) The pH value of acids are below 7 but the pH value of
alkalis are above 7.
(iii) Acid change blue litmus paper into red while alkalis
change red litmus paper into blue.
(b) State the meaning of the following terms.
(i) Saturated solution
A saturated solution contains the maximum amount of
dissolve solute possible and no solute can dissolve in it.
(ii) Concentrated solution.
Concentrated solution has a large amount of solute but
can dissolve a little more solute in it.
cockroach frog lizard peguin bats
P Q R S T U
Figure 4
7 (a) (i) P is different from the other animals. What group does P
belong to ?
Fish
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 259 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(ii) What are the different characteristic of P from the other
animals?
It lives in water.
(b) State three chacteristics of S animal.
(i) It is cold blooded.
(ii) It has back bone.
(iii) Breath through lung.
(c) (i) Which group of animal are cold-blooded?
(i) P ( Fish )
(ii) Q ( Insect )
(iii) R ( Amphibians)
(iv) S ( Reptile )
(ii) Define what its mean by cold-blooded?
Body temperature changes with the enviroment.
Cellophone tape
Glass cover
Thread
Damp filter paper
Anhydrous
calcium
chloride Water
Figure 5
8 A student set up the apparatus as shown in Figure 5 to study the rate of
water. The two sets of apparatus were placed in the pieces of filter paper
in the bell-jar were observed to find out which one dried up first.
(a) (i) Name one variable that was manipulated by the student.
The humidity of air.
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 260 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
Science Form 2
(ii) Name two variables that were kept constant throughout
the experiment.
Volume of water and the surrounding temperature.
(b) What is the purpose of having a beaker containing water in bell-jar
Q?
To increase the humidity of the air in bell-jar Q.
(c) What is the purpose of having a beaker containing water in bell-jar
Q?
To dry up the air in bell-jar P.
(d) Name two factors that affect the rate of evaporation of water
besides the one studied n the experiment above.
(i) The temperature of the surroundings.
(ii) The surface area of the water.
(e) (i) What result that the student can conclude from the
experiment above ?
The rate of evapovation of water increace in air with lower
humidity
(ii) Which piece of filter paper dries up first?
The piece of filter paper in bell-jar P
PMR Module Test Paper_Set 3 261 © Amazing Tunas Enterprise
También podría gustarte
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- List of Chinese Institutions Admitting International Students Under ChineseDocumento8 páginasList of Chinese Institutions Admitting International Students Under ChineseMuhammad Zubair BhattiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Module Form 5 BIOLOGYDocumento111 páginasModule Form 5 BIOLOGYENtertaiment 4lifeAún no hay calificaciones
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Complex Number IdentitiesDocumento3 páginasComplex Number IdentitiesKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- Calculus 4 - Complex Numbers - SolutionsDocumento3 páginasCalculus 4 - Complex Numbers - SolutionsKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- Chap 01 - Set 1Documento8 páginasChap 01 - Set 1Khor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Weekly PlannerDocumento1 páginaWeekly PlannerKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Choice Questions: InstructionDocumento12 páginasMultiple Choice Questions: InstructionKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Chap 02 - Set 2Documento7 páginasChap 02 - Set 2Khor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Modern Printable 2018 Calendar Monthly Planner ApieceofrainbowDocumento12 páginasModern Printable 2018 Calendar Monthly Planner ApieceofrainbowKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Chapter 2 ₪ Nutrition ₪ Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento9 páginasChapter 2 ₪ Nutrition ₪ Multiple Choice QuestionsKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- Chap 01 - Set 2Documento8 páginasChap 01 - Set 2Khor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento7 páginasMultiple Choice QuestionsKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- Homework PaperDocumento2 páginasHomework PaperKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- Adorablest Free Marble Printable PDFDocumento1 páginaAdorablest Free Marble Printable PDFKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- Creating Stdy GuidesDocumento5 páginasCreating Stdy GuidesKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- 100 Days of Productivity PDFDocumento1 página100 Days of Productivity PDFKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Form 3 Chap 7 Exercise Complete)Documento19 páginasScience Form 3 Chap 7 Exercise Complete)Henry Hoe100% (2)
- Graph 5mm A4 PDFDocumento1 páginaGraph 5mm A4 PDFKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Chap 02 - Set 3Documento7 páginasChap 02 - Set 3Khor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento6 páginasMultiple Choice QuestionsKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap 02 Set 1 AnswerDocumento261 páginasChap 02 Set 1 AnswerKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Chap 01 - Set 1Documento8 páginasChap 01 - Set 1Khor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap 01 - Set 2Documento8 páginasChap 01 - Set 2Khor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap 01 - Set 2Documento8 páginasChap 01 - Set 2Khor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Name : Chapter 1 - Scientific InvestigationDocumento10 páginasName : Chapter 1 - Scientific InvestigationRozaini Othman84% (32)
- Chap 01 - Set 2Documento8 páginasChap 01 - Set 2Khor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Form 3 Chap 7 Exercise Complete)Documento19 páginasScience Form 3 Chap 7 Exercise Complete)Henry Hoe100% (2)
- DIY Grid PaperDocumento1 páginaDIY Grid PaperKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- SPM 2017 Math Additional Paper 2 QuestionsDocumento30 páginasSPM 2017 Math Additional Paper 2 QuestionsKhor Han YiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- Stomach: David A. Mahvi, David M. MahviDocumento44 páginasStomach: David A. Mahvi, David M. MahviXuân SơnAún no hay calificaciones
- (Gastrointestinal Function) Analysis Report Card: Actual Testing ResultsDocumento2 páginas(Gastrointestinal Function) Analysis Report Card: Actual Testing ResultsShashikanth RamamurthyAún no hay calificaciones
- NCERT - Exemplar - Life ProcessesDocumento26 páginasNCERT - Exemplar - Life ProcessesRagini BaghelAún no hay calificaciones
- Severe Gastric ImpactionDocumento4 páginasSevere Gastric ImpactionNanda Ayu Cindy KashiwabaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio MCQ TestDocumento23 páginasBio MCQ TestMalay ParikhAún no hay calificaciones
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- Digestive System TGDocumento19 páginasDigestive System TGMadeleine AgiusAún no hay calificaciones
- Du and Ren Meridians 2Documento79 páginasDu and Ren Meridians 2Bryant Villarin Baldivicio100% (1)
- Text Mode - Text Version of The ExamDocumento10 páginasText Mode - Text Version of The ExamAcbel RnucoAún no hay calificaciones
- CBSE Science Notes - Class 10Documento91 páginasCBSE Science Notes - Class 10dinesh_kp764783% (6)
- 3.Ph Partition TheoryDocumento36 páginas3.Ph Partition Theoryamk_19Aún no hay calificaciones
- Digestive System of Silkworm LarvaDocumento17 páginasDigestive System of Silkworm LarvaRaghvendra NiranjanAún no hay calificaciones
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- Space Quest 6 The Spinal Frontier WalkthroughDocumento11 páginasSpace Quest 6 The Spinal Frontier WalkthroughBladeStarAún no hay calificaciones
- Haad 3 Questions GiDocumento16 páginasHaad 3 Questions GiPatpat De Guzman67% (3)
- Demo Digestive DLPDocumento8 páginasDemo Digestive DLPRimuru TempestAún no hay calificaciones
- Sample Case StudyDocumento77 páginasSample Case StudyIgui Malenab RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- Compilation Medsurg PrelimsDocumento29 páginasCompilation Medsurg PrelimsEunice CuñadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Eating Fruit On Empty StomachDocumento5 páginasEating Fruit On Empty StomachCandice Dela Sierra GermataAún no hay calificaciones
- Dissection of The RatDocumento15 páginasDissection of The RatSandeep PM100% (1)
- Biology Revision Notes Part2Documento10 páginasBiology Revision Notes Part2volvanskyAún no hay calificaciones
- Vitamin B12 DeficiencyDocumento2 páginasVitamin B12 DeficiencyFarina AcostaAún no hay calificaciones
- Summative q2 Weeks 1-2Documento21 páginasSummative q2 Weeks 1-2Joehan DimaanoAún no hay calificaciones
- DigestionDocumento44 páginasDigestiontuyuAún no hay calificaciones
- The structure of the small intestine allows digestion and absorptionDocumento24 páginasThe structure of the small intestine allows digestion and absorptionHana ElattarAún no hay calificaciones
- Acute AppendicitisDocumento29 páginasAcute AppendicitisSilhouette Dream100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcome Criteria Actual EvaluationDocumento4 páginasNursing Care Plan Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Goal Nursing Intervention Rationale Outcome Criteria Actual EvaluationPabhat Kumar50% (2)
- Best Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad - Healix HospitalsDocumento14 páginasBest Gastroenterologist in Hyderabad - Healix HospitalsVarsha ReddyAún no hay calificaciones
- Enzymology To Kreb's CycleDocumento34 páginasEnzymology To Kreb's Cycleferdinand padillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Veterinary AcupunctureDocumento305 páginasVeterinary AcupunctureMihalache Alex100% (7)
- A Case Study On AmeobiasisDocumento34 páginasA Case Study On AmeobiasisKhemz Dalde LimAún no hay calificaciones
- Jurnal Double Kontras FIXDocumento33 páginasJurnal Double Kontras FIXWisnuHeriPurwantoAún no hay calificaciones
- GMAT Foundations of Verbal: Practice Problems in Book and OnlineDe EverandGMAT Foundations of Verbal: Practice Problems in Book and OnlineAún no hay calificaciones
- Medical English Dialogues: Clear & Simple Medical English Vocabulary for ESL/EFL LearnersDe EverandMedical English Dialogues: Clear & Simple Medical English Vocabulary for ESL/EFL LearnersAún no hay calificaciones
- The LSAT Law School Admission Test Study Guide Volume I - Reading Comprehension, Logical Reasoning, Writing Sample, and Analytical Reasoning Review Proven Methods for Passing the LSAT Exam With ConfidenceDe EverandThe LSAT Law School Admission Test Study Guide Volume I - Reading Comprehension, Logical Reasoning, Writing Sample, and Analytical Reasoning Review Proven Methods for Passing the LSAT Exam With ConfidenceAún no hay calificaciones
- AP World History: Modern Premium, 2024: Comprehensive Review with 5 Practice Tests + an Online Timed Test OptionDe EverandAP World History: Modern Premium, 2024: Comprehensive Review with 5 Practice Tests + an Online Timed Test OptionCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- AP English Language and Composition Premium, 2024: 8 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeDe EverandAP English Language and Composition Premium, 2024: 8 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeAún no hay calificaciones
- Digital SAT Reading and Writing Practice Questions: Test Prep SeriesDe EverandDigital SAT Reading and Writing Practice Questions: Test Prep SeriesAún no hay calificaciones
- Digital SAT Preview: What to Expect + Tips and StrategiesDe EverandDigital SAT Preview: What to Expect + Tips and StrategiesCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (3)
- AP Computer Science A Premium, 2024: 6 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeDe EverandAP Computer Science A Premium, 2024: 6 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeAún no hay calificaciones