Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Classification and Comparison of Receptor Types
Cargado por
Raymart RaymundoDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Classification and Comparison of Receptor Types
Cargado por
Raymart RaymundoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
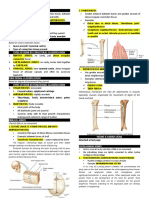
Classification and Comparison of Receptor Types
Type Location Stimulus Modality Adaptability Fibers
Non-encapsulated Receptors
Free nerve endings Epidermis, cornea, Mechanoreceptor Pain (fast), Rapid A delta
dermis, ligaments, joint, Pain (slow), touch C
Capsules, bone, dental (crude),
pulp Pressure,
Heat and cold
Merkel disc Hairless skin Mechanoreceptor Touch Slow A beta
Hair follicle receptors Hairy skin Mechanoreceptor Touch Rapid A beta
Encapsulated Receptors
Meissner’s corpuscle Dermal papillae of Mechanoreceptor Touch Rapid A beta
skin of palm
Pacinian corpuscles Dermis, ligaments, jt. Mechanoreceptor Vibration Rapid A beta
capsules, peritoneum,
ex. genitalia,
Ruffini corpuscles Dermis of hairy skin Mechanoreceptor Stretch Slow A beta
Neuromuscular Skeletal muscles Mechanoreceptor Stretch-muscle length Fast A alpha
spindles A beta
Neurotendinous tendons Mechanoreceptor Compression- muscle Fast A alpha
spindles tension
RECEPTOR ENDINGS
Mechanoreceptors These respond to mechanical deformation
Thermoreceptors These respond to changes in temperature; some receptors respond
to cold and others to heat
Nociceptors These respond to any stimuli that bring about damage to the tissue
Electromagnetic receptors The rods and cones of the eyes are sensitive to changes in light
intensity and wavelength
Chemoreceptors These respond to chemical changes associated with taste and smell
and oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations in the blood
También podría gustarte
- Common Nursing AbbreviationsDocumento8 páginasCommon Nursing AbbreviationsHana-Lou Taquiqui100% (1)
- Neptune Sign House AspectDocumento80 páginasNeptune Sign House Aspectmesagirl94% (53)
- Axial Skeleton SkullDocumento36 páginasAxial Skeleton SkulltiiandiAún no hay calificaciones
- Seizure Care Plan LogDocumento3 páginasSeizure Care Plan LogLevilyn IbañezAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture - 3 Cell Metabolism: Dr. S. Annie Jeyachristy Lecturer, Unit of Biochemistry Faculty of MedicineDocumento15 páginasLecture - 3 Cell Metabolism: Dr. S. Annie Jeyachristy Lecturer, Unit of Biochemistry Faculty of MedicinecheckmateAún no hay calificaciones
- Cancer Biology, a Study of Cancer Pathogenesis: How to Prevent Cancer and DiseasesDe EverandCancer Biology, a Study of Cancer Pathogenesis: How to Prevent Cancer and DiseasesAún no hay calificaciones
- Joints TransesDocumento19 páginasJoints TransesskidamarinkAún no hay calificaciones
- 16.classification of JointsDocumento19 páginas16.classification of JointsdenekeAún no hay calificaciones
- Common Medication Classifications and Adverse/Side Effects: This Is Not An All Inclusive ListDocumento2 páginasCommon Medication Classifications and Adverse/Side Effects: This Is Not An All Inclusive ListHashim Mushtasin RezaAún no hay calificaciones
- Muscles ReviewDocumento32 páginasMuscles ReviewCorine RepatoAún no hay calificaciones
- General Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas ADocumento33 páginasGeneral Orientation To Human Anatomy: Atlas AEmilie ArvidsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricDocumento23 páginasChapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricMariaAún no hay calificaciones
- Major Arteries and Their BranchesDocumento6 páginasMajor Arteries and Their BranchesPriya Farooq100% (1)
- BIO 230 Exam 1 ReviewDocumento31 páginasBIO 230 Exam 1 ReviewRomo AnthonyAún no hay calificaciones
- Brain Attack: StrokeDocumento49 páginasBrain Attack: Strokeceudmd3d100% (1)
- Encephalitis Is An Acute Inflammation of The Brain. Encephalitis With Meningitis IsDocumento4 páginasEncephalitis Is An Acute Inflammation of The Brain. Encephalitis With Meningitis IsDivya GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 1 Study GuideDocumento4 páginasUnit 1 Study GuideNic Alcala100% (1)
- Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Blood Supply To The BrainDocumento6 páginasMedical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes: Blood Supply To The BrainsoyyosoloyoAún no hay calificaciones
- Skeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)Documento10 páginasSkeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)anon_660872041Aún no hay calificaciones
- Anatomy of The HeartDocumento48 páginasAnatomy of The HeartRavi100% (1)
- Session 2 Memorization Hacks in Nursing & Learning About Meal PlanDocumento69 páginasSession 2 Memorization Hacks in Nursing & Learning About Meal Planataraxialli100% (1)
- Digestive Organs and ProcessesDocumento70 páginasDigestive Organs and ProcessesCarol FuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- Diabetes Mellitus: Dr. Sajid Abbas JaffriDocumento37 páginasDiabetes Mellitus: Dr. Sajid Abbas JaffriMaham ZarrinAún no hay calificaciones
- Medical TerminologyDocumento14 páginasMedical TerminologyCharmy UbiñaAún no hay calificaciones
- Energy Efficient Solar-Powered Street Lights Using Sun-Tracking Solar Panel With Traffic Density Monitoring and Wireless Control SystemDocumento9 páginasEnergy Efficient Solar-Powered Street Lights Using Sun-Tracking Solar Panel With Traffic Density Monitoring and Wireless Control SystemIJRASETPublicationsAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio 235 Midterm 1 NotesDocumento53 páginasBio 235 Midterm 1 NotesNita JosephAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio 102 Handout Muscular SysDocumento3 páginasBio 102 Handout Muscular Sysgjsup100% (1)
- Math Curriculum Overview Grades 1 8Documento1 páginaMath Curriculum Overview Grades 1 8GuiselleAún no hay calificaciones
- Servo Magazine 01 2005Documento84 páginasServo Magazine 01 2005dangtq8467% (3)
- Activity Emcee Mid-Year INSET 2021Documento3 páginasActivity Emcee Mid-Year INSET 2021Abegail A. Alangue-Calimag67% (6)
- Axial Skeleton PDFDocumento48 páginasAxial Skeleton PDFSharadambigai SamarasanAún no hay calificaciones
- Human Nervous-SystemDocumento32 páginasHuman Nervous-SystemhwzeeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Healthy Meal Shake Recipes: Recipes Made With French Vanilla (FV) Shake MixDocumento8 páginasHealthy Meal Shake Recipes: Recipes Made With French Vanilla (FV) Shake MixdhruvAún no hay calificaciones
- Bones of The SkullDocumento3 páginasBones of The SkullJethro Floyd QuintoAún no hay calificaciones
- Licensed Practical Nurse, LPN, Nurse Tech, Nurse Aide, Nursing ADocumento4 páginasLicensed Practical Nurse, LPN, Nurse Tech, Nurse Aide, Nursing Aapi-121395809Aún no hay calificaciones
- Formally Resign From My Position As Staff Nurse. I Am Issuing My Notice of Resignation and My Last Day of Work Will Be On July 31, 2019Documento1 páginaFormally Resign From My Position As Staff Nurse. I Am Issuing My Notice of Resignation and My Last Day of Work Will Be On July 31, 2019Dave Zamiel ArellanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento46 páginasHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyBegumHazinAún no hay calificaciones
- Analyzing and Defining Medical TermsDocumento7 páginasAnalyzing and Defining Medical Termsmarcus colgroveAún no hay calificaciones
- Anatomy and Physiology Reviewer - MTMS 2020Documento4 páginasAnatomy and Physiology Reviewer - MTMS 2020Myrielle Trisha SAYREAún no hay calificaciones
- Kimberly F. v. Mary Hitchcock, 1st Cir. (1993)Documento34 páginasKimberly F. v. Mary Hitchcock, 1st Cir. (1993)Scribd Government DocsAún no hay calificaciones
- 6 SURGERY II 6 - Pediatric UrologyDocumento6 páginas6 SURGERY II 6 - Pediatric UrologyDeann RoscomAún no hay calificaciones
- Blood Test Reference Ranges ChartDocumento3 páginasBlood Test Reference Ranges ChartQaSeh ISnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Endocrine Disorders Julie Mann, NP - Case StudyDocumento10 páginasEndocrine Disorders Julie Mann, NP - Case Studysimonedarling75% (4)
- Circulatory SystemDocumento2 páginasCirculatory SystemcatchivanAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT - 9 Digestive SystemDocumento187 páginasUNIT - 9 Digestive SystemChandan ShahAún no hay calificaciones
- Genes For All DisordersDocumento86 páginasGenes For All Disordersvenkyreddy97Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Anatomy SCDocumento92 páginas1 Anatomy SCAmber Ian Bouie Divina-DayaoAún no hay calificaciones
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento14 páginasAnatomy and PhysiologyDonita Meña LaroyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fragile X SyndromeDocumento11 páginasFragile X SyndromeMartinAún no hay calificaciones
- Treatments for schizophrenia can improve livesDocumento3 páginasTreatments for schizophrenia can improve livesFarhana SobriAún no hay calificaciones
- Diabetes WorksheetDocumento2 páginasDiabetes WorksheetAstrid TelloAún no hay calificaciones
- Patient Care SkillsDocumento15 páginasPatient Care SkillsIts John100% (1)
- 3.7 Organ Transplantation PDFDocumento3 páginas3.7 Organ Transplantation PDFbrownieallennAún no hay calificaciones
- Chronic Inflammation Causes, Features and EffectsDocumento24 páginasChronic Inflammation Causes, Features and EffectsTommys100% (1)
- Blood PanelsDocumento7 páginasBlood Panelslisalov100% (1)
- Kines Anatomy Ch. 14-16Documento36 páginasKines Anatomy Ch. 14-16icedragon727Aún no hay calificaciones
- List of cranial nerves and their functionsDocumento2 páginasList of cranial nerves and their functionsKay Lumpas Cruda100% (1)
- Blood and Its Components-NotesDocumento10 páginasBlood and Its Components-NotesKelvin RequenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Study Guide QuestionsDocumento4 páginasStudy Guide QuestionszaidaAún no hay calificaciones
- Memory Mantra: Learn 10 Times FasterDocumento13 páginasMemory Mantra: Learn 10 Times FasterDevesh JoshiAún no hay calificaciones
- Myocardial Infarction MIDocumento23 páginasMyocardial Infarction MIأبو محمدAún no hay calificaciones
- Medical TerminologyDocumento107 páginasMedical TerminologyonmcvAún no hay calificaciones
- Technique: Preventing and Controlling Infections in Home Care and HospiceDocumento7 páginasTechnique: Preventing and Controlling Infections in Home Care and HospiceOlaMostafaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nursing Care for Loss, Grief and DeathDocumento4 páginasNursing Care for Loss, Grief and DeathNina Anne ParacadAún no hay calificaciones
- Baby Doctor's Guide To Anatomy and Physiology: Science for Kids Series - Children's Anatomy & Physiology BooksDe EverandBaby Doctor's Guide To Anatomy and Physiology: Science for Kids Series - Children's Anatomy & Physiology BooksAún no hay calificaciones
- Pedestrian Safety in Road TrafficDocumento9 páginasPedestrian Safety in Road TrafficMaxamed YusufAún no hay calificaciones
- Tracer Survey of Bsit Automotive GRADUATES BATCH 2015-2016 AT Cebu Technological UniversityDocumento8 páginasTracer Survey of Bsit Automotive GRADUATES BATCH 2015-2016 AT Cebu Technological UniversityRichard Somocad JaymeAún no hay calificaciones
- Identifying Research ProblemsDocumento29 páginasIdentifying Research ProblemsEdel Borden PaclianAún no hay calificaciones
- Mosek UserguideDocumento81 páginasMosek UserguideadethroAún no hay calificaciones
- IS BIOCLIMATIC ARCHITECTURE A NEW STYLE OF DESIGNDocumento5 páginasIS BIOCLIMATIC ARCHITECTURE A NEW STYLE OF DESIGNJorge DávilaAún no hay calificaciones
- ASTM C 136 Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse Aggregates (D)Documento5 páginasASTM C 136 Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse Aggregates (D)Yasir DharejoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sublime QR CodeDocumento6 páginasSublime QR Codejeff_sauserAún no hay calificaciones
- RBI and Maintenance For RCC Structure SeminarDocumento4 páginasRBI and Maintenance For RCC Structure SeminarcoxshulerAún no hay calificaciones
- 62046PSYCHICSDocumento1 página62046PSYCHICSs0hpokc310Aún no hay calificaciones
- Remapping The Small Things PDFDocumento101 páginasRemapping The Small Things PDFAme RaAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Prepare Squash Specimen Samples For Microscopic ObservationDocumento3 páginasHow To Prepare Squash Specimen Samples For Microscopic ObservationSAMMYAún no hay calificaciones
- Subject and Power - FoucaultDocumento10 páginasSubject and Power - FoucaultEduardo EspíndolaAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 1016@j Ultras 2016 09 002Documento11 páginas10 1016@j Ultras 2016 09 002Ismahene SmahenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2: Science, Technology, and Society in Human Condition Lesson 1: Human FlourishingDocumento5 páginasChapter 2: Science, Technology, and Society in Human Condition Lesson 1: Human FlourishingJcAún no hay calificaciones
- Writing and Presenting A Project Proposal To AcademicsDocumento87 páginasWriting and Presenting A Project Proposal To AcademicsAllyAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is Architecture?Documento17 páginasWhat Is Architecture?Asad Zafar HaiderAún no hay calificaciones
- Mind MapDocumento1 páginaMind Mapjebzkiah productionAún no hay calificaciones
- CIPP ModelDocumento36 páginasCIPP ModelIghfir Rijal TaufiqyAún no hay calificaciones
- Omega Fluid PDFDocumento2 páginasOmega Fluid PDFapatzinfedAún no hay calificaciones
- Laser Plasma Accelerators PDFDocumento12 páginasLaser Plasma Accelerators PDFAjit UpadhyayAún no hay calificaciones
- Roadmap For SSC CGLDocumento11 páginasRoadmap For SSC CGLibt seoAún no hay calificaciones
- RealPOS 70Documento182 páginasRealPOS 70TextbookAún no hay calificaciones
- Structural Testing Facilities at University of AlbertaDocumento10 páginasStructural Testing Facilities at University of AlbertaCarlos AcnAún no hay calificaciones
- HAU Theology 103 Group Goal Commitment ReportDocumento6 páginasHAU Theology 103 Group Goal Commitment ReportEM SagunAún no hay calificaciones
- MGMT 410 Book ReportDocumento1 páginaMGMT 410 Book ReportLester F BoernerAún no hay calificaciones