Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Sbl100 Laboratory
Cargado por
Kuldeep KumarDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Sbl100 Laboratory
Cargado por
Kuldeep KumarCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
SBL100 LABORATORY
Name & Entry No.: Wednesday 1-3 slot
1) Jay Prakash Patidar (2015CE10331)
2) Kuldeep Kumar Meena (2015ce10335)
AIM: To understand how to visualize and/or measure biomolecules
in this case proteins.
INTRODUCTION:
General introduction: Proteins are large biomolecules, or
macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid
residues. CBB Dye (Coomassie Brilliant Blue ) used to visualize proteins
via a regressive staining approach in which gels are saturated with dye
and then destained with an aqueous solution.
Principal: The Bradford assay, a colorimetric protein assay, is based on
an absorbance shift of the dye Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250. Under
acidic conditions the red form of the dye is converted into its bluer
form, binding to the protein being assayed. The dye forms a strong,
noncovalent complex with the protein's carboxyl group by Van der
Waals force and amino group through electrostatic interactions.
During the formation of this complex, the red form of Coomassie dye
first donates its free electron to the ionizable groups on the protein,
which causes a disruption of the protein's native state, consequently
exposing its hydrophobic pockets. These pockets in the
protein's tertiary structure bind non-covalently to the non-polar region
of the dye via the first bond interaction (van der Waals forces) which
position the positive amine groups in proximity with the negative
charge of the dye. The bond is further strengthened by the second
bond interaction between the two, the ionic interaction. The binding of
the protein stabilizes the blue form of the Coomassie dye; thus the
amount of the complex present in solution is a measure for the protein
concentration, and can be estimated by use of an absorbance reading.
*Beer Lambert law: BeerLambertBouguer law relates
the attenuation of light to the properties of the material through which
the light is travelling. It is linear relation between absorbance and
concentration of an absorbing species.
MATERIAL AND REAGENTS USED:
Material Required:
1) Mortar pestle
2) Beaker
3) Micro pipet
Reagent required:
1) BSA(Bovine serum albumin)
2) CBB Dye(Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250)
3) Buffer(PBS-Phosphate-buffered saline, PEB-Protein Extraction
Buffer)
4) Ethanol
5) Water
METHEDOLOGY:
1) First find the standard plot for absorbance and concentration.
2) Find the absorbance of unknown solution.
3) Using the standard plot find concentration of protein.
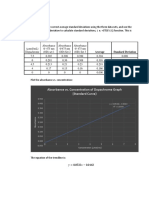
OBSERVATION AND RESULTS:
Observation-
Conc of BSA Vol of BSA (ul) Vol of PBS(ul) Abs.
(ug/ml)
0 0 400 0
5 10 390 0.192
10 20 380 0.338
15 30 370 0.406
20 40 360 0.54
25 50 350 0.633
30 60 340 0.653
35 70 330 0.703
40 80 320 0.735
Abs Reading of Leaf-
Fresh = 0.244
At Room temperature = 0.189
At 40C = 0.179
Standard plot-
Abs V/s Conc
1
0.9 y = 0.0217x
0.8 R = 0.8656
0.7
0.6
Abs.
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45
Concntration of BSA(ug/ml)
CALCULATION-
Y=0.0217x
Abs= 0.0217 Conc.
Dilution factor (DF)=(Final Volume)/ (Initial Volume)=(2000)/10 = 200
Conc. Of Protein = X * 200
Protein Abs Concentration(ug/ml)
Fresh condition 0.244 2248.82
At RT 0.189 1741.94
At 40C 0.179 1649.77
Order of Protein Conc.
Fresh> RT > 40C
Generally order should be Fresh > 40C >RT
But our order differ because we kept the protein extract for 2 weeks and it get
contaminated so protein conc. At room temp. increased w.r.t. 40C.
También podría gustarte
- CamScanner document scansDocumento33 páginasCamScanner document scansNavish Goyal100% (1)
- CLL110 MajorDocumento2 páginasCLL110 MajorManisha MishraAún no hay calificaciones
- BIOL1181 and ONPS2340 Milk AssayDocumento6 páginasBIOL1181 and ONPS2340 Milk Assayamal_postAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Practical XIIDocumento18 páginasChemistry Practical XIISiddharth SharanAún no hay calificaciones
- Mi LifeStyle Marketing Global Private LimitedDocumento10 páginasMi LifeStyle Marketing Global Private LimitedAdrito PramanikAún no hay calificaciones
- Company Info - Print Financials PDFDocumento2 páginasCompany Info - Print Financials PDFutkarsh varshneyAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual k11mk4 enDocumento83 páginasManual k11mk4 enВесна РадинAún no hay calificaciones
- Balance Sheet PDFDocumento1 páginaBalance Sheet PDFMikhil Pranay SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry Shortlisting PDFDocumento3 páginasChemistry Shortlisting PDFShafia BatoolAún no hay calificaciones
- Eicher Motors BSDocumento2 páginasEicher Motors BSVaishnav SunilAún no hay calificaciones
- April 2022 - BoltDocumento68 páginasApril 2022 - BoltbhanuAún no hay calificaciones
- Insights On Basic Electronics EngineeringDocumento277 páginasInsights On Basic Electronics EngineeringShubham SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ragnarok X SEA Monster Leveling GuideDocumento19 páginasRagnarok X SEA Monster Leveling Guidemasedoo firdausAún no hay calificaciones
- Custom Actions DevelopmentDocumento24 páginasCustom Actions DevelopmentDuy Nguyen HoAún no hay calificaciones
- ACR - Plugin Maxis Cheating Fix ReadmeDocumento1 páginaACR - Plugin Maxis Cheating Fix ReadmeAshani Dilshani ChelliahAún no hay calificaciones
- NBP Online Challan For Admission BZU MultanDocumento1 páginaNBP Online Challan For Admission BZU MultanAmjid Afridi100% (1)
- BSC MarksheetDocumento5 páginasBSC MarksheetxyzAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 - MFRS 116Documento60 páginasChapter 1 - MFRS 116Muhammad HazlamiAún no hay calificaciones
- BitConnect SheetDocumento144 páginasBitConnect SheetAchmad Ichsan FauziAún no hay calificaciones
- UAF CGPA CalculatorDocumento18 páginasUAF CGPA CalculatorTalat Mehmood DogarAún no hay calificaciones
- Self Billing Agreement PDFDocumento1 páginaSelf Billing Agreement PDFgabrielAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem 161.1 Exer 3.2Documento7 páginasChem 161.1 Exer 3.2Julie Ann FelicesAún no hay calificaciones
- YesssDocumento6 páginasYesssashAún no hay calificaciones
- Report - Cation ExchangerDocumento5 páginasReport - Cation ExchangerMai HoangAún no hay calificaciones
- SpecDocumento8 páginasSpecJirapat ThonglekpechAún no hay calificaciones
- Method For Testing Trace Heavy Metal Concentration in Industrial Wastewater by GF AADocumento6 páginasMethod For Testing Trace Heavy Metal Concentration in Industrial Wastewater by GF AADaniel Camilo CarreñoAún no hay calificaciones
- Results and Data CMT 463 Exp 3Documento7 páginasResults and Data CMT 463 Exp 3IzzyanIsaAún no hay calificaciones
- Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy: John Kristoffer M. Japzon Ronell Q. LeeDocumento36 páginasAtomic Absorption Spectroscopy: John Kristoffer M. Japzon Ronell Q. LeeIbrahim BouniAún no hay calificaciones
- Protein Assay by The Bradford MethodDocumento10 páginasProtein Assay by The Bradford MethodMichelle79% (14)
- Protein Estimation ReportDocumento3 páginasProtein Estimation ReportSudip MajiAún no hay calificaciones
- Separating Acetic Acid and Water by DistillationDocumento8 páginasSeparating Acetic Acid and Water by DistillationSuzanne Clariz M. BaltazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Foster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Documento7 páginasFoster Cole 101230199 Malaïka Zarrouki 2021-01-29Cole FosterAún no hay calificaciones
- BSG Practical Report 1Documento10 páginasBSG Practical Report 1Chai MichelleAún no hay calificaciones
- Spectrophotometric Study of Complexes by Job's Method: Report of The Minor UGC Project EntitledDocumento19 páginasSpectrophotometric Study of Complexes by Job's Method: Report of The Minor UGC Project EntitledM Irfan Khan100% (1)
- Analytical Chemistry: Calibration TechniquesDocumento24 páginasAnalytical Chemistry: Calibration TechniquesSENG LEE LIMAún no hay calificaciones
- Acid-Base Indicators Spectrophotometric Ka LabDocumento6 páginasAcid-Base Indicators Spectrophotometric Ka Labmuskaan0% (2)
- Lab AnalysisDocumento4 páginasLab AnalysisErnestasBlaževičAún no hay calificaciones
- Zoe Garwood Lab 7 Affinity ChromatographyDocumento5 páginasZoe Garwood Lab 7 Affinity ChromatographyZoe A GarwoodAún no hay calificaciones
- Figures and TablesDocumento3 páginasFigures and TablesAngeline RabuyoAún no hay calificaciones
- BIOL1177 SM1 2020 Session 2 ProformaDocumento7 páginasBIOL1177 SM1 2020 Session 2 ProformaThisarieAún no hay calificaciones
- Exercise 1: Spectrochemical Analysis: BE132P Instrumentation in Biological Engineering 1Documento7 páginasExercise 1: Spectrochemical Analysis: BE132P Instrumentation in Biological Engineering 1Bernadette Virola CuevasAún no hay calificaciones
- LDH OutlineDocumento7 páginasLDH OutlinejahnAún no hay calificaciones
- Title Spectrophotometric Determination oDocumento6 páginasTitle Spectrophotometric Determination oAmualaw BiraraAún no hay calificaciones
- E4 Spectrophotometric Protein AssaysDocumento25 páginasE4 Spectrophotometric Protein AssaysGlenn Vincent TumimbangAún no hay calificaciones
- Determinar El Peso Molecular Del Reservorio: Datos Del Reservorio Valor Unidad Composicion Molar (%) M Olar PM (Lb-Mol)Documento3 páginasDeterminar El Peso Molecular Del Reservorio: Datos Del Reservorio Valor Unidad Composicion Molar (%) M Olar PM (Lb-Mol)Jimmy JohnsAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 3: Ternary Phase Diagram (Liquid-Liquid Extraction)Documento15 páginasExperiment 3: Ternary Phase Diagram (Liquid-Liquid Extraction)Noor Nasuha Noor AriffinAún no hay calificaciones
- Practical 1 - Spectrophotometry TechniquesDocumento13 páginasPractical 1 - Spectrophotometry TechniquesDhanen DranAún no hay calificaciones
- Name: Navhaya L.T Student Number: 201927903 Course Code: BCH223 Practical No: 1 Title: Polyphenol Oxidase Activity of Bananas Lecturer: NT MazombaDocumento11 páginasName: Navhaya L.T Student Number: 201927903 Course Code: BCH223 Practical No: 1 Title: Polyphenol Oxidase Activity of Bananas Lecturer: NT MazombaLeo VandikAún no hay calificaciones
- Konversi Satuan HardnessDocumento9 páginasKonversi Satuan HardnessFaiz NaufalAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 1: The Visible Spectra of Soft Drinks: A. Pre-Laboratory QuestionsDocumento5 páginasExperiment 1: The Visible Spectra of Soft Drinks: A. Pre-Laboratory QuestionsMuhd Mirza HizamiAún no hay calificaciones
- Adsorption From Solutions, Acetic Acid On Charcoal: Lorenz John T. ChuDocumento7 páginasAdsorption From Solutions, Acetic Acid On Charcoal: Lorenz John T. ChuZhu Chen ChuanAún no hay calificaciones
- CaffeieneDocumento8 páginasCaffeieneHawta AbdullaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutri Meta Lab 2 CombinedDocumento16 páginasNutri Meta Lab 2 CombinedvlcjAún no hay calificaciones
- BSL BLOK B HASIL ANALISA WQ, 19 Februari 2024Documento1 páginaBSL BLOK B HASIL ANALISA WQ, 19 Februari 2024Feny GunawanAún no hay calificaciones
- 01.ex Name Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron.Documento4 páginas01.ex Name Spectrophotometric Determination of Iron.Md Sohel RanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Exercicis UVvis - SoluciãDocumento17 páginasExercicis UVvis - SoluciãclerrosseAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment No: 6: Feed Tanks Batch ReactorDocumento5 páginasExperiment No: 6: Feed Tanks Batch Reactorfareeha saeedAún no hay calificaciones
- Korbach and Stewart benzene hydrogenation rates and conversionsDocumento4 páginasKorbach and Stewart benzene hydrogenation rates and conversionsRicardo HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Water Production and DisposalDocumento10 páginasWater Production and DisposalVenkataramana AvulaAún no hay calificaciones
- ENZYMOLOGYDocumento41 páginasENZYMOLOGYbarbie.monster89Aún no hay calificaciones
- Power Quality FACTsDocumento5 páginasPower Quality FACTsshashiAún no hay calificaciones
- Air Pollution: Types of PollutionsDocumento14 páginasAir Pollution: Types of PollutionsJia Ping Jia PingAún no hay calificaciones
- Concrete beam rebar tableDocumento1 páginaConcrete beam rebar tablesikandar abbasAún no hay calificaciones
- G.L.Bajaj Institute of Technology & Management Greater NoidaDocumento3 páginasG.L.Bajaj Institute of Technology & Management Greater NoidaShubhanshu RanjanAún no hay calificaciones
- 6 Exercises To Heal Diastasis Recti And Get Rid Of Your Mommy TummyDocumento9 páginas6 Exercises To Heal Diastasis Recti And Get Rid Of Your Mommy TummyLinda Pride100% (3)
- Design & Optimization of Bed Material Screening Machine For AFBC BoilerDocumento11 páginasDesign & Optimization of Bed Material Screening Machine For AFBC BoilermansukhAún no hay calificaciones
- DTXM UsDocumento2 páginasDTXM UsvandalizerertAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Increase Flow In Lamy Fountain PensDocumento21 páginasHow To Increase Flow In Lamy Fountain PensPHILL.MARTIN3356Aún no hay calificaciones
- Snow White Is A Gangster (MHSG Sequel) COMPLETEDDocumento459 páginasSnow White Is A Gangster (MHSG Sequel) COMPLETEDReign Candarell67% (3)
- Drug Dosing in Obese Patients: A Dilemma: International Journal of Advances in PharmaceuticsDocumento7 páginasDrug Dosing in Obese Patients: A Dilemma: International Journal of Advances in PharmaceuticsYuppie RajAún no hay calificaciones
- Micro Programmable Logic Controller: User's ManualDocumento643 páginasMicro Programmable Logic Controller: User's Manualcasmadi casmadiAún no hay calificaciones
- Annual medical screening and emergency services includedDocumento17 páginasAnnual medical screening and emergency services includedAlina OprinaAún no hay calificaciones
- ITP - Data & Telephone InstallationDocumento6 páginasITP - Data & Telephone InstallationGultom Juliana LiliesAún no hay calificaciones
- 1999 Reneker Fong Chun Beaded Nanofibers Formed During ElectrospinningDocumento8 páginas1999 Reneker Fong Chun Beaded Nanofibers Formed During ElectrospinningEub EuAún no hay calificaciones
- BSIT 3E- BA FL101-FOREIGN LANGUAGE Activity No. 6 Translate English to PinyinDocumento2 páginasBSIT 3E- BA FL101-FOREIGN LANGUAGE Activity No. 6 Translate English to PinyinCel Rellores SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- AdverbsDocumento7 páginasAdverbslatifa hachemiAún no hay calificaciones
- Hydrogen Station Standards Workshop ReviewDocumento24 páginasHydrogen Station Standards Workshop ReviewDiana DhominicAún no hay calificaciones
- Jenima MSC - Bio1-TechDocumento4 páginasJenima MSC - Bio1-TechPavan KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 The D and F Block ElementsDocumento25 páginasChapter 8 The D and F Block Elementspriyanka kAún no hay calificaciones
- Ancient Greek Ideas On Elements and AtomDocumento23 páginasAncient Greek Ideas On Elements and AtomEmerlyn PanganibanAún no hay calificaciones
- My ScramjetDocumento13 páginasMy ScramjetHimanshu GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Danto - Basic ActionsDocumento9 páginasDanto - Basic ActionsIngrid NicAún no hay calificaciones
- Black Metal Distortion Guitar PatchDocumento1 páginaBlack Metal Distortion Guitar PatchPedro Carmelo SoaresAún no hay calificaciones
- SAUDI ARAMCO PNEUMATIC TEST CHECKLISTDocumento5 páginasSAUDI ARAMCO PNEUMATIC TEST CHECKLISTkarthi51289Aún no hay calificaciones
- 404 D22 TAG1800 TPD1711 E5 Technical Data SheetDocumento11 páginas404 D22 TAG1800 TPD1711 E5 Technical Data SheetOmar Orlando Rincon FigueroaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lexical Expressive Means and Stylistic DevicesDocumento27 páginasLexical Expressive Means and Stylistic DevicesTania ShramAún no hay calificaciones
- Enthalpy MethodDocumento15 páginasEnthalpy MethodSubodh MhatreAún no hay calificaciones
- Mail From Yoichi Shimatsu Regarding Nano Travel 04 Jan 2022Documento4 páginasMail From Yoichi Shimatsu Regarding Nano Travel 04 Jan 2022tavdeash238Aún no hay calificaciones
- SWIMMING POOL CERTIFICATION GUIDEDocumento12 páginasSWIMMING POOL CERTIFICATION GUIDEjohanesAún no hay calificaciones
- University of Calgary: New Measurement-While-Drilling Surveying Technique Utilizing Sets of Fiber Optic Rotation SensorsDocumento289 páginasUniversity of Calgary: New Measurement-While-Drilling Surveying Technique Utilizing Sets of Fiber Optic Rotation SensorsJames ConnerAún no hay calificaciones