Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Part - IV Class - XII Physics Chapter - : 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Cargado por
royalrajoria4912Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Part - IV Class - XII Physics Chapter - : 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Cargado por
royalrajoria4912Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
Part IV
Class XII Physics
Chapter 9 Ray optics and optical instruments
Q30 : (a) At what distance should the lens be held from the figure in
Exercise 9.29 in order to view the squares distinctly with the maximum possible magnifying
power?
(b) What is the magnification in this case?
(c) Is the magnification equal to the magnifying power in this case?
Explain.
Q31 : What should be the distance between the object in Exercise 9.30 and the magnifying glass if
the virtual image of each square in the figure is to have an area of 6.25 mm2. Would you be
able to see the squares distinctly with your eyes very close to the magnifier?
[Note: Exercises 9.29 to 9.31 will help you clearly understand the difference between
magnification in absolute size and the angular magnification (or magnifying power) of an
instrument.]
Q32 : Answer the following questions:
(a) The angle subtended at the eye by an object is equal to the angle subtended at the eye by
the virtual image produced by a magnifying glass. In what sense then does a magnifying glass
provide angular magnification?
(b) In viewing through a magnifying glass, one usually positions one's eyes very close to the
lens. Does angular magnification change if the eye is moved back?
(c) Magnifying power of a simple microscope is inversely proportional to the focal length of
the lens. What then stops us from using a convex lens of smaller and smaller focal length and
achieving greater and greater magnifying power?
(d) Why must both the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope have short
focal lengths?
(e) When viewing through a compound microscope, our eyes should be positioned not on the
eyepiece but a short distance away from it for best viewing. Why? How much should be that
short distance between the eye and eyepiece?
Q33 : An angular magnification (magnifying power) of 30X is desired using an objective of focal
length 1.25 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5 cm. How will you set up the compound
microscope?
Q34 : An angular magnification (magnifying power) of 30X is desired using an objective of focal
length 1.25 cm and an eyepiece of focal length 5 cm. How will you set up the compound
microscope?
Q35 : A small telescope has an objective lens of focal length 140 cm and an eyepiece of focal length
5.0 cm. What is the magnifying power of the telescope for viewing distant objects when
(a) the telescope is in normal adjustment (i.e., when the final image is at infinity)?
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
(b) the final image is formed at the least distance of distinct vision (25 cm)?
Q36 : (a) For the telescope described in Exercise 9.34 (a), what is the separation between the
objective lens and the eyepiece?
(b) If this telescope is used to view a 100 m tall tower 3 km away, what is the height of the
image of the tower formed by the objective lens?
(c) What is the height of the final image of the tower if it is formed at 25 cm?
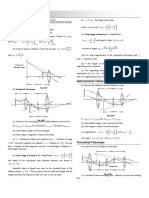
Q37 : A Cassegrain telescope uses two mirrors as shown in Fig. 9.33. Such a telescope is built with
the mirrors 20 mm apart. If the radius of curvature of the large mirror is 220 mm and the
small mirror is 140 mm, where will the final image of an object at infinity be?
Q38 : Light incident normally on a plane mirror attached to a galvanometer coil retraces
backwards as shown in Fig. 9.36. A current in the coil produces a deflection of 3.5of the
mirror. What is the displacement of the reflected spot of light on a screen placed 1.5 m away?
Q39 : Figure 9.37 shows an equiconvex lens (of refractive index 1.50) in contact with a liquid layer
on top of a plane mirror. A small needle with its tip on the principal axis is moved along the
axis until its inverted image is found at the position of the needle. The distance of the needle
from the lens is measured to be 45.0 cm. The liquid is removed and the experiment is
repeated. The new distance is measured to be 30.0 cm. What is the refractive index of the
liquid?
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
También podría gustarte
- Optics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionDe EverandOptics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5)
- Optical InstrumentDocumento4 páginasOptical InstrumentBAAP ka papaAún no hay calificaciones
- OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS TestDocumento2 páginasOPTICAL INSTRUMENTS TestBee PAún no hay calificaciones
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Only (3 Marks) of OPTICSDocumento4 páginasCBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Only (3 Marks) of OPTICSPramit RanjanAún no hay calificaciones
- XII PHYSICS Sample Paper For CBSEDocumento2 páginasXII PHYSICS Sample Paper For CBSEHari Om SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Optics 1Documento3 páginasOptics 1Pubg AppleAún no hay calificaciones
- Ray Optics AssignmentDocumento3 páginasRay Optics AssignmentKamya SriAún no hay calificaciones
- Optical Instrument (Numerical)Documento5 páginasOptical Instrument (Numerical)navrosepreetsingh8a4hhps14Aún no hay calificaciones
- 9 RayopticsDocumento8 páginas9 RayopticsViredra Vikash C MAún no hay calificaciones
- OpticsDocumento29 páginasOpticsVr MageshAún no hay calificaciones
- Worksheet-1 (Ray Optics)Documento4 páginasWorksheet-1 (Ray Optics)Ritika SunilAún no hay calificaciones
- Worksheet CBSE Class 10 LightDocumento6 páginasWorksheet CBSE Class 10 Lightroythomasc50% (4)
- Level 1: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Revision Work Sheet - 5Documento3 páginasLevel 1: Ray Optics and Optical Instruments Revision Work Sheet - 5RaziaAún no hay calificaciones
- Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Documento7 páginasLight - Reflection and Refraction Part 2Saji JayarajAún no hay calificaciones
- Asian-School Light Reflection and Refraction Sample Paper 2019Documento2 páginasAsian-School Light Reflection and Refraction Sample Paper 2019Vineet SierraAún no hay calificaciones
- Light-NCERT Notes Class 10Documento2 páginasLight-NCERT Notes Class 10akashraj7713Aún no hay calificaciones
- Test Optical InstrumentDocumento1 páginaTest Optical Instrumentp03947806Aún no hay calificaciones
- Optics Important QuestionsDocumento25 páginasOptics Important Questionsmohitkumarr2411Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ray Optics PDFDocumento36 páginasRay Optics PDFHrishikesh BhatAún no hay calificaciones
- 12 Phy Assignment Ray Optics 1695915852Documento3 páginas12 Phy Assignment Ray Optics 1695915852Pratibaa LAún no hay calificaciones
- Phys ExerciseDocumento32 páginasPhys ExerciseJay Bwoy Ug100% (1)
- ISC Board Questions On Ray Optics Grade 12Documento6 páginasISC Board Questions On Ray Optics Grade 12iraAún no hay calificaciones
- Worksheet-22 Reflection & Refraction of LightDocumento2 páginasWorksheet-22 Reflection & Refraction of Lightanjalitashu01Aún no hay calificaciones
- Phy - Wave OpticsDocumento2 páginasPhy - Wave Opticsdebadrita senguptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Quality Questions On Ray and Wave OpticsDocumento3 páginasQuality Questions On Ray and Wave OpticsLeonard PhilipAún no hay calificaciones
- Ray Optics: Previous Years' Board QuestionsDocumento5 páginasRay Optics: Previous Years' Board QuestionsRudra SathwaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Ray Optics Questions STD Xii Holiday HWDocumento5 páginasRay Optics Questions STD Xii Holiday HWamritmohanty1000Aún no hay calificaciones
- LIGHT-PAST PAPER QnsDocumento6 páginasLIGHT-PAST PAPER QnsARSHAD JAMIL100% (1)
- Ray OpticsDocumento11 páginasRay OpticsxkryxxzAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Part 2 E.V PDFDocumento5 páginasPhysics Part 2 E.V PDFShira YukiAún no hay calificaciones
- OpticsDocumento6 páginasOpticsAshok PradhanAún no hay calificaciones
- GHJGJHDocumento9 páginasGHJGJHKaran RanaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 - Light Reflection and Refraction (Prashant Kirad)Documento11 páginas1 - Light Reflection and Refraction (Prashant Kirad)Kshitiz sharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Exam - OpticsDocumento6 páginasExam - OpticsMahbubur Bhuiyan100% (1)
- Homework+5 20220607Documento1 páginaHomework+5 20220607許廷睿Aún no hay calificaciones
- XII Physics Paper CBSEDocumento4 páginasXII Physics Paper CBSESanjna ParikhAún no hay calificaciones
- Ay Optics Practice QuesDocumento9 páginasAy Optics Practice QuesBAAP ka papaAún no hay calificaciones
- 5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFDocumento45 páginas5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFPiyushAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics UT6Documento1 páginaPhysics UT6Harsh YadavAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics XII CH 9 CASE STUDY Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocumento15 páginasPhysics XII CH 9 CASE STUDY Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsNjan KL16么PorottaAún no hay calificaciones
- Extra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Documento5 páginasExtra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Zoha AzizAún no hay calificaciones
- Competancy Based Quesions - Ray OpticsDocumento8 páginasCompetancy Based Quesions - Ray OpticsmapuclouddigitalworldAún no hay calificaciones
- Wave Optics QBDocumento2 páginasWave Optics QBshivya aroraAún no hay calificaciones
- 10-Light - Reflection and RefractionDocumento3 páginas10-Light - Reflection and RefractionKrsna JaiswalAún no hay calificaciones
- g10 ScienceDocumento21 páginasg10 ScienceMOHAMMADMUNAWARSAIFAún no hay calificaciones
- PhysicsDocumento2 páginasPhysicschamp delacruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Open Book Test - OpticsDocumento9 páginasOpen Book Test - OpticsGagandeep WadhawanAún no hay calificaciones
- Group Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkDocumento5 páginasGroup Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkMadhvi ShardaAún no hay calificaciones
- FHSC1034 Tutorial 6Documento2 páginasFHSC1034 Tutorial 6Krishnaah SmuglerzzAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial 1 Intro To PhotonicsDocumento4 páginasTutorial 1 Intro To Photonicsamitgh88Aún no hay calificaciones
- OPTICSDocumento16 páginasOPTICSSoumyajeet PradhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Expt 4. Reflection of Light ConclusionDocumento2 páginasExpt 4. Reflection of Light ConclusionKiara De Leon67% (3)
- Revision Assignment - Reflection and RefractionDocumento5 páginasRevision Assignment - Reflection and RefractionanaythesuperheroAún no hay calificaciones
- UP2 HW CH 36 S Image FormationDocumento8 páginasUP2 HW CH 36 S Image FormationVanillasky06Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ray Optics and Optical Instruments: Very Short Answer Type QuestionsDocumento5 páginasRay Optics and Optical Instruments: Very Short Answer Type QuestionsAvni RaghavAún no hay calificaciones
- 2224 - Physics (IIT 4)Documento4 páginas2224 - Physics (IIT 4)1harshikaAún no hay calificaciones
- 10th Question From Board Paper Light - PrintDocumento2 páginas10th Question From Board Paper Light - PrintManash SinghaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sample Paper - 2011 Class - X Subject - Physics Light: Reflection and RefractionDocumento2 páginasSample Paper - 2011 Class - X Subject - Physics Light: Reflection and RefractionArslaan MD BelalAún no hay calificaciones
- Light - Reflection and Refraction: Questions To PracticeDocumento4 páginasLight - Reflection and Refraction: Questions To PracticeH E Man ShuAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebraic Expressions and Algebraic Formulas Algebraic ManipulationDocumento3 páginasAlgebraic Expressions and Algebraic Formulas Algebraic Manipulationroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- 12 Maths Key Notes CH 01 Relations and FunctionsDocumento2 páginas12 Maths Key Notes CH 01 Relations and Functionsroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Set - 001Documento10 páginasPractice Set - 001royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quant 001Documento5 páginasQuant 001royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- Wave Optics NcertDocumento35 páginasWave Optics NcertAbhijit SanjeevAún no hay calificaciones
- Cbse Class 9 Science Solved Practice Paper Set IDocumento19 páginasCbse Class 9 Science Solved Practice Paper Set Iroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- Quant 001Documento5 páginasQuant 001royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- 11 Mathematics Mixed Test 02Documento4 páginas11 Mathematics Mixed Test 02Nitin KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- NCERT Solutions: CLASS - X Mathematics Chapter-01 Real Numbers (Exercise 1.1)Documento3 páginasNCERT Solutions: CLASS - X Mathematics Chapter-01 Real Numbers (Exercise 1.1)royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Mathematics Ncert Ch08 Introduction To Trigonometry Ex 8.3 Ans CcaDocumento2 páginas10 Mathematics Ncert Ch08 Introduction To Trigonometry Ex 8.3 Ans Ccaroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- BSC Match Point (Jan-Sep) 2017Documento18 páginasBSC Match Point (Jan-Sep) 2017royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- 11 Mathematics Mixed Test 01Documento5 páginas11 Mathematics Mixed Test 01Sarthak MehraAún no hay calificaciones
- 07 Maths Key Notes Ch9 Rational NumbersDocumento2 páginas07 Maths Key Notes Ch9 Rational Numbersroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- 07 Maths Key Notes Ch9 Rational NumbersDocumento2 páginas07 Maths Key Notes Ch9 Rational Numbersroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- User GuideDocumento77 páginasUser Guideroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- 09 Science Is Matter Around Us Pure Test 01Documento1 página09 Science Is Matter Around Us Pure Test 01royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- Life Process 001Documento1 páginaLife Process 001royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- 201Documento24 páginas201royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- Carbon & Its Compounds: Nec Academy of ScienceDocumento2 páginasCarbon & Its Compounds: Nec Academy of Scienceroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- TableDocumento1 páginaTableroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- MultiTasking Staff Non Tachnical Exam Paper Held On 20-02-2011 General Awareness WWW - Sscportal.inDocumento4 páginasMultiTasking Staff Non Tachnical Exam Paper Held On 20-02-2011 General Awareness WWW - Sscportal.inroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- MultiTasking Staff Non Tachnical Exam Paper Held On 20-02-2011 General Intelligence Reasoning WWW - Sscportal.inDocumento3 páginasMultiTasking Staff Non Tachnical Exam Paper Held On 20-02-2011 General Intelligence Reasoning WWW - Sscportal.inroyalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- CWE PO CL Queries PDFDocumento1 páginaCWE PO CL Queries PDFsatishsatishandsatishAún no hay calificaciones
- Discrete Math MCA21Documento2 páginasDiscrete Math MCA21api-3732063Aún no hay calificaciones
- Discrete Math MCA21Documento2 páginasDiscrete Math MCA21api-3732063Aún no hay calificaciones
- Reasoning 01Documento1 páginaReasoning 01royalrajoria4912Aún no hay calificaciones
- Discrete Math MCA21Documento2 páginasDiscrete Math MCA21api-3732063Aún no hay calificaciones
- Punjab and Sind Bank PO: Test-I: Reasoning AbilityDocumento17 páginasPunjab and Sind Bank PO: Test-I: Reasoning AbilityKumara GuruAún no hay calificaciones
- CBS Challan For Clerical CadreDocumento1 páginaCBS Challan For Clerical Cadregupta123Aún no hay calificaciones
- 317114162-EDDY-CURRENT-AND-APPLICATIONS-PROJECT Class 12 Physics Investigatory ProjectDocumento9 páginas317114162-EDDY-CURRENT-AND-APPLICATIONS-PROJECT Class 12 Physics Investigatory Projectpseudo network67% (9)
- USS Physics Split PDF 1659623115749 RemovedDocumento14 páginasUSS Physics Split PDF 1659623115749 Removeduzx yzxAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Choice Questions: Remote Sensing Exercises For INF GEO 4310Documento4 páginasMultiple Choice Questions: Remote Sensing Exercises For INF GEO 4310Srinivas Shetty100% (1)
- University Physics III - Optics and Modern PhysicsDocumento630 páginasUniversity Physics III - Optics and Modern PhysicsFeiFei Sun100% (1)
- Doon International School City Campus Dalanwala, DehradunDocumento5 páginasDoon International School City Campus Dalanwala, DehradunRaj VishwakarmaAún no hay calificaciones
- 5th IOAA Short Questions - Solutions-For-LeadersDocumento15 páginas5th IOAA Short Questions - Solutions-For-LeadersBob SmithAún no hay calificaciones
- Momentum and Impulse ReadingDocumento7 páginasMomentum and Impulse ReadingParvinder Bhardwaj0% (1)
- Solucionario Capitulo 29 Paul e TippensDocumento21 páginasSolucionario Capitulo 29 Paul e TippensMiguel Zepeda50% (2)
- Phys 1402 Final ReviewDocumento8 páginasPhys 1402 Final ReviewAline MurilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetic WireDocumento7 páginasMagnetic Wiremike9420Aún no hay calificaciones
- 05-06-MW3211 Optical Power Meter PDFDocumento1 página05-06-MW3211 Optical Power Meter PDFonlyyou1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Diffraction Grating: OpticsDocumento4 páginasIntroduction To Diffraction Grating: OpticsKairavmeet singh BoparaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Solutions Tutorial 5Documento12 páginasSolutions Tutorial 5Nur Aqilah Abdullah HashimAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial 18A: Photoelectric Effect Photoelectric EffectDocumento2 páginasTutorial 18A: Photoelectric Effect Photoelectric EffectAgus LeonardiAún no hay calificaciones
- FORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION NotesDocumento3 páginasFORCE AND LAWS OF MOTION NotesyoutuberAún no hay calificaciones
- CoherenceDocumento20 páginasCoherenceRajni Aggarwal0% (1)
- Dr. Mukesh Kumar: Department of Physics IIT Ropar Office: 2 Floor, #206 Ph. No.: 01881-24-2263 EmailDocumento24 páginasDr. Mukesh Kumar: Department of Physics IIT Ropar Office: 2 Floor, #206 Ph. No.: 01881-24-2263 Emailhimanshu singhAún no hay calificaciones
- Light Shadow & ReflectionDocumento4 páginasLight Shadow & ReflectionMohan Reddy Kothapeta0% (1)
- Interference of LightDocumento7 páginasInterference of LightJohn JohnsonAún no hay calificaciones
- AIMDocumento12 páginasAIMsangeetha RajaAún no hay calificaciones
- Refraction and Reflection of Ultrasonic Waves at Interfaces 5.1 Application of Snell's Law in Ultrasonic TestingDocumento25 páginasRefraction and Reflection of Ultrasonic Waves at Interfaces 5.1 Application of Snell's Law in Ultrasonic Testingknizam1971Aún no hay calificaciones
- E&M Multiple Choice Answers 2004Documento3 páginasE&M Multiple Choice Answers 2004KLC12345100% (1)
- Dielectric Materials: Presented by Nirav Jani Roll No:-18 (General) Materials Science (3 Semester)Documento19 páginasDielectric Materials: Presented by Nirav Jani Roll No:-18 (General) Materials Science (3 Semester)Tvarit PatelAún no hay calificaciones
- MicroscopeDocumento6 páginasMicroscopeapi-267979304Aún no hay calificaciones
- 6 HV Transient Analysis in Power SystemDocumento28 páginas6 HV Transient Analysis in Power SystemGilang Satria PasekaAún no hay calificaciones
- KinoptikDocumento7 páginasKinoptikSándor SzabóAún no hay calificaciones
- Theoretical Modeling of Tm-Doped Silica Fiber LasersDocumento9 páginasTheoretical Modeling of Tm-Doped Silica Fiber Lasersteektak1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physics PowerpointDocumento14 páginasPhysics PowerpointRachel AmairaAún no hay calificaciones
- Optical Properties of Liquid CrystalDocumento2 páginasOptical Properties of Liquid CrystalericklclAún no hay calificaciones
- Summative Test in Science 7 Week 1 & 2Documento5 páginasSummative Test in Science 7 Week 1 & 2Esther Mae Ann TrugilloAún no hay calificaciones
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDe EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (2193)
- The Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityDe EverandThe Beauty of Falling: A Life in Pursuit of GravityAún no hay calificaciones
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDe EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (69)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDe EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldDe EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (64)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyDe EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyAún no hay calificaciones
- Higgs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpaceDe EverandHiggs Discovery: The Power of Empty SpaceCalificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (30)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessDe EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (6)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDe EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (5)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidDe EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1395)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayDe EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (125)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismDe EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (500)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDe EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (410)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldDe EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (60)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessDe EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (57)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombDe EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (8)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldDe EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (54)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseDe EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (13)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectDe EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (20)
- Beyond Weird: Why Everything You Thought You Knew about Quantum Physics Is DifferentDe EverandBeyond Weird: Why Everything You Thought You Knew about Quantum Physics Is DifferentCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (25)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowDe EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (49)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityDe EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (76)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)De EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (157)
- The Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxDe EverandThe Universe: The book of the BBC TV series presented by Professor Brian CoxCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (27)