Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Oxygen Index: BS 2782:141 & ISO 4589-2
Cargado por
mani_208eeTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Oxygen Index: BS 2782:141 & ISO 4589-2
Cargado por
mani_208eeCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
OXYGEN INDEX
BS 2782:141 & ISO 4589-2
This is a widely used, but frequently misinterpreted test which provides a single figure related to
ignitability.
Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) is the per cent concentration of oxygen at which a small specimen will
only just burn downwards in a candle like manner. The test is probably the most well-known of the
standard fire tests. The apparatus holds a small specimen of material which is clamped vertically in a
tube in an atmosphere where the relative concentration of oxygen and nitrogen can be changed.
The aim is to test the flammability of the sample with a small pilot flame to find the minimum
oxygen concentration required to just sustain combustion of the sample. The result is usually
expressed as:
The test result is on a numerical scale which simplifies comparison of materials. It is very repeatable
and is used for quality assurance and to indicate the potential flammability of a material. However it
is essentially a small flame test and while a high index is indicative of a less easily ignited and less
flammable material, materials with high limiting oxygen index (LOI) values (i.e. greater than 21)
undergo flaming combustion at oxygen concentrations below 5%, in a fully developed, real fire. This
is one of the very few test apparatus where steady burning conditions can be replicated on a small
scale.
SOME TYPICAL
LOI
VALUES
Std Polyurethane foam 16.5
PMMA (Perspex) 17.3
Poly(ethylene) 17.4
Poly(propylene) 17.4
Poly(styrene) 17.8
Plywood 23.0
Nylon 6.6 24-29
Polycarbonate 25-44
Nomex 28.5
Polyester (GRP) 21-43
Phenolic 26-64
PVC (unplasticised) 45-49
(PTFE) 95
También podría gustarte
- E 606 - 92 R98 RtywngDocumento15 páginasE 606 - 92 R98 RtywngAnthony GómezAún no hay calificaciones
- Determination of Wear Metals and Contaminants in Used Lubricating Oils or Used Hydraulic Fluids by Rotating Disc Electrode Atomic Emission SpectrometryDocumento5 páginasDetermination of Wear Metals and Contaminants in Used Lubricating Oils or Used Hydraulic Fluids by Rotating Disc Electrode Atomic Emission SpectrometryJam GuardiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Pyrogen Regulatory USP PDFDocumento3 páginasPyrogen Regulatory USP PDFAlya Ghina AqilaAún no hay calificaciones
- IsoDocumento2 páginasIsoLeonardo GuzAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding UL 94 Certifications and LimitationsDocumento2 páginasUnderstanding UL 94 Certifications and LimitationsLakshmi PrasannaAún no hay calificaciones
- As 2282.2-1999 Methods For Testing Flexible Cellular Polyurethane Measurement of Dimensions of Test SpecimensDocumento2 páginasAs 2282.2-1999 Methods For Testing Flexible Cellular Polyurethane Measurement of Dimensions of Test SpecimensSAI Global - APACAún no hay calificaciones
- E367 16Documento6 páginasE367 16arcadioscoAún no hay calificaciones
- ASTM E2347 - Indentation Softening Temperature by Thermomechanical Analisys PDFDocumento5 páginasASTM E2347 - Indentation Softening Temperature by Thermomechanical Analisys PDFAugusto ManuelAún no hay calificaciones
- Astm 4964Documento5 páginasAstm 4964Ugur Demircan100% (2)
- C 1819 - 15 PDFDocumento17 páginasC 1819 - 15 PDFConnieAún no hay calificaciones
- Pseudomonas SP, Salmonella SP, Escherichia Coli) - Gram-Positive Bacteria and Fungi Also ProduceDocumento9 páginasPseudomonas SP, Salmonella SP, Escherichia Coli) - Gram-Positive Bacteria and Fungi Also ProduceMingielee100% (1)
- Theory Sine Sweep Vs Random Vibration TestingDocumento2 páginasTheory Sine Sweep Vs Random Vibration TestingblakolAún no hay calificaciones
- Skerik Grey Scale Test (Introduction)Documento1 páginaSkerik Grey Scale Test (Introduction)zazaAún no hay calificaciones
- ASTM B557 10 Standard Test MethodDocumento15 páginasASTM B557 10 Standard Test MethodmehmetAún no hay calificaciones
- Pds Hempel's Urethane 5595u En-UsDocumento2 páginasPds Hempel's Urethane 5595u En-UsFreddy Carl FredricksenAún no hay calificaciones
- XRD PDFDocumento21 páginasXRD PDFBoby Royan Naira AzdlilAún no hay calificaciones
- Toxicity PDFDocumento8 páginasToxicity PDFnameyouAún no hay calificaciones
- NDT and Eddy Current TestingDocumento8 páginasNDT and Eddy Current TestingTonyo AyshiyuAún no hay calificaciones
- E 1254 - 03 Rteyntq - PDFDocumento3 páginasE 1254 - 03 Rteyntq - PDFMarceloAún no hay calificaciones
- D6578Documento6 páginasD6578roshni100% (2)
- NIOSH 2549 - Compuestos Orgánicos Volátiles PDFDocumento8 páginasNIOSH 2549 - Compuestos Orgánicos Volátiles PDFNoe Adrianzen MAún no hay calificaciones
- App.20240520 ReviewerDocumento35 páginasApp.20240520 ReviewerMd Shafinur MuradAún no hay calificaciones
- PVC and FireDocumento9 páginasPVC and FirePinyaporn VeerapraditAún no hay calificaciones
- Ma Et Al.Documento12 páginasMa Et Al.lnhipulanAún no hay calificaciones
- Zeus FlammabilityDocumento6 páginasZeus FlammabilityplinarioAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluation of Oxygen Reduction System (ORS) in Large-Scale Fire TestsDocumento7 páginasEvaluation of Oxygen Reduction System (ORS) in Large-Scale Fire TestsNaty RoblesAún no hay calificaciones
- Low Cost Carbon Fibre in Automotive ApplicationDocumento12 páginasLow Cost Carbon Fibre in Automotive ApplicationMuthu BalajiAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.6. Sepracion de Gases Con Membranas InglesDocumento29 páginas1.6. Sepracion de Gases Con Membranas InglesMa. Guadalupe Sierra LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cable Testing OxygenIndexFlameDocumento2 páginasCable Testing OxygenIndexFlameVijayaKumarThiruvenkataswamyAún no hay calificaciones
- Smoke Suppression in Plasticised ChlorinDocumento4 páginasSmoke Suppression in Plasticised Chlorinxfactor gangaarAún no hay calificaciones
- S Performance in FiresDocumento28 páginasS Performance in FiresMirceaAún no hay calificaciones
- FS11 Proc Chiti PDFDocumento12 páginasFS11 Proc Chiti PDFJarrod CurrinAún no hay calificaciones
- 12F0003X00 Anixter LSZH WP W&C EN US PDFDocumento6 páginas12F0003X00 Anixter LSZH WP W&C EN US PDFPratham KashyapAún no hay calificaciones
- Air Purification by Pavement Blocks, Final Results of The Research at The BRRCDocumento7 páginasAir Purification by Pavement Blocks, Final Results of The Research at The BRRCMelani AlvaAún no hay calificaciones
- Moam - Info - Iso Ts 19700 Iafss - 5b843e50097c4762708b472bDocumento12 páginasMoam - Info - Iso Ts 19700 Iafss - 5b843e50097c4762708b472bDwika YanuariAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparison of Formaldehyde Concentrations in Emission Test Chambers Using EN 717-1 and EN 16516Documento8 páginasComparison of Formaldehyde Concentrations in Emission Test Chambers Using EN 717-1 and EN 16516Andrea CorradiAún no hay calificaciones
- Flame Retardant Properties of Polyurethane Expandable P - 2014 - Procedia EngineDocumento6 páginasFlame Retardant Properties of Polyurethane Expandable P - 2014 - Procedia EnginejanainaAún no hay calificaciones
- Flammability TestDocumento6 páginasFlammability TestAlpesh SolankiAún no hay calificaciones
- 2007 Ok o Ssmetric Study SummaryDocumento0 páginas2007 Ok o Ssmetric Study SummaryAgatha ZerrudoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ket Hop NhomDocumento9 páginasKet Hop Nhománh nguyễnAún no hay calificaciones
- On Measurement of SmokeDocumento20 páginasOn Measurement of SmokeAllen DY YangAún no hay calificaciones
- 64 AnalysisDocumento5 páginas64 AnalysisSaran CityAún no hay calificaciones
- Fire Properties of Polyvinyl ChlorideDocumento30 páginasFire Properties of Polyvinyl ChlorideGeorge Cobra100% (3)
- Byproduct Analysis of PO XLPEDocumento1 páginaByproduct Analysis of PO XLPETANMAY NAYAKAún no hay calificaciones
- Energy Values Non-RecycledPlastics Final PDFDocumento27 páginasEnergy Values Non-RecycledPlastics Final PDFRitesh PatelAún no hay calificaciones
- Experimental Analysis of Minimum Ignition Temperature of Coal Dust Layers in Oxy-Fuel Combustion AtmospheresDocumento10 páginasExperimental Analysis of Minimum Ignition Temperature of Coal Dust Layers in Oxy-Fuel Combustion AtmospheresAnand SehgalAún no hay calificaciones
- Fire Phenomena of Rigid Polyurethane FoamsDocumento22 páginasFire Phenomena of Rigid Polyurethane FoamsNicola MelaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 s2.0 S1877705812044931 MainDocumento14 páginas1 s2.0 S1877705812044931 MainJoão SegundahAún no hay calificaciones
- tmp66BF TMPDocumento7 páginastmp66BF TMPFrontiersAún no hay calificaciones
- Polymers: Development of A Halogen Free Flame Retardant Masterbatch For Polypropylene FibersDocumento15 páginasPolymers: Development of A Halogen Free Flame Retardant Masterbatch For Polypropylene FibersAnonymous PHCzwD8eAOAún no hay calificaciones
- Sb2o3 Ath PVCDocumento6 páginasSb2o3 Ath PVCnilayAún no hay calificaciones
- Combustible HandbookDocumento34 páginasCombustible Handbookrobisiz7299Aún no hay calificaciones
- SAT Subject Chemistry SummaryDocumento25 páginasSAT Subject Chemistry SummaryYoonho LeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Flame and Smoke in Vinyl Chloride Polymers  " Commercial Usage and Current DevelopmentsDocumento25 páginasFlame and Smoke in Vinyl Chloride Polymers  " Commercial Usage and Current Developmentsabilio_j_vieiraAún no hay calificaciones
- 476 ApicellaDocumento6 páginas476 ApicellaSudhir PatelAún no hay calificaciones
- Aiaa 45148 268Documento6 páginasAiaa 45148 268Kiran ManoharanAún no hay calificaciones
- Reduced Graphene Oxide As Efficient and Stable Hole Transporting Material in Mesoscopic Perovskite Solar CellsDocumento13 páginasReduced Graphene Oxide As Efficient and Stable Hole Transporting Material in Mesoscopic Perovskite Solar CellsChandra Bhal SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Presented By:: Satabdy Jena Mtech (Power and Energy Systems) ROLL NO.: T14EE003 Nit MeghalayaDocumento23 páginasPresented By:: Satabdy Jena Mtech (Power and Energy Systems) ROLL NO.: T14EE003 Nit MeghalayaHamza Ali MinhasAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab Report 02Documento5 páginasLab Report 02Nouma SalehaAún no hay calificaciones
- A Measurement of Total Reactive Nitrogen NOy Together With NO2 NO and O3 Via Cavity Ring-Down SpectrosDocumento7 páginasA Measurement of Total Reactive Nitrogen NOy Together With NO2 NO and O3 Via Cavity Ring-Down SpectrosbilldubeAún no hay calificaciones
- Customer Service: Enjoy 24/7 Peace of Mind With Flexible Service Offerings From Schneider ElectricDocumento8 páginasCustomer Service: Enjoy 24/7 Peace of Mind With Flexible Service Offerings From Schneider Electricmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- KHSH-9MK6CZ R0 enDocumento81 páginasKHSH-9MK6CZ R0 enmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical Switchgear Safety: A Guide For Owners and UsersDocumento9 páginasElectrical Switchgear Safety: A Guide For Owners and Usersmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- CVA Range: Linear and Quarter-TurnDocumento32 páginasCVA Range: Linear and Quarter-Turnmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- 8.1 Exit Lighting and Exit Sign: Other SystemsDocumento22 páginas8.1 Exit Lighting and Exit Sign: Other Systemsmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- High Voltage Xlpe Cable Systems Technical User Guide For 127 - 500 KVDocumento12 páginasHigh Voltage Xlpe Cable Systems Technical User Guide For 127 - 500 KVmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ebitt Motor Katalog R01Documento9 páginasEbitt Motor Katalog R01mani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Iris Power Epoxy Mica Capacitors (80 PF) : Partial Discharge Sensors For Testing Motors and GeneratorsDocumento2 páginasIris Power Epoxy Mica Capacitors (80 PF) : Partial Discharge Sensors For Testing Motors and Generatorsmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Iris Power Epoxy Mica Capacitors (80 PF) : Partial Discharge Sensors For Testing High Voltage Electrical EquipmentDocumento2 páginasIris Power Epoxy Mica Capacitors (80 PF) : Partial Discharge Sensors For Testing High Voltage Electrical Equipmentmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Exmax Range: Keeping The World FlowingDocumento12 páginasExmax Range: Keeping The World Flowingmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Iris Power Stator Slot Couplers Brochure PDFDocumento1 páginaIris Power Stator Slot Couplers Brochure PDFmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Fail Safe Unit FQM 05.1 - FQM 12.1 Fqmex 05.1 - Fqmex 12.1: Assembly, Operation, Commissioning Operation InstructionsDocumento40 páginasFail Safe Unit FQM 05.1 - FQM 12.1 Fqmex 05.1 - Fqmex 12.1: Assembly, Operation, Commissioning Operation Instructionsmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- AFOP - Armoured Fiber Optic Patchcord: DescriptionDocumento2 páginasAFOP - Armoured Fiber Optic Patchcord: Descriptionmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- KEMROC New Products (EN)Documento5 páginasKEMROC New Products (EN)mani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Schneider Electric Industries: Date: Wednesday, March 25, 2020Documento2 páginasSchneider Electric Industries: Date: Wednesday, March 25, 2020mani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Schneider Electric Industries: Date: Wednesday, March 25, 2020Documento2 páginasSchneider Electric Industries: Date: Wednesday, March 25, 2020mani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Performance With Ultra Low Maintenance: Ultima SLM Ni-Cd BatteryDocumento8 páginasPerformance With Ultra Low Maintenance: Ultima SLM Ni-Cd Batterymani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Aboveground Tank Overfill Protection Part 1 - General Discussion and Assessment of API RecommendationsDocumento12 páginasAboveground Tank Overfill Protection Part 1 - General Discussion and Assessment of API Recommendationsmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Catalogue Technor - GB - 0919Documento244 páginasCatalogue Technor - GB - 0919mani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Aboveground Tank Overfill Protection Part 1 - General Discussion and Assessment of API RecommendationsDocumento12 páginasAboveground Tank Overfill Protection Part 1 - General Discussion and Assessment of API Recommendationsmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- Low Voltage Drive - SJ 700i (415V) (30 KW To 450 KW) CatalogueDocumento12 páginasLow Voltage Drive - SJ 700i (415V) (30 KW To 450 KW) Cataloguemani_208ee100% (1)
- Cummins - Understanding Generator Set RatingsDocumento8 páginasCummins - Understanding Generator Set Ratingsmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
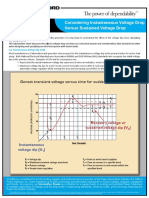
- Considering Instantaneous Voltage Drop Versus Sustained Voltage DropDocumento2 páginasConsidering Instantaneous Voltage Drop Versus Sustained Voltage Dropmani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones
- CatalogueDocumento36 páginasCataloguemani_208eeAún no hay calificaciones