Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
BC Review 2
Cargado por
FlorangTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
BC Review 2
Cargado por
FlorangCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Part (II) Nitrogenous molecules metabolism
Amino acids metabolism
1. Protein/amino acids catabolism:
Protein turnover
Normal cellular protein degradation
PEST sequence (rich in P, E, S, and T) target proteins for rapid degradation
In lysosome (ATP-independent processes): extracellular, membrane-associated
and long-lived intracellular proteins.
ATP and Ubiquitin-tag proteasome (abnormal and short-lived proteins in
cytosol)
Dietary protein surplus
Provide up to 90% metabolic energy in carnivores after meal.
Amino acids can not be stored.
Starvation or diabetes mellitus
Protein is used as fuel
Kwashiorkor: results when a child is weaned onto a starchy diet poor in
protein
Marasmus: both caloric intake and specific amino acids are deficient.
Nitrogen balance
Positive: an access of ingested over excreted, accompanies growth and
pregnancy
Negative: output exceeds intake, may follow surgery, advanced cancer, and
kwashiorkor or marasmus.
2. Amino acid catabolism:
Amino group: NH4+ (NH3)2CO (in mammal, urea cycle)
C-skeleton: all enter TCA cycle
Glucogenic a.a.
Degraded to pyruvate, a-ketoglutarate, succinyl-CoA, fumarate,
oxaloacetate glucose and glycogen.
Ketogenic a.a.
Degraded to acetoacetyl-CoA and or acetyl-CoA (6 a.a.) ketone
bodies (acetone, acetoacetate, D--hydroxybutyrate).
Untreated diabetes: liver will produce large amounts of ketone bodies
from fatty acids and ketongenic a.a.
Leu is an exclusively ketogenic a.a. that is common in proteins. Its
degradation makes a substantial contribution to ketosis under starvation
conditions.
Classification by biological function (glucogenic, ketogenic):
Glucogenic Ketogenic Glucogenic and ketogenic
Ala, Arg, Asp Leu Ile
Cys Lys Phe
Glu, Gly Trp
His Tyr
Met
Pro, (Hyp)
Ser
Thr
350775789.doc -1- 4/7/2017
Val
3. Amino acid degradation in human:
Amino group:
Transamination (aminotransferase or transaminase; requires PLP-pyridoxal
phosphate as a cofactor)
SALT test (alanine aminotransferase, or GPT)
SAST test (aspartate , or GOT)
Transfer NH4+ to liver in the form of: Glu, Gln, Ala
In muscle tissue: pyruvate + NH4+ alanine
Glucose-alanine cycle + Glucose-lactate cycle = Cori cycle
Deamination (trans-deamination) in liver by glutamate dehydrogenase
Requires NAD+ or NADP+
Allosterically regulated (reflects energy needs):
Activator: GDP, ADP
Inhibitor: GTP, ATP
Acidosis and Gln processing in kidney
N excretion: almost exclusively in liver:
NH4+ urea (urea cycle)
5 enzymatic steps (4 steps in urea cycle)
2 cellular compartments involved
Urea bloodstream kidney excreted into urine
Urea cycle enzyme defect ammonia intoxication
Carbamoly phosphate synthetase I (hyperammonemia type I)
Supplement of carbamoyl glutamate (N-acetylglutamate analog)
Ornithine transcarbamoylase (hyperammonemia type II)
Argininosuccinate synthetase (citrullinemia)
Feeding arginine promotes N excretion
Feeding benzoate, phenylbutyrate (aromatic keto acids)
Argininosuccinate lyase (argininosuccinicaciduria)
Feeding arginine and benzoate
Arginase (hyperargininemia)
Low protein diet
C-skeleton: all enter mainstream metabolic pathway, TCA cycle.
Cofactor for one C-transfer:
Biotin (transfer CO2)
Tetrahydrofolate (H4 folate) (transfer HC=O, -HCOH, or CH3)
H4 folate deficiency and pernicious anemia
S-adenosylmethionine (adoMet, SAM) (transfer CH3)
BCAA (Val, Leu, and Ile)
Degraded in extrahepatic tissue (muscle, adipose tissue, kidney and
brain)
Branched-chain aminotransferase
Branched-chain -keto acid dehydrogenase complex
Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)/branched-chain ketonuria
Diet restriction, branched-chain keto acids supplement.
Phenylalanine and tyrosine
Phe Tyr: phenylalanine hydroxylase and phenylketouria (PKU)
350775789.doc -2- 4/7/2017
The artificial sweetener: aspartame
Tyrosine degradation
Homogentisate dioxygenase defect alkaptonuria
4. Principal serum enzymes used in clinical diagnosis: (from Harpers 26th ed. Table 7.2)
Serum Enzyme Major diagnostic use
Aminotransferases: Myocardial infarction
AST, or SGOT Viral hepatitis
ALT, or SGPT
Amylase Acute pancreatitis
Ceruloplasmin Hepatolenticular degeneration
(Wilsons disease)
Creatine kinase Muscle disorders and myocardial infarction
-Glutamyl transpeptidase Various liver diseases
Lactate dehydrogenase (isozymes) Myocardial infarction
Lipase Acute pancreatitis
Phosphatase, acid Metastatic carcinoma of the prostate
Phosphatase, alkaline (isozymes) Various bone disorders, obstructive liver diseases
From Lehninger 3rd ed.
5. Classification by nutrition: essential vs. nonessential amino acid: * semi-essential.
Nutritionally essential Nutritionally nonessential
Arginine* Alanine
Histidine Asparagine
Isoleucine Aspartate
Leucine Cysteine
Lysine Glutamate
Methionine Glutamine
Phenylalanine Glycine
Threonine Proline
Tryptophan Serine
Valine Tyrosine
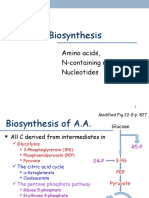
6. Amino acid biosynthesis:
N enters the pathway in the form of:
350775789.doc -3- 4/7/2017
Glu (aminotransferase), Gln (amidotransferase)
C-skeleton is derived from:
Glycolysis (3-phosphoglycerate/3-PG, phosphoenolpyruvate/PEP, pyruvate)
Citric acid cycle (-KG, OAA)
Pentose phosphate pathway (Ribose 5-phosphate, erythrose 4-phosphate)
7. Amino acid biosynthesis in human:
Essential a.a.: complex chemical structure, require multiple steps, human body has lost
the ability to do the job
Non-essential a.a.: short biosynthetic pathways (only few steps)
-ketoglutarate Glu, Gln, Arg, Pro
3-phosphoglycerate Ser, Gly, Cys
Cys from Met (S) and Ser (C-skeleton)
Oxaloacetate Asp, Asn
Pyruvate Ala
Tyr from Phe (phenylalanine hydroxylase)
Phenylalanine hydroxylase is a mixed-function oxygenases, which
catalyze simultaneous hydroxylation of a substrate by an oxygen atom
of O2 and reduction of the other oxygen atom to H2O.
Phenylalanine hydroxylase requires a cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin.
Dihydrobiopterin reductase defect: PKU, L-dopa
Supplementing the diet with H4 biopterin itself is ineffective
because it is unstable and does not cross the BBB.
350775789.doc -4- 4/7/2017
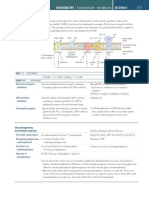
NAD+ H4 biopterin Phenylalanine
O2
Dihydrobiopterin Phenylalanine hydroxylase
reductase
H2O
+
NADH + H H2 biopterin Tyrosine (-OH)
Hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine (in collagen): no specialized tRNA, not
from dietary intake (degraded completely)
Derived from Pro and Lys after incorporation into peptides (post-
translational modification)
The hydroxylases are mixed-function oxygenases that require
substrate, molecular O2, ascorbate, Fe2+, and -ketoglutarate.
Pro + -KG + O2 (ascorbate, Fe2+) Hydroly-Pro + succinate
BCAA (Val, Leu, Ile) can be formed by transamination with their
corresponding -keto acids (supplied in diet).
Ammonia intoxication.
Regulation
Allosteric feedback inhibition
End product acts as a modulator for the allosteric enzyme.
Simple and concerted inhibition.
Glutamine synthetase
Allosteric regulation
Covalent modification
8. S-adenosylmethionine (S-adoMet, SAM)
Cofactor for methyl group transfer: activated methyl cycle
From ATP + Met (by methionine adenosyl transferase) (Fig 18-17)
Triphosphate of ATP is displaced by S from Met.
Similar reaction in coenzyme B12 synthesis.
Met is regenerated by addition of a methyl group to homocysteine (by
methionine synthase)
The 1-carbon donor: H4 folate or methylcobalamin derived from
coenzyme B12.
The methyl group of methylcobalamin is derived from N5-methyl H4
folate.
B12 deficiency: may trap folate in N5-methyl form pernicious
anemia.
350775789.doc -5- 4/7/2017
Molecules derived from amino acids:
9. Porphyrins (Gly + Succinyl-CoA)
Multiple steps
ALA synthestase (ALAS1, drug-induced ALAS1 de-repression)
ALA dehydratase (Zn containing enzyme), can be inhibited by Pb (lead).
Degraded to linear tetrapyrrole derivative: bilirubin (jaundice).
10. Creatine (Gly + Arg + Met/S-adoMet )
Cr + ATP CrP + ADP (by creatine kinase)
Creatine (Cr) and phosphocreatine (PCr, or CrP)
Energy buffer in skeletal muscle
Creatinine: from CrP by irreversible, nonenzymatic dehydration and loss of phosphate.
The 24-hour urinary excretion of creatinine is proportionate to muscle mass.
11. Glutathione (GSH), (Gly, Glu and Cys)
As a redox buffer.
Maintain Cys in the reduced form (-SH).
Iron of heme in the ferrous (Fe2+) state.
Serve as a reducing agent for glutaredoxin in deoxyribonucleotide synthesis.
(Fig 22-37)
Remove toxic peroxides under aerobic conditions.
Oxidized form: GSSG = two GSH linked by a disulfide bond.
2 GSH + R-O-O-H GSSH + H2O + R-OH
Catalyzed by glutathione peroxidase (containing selenium, Se, in the form of
selenocysteine).
12. D-amino acids
Bacterial cell wall.
D-alanine and D-glutamate
Derived from L-isomers by racemase (PLP as coenzyme), which is the prime
target for pharmaceutical agents (side-effect on other PLP-requiring enzymes)
L-fluoroalanine: tested as antibacterial drug
Cycloserine: to treat tuberculosis
Peptide antibiotics.
13. From aromatic a.a. to many plant substances
From Phe and Tyr
Tannins (): inhibit oxidation in wines
Morphine: potent physiological effects
Flavor components: cinnamon oil, nutmeg (), cloves (), vanilla,
and cayenne pepper ().
14. Amino acids are converted to biological amines by decarboxylation (PLP as a cofactor):
From Tyr
Dopa, dopamine ( Parkinsons disease, schizophrenia)
Dopa melanin
Dopamine norepinephrine (requires ascorbate, Cu2+)
Norepinephrine epinephrine (requires adoMet)
From Glu
350775789.doc -6- 4/7/2017
GABA (-aminobutyrate): epileptic seizures
GABA analogs to treat epilepsy and hypertension
Or use inhibitors of GABA aminotransferase (GABA-degrading
enzyme)
From His
Hitamine (allergic reaction, stimulate gastric acid)
Cimetidine (Tagamet): histamine receptor antagonist: structural analog
of histamine, it promotes healing of duodenal ulcers by inhibiting
secretion of gastric acid
From Trp
Nicotinate (niacin), a precursor of NAD and NADP.
Serotonin: a potent vasoconstrictor and smooth muscle stimulator.
Serotonin melatonin.
From Met and ornithine (by ornithine decarboxylase, PLP-requiring enzyme)
Spermine and spermidine: used in DNA packaging.
Required in large amounts in rapidly dividing cells.
African sleeping sickness (trypanosome-caused disease, ):
ornithine decarboxylase has a much slower turnover rate in
trypanosome than in human (human, fast turnover, less side-effect of
enzyme inhibitor)
DMFO (difluoromethylornithine): suicide inhibitor or mechanism-
based inhibitor.
15. From Arg
NO (nitric oxide), gas, unstable and can not be stored.
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS): 4 cofactors (FMN, FAD, H4 biopterin, Fe3+-heme)
Synthesis is stimulated by NOS with Ca2+-CaM.
Neurotransmission, blood clotting, and the control of blood pressure.
16. Summary of the biosynthesis of some important amines:
Amine Amino acid precursor Distinguishing features of pathways
Acetylcholine Ser, Met S-adoMet is methylating agent
Norepinephrine Tyr L-dopa is intermediate and precursor of melanins
Epinephrine Tyr, Met S-adoMet-dependent tyrosine aminotransferase induced by
glucocorticoids
Serotonin Trp 5-hydroxytryptophan intermediate
-aminobutyrate Glu Decarboxylation reaction
(GABA)
Histamine His Decarboxylation reaction
Spermine Ornithine, Met Spermidine is intermediate
Creatine Arg, Gly, Met Guanidino group transferred to glycine
Purine Gly, Asp, Gln Gly part of the carbon skeleton
nucleotide
Pyrimidine Asp, Gln Asp part of the carbon skeleton
nucleotide
350775789.doc -7- 4/7/2017
Nucleotide metabolism
17. Nucleotide
Chemical structure:
Phosphate group (monophosphate)
Pentose (ribose, deoxyribose)
Nitrogenous base (A, G, C, U, T)
Absorb UV light (max. ~ 260 nm)
Polynucleotide: NT1 (5-P) + NT2 (3 OH- of ribose) 35 phosphodiester bond.
RNA is less stable as the 2-OH functions as a nucleophile during hydrolysis of
the 3,5-phosphodiester bond.
Directional molecules: 5 3.
5-end: free or phosphorylated 5-OH
3-end: free 3-OH
18.
Gln
N
Asp
CO2 N
Nucleotide synthesis: de novo pathways and salvage pathways:
Purine (two rings, shorter name) de novo synthesis:
PRPP, Gln x 2, Gly, Formate x 2, CO2, Asp inosine monophosphate (IMP)
IMP AMP (GTP hydrolysis); IMP GMP (ATP hydrolysis).
1-C transfer (formate): requires H4 folate (folic acid)
Deficiency of folic acid purine deficiency state
Inhibition of H4 folate formation cancer chemotherapy.
e.g. azaserine, diazanorleucine, 6-mercaptopurine, and mycophenolic
acid.
Purine salvage pathway (less energy required):
Purine base + PRPP Purine nucleotide + PPi (pyrophosphate) or
Purine nucleoside + ATP Purine nucleotide + ADP.
Liver is the major site of purine nucleotide biosynthesis.
Regulation (allosteric feedback + reciprocal energy use):
Ribose 5-phosphate PRPP AMP, ADP, GMP, and GDP
IMP AMP (GTP hydrolysis); IMP GMP (ATP hydrolysis).
Ribonucleotide vs. deoxyribonucleotide. (reduction at the level of diphosphate).
Requires: thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase, and NADPH.
Pyrimidine (one ring, longer name)orotate + PRPP UMP CMP
UDP dUDP dUMP dTMP (thymidylate synthase + 1 C-transfer)
Dihydrofolate reductase is required and it is a target for the anticancer drug
methotrexate (competitive inhibitor).
Disorders of folate and vitamin B12 metabolism results in deficiencies of TMP.
350775789.doc -8- 4/7/2017
Thymidylate synthase is inhibited by fluorouracil and Aminopterin
(mechanism-based inhibitor).
Pyrimidine catabolism: NH4+ urea, all soluble compound
Thymine -aminoisobutyrate (Harper 26th, p.300)
methylmalonylsemialdehyde (an intermediate of Val catabolism)
succinyl-CoA (Lehninger 3rd, Fig 22-44).
Excretion of -aminoisobutyrate increases in leukemia and severe x-
ray radiationexposure due to increased destruction of DNA. However,
many persons of Chinese or Japanese ancestry routinely excrete -
aminoisobutyrate.
Cytosine uracil -alanine.
Disorders of purine catabolism. Purine is degraded to uric acid.
Gout
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome:
Defect in hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT,
HGPRTase, purine salvage enzyme)
Von Gierkes diseases
Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency.
Enhanced PRPP precursor (R5P).
Hypouricemia
Xanthine oxidase deficiency (allopurinol is a competitive inhibitor)
Immunodificiency
Accumulation of dGTP and dATP, which inhibit ribonucleotide
reductase and thereby deplete cells of DNA precursors.
Both T cells and B cells are sparse and dysfunctional: adenosine
deaminase deficiency. sterile bubble environment.
T cell deficiency but B cell normal: purine nucleoside phosphorylase
deficiency.
Many chemotherapeutic agents target enzymes in the nucleotide biosynthetic pathway.
Cancer cells has a more active salvage pathway
Compounds that inhibit glutamine amidotransferases (N donor)
Glutamine analogs: azaserine and acivicin.
Thymidylate snythase and dihydrofolate reductase: enzymes that
provide the only cellular pthway for thymine synthesis.
Fluorouracil FdUMP: acts on thymidylate synthase
(mechanism-based).
Methotrexate: inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (competitive
inhibitor)
Aminopterin: inhibits dihydrofolate reductase.
Allopurinol (purine analog) used in against African trypanosomiasis.
Allopurinol is also an alternative substrate for orotate
phosphoribosyltransferase, competes with orotic acid.
350775789.doc -9- 4/7/2017
19. Review of amino acids:
Amino acid Features
Gly Break -helix, to form -turn;
Triple helix in collagen;
Creatine, heme/porphrin, purines.
-alanine L-Ala pyruvate (by ALT or SGPT);
D-ala in bacterial wall and some antibiotics.
-alanine A metabolite of cysteine;
Present in coenzyme A as -alanyl dipeptides (carnosine) (in pantotheinic acid CoA);
Product of degradation of pyrimidine (cytosine and uracil).
Cys The thioethanolamine portion of coenzyme A (CO2 + -mercaptoethylamine/Cys CoA);
CO2 + -mercaptoethylamine/Cys taurine bile salt. (the taurine that conjugates with bile
acids such as taurocholic acid).
Ser Serine protease (trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase); catalytic mechanism: covalent catalysis;
Irreversible inhibitor (diisopropylfluorophosphate, DIFP);
Ser ethanolamine choline phosphatidylcholine/Lecithin
choline acetylcholine
Ser (palmitoyl-CoA) Sphingosine
O-linked glycosylation site, phosphorylation site.
Thr O-linked glycosylation site, phosphorylation site.
Asp Asp protease (HIV-1 protease, inhibited by pepstatin); covalent catalysis;
General acid-base catalysis (lysozyme, trypsin, chymotrypsin);
Provide NH3+ in urea and purine (inosine) biosynthesis;
Provide C-skeleton in pyrimidine ring biosynthesis.
Glu General acid-base catalysis (lysozyme)
Covalent catalysis (carboxypeptidase A)
Guutathione: GSH peroxidase/Se.
Pro Break -helix, induce -turn;
Pro and HO-Pro in collagen (and HO-Lys): hydroxylation via oxidase and ascorbate.
Val, Leu, Ile BCAA: contained -oxidation;
Energy source of muscle, not degraded in liver
Met Specific cleavaged by CNBr (cyanogens bromide) at C-terminus;
Precursor of S-adoMet, spermine, spermidine
Arg Trypsin cleaves the carboxyl site of Arg and Lys residues in peptide;
Semi-essential a.a.;
Precursor of NO, creatine
Lys Trypsin cleaves the carboxyl site of Arg and Lys residues in peptide;
Protein/Lys-NH3+ + -OOC-ubiquitin ubiquitin-dependent degradation.
Trp Nicotinate (a precursor of NAD and NADP); Serotonin
His Semi-essential a.a.;
General acid-base catalysis: chymotrypsin; trypsin.
350775789.doc - 10 - 4/7/2017
También podría gustarte
- Biochemistry II Protein (Metabolism of Amino Acids) (New Edition)Documento78 páginasBiochemistry II Protein (Metabolism of Amino Acids) (New Edition)Rekti Viony100% (1)
- Unconscious Child AssessmentDocumento52 páginasUnconscious Child Assessmentar bindraAún no hay calificaciones
- PCP Exam Topics in Major Medical SpecialtiesDocumento1 páginaPCP Exam Topics in Major Medical SpecialtiesBobet ReñaAún no hay calificaciones
- Breast CancerDocumento6 páginasBreast Cancersarguss14Aún no hay calificaciones
- BiochemistryDocumento68 páginasBiochemistryNahid MerghaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiology Arteritis ChartDocumento3 páginasCardiology Arteritis ChartM PatelAún no hay calificaciones
- Pharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicDocumento13 páginasPharmacology: Teratogenic CarcinogenicSherlock HolmesAún no hay calificaciones
- Endocrine ChartDocumento28 páginasEndocrine ChartNiki NikolićAún no hay calificaciones
- Medical Picture MnemonicsDocumento26 páginasMedical Picture MnemonicsNithya VisvesvaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseases - BiochemDocumento4 páginasDiseases - BiochemJay FeldmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Epilepsy: Causes of Seizures (Non-Epileptic)Documento5 páginasEpilepsy: Causes of Seizures (Non-Epileptic)humdingerAún no hay calificaciones
- Renal Physiology IDocumento16 páginasRenal Physiology IJubilee Christiene AngAún no hay calificaciones
- Adrenergic PharmacologyDocumento6 páginasAdrenergic Pharmacologyjess6001Aún no hay calificaciones
- Gastrointestinal & NutritionBlock3 PDFDocumento170 páginasGastrointestinal & NutritionBlock3 PDFTed DoyleAún no hay calificaciones
- AtelectasisDocumento3 páginasAtelectasisLouis FortunatoAún no hay calificaciones
- Normal Lab Values (USMLE Step 1)Documento12 páginasNormal Lab Values (USMLE Step 1)nmp274Aún no hay calificaciones
- Adrenergic Receptors ChartDocumento1 páginaAdrenergic Receptors ChartLeon ChenAún no hay calificaciones
- Bates' Visual Guide To Physical Examination Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and EarsDocumento9 páginasBates' Visual Guide To Physical Examination Vol. 7: Head, Eyes, and EarsArlene DaroAún no hay calificaciones
- Pediatrics - Neonatal Jaundice PDFDocumento2 páginasPediatrics - Neonatal Jaundice PDFJasmine KangAún no hay calificaciones
- AntimicrobialsDocumento1 páginaAntimicrobialsRomaine Barrett100% (1)
- GI Diarrheal Micro ChartDocumento3 páginasGI Diarrheal Micro ChartEvan MillerAún no hay calificaciones
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocumento5 páginasPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SAún no hay calificaciones
- Medical MneumonicsDocumento139 páginasMedical MneumonicsdrtpkAún no hay calificaciones
- Usmleworld NotesDocumento181 páginasUsmleworld NotesAaiza AamerAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Pathology Reference Range 2017Documento19 páginasChemical Pathology Reference Range 2017Shobana RaveendranAún no hay calificaciones
- USMLE VitaminsDocumento2 páginasUSMLE VitaminssabweedAún no hay calificaciones
- Bipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomsDocumento2 páginasBipolar Disorder Background: Hypomania Has The Same Symptoms of Mania Without Psychotic SymptomshumdingerAún no hay calificaciones
- CasestudyDocumento5 páginasCasestudyapi-134033366Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electrolytes ImbalancesDocumento4 páginasElectrolytes ImbalancesPeter John Ruiz100% (1)
- Hemolytic DiseaseDocumento10 páginasHemolytic DiseaseChino Paolo SamsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Chart - WBC DisordersDocumento1 páginaChart - WBC DisordersSamuel RothschildAún no hay calificaciones
- Abg InterpretationDocumento1 páginaAbg InterpretationPrincess EspadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Uworld JournalDocumento3 páginasUworld JournalJayAún no hay calificaciones
- Pediatrics Block 1Documento258 páginasPediatrics Block 1Ghada ElhassanAún no hay calificaciones
- ATP Production AEROBIC Metabolism: ST STDocumento11 páginasATP Production AEROBIC Metabolism: ST STSiir Pwnsalot100% (1)
- Bca Protein Metab 2Documento69 páginasBca Protein Metab 2Genina MaylemAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.protein Digestion, Urea Cy, MbbsDocumento81 páginas1.protein Digestion, Urea Cy, MbbsDebarghya MukherjeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Edited & Recomposed by DR - Liniyanti D.Oswari, Msc. For Medical Students in Block 8Documento40 páginasEdited & Recomposed by DR - Liniyanti D.Oswari, Msc. For Medical Students in Block 8YUFFAAún no hay calificaciones
- New EnzymesDocumento64 páginasNew Enzymeslovi bahunAún no hay calificaciones
- 11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento68 páginas11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcheckmateAún no hay calificaciones
- Metabolism of N-Containing MoleculesDocumento37 páginasMetabolism of N-Containing MoleculesFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento56 páginasCarbohydrate MetabolismPradini SugihartoAún no hay calificaciones
- General Reaction of Amino Acid BreakdownDocumento20 páginasGeneral Reaction of Amino Acid BreakdownjessicatieuuAún no hay calificaciones
- MetabolismDocumento11 páginasMetabolismMituSamadderAún no hay calificaciones
- Metabolism OF Amino Acids: Yulia SuciatiDocumento37 páginasMetabolism OF Amino Acids: Yulia SuciatiAfnan AlkaffAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismDocumento12 páginasLec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismyanAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 6 - General and Characteristics. Water Soluble VitaminsDocumento29 páginasLecture 6 - General and Characteristics. Water Soluble VitaminsEiad SamyAún no hay calificaciones
- 2021 CHO Metabolism 1Documento48 páginas2021 CHO Metabolism 1xb2k9gzkc9Aún no hay calificaciones
- Individual Amino Acid 2Documento52 páginasIndividual Amino Acid 2Mai Elsayed OmaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Lipid Metabolism IDocumento35 páginasLipid Metabolism IGeorgios PlethoAún no hay calificaciones
- ETC and oxidative phosphorylationDocumento6 páginasETC and oxidative phosphorylationAvanca LouisAún no hay calificaciones
- 13 - GluconeogenesisDocumento23 páginas13 - GluconeogenesischeckmateAún no hay calificaciones
- 09 01 Aminoacid 2012 ENDocumento56 páginas09 01 Aminoacid 2012 ENanthony.johAún no hay calificaciones
- Gluconeogenesis: Synthesizing Glucose from Non-Carbohydrate PrecursorsDocumento31 páginasGluconeogenesis: Synthesizing Glucose from Non-Carbohydrate Precursorsemery100% (1)
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocumento17 páginasOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorAún no hay calificaciones
- Vitamins and MineralsDocumento91 páginasVitamins and MineralsPyaesone AungAún no hay calificaciones
- Glycolysis and Fermentation: Key Pathways and RegulationDocumento14 páginasGlycolysis and Fermentation: Key Pathways and RegulationBONAVENTURA ALVINO DESMONDAAún no hay calificaciones
- biochemistryDocumento33 páginasbiochemistryochotpremAún no hay calificaciones
- Aa MetabolismDocumento146 páginasAa MetabolismThuy LeAún no hay calificaciones
- 固定義齒學概論 15 DeliveryandCementationofaCastRestorationDocumento9 páginas固定義齒學概論 15 DeliveryandCementationofaCastRestorationFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Metabolism of N-Containing MoleculesDocumento37 páginasMetabolism of N-Containing MoleculesFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- CD10Documento5 páginasCD10FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- 暑假生物化學作業II 2010Documento1 página暑假生物化學作業II 2010FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BC Aa Biosynthesis PDFDocumento35 páginasBC Aa Biosynthesis PDFFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochem CH - 18Documento48 páginasBiochem CH - 18FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- 固定義齒學概論 15 DeliveryandCementationofaCastRestorationDocumento9 páginas固定義齒學概論 15 DeliveryandCementationofaCastRestorationFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BIOCHEM Exercise 1Documento1 páginaBIOCHEM Exercise 1FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BC Summer ReadingDocumento6 páginasBC Summer ReadingFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BIOCHEM CH - 18sDocumento6 páginasBIOCHEM CH - 18sFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Biosynthesis of Amino Acids, Nucleotides and Related MoleculesDocumento56 páginasBiosynthesis of Amino Acids, Nucleotides and Related MoleculesFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BC AaDocumento33 páginasBC AaFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- 固定義齒學概論 15 DeliveryandCementationofaCastRestorationDocumento9 páginas固定義齒學概論 15 DeliveryandCementationofaCastRestorationFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BC CH - 22sDocumento12 páginasBC CH - 22sFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbs, lipids, and glycoproteins functionsDocumento2 páginasCarbs, lipids, and glycoproteins functionsFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BC Supplement 18 22Documento15 páginasBC Supplement 18 22FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochemical Genetics: Chen-En Tsai, MD, PHDDocumento17 páginasBiochemical Genetics: Chen-En Tsai, MD, PHDFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiac MarkersDocumento2 páginasCardiac MarkersFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- HemoglobinopathyDocumento36 páginasHemoglobinopathyFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Part (II) Nitrogenous Molecules MetabolismDocumento10 páginasPart (II) Nitrogenous Molecules MetabolismFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BC Aa BiosynthesisDocumento38 páginasBC Aa BiosynthesisFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Learning objectives:: 第十八章: Amino Acid Oxidation and the Production of Urea (胺基酸分解與尿素生成)Documento2 páginasLearning objectives:: 第十八章: Amino Acid Oxidation and the Production of Urea (胺基酸分解與尿素生成)FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- BC Review - IDocumento11 páginasBC Review - IFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochem Enzyme 6Documento42 páginasBiochem Enzyme 6FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochem Protein Function 5Documento27 páginasBiochem Protein Function 5FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochem Proteins 4Documento41 páginasBiochem Proteins 4FlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochem Proteins 3cDocumento28 páginasBiochem Proteins 3cFlorangAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochem Amino Acids 3bDocumento18 páginasBiochem Amino Acids 3bFlorangAún no hay calificaciones