Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Glucose and Albumin (Qualitative Test)
Cargado por
Pearl Miranda100%(2)100% encontró este documento útil (2 votos)
2K vistas2 páginasSummary of Qualitative tests for Glucose and Albumin
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoSummary of Qualitative tests for Glucose and Albumin
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
100%(2)100% encontró este documento útil (2 votos)
2K vistas2 páginasGlucose and Albumin (Qualitative Test)
Cargado por
Pearl MirandaSummary of Qualitative tests for Glucose and Albumin
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 2
MOORE
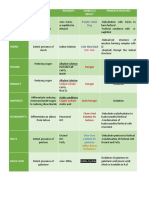
TEST FOR GLUCOSE REAGENTS PRINCIPLE POSITIVE RESULT
Fehlings Method Fehlings A -Mixture of Fehlings A and B would cause
-dist. H20 the aqueous tartrate ions to chelate to Cu
-CuSO4 ions forming a bistartratocuprate (II) Yellow or red precipitate
Fehlings B complex. This complex oxidizes the
-Rochelle salt (KNa aldehyde to a carboxylate anion, and in
tartrate) the process the copper (II) ions of the
-KOH complex are reduced to copper (I) ions.
Trommers Method 10% KOH/NaOH Copper sulfate, in an alkaline solution, is Yellow or red precipitate
10% CuSO4 reduced by the aldehyde group to Copper
(I) oxide
Nylanders Method Nylanders rgt: Under alkaline solution, reducing sugars Black color
Rochelle salt (KNa reduce bismuth salt to black metallic Trace: brown color
tartrate) bismuth.
Bismuth subnitrite
10% KOH/NaOH
Moore Hellers 10% KOH In the presence of strong alkali and heat,
Method glucose (and other reducing sugars) is
converted into caramel
Osazone Phenyl hydrazine Phenyl hydrazine reacts with the reducing Yellow, needle-shape: glucose,
hydrochloride sugars at 100C to form phenyl mannose, fructose
Sodium acetate hydrazones which will react with phenyl Mushroom- shaped/cotton ball:
Glacial acetic acid hydrazine to form osazones(crystalline lactose
shaped). Flower-shaped: maltose
Haines Method -Copper sulfate Based on the presence of reducing agent,
-Glycerin cupric ions are reduced to insoluble Yellow or red precipitate
-KOH cuprous oxide
-Distilled H20
Somogyis Method -Alkaline copper Tartrate In the presence of reducing sugars, copper Blue color
Arsenomolybdic acid (II) ions are reduced to form cuprous oxide,
which is treated with aresenomolybdic
acid. Molybdic acid present in the solution
is reduced to molybdenum blue.
TEST FOR ALBUMIN REAGENT PRINCIPLE POSITIVE RESULT
Hellers Nitric acid test Conc nitric acid White ring at point of contact
Picric acid test Saturated picric acid Turbidity or precipitate
Roberts Test Roberts rgt:
-Saturated MgSO4 White ring at point of contact
-Conc nitric acid
Sulfosalycilic acid 3% sulfosalicylic acid PROTE DEGREE OF TURBIDITY
- IN No increase in turbidity
Trac <6 Noticeable turbidity
e 6-30 Distinct turbidity, no granulation
1+ 30-100 Turbidity, granulation, no
2+ 100- flocculation
3+ 200 Turbidity, granulation, flocculation
4+ 200- Clumps of protein
400
>400
Trichloroacetic acid Trichloroacetic acid Turbidity or precipitate
También podría gustarte
- WBC Anomalies GuideDocumento20 páginasWBC Anomalies GuideJosephine Piedad100% (1)
- ASTM A1011 NovaDocumento9 páginasASTM A1011 NovaAlonso BrocheroAún no hay calificaciones
- Structural Welding ManualDocumento76 páginasStructural Welding ManualThomasman43Aún no hay calificaciones
- Carbs StainingDocumento32 páginasCarbs StainingIseth ISethAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochemical - TestsDocumento5 páginasBiochemical - TestsMohsen Haleem100% (1)
- Electrolytes PDFDocumento5 páginasElectrolytes PDFFrances FranciscoAún no hay calificaciones
- Parasitology Lecture OverviewDocumento17 páginasParasitology Lecture Overviewlouie100% (1)
- Qualitative Test For CarbohydratesDocumento4 páginasQualitative Test For CarbohydratesmegmayorAún no hay calificaciones
- Compre HistopatDocumento21 páginasCompre HistopatMark FuerteAún no hay calificaciones
- Microbiology Laboratory (Faculty of Pharmacy UST)Documento9 páginasMicrobiology Laboratory (Faculty of Pharmacy UST)Bianca OcampoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tubular TYK Fabrication and Inspection: It Is Important To Plan Ahead For These Complex WeldsDocumento5 páginasTubular TYK Fabrication and Inspection: It Is Important To Plan Ahead For These Complex Weldsluz82Aún no hay calificaciones
- MICROTOMYDocumento5 páginasMICROTOMYMarc Lloyd Alfonso100% (1)
- Biochemical Test of BacteriaDocumento33 páginasBiochemical Test of Bacteriaaziskf100% (2)
- Histopathology Lab Management ProceduresDocumento29 páginasHistopathology Lab Management ProceduresShara AboAún no hay calificaciones
- BLOOD BANK LECTURER: A CONCISE HISTORYDocumento36 páginasBLOOD BANK LECTURER: A CONCISE HISTORYDixie MartonitoAún no hay calificaciones
- UAReview Landis 2017 Rev1Documento17 páginasUAReview Landis 2017 Rev1Dayledaniel SorvetoAún no hay calificaciones
- API 571 Damage MechanismsDocumento42 páginasAPI 571 Damage MechanismsIsmail Jamaluddin100% (1)
- Mycology and VirologyDocumento8 páginasMycology and VirologyMaybelle Acap PatnubayAún no hay calificaciones
- Non-Enteric Gastrointestinal PathogensDocumento11 páginasNon-Enteric Gastrointestinal PathogensOrhan AsdfghjklAún no hay calificaciones
- Physical Exam of Urine SummaryDocumento3 páginasPhysical Exam of Urine SummaryBiancake Sta. AnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Meta Lab ManualDocumento66 páginasMeta Lab Manualharshal wasnik100% (1)
- NEMATODES NotesDocumento34 páginasNEMATODES NotesbebibobuAún no hay calificaciones
- COMPREHENSIVE MycoviroDocumento208 páginasCOMPREHENSIVE MycoviroMartin JustoAún no hay calificaciones
- HEMA 1 QUIZ multiple choice and matching practiceDocumento2 páginasHEMA 1 QUIZ multiple choice and matching practiceChristian John Mabalot CarilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemical Examination of UrineDocumento6 páginasChemical Examination of UrinehermanskyAún no hay calificaciones
- Staining of Tissue Pigments and DepositsDocumento4 páginasStaining of Tissue Pigments and DepositsAnonymous 8rsxG4100% (2)
- Vitamin B12 and FolateDocumento12 páginasVitamin B12 and FolateAllessandria DimaggioAún no hay calificaciones
- HaradamoriDocumento2 páginasHaradamorinicole castillo100% (1)
- Clinical Microscopy (Fecalysis)Documento2 páginasClinical Microscopy (Fecalysis)Sheng Ramos AglugubAún no hay calificaciones
- Cytochemical StainsDocumento4 páginasCytochemical StainsMartin PinedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cytochemistry Chapter SummaryDocumento3 páginasCytochemistry Chapter SummaryNathaniel SimAún no hay calificaciones
- Common Plating Media For Clinical Bacteriology (From Bailey & Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology, 12th Ed)Documento2 páginasCommon Plating Media For Clinical Bacteriology (From Bailey & Scott's Diagnostic Microbiology, 12th Ed)Elizabeth Enjambre HernaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Enzymes: Concentration, Kinetics, Classification, AssaysDocumento13 páginasEnzymes: Concentration, Kinetics, Classification, AssaysAedren TrillanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical Chemistry 1 - Notes NPNDocumento4 páginasClinical Chemistry 1 - Notes NPNlcrujidoAún no hay calificaciones
- (MID) IMMUNOSERO - Chapter 13 - Hypersensitivity (Reviewer)Documento6 páginas(MID) IMMUNOSERO - Chapter 13 - Hypersensitivity (Reviewer)Aisle Malibiran PalerAún no hay calificaciones
- AUBF Finals Vaginal SecretionsDocumento37 páginasAUBF Finals Vaginal SecretionsLyra Dennise LlidoAún no hay calificaciones
- Isolation and Characterization of ProteinsDocumento3 páginasIsolation and Characterization of ProteinsLor Sales0% (1)
- Cytochemistry LectureDocumento7 páginasCytochemistry Lecturemma1976Aún no hay calificaciones
- Hema I Chapter 12 - ESRDocumento30 páginasHema I Chapter 12 - ESRTesfaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fecal Exam TechniquesDocumento33 páginasFecal Exam TechniquesClaire GonoAún no hay calificaciones
- Red Cell Suspension Preparation and Reverse Typing ProcedureDocumento2 páginasRed Cell Suspension Preparation and Reverse Typing Procedurediversedct100% (4)
- MT Laws and Lab ManDocumento8 páginasMT Laws and Lab ManGene Narune GaronitaAún no hay calificaciones
- PMLS (Mod 1-3)Documento23 páginasPMLS (Mod 1-3)Ja NaeAún no hay calificaciones
- Decalcifying AgentsDocumento5 páginasDecalcifying AgentsLe Aura Mari Castillo100% (2)
- Faults Occurring During TrimmingDocumento4 páginasFaults Occurring During TrimmingMary Christelle100% (3)
- Blood ComponentsDocumento51 páginasBlood ComponentsMandy A. Delfin100% (1)
- 2021 06 Microbiology by Charles ArconadoDocumento8 páginas2021 06 Microbiology by Charles ArconadoFrankrine SolanoAún no hay calificaciones
- BB Other Blood Group SystemsDocumento5 páginasBB Other Blood Group SystemsGianna Sablan100% (1)
- Compre-Quiz For MedtechDocumento18 páginasCompre-Quiz For MedtechynaellyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lemar CC 2020Documento27 páginasLemar CC 2020TRIXIE CYRAH MIRANDA SALAVIAAún no hay calificaciones
- Histopathology MLS 304B UpdateDocumento23 páginasHistopathology MLS 304B UpdateBarakat IsmailAún no hay calificaciones
- Top 20 Blood Banking ConceptsDocumento16 páginasTop 20 Blood Banking ConceptsM CAún no hay calificaciones
- Alkaline PH Acid PH N Amorphous Phosphate Uric AcidDocumento3 páginasAlkaline PH Acid PH N Amorphous Phosphate Uric AcidSurriya NawazAún no hay calificaciones
- Clinical Microscopy ReviewerDocumento7 páginasClinical Microscopy ReviewerDayledaniel SorvetoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersDocumento27 páginas2.13.08 Cold Agglutinin RogersJessica StewartAún no hay calificaciones
- MUST TO KNOW CC RODRIGUEZ Flashcards - QuizletDocumento32 páginasMUST TO KNOW CC RODRIGUEZ Flashcards - QuizletWho KnowsAún no hay calificaciones
- cc2 Lectures AllDocumento256 páginascc2 Lectures AllJayson Dagohoy SudioAún no hay calificaciones
- BSC Licensure Sample QuestionsDocumento144 páginasBSC Licensure Sample QuestionsSAMMY0% (1)
- Chapter 24 - Extrinsic Defects Leading To Increased Erythrocyte Destruction - Non Immune CausesDocumento5 páginasChapter 24 - Extrinsic Defects Leading To Increased Erythrocyte Destruction - Non Immune CausesNathaniel SimAún no hay calificaciones
- Tests Purpose Reagents Visible (+) Result Principle InvolvedDocumento2 páginasTests Purpose Reagents Visible (+) Result Principle InvolvedjurieAún no hay calificaciones
- Qualitative Analysis Table For RecordDocumento5 páginasQualitative Analysis Table For RecordAnanda VijayasarathyAún no hay calificaciones
- A. ANTHRAQUINONE GLYCOSIDE TESTDocumento7 páginasA. ANTHRAQUINONE GLYCOSIDE TESTWestinAún no hay calificaciones
- Analyse Organic and Inorganic Unknowns WORDDocumento5 páginasAnalyse Organic and Inorganic Unknowns WORDcydney mackenzieAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochem CombinedDocumento14 páginasBiochem CombinedAmber De la CernaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chemistry 3B: Sulphate SolubilityDocumento11 páginasChemistry 3B: Sulphate SolubilityRaniaKaliAún no hay calificaciones
- Unconventional Machining ProcessDocumento39 páginasUnconventional Machining Processuday bavandla100% (1)
- Indian Boiler Regulations: (Xiii)Documento1 páginaIndian Boiler Regulations: (Xiii)Vishal SoniAún no hay calificaciones
- Ji MMMMMMMMMMDocumento6 páginasJi MMMMMMMMMMGeorgian GradeaAún no hay calificaciones
- SKD61Documento6 páginasSKD61Jigar M. UpadhyayAún no hay calificaciones
- BS en 755-7 1995 TablesDocumento6 páginasBS en 755-7 1995 TablesestabejaAún no hay calificaciones
- Defect in Casting For Amie Manufacturing Technology and Manufacturing ScienceDocumento33 páginasDefect in Casting For Amie Manufacturing Technology and Manufacturing ScienceparameshwaranpraveenAún no hay calificaciones
- Colour ChartDocumento1 páginaColour ChartgawaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chem (Final)Documento17 páginasChem (Final)Jaynie Lee VillaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Classifications of Magnetic MaterialsDocumento3 páginasClassifications of Magnetic MaterialsNasha Agarwal100% (1)
- Symbol Equations You Need To Be Familiar WithDocumento3 páginasSymbol Equations You Need To Be Familiar WithKamrul Alam MasumAún no hay calificaciones
- Komatsu Cat FinalDocumento29 páginasKomatsu Cat FinalcperaltaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aluminum 5052 H38Documento2 páginasAluminum 5052 H38Vishal VaishnavAún no hay calificaciones
- Weld DecayDocumento1 páginaWeld DecayGawan SagoroAún no hay calificaciones
- A Case Study of Stainless Steel Water Supply Pipe Corrosion Caused by Weld Heat TintDocumento23 páginasA Case Study of Stainless Steel Water Supply Pipe Corrosion Caused by Weld Heat Tintsusanweb100% (1)
- ASME V Liquid Penentrant ExaminationDocumento10 páginasASME V Liquid Penentrant ExaminationAlejandroAún no hay calificaciones
- Indoor Luminaires: Price List June 2016Documento4 páginasIndoor Luminaires: Price List June 2016khraieric16Aún no hay calificaciones
- Saint Gobain Sluice ValvesDocumento2 páginasSaint Gobain Sluice ValveskibzeamAún no hay calificaciones
- Vanessa Basic Datasheet-Valves PDFDocumento10 páginasVanessa Basic Datasheet-Valves PDFGogyAún no hay calificaciones
- Qcs 2010 Section 16 Part 10 Protective TreatmentDocumento5 páginasQcs 2010 Section 16 Part 10 Protective Treatmentbryanpastor106Aún no hay calificaciones
- VSR - Popustanje Napetosti VibriranjermDocumento8 páginasVSR - Popustanje Napetosti Vibriranjermdag9Aún no hay calificaciones
- Metal Casting Metal Casting Metal Casting Metal Casting Design, Materials, Economics Design, Materials, Economics G GDocumento42 páginasMetal Casting Metal Casting Metal Casting Metal Casting Design, Materials, Economics Design, Materials, Economics G Gzubairsajid_87Aún no hay calificaciones
- Astm E342Documento3 páginasAstm E342Wahyu Priyo KustamantoAún no hay calificaciones
- Broom Manufacture Machine: StartDocumento62 páginasBroom Manufacture Machine: StartHaziq PazliAún no hay calificaciones
- Udlp-Tacom Welding Code, Almn (Ansi-Aws d1.2)Documento120 páginasUdlp-Tacom Welding Code, Almn (Ansi-Aws d1.2)mtcengineering100% (2)
- 2009 Dual Man - CNC FleetDocumento1 página2009 Dual Man - CNC FleetGeorge KeithAún no hay calificaciones