Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Lec6w Processintegration Ee143 CTN
Cargado por
stansilaw0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
33 vistas15 páginasmicrofabrication technology 18
Título original
Lec6w.processIntegration.ee143.Ctn(1)
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentomicrofabrication technology 18
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
33 vistas15 páginasLec6w Processintegration Ee143 CTN
Cargado por
stansilawmicrofabrication technology 18
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 15
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lecture 6: Process Integration
Announcements:
Lecture in 180 Tan Hall today and from now
on -- ETS can record from this room
ETS recording today
I have Lecture 1 (with poor sound) and
Lecture 5 recorded -- will transfer to ETS
for posting on YouTube
-----------------------------------------Lecture Topics:
Example NMOS Process (finish this)
Masks & Alignment
Design Rules
-----------------------------------------Last Time:
Started NMOS process flow
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 1
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 2
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 3
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 4
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 5
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 6
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 7
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 8
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
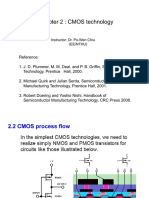
Example: NMOS Process
Layout:
Process Flow:
1. Silicon oxidation: target = 100nm
2. LPCVD Si3N4: target = 100nm
3. Lithography: Mask I (active area)
4. Etch Si3N4 to clear it in field areas
5. Field isolation implant: B+ (p-type)
6. Remove PR
7. Grow 1mm of SiO2 by thermal oxidation
(LOCOS oxidation)
8. Blanket etch all Si3N4 in hot phosphoric acid
wet etchant
9. Threshold voltage implant: B+ (no mask)
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 9
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
10. Remove 100nm of damaged oxide via a timed
wet etch in hydrofluoric acid (HF)
11. Grow 100nm of gate thermal oxide in an
ultra-clean furnace
12. LPCVD situ phosphorous-doped gate polysilicon
13. Lithography: Mask II (gate polysilicon)
14. Dry etch polysilicon to clear the field areas
15. Remove PR
16. D/S ion implantation: P or As (n-type)
17. Oxidize a bit (10nm) and anneal at 1050 oC to
activate dopants and drive-in diffusion
18. LPCVD PSG: target = 1m
19. Reflow PSG (& a little bit of diffusion) at
950oC
20. Lithography: Mask III (contact hole)
21. Dry/wet etch SiO2 down to n+ S/D regions
22. Sputter Al: target = 1m
23. Lithography: Mask IV (metal)
24. Dry etch Al
25. Deposit via LTO or PECVD Si 3N4 to serve as
passivation
26. Lithography: Mask V (bond pad contacts)
27. Etch passivation layer down to metal
28. (optional) spin double-thick PR over the front
side
29. Etch backside layers via successive wet
processes (to allow biasing of the substrate)
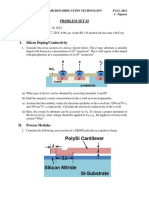
Through step 2:
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 10
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Through step 5:
Through step 12:
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 11
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Through step 16:
Through step 21:
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 12
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 13
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 14
EE 143: Microfabrication Technology
CTN 9/16/14
Lec 6 -- Copyright @ 2014 Regents of the UC -- Page 15
También podría gustarte
- Cue and Cut: A practical approach to working in multi-camera studiosDe EverandCue and Cut: A practical approach to working in multi-camera studiosAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Process DiffusionDocumento104 páginasBasic Process DiffusionBalamurugan Velayutham100% (1)
- 2CMOSFabricationMNIT (DEc2006)Documento46 páginas2CMOSFabricationMNIT (DEc2006)Arjun YadavAún no hay calificaciones
- Information Symposium Measurement and Control Techniques in Rolling: Luxembourg, 2 and 3 September 1981De EverandInformation Symposium Measurement and Control Techniques in Rolling: Luxembourg, 2 and 3 September 1981Aún no hay calificaciones
- Vlsi Design: Prepared Prepared Prepared Prepared by by by byDocumento30 páginasVlsi Design: Prepared Prepared Prepared Prepared by by by byVenkata SatishAún no hay calificaciones
- CMOS Process FlowDocumento39 páginasCMOS Process FlowYashaswa JainAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture CMOS NWELL and TwinTub ProcessDocumento33 páginasLecture CMOS NWELL and TwinTub Processilias ahmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 2 Fabrication ProcessDocumento8 páginasUnit 2 Fabrication Processbhupendra1977Aún no hay calificaciones
- IC Manufacturing SMT Process FlowDocumento41 páginasIC Manufacturing SMT Process FlowAnirban KarAún no hay calificaciones
- EE432/EE532 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques: Final Lab ReportDocumento28 páginasEE432/EE532 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques: Final Lab Reportapi-546410997Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lost Foam Casting (LFC)Documento26 páginasLost Foam Casting (LFC)Gurudutta Mishra100% (3)
- Microsoft Powerpoint - Vlsi Design AspectDocumento89 páginasMicrosoft Powerpoint - Vlsi Design AspectAKASHDIP DUTTAAún no hay calificaciones
- Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveDocumento21 páginasDigital Integrated Circuits: A Design PerspectiveAhmad ShdifatAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 02Documento35 páginasCH 02greeshmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mos FabricationDocumento35 páginasMos FabricationNhật HoàngAún no hay calificaciones
- CMOS/Processing TechnologyDocumento15 páginasCMOS/Processing TechnologyYidnekachwe MekuriaAún no hay calificaciones
- CMOS FabricationDocumento27 páginasCMOS FabricationspvenuAún no hay calificaciones
- CMOS Process FlowDocumento35 páginasCMOS Process Flowag21937570Aún no hay calificaciones
- A Teacher-Student Conversation On "Cmos Fabrication Process Flow"Documento70 páginasA Teacher-Student Conversation On "Cmos Fabrication Process Flow"Calcutta University RPE 2020Aún no hay calificaciones
- Printout VLSIDocumento8 páginasPrintout VLSIjanardhanan1711Aún no hay calificaciones
- MINOR2 DfinalocxDocumento32 páginasMINOR2 DfinalocxVenkatesh KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2: CMOS Technology: Instructor: Dr. Po-Wen Chiu (EE/NTHU)Documento35 páginasChapter 2: CMOS Technology: Instructor: Dr. Po-Wen Chiu (EE/NTHU)王靖堯Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 12 PDFDocumento14 páginasLec 12 PDFPrashant SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Microelectronic ManufacturingDocumento39 páginasMicroelectronic ManufacturingT uohzAún no hay calificaciones
- Analog Digital VLSI Design: Discipline/eee/agupta/advd/advd - HTMDocumento78 páginasAnalog Digital VLSI Design: Discipline/eee/agupta/advd/advd - HTMhkajaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Topics: Basic Fabrication Steps. Transistor Structures. Basic Transistor Behavior. Latch UpDocumento24 páginasTopics: Basic Fabrication Steps. Transistor Structures. Basic Transistor Behavior. Latch Uppra_zara2637Aún no hay calificaciones
- Isolation: CMOS Processing TechnologyDocumento15 páginasIsolation: CMOS Processing TechnologyAshwani RanaAún no hay calificaciones
- MOSCAP FabricationDocumento34 páginasMOSCAP FabricationAnjireddy ThatiparthyAún no hay calificaciones
- hw2 Ee143 f14 WebDocumento2 páginashw2 Ee143 f14 WebstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process: Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College LondonDocumento18 páginasTopic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process: Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College LondonRafael Sanchotene SilvaAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIT-1: TOPIC: MOS Process, NMOS Process, CMOS ProcessDocumento36 páginasUNIT-1: TOPIC: MOS Process, NMOS Process, CMOS ProcessashishAún no hay calificaciones
- CMOS Fabrication: (With Extended Comments)Documento26 páginasCMOS Fabrication: (With Extended Comments)srivardhana7Aún no hay calificaciones
- VLSI Lecture5 ManufacturingDocumento45 páginasVLSI Lecture5 Manufacturingdangerous319Aún no hay calificaciones
- CMOS Fabrication and LayoutDocumento14 páginasCMOS Fabrication and LayoutRose Beth AndayaAún no hay calificaciones
- hw3 Ee143 f14 WebDocumento4 páginashw3 Ee143 f14 WebstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Vlsi Design UNIT-1: Lecture-3Documento11 páginasVlsi Design UNIT-1: Lecture-3Erica WhiteheadAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrated Analog/Digital Bicmos ProcessDocumento8 páginasIntegrated Analog/Digital Bicmos ProcessJyothi PoornaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 7: Tecnología Y Fabricación de CisDocumento21 páginasTema 7: Tecnología Y Fabricación de CisSai SadiqAún no hay calificaciones
- Fabrikasi ICDocumento47 páginasFabrikasi ICNanamaliamAún no hay calificaciones
- hw9 Ee143 f14 WebDocumento6 páginashw9 Ee143 f14 WebstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Deep Submicron CMOS Tech DSMDocumento68 páginasDeep Submicron CMOS Tech DSMneva91Aún no hay calificaciones
- CMOS Processing Technology Silicon: A Semiconductor With Resistance Between That of Conductor and AnDocumento18 páginasCMOS Processing Technology Silicon: A Semiconductor With Resistance Between That of Conductor and AntmdmurthyAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 5 - VLSI Design - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocumento12 páginasUnit 5 - VLSI Design - WWW - Rgpvnotes.intanishachaturvedi2025Aún no hay calificaciones
- TPH Sog Sol Exe Eaw All Found CBPXXXX A 0 EnglishDocumento29 páginasTPH Sog Sol Exe Eaw All Found CBPXXXX A 0 EnglishMarouane FouadAún no hay calificaciones
- CMOS Tech-2UP (12 - 11 - 03)Documento29 páginasCMOS Tech-2UP (12 - 11 - 03)Mountsinai CscAún no hay calificaciones
- ALD in Semiconductor ProcessingDocumento26 páginasALD in Semiconductor ProcessingWeiHsinAún no hay calificaciones
- Cmos Fabrication TechnologyDocumento36 páginasCmos Fabrication TechnologyKhadarAún no hay calificaciones
- 2016 ch3-CMOS Technology PDFDocumento31 páginas2016 ch3-CMOS Technology PDFTrần Anh TânAún no hay calificaciones
- Program 2008Documento7 páginasProgram 2008toto1313Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sample Project ScheduleDocumento1 páginaSample Project ScheduleIPC Vietnam100% (2)
- VLSI CMOS Fabrication TechnologyDocumento15 páginasVLSI CMOS Fabrication TechnologyRamanaButterflyAún no hay calificaciones
- NOx Reduction TA Study v1 - December2005Documento70 páginasNOx Reduction TA Study v1 - December2005Dilnesa Ejigu100% (1)
- RAPDDocumento4 páginasRAPD123vidyaAún no hay calificaciones
- 421 Lab ManualDocumento17 páginas421 Lab ManualAiman LatifAún no hay calificaciones
- Faculty of Engineering Lab Sheet Processing and Fabrication Technology EEN3106Documento15 páginasFaculty of Engineering Lab Sheet Processing and Fabrication Technology EEN3106KarimovaRaikhanovnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Complementary MetalDocumento5 páginasComplementary MetalesaidanAún no hay calificaciones
- chymney-Hadek-Karrena CR-24-2Documento8 páginaschymney-Hadek-Karrena CR-24-2dnageshm4n244Aún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Pecvd Plasma Processes (Sih Based) : Pecvd Sinx: Sih + NH (+H) or Sih + N (+H)Documento36 páginasBasic Pecvd Plasma Processes (Sih Based) : Pecvd Sinx: Sih + NH (+H) or Sih + N (+H)Anonymous lidok7lDiAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture38 PDFDocumento2 páginasLecture38 PDFstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec26w.deviceCharacterization - Ee143 f14.CtnDocumento16 páginasLec26w.deviceCharacterization - Ee143 f14.CtnstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec3w MaterialsI Ee143 f14 PDFDocumento3 páginasLec3w MaterialsI Ee143 f14 PDFstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Module4.Etching - Ee143 f14.CtnDocumento20 páginasModule4.Etching - Ee143 f14.CtnstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Module6.Diffusion - Ee143 F14.ctnguyenDocumento13 páginasModule6.Diffusion - Ee143 F14.ctnguyenstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- hw1 Ee143 f14 Web PDFDocumento3 páginashw1 Ee143 f14 Web PDFstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Module5.IonImplantation - Ee143 F14.ctnguyenDocumento6 páginasModule5.IonImplantation - Ee143 F14.ctnguyenstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- SP 2005 Lecture06 PreviewDocumento1 páginaSP 2005 Lecture06 PreviewstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- SP 2005 Lecture08 CIMDocumento13 páginasSP 2005 Lecture08 CIMstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- EE 143 Microfabrication Technology Fall 2014: Prof. Clark T.-C. NguyenDocumento9 páginasEE 143 Microfabrication Technology Fall 2014: Prof. Clark T.-C. NguyenstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- SP 2005 Lecture09 PDFDocumento17 páginasSP 2005 Lecture09 PDFstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- 3.155J/6.152J Lecture 21: Fluids Lab Testing: Prof. Akintunde I. Akinwande Massachusetts Institute of Technology 5/2/2005Documento13 páginas3.155J/6.152J Lecture 21: Fluids Lab Testing: Prof. Akintunde I. Akinwande Massachusetts Institute of Technology 5/2/2005stansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 1Documento12 páginas3 1stansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Poly Gate pMOS: What Does Materials ScienceDocumento11 páginasPoly Gate pMOS: What Does Materials SciencestansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Oxidation of Si: 3.155J/6.152J Sept. 27, 2004Documento11 páginasOxidation of Si: 3.155J/6.152J Sept. 27, 2004stansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- SP 2005 Lecture05 PreviewDocumento1 páginaSP 2005 Lecture05 PreviewstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- SP 2005 Lecture04 PreviewDocumento2 páginasSP 2005 Lecture04 PreviewstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- SP 2005 Lecture03 PreviewDocumento1 páginaSP 2005 Lecture03 PreviewstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- SP 2005 Lecture04 PDFDocumento14 páginasSP 2005 Lecture04 PDFstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- 3.155J/6.152J Lecture 2: IC Lab Overview: Massachusetts Institute of Technology 02/09/2004Documento19 páginas3.155J/6.152J Lecture 2: IC Lab Overview: Massachusetts Institute of Technology 02/09/2004stansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- SP 2005 Lecture01Documento14 páginasSP 2005 Lecture01stansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Lithography Sequence: Lithography Process Requirements The PhotoresistDocumento3 páginasLithography Sequence: Lithography Process Requirements The PhotoresiststansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Social Justice MattersDocumento297 páginasSocial Justice MattersstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Typical Procedure For Lithography IV. Exposure System/OpticsDocumento1 páginaTypical Procedure For Lithography IV. Exposure System/OpticsstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Gas Power CyclesDocumento47 páginasGas Power CyclesstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec8w.lithographyII - Ee143 f14.CtnDocumento5 páginasLec8w.lithographyII - Ee143 f14.CtnstansilawAún no hay calificaciones
- First Semester Engineering Chemistry - I Question BankDocumento7 páginasFirst Semester Engineering Chemistry - I Question BankPRIYA RAJI0% (1)
- Approved AbstractsDocumento19 páginasApproved Abstractsanjaiah_19945Aún no hay calificaciones
- Etch Rates For Micromachining Processing PDFDocumento2 páginasEtch Rates For Micromachining Processing PDFJohnathanAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 14 The Nano WorldDocumento13 páginasLesson 14 The Nano Worldivy galvezAún no hay calificaciones
- 2022 Yds 1Documento32 páginas2022 Yds 1Ahmet Taha ÖzençAún no hay calificaciones
- BiosensorsDocumento47 páginasBiosensorsNeval YilmazAún no hay calificaciones
- Nano Science NotesDocumento1 páginaNano Science NotesamritnashuAún no hay calificaciones
- 15me30c8 - Material For Engineering Application - End Sem Question Paper - Set 4Documento2 páginas15me30c8 - Material For Engineering Application - End Sem Question Paper - Set 4Himanshu MishraAún no hay calificaciones
- Bionanomachines in ActionDocumento32 páginasBionanomachines in Actiondebarpitasahoo73Aún no hay calificaciones
- Review On Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles - Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism PDFDocumento24 páginasReview On Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles - Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism PDFKarol EsMaAún no hay calificaciones
- Name: Unit 3: Question For ReflectionDocumento3 páginasName: Unit 3: Question For Reflectionjenessa binAún no hay calificaciones
- AbstractsDocumento146 páginasAbstractsAnibal RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Bioinspired Intelligent Nanostructural Materials PDFDocumento360 páginasBioinspired Intelligent Nanostructural Materials PDFOtavio Ferreira MartinsAún no hay calificaciones
- Biomaterial AssignmentDocumento4 páginasBiomaterial AssignmentAhmad DboukAún no hay calificaciones
- Simulation of Young's Modulus of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Molecular DynamicsDocumento8 páginasSimulation of Young's Modulus of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Molecular DynamicsYahia BobAún no hay calificaciones
- Module Listing - AY1617 - Updated PDFDocumento4 páginasModule Listing - AY1617 - Updated PDFcmAún no hay calificaciones
- FinFET History Fundamentals FutureDocumento55 páginasFinFET History Fundamentals FutureMurali Shanmuga Sundaram100% (2)
- Unconventional Programming Paradigms 2004Documento226 páginasUnconventional Programming Paradigms 2004Yopghm698Aún no hay calificaciones
- NanosensorsDocumento2 páginasNanosensorslvrevathiAún no hay calificaciones
- Abstracts Cimtec 2012Documento164 páginasAbstracts Cimtec 2012Meltem Güngör100% (1)
- 1the Nanoscience of KajalDocumento2 páginas1the Nanoscience of KajalRashpal TakAún no hay calificaciones
- Diferencial de Barrido 1Documento20 páginasDiferencial de Barrido 1Adam TejadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nanotechnology For Water Treatment and Purification Volume 22Documento385 páginasNanotechnology For Water Treatment and Purification Volume 22Lorena Molina Calderon100% (2)
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocumento11 páginasReview of Related Literature and Studiesczargee27Aún no hay calificaciones
- Advantages and Disadvantages of NanotechnologyDocumento11 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of NanotechnologyAriana Athena V. PanuncioAún no hay calificaciones
- CrowdReviews Partnered With Madridge Publishers To Announce: International Conference On Materials Science and ResearchDocumento3 páginasCrowdReviews Partnered With Madridge Publishers To Announce: International Conference On Materials Science and ResearchPR.comAún no hay calificaciones
- Group 3: Nanotechnology in The PhilippinesDocumento4 páginasGroup 3: Nanotechnology in The PhilippinesIsidro ComonAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter - 3 Diversity in NanosystemsDocumento9 páginasChapter - 3 Diversity in NanosystemsKarthik VkAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamentals of Nanoscience I: Fni 1A 1Documento22 páginasFundamentals of Nanoscience I: Fni 1A 1mmiliyasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ea8 Tite Mo MaliitDocumento2 páginasEa8 Tite Mo Maliitalliyah valerioAún no hay calificaciones