Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Alkenes and Alkynes I
Cargado por
Arlene F. MontalboDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Alkenes and Alkynes I
Cargado por
Arlene F. MontalboCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Alkenes and Alkynes I: Structure and Preparation
Alkene - Hydrocarbon With Carbon-Carbon Double Bond
Also called an olefin but alkene is better
Includes many naturally occurring materials
Flavors, fragrances, vitamins
Important industrial products
These are feedstocks for industrial processes
Nomenclature
Suffix -ene
Find longest continuous carbon chain containing the double bond for root
name
Number carbons in chain so that double bond carbons have lowest possible
numbers
Rings have cyclo prefix
Many Alkenes Are Known by Common Names
Ethylene = ethene
Propylene = propene
Isobutylene = 2-methylpropene
Isoprene = 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene
Name the following Alkenes
CH3
CH2 CHCH2CH2CHCH3
CH3
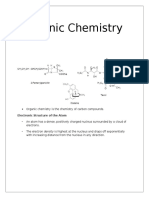
Electronic Structure of Alkenes
Carbon atoms in a double bond are sp2-hybridized
Three equivalent orbitals at 120 separation in plane
Fourth orbital is atomic p orbital
Combination of electrons in two sp2 orbitals of two atoms forms bond
between them
Additive interaction of p orbitals creates a bonding orbital
Subtractive interaction creates a anti-bonding orbital
Occupied orbital prevents rotation about -bond
Rotation prevented by bond - high barrier, about 268 kJ/mole in ethylene
Cis-Trans Isomerism in Alkenes
The presence of a carbon-carbon double can create two possible structures
cis isomer - two similar groups on same side of the double bond
trans isomer similar groups on opposite sides
Each carbon must have two different groups for these isomers to occur
Cis or Trans?
Cis, Trans Isomers Require That End Groups Must Differ in Pairs
180rotation superposes
Bottom pair cannot be superposed without breaking C=C
Sequence Rules: The E,Z Designation
Neither compound is clearly cis or trans
Substituents on C1 are different than those on C2
We need to define similarity in a precise way to
distinguish the two stereoisomers
Cis, trans nomenclature only works for disubstituted double
bonds
Develop a System for Comparison of Priority of Substituents
Assume a valuation system
If Br has a higher value than Cl
If CH3 is higher than H
Then, in A, the higher value groups are on
sides
In B, they are on the same side
opposite
Requires a universally accepted valuation
E,Z Stereochemical Nomenclature
Priority rules of Cahn, Ingold, and Prelog
Compare where higher priority group is with respect to
bond and designate as prefix
E -entgegen, opposite sides
Z - zusammen, together on the same side
Ranking Priorities: Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules
Must rank atoms that are connected at comparison point
Higher atomic number gets higher priority
Br > Cl > O > N > C > H
In this case,The higher priority groups are opposite: (E )-2-bromo-2-chloro-propene
Extended Comparison
If atomic numbers are the same, compare at next connection point at same
distance
Compare until something has higher atomic number
Do not combine always compare
Dealing With Multiple Bonds
Substituent is drawn with connections shown and no double or triple bonds
Added atoms are valued with 0 ligands themselves
Alkene Stability
Cis alkenes are less stable than trans alkenes
Compare heat given off on hydrogenation: Ho
Less stable isomer is higher in energy
And gives off more heat
tetrasubstituted > trisubstituted > disubstituted > monosusbtituted
hyperconjugation stabilizes alkyl
Prepartion of Alkenes
Dehydration of an Alcohol
También podría gustarte
- Passion Fruit Seed Oil Getpdf 014427Documento1 páginaPassion Fruit Seed Oil Getpdf 014427Arlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Food Chem. 2007-106-1046-56 PDFDocumento11 páginasFood Chem. 2007-106-1046-56 PDFArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 páginas6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Green Tea: This Article Is About The Type of Tea. For Other Uses, SeeDocumento15 páginasGreen Tea: This Article Is About The Type of Tea. For Other Uses, SeeArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- OrangesDocumento22 páginasOrangesArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- FoodSciSafety Flyer April2013Documento2 páginasFoodSciSafety Flyer April2013Arlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.the Perception of Local Street Food Vendors PDFDocumento22 páginas1.the Perception of Local Street Food Vendors PDFArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Orange Juic1Documento10 páginasOrange Juic1Arlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Proximate Analysis Phytochemical Screening and Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content of The Ethanolic Extract of Molave V PDFDocumento5 páginasProximate Analysis Phytochemical Screening and Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content of The Ethanolic Extract of Molave V PDFArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Inhibitory Activity of Euphorbia Hirta Tawa Tawa Extracts Against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Other Non MycobacterialDocumento4 páginasInhibitory Activity of Euphorbia Hirta Tawa Tawa Extracts Against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis and Other Non MycobacterialArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Crude FiberDocumento2 páginasCrude FiberArlene F. Montalbo100% (1)
- Orange Nutrition Facts-Vit C, Fiber BenefitsDocumento4 páginasOrange Nutrition Facts-Vit C, Fiber BenefitsArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 ThermochemistryDocumento57 páginas7 ThermochemistryArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Genetic EngineeringDocumento11 páginasGenetic EngineeringArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Euphorbia Hirta TawaDocumento3 páginasEuphorbia Hirta TawaArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- The Ideal Gas LawsDocumento7 páginasThe Ideal Gas LawsArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Organic ChemistryDocumento9 páginasOrganic ChemistryArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Cloning and Genetic Engineering of Animals For Food Production SummaryDocumento4 páginasCloning and Genetic Engineering of Animals For Food Production SummaryArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Effectivity of Euphorbia Hirta in Dengue TreatmentDocumento1 páginaEffectivity of Euphorbia Hirta in Dengue TreatmentArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Dean Medina CompilationDocumento165 páginasDean Medina CompilationArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- 06 Numerical Differentiation IntegrationDocumento50 páginas06 Numerical Differentiation IntegrationArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Atkins Chapter 7Documento1 páginaAtkins Chapter 7Arlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Atkins Chapter 4Documento1 páginaAtkins Chapter 4Arlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 24 Practice QuestionsDocumento7 páginasChapter 24 Practice QuestionsArlene F. Montalbo100% (1)
- PhychemDocumento16 páginasPhychemArlene F. MontalboAún no hay calificaciones
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- Mythi From AndromedaDocumento383 páginasMythi From AndromedaRico MinnerAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding Oscilloscope BasicsDocumento29 páginasUnderstanding Oscilloscope BasicsRidima AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 2Documento42 páginasModule 2DhananjayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ijimekko To Nakimushi-Kun (The Bully and The Crybaby) MangaDocumento1 páginaIjimekko To Nakimushi-Kun (The Bully and The Crybaby) MangaNguyễn Thị Mai Khanh - MĐC - 11A22Aún no hay calificaciones
- Feasibility StudyDocumento47 páginasFeasibility StudyCyril Fragata100% (1)
- Computer Portfolio (Aashi Singh)Documento18 páginasComputer Portfolio (Aashi Singh)aashisingh9315Aún no hay calificaciones
- USA V BRACKLEY Jan6th Criminal ComplaintDocumento11 páginasUSA V BRACKLEY Jan6th Criminal ComplaintFile 411Aún no hay calificaciones
- Easa Ad Us-2017-09-04 1Documento7 páginasEasa Ad Us-2017-09-04 1Jose Miguel Atehortua ArenasAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 1 Family PlanningDocumento84 páginasLecture 1 Family PlanningAlfie Adam Ramillano100% (4)
- 2.4 Avogadro's Hypothesis+ Equivalent MassesDocumento12 páginas2.4 Avogadro's Hypothesis+ Equivalent MassesSantosh MandalAún no hay calificaciones
- Elmeasure Solenoid Ates CatalogDocumento12 páginasElmeasure Solenoid Ates CatalogSEO BDMAún no hay calificaciones
- Design and Analysis of Crankshaft ComponentsDocumento21 páginasDesign and Analysis of Crankshaft Componentssushant470% (1)
- Transformer Oil Testing MethodsDocumento10 páginasTransformer Oil Testing MethodsDEE TOTLVJAAún no hay calificaciones
- Planview Innovation Management Maturity Model PDFDocumento1 páginaPlanview Innovation Management Maturity Model PDFMiguel Alfonso Mercado GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- Positioning for competitive advantageDocumento9 páginasPositioning for competitive advantageOnos Bunny BenjaminAún no hay calificaciones
- NameDocumento5 páginasNameMaine DagoyAún no hay calificaciones
- FALL PROTECTION ON SCISSOR LIFTS PDF 2 PDFDocumento3 páginasFALL PROTECTION ON SCISSOR LIFTS PDF 2 PDFJISHNU TKAún no hay calificaciones
- Master of Commerce: 1 YearDocumento8 páginasMaster of Commerce: 1 YearAston Rahul PintoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practical Research 2: Self-Learning PackageDocumento3 páginasPractical Research 2: Self-Learning PackagePrinces BaccayAún no hay calificaciones
- 2007 Bomet District Paper 2Documento16 páginas2007 Bomet District Paper 2Ednah WambuiAún no hay calificaciones
- ROM Flashing Tutorial For MTK Chipset PhonesDocumento5 páginasROM Flashing Tutorial For MTK Chipset PhonesAriel RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Doe v. Myspace, Inc. Et Al - Document No. 37Documento2 páginasDoe v. Myspace, Inc. Et Al - Document No. 37Justia.comAún no hay calificaciones
- Modern Indian HistoryDocumento146 páginasModern Indian HistoryJohn BoscoAún no hay calificaciones
- Course Tutorial ASP - Net TrainingDocumento67 páginasCourse Tutorial ASP - Net Traininglanka.rkAún no hay calificaciones
- Give Five Examples Each of Nature Having Reflection Symmetry and Radial Symmetry Reflection Symmetry Radial Symmetry Butterfly StarfishDocumento12 páginasGive Five Examples Each of Nature Having Reflection Symmetry and Radial Symmetry Reflection Symmetry Radial Symmetry Butterfly StarfishANNA MARY GINTOROAún no hay calificaciones
- Yanmar America publication listing for engine parts, service, and operation manualsDocumento602 páginasYanmar America publication listing for engine parts, service, and operation manualsEnrique Murgia50% (2)
- Device Interface Device Type (Router, Switch, Host) IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayDocumento2 páginasDevice Interface Device Type (Router, Switch, Host) IP Address Subnet Mask Default GatewayRohit Chouhan0% (1)
- BMS Technical ManualDocumento266 páginasBMS Technical Manualiago manziAún no hay calificaciones
- Steps To Configure Linux For Oracle 9i Installation: 1. Change Kernel ParametersDocumento5 páginasSteps To Configure Linux For Oracle 9i Installation: 1. Change Kernel ParametersruhelanikAún no hay calificaciones
- Deluxe Force Gauge: Instruction ManualDocumento12 páginasDeluxe Force Gauge: Instruction ManualThomas Ramirez CastilloAún no hay calificaciones