Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Lesson Plan: LP-EC1451 LP Rev. No: 02 Date: 05/12/2009 Page 01 of 06
Cargado por
Lokesh SharmaTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Lesson Plan: LP-EC1451 LP Rev. No: 02 Date: 05/12/2009 Page 01 of 06
Cargado por
Lokesh SharmaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
DOC/LP/01/28.02.
02
LESSON PLAN
LP-EC1451
LP Rev. No: 02
Sub Code & Name : EC1451 MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
Unit: I
Branch: EC
Semester: VIII
Date: 05/12/2009
Page 01 of 06
Unit I Syllabus:
Cellular Concept and System Design Fundamentals:
Introduction to wireless communication: Evolution of mobile communications, mobile radio systemsExamples, trends in cellular radio and personal communications.
Cellular Concept: Frequency reuse, channel assignment, hand off, Interference and system capacity, tracking
and grade of service, Improving Coverage and capacity in Cellular systems.
Objective:
At the end of this unit, students are expected to be familiar with
1. Cellular radio system concept, Frequency reuse concept and handoff principles.
2. Techniques for improving Coverage and Capacity.
3. The principles of trunking and Calculation of grade of Service.
S.No
Topics to be covered
Time in
minutes
Books
Referred
Teaching
Aids
Introduction to Mobile Communication and Overall View of the Syllabus
and Lesson Plan
50m
1,2,3
BB
Introduction to Wireless Communication:
Evolution of Mobile communications (P.No: 1 To 3 of TB-1), Mobile RadioThe First 100 Years (P.No: 1 To 6 of RB-3), Historical Overview (P.No: 366
To 373 of RB-2)
50m
1,2,3
BB
Mobile Radio Systems-Examples
Mobile Radio Telephony in the US (P.No: 4 To 6 of T1), Examples &
Comparisons of Wireless Communication Systems (P.No: 4 To 19 of T1),
Cellular Network Planning (P.No: 6 To 17 of R3)
50m
1,3
BB
Trends in Cellular Radio and Personal Communication: How a cellular
telephone call is made (P.No: 20 To 21 of T1) Commercial Vs. Military Uses
(P.No: 17 To 19 of R3)
50m
1,3
BB
Cellular Concept: Frequency Reuse (P.No:58 To 61 of T1), Frequency
Reuse Factor (P.No:319To320 of R3), Channel Assignment (P.No:62 of T1)
50m
1,3
BB
Hand off Strategies, Prioritizing Handoff & Practical Handoff Considerations
(P.No: 62 To 67 of T1), Break Before Make & Make Before Break (P.No:
619 To 622 of R3)
50m
1,3
BB
Interference and System Capacity (P.No: 67 To 77 of T1)
Co-channel Interference and System Capacity, (P.No: 422 To 423 of R3)
Adjacent Channel Interference,
Channel Planning for Wireless Systems and Power Control Management
50m
1,3
BB
Trunking and Grade of Service (P.No: 77 To 86 of T1)
50m
BB
Improving Coverage and Capacity in Cellular systems-Cell Splitting,
Sectoring, Repeaters, Micro-cell Zone Concept (P.No: 86 To 96 of T1)
50m
BB
DOC/LP/01/28.02.02
LESSON PLAN
LP-EC1451
LP Rev. No: 02
Sub Code & Name : EC1451 MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
Unit: II
Branch: EC
Semester: VIII
Date: 05/12/2009
Page 02 of 06
UNIT II SYLLABUS
MOBILE RADIO PROPAGATION
Free space propagation model, reflection, diffraction, scattering, link budget design, Outdoor Propagation
models, Indoor propagation models, Small scale Multipath propagation, Impulse model, Small scale Multipath
measurements, parameters of Mobile multipath channels, types of small scale fading, statistical models for
multipath fading channels.
Objective:
From this unit the students will know about the
1.
Radio propagation models
2.
Prediction of the large scale effects of radio propagation in many operating environment.
3.
Small propagation effects such as fading, time delay spread and Doppler spread.
S.No
Topics to be covered
10
Introduction to Radio Wave Propagation (P.No: 105 To 106 of T1)
Free Space Propagation Model (P.No: 107 To 110 of T1),
(P.No: 221 To 230 of R2)
Reflection: Reflection from Dielectrics, Brewster Angle, Reflection from
Perfect Conductors (P.No: 114 To 120 of T1) Diffraction: Fresnel Zone
Geometry, Knife Edge Diffraction Model, Multiple Knife Edge Diffraction
Model (P.No: 126 To 135 of T1) Scattering: Radar Cross Section Model
(P.No: 135 To 138 of T1)
Link budget design: Log Distance Path Loss Model, Log Normal
Shadowing, Determination of Percentage Coverage Area (P.No: 138 To
144 of T1) Outdoor Propagation Model: Longley Rice Model, Durkins
Model, Okumura Model, Hata Model, PCS Extension to Hata Model,
Walfisch & Bertoni Model, Wideband PCS Micro Cell Model (P.No: 157
To 166 of T1)
Indoor propagation models: Partition Losses-Same Floor, Between
Floors, Log Distance Path Loss Model, Ericsson Multiple Break Point
Model, Attenuation Factor Model (P.No: 157 To 166 of T1)
Small Scale Multipath propagation: Factors Influencing Small Scale
Fading Doppler Shift, Fading Effects Due to Doppler Spread (P.No: 177
To 180 of T1) (P.No: 233 To 239 of R2)
Impulse Model of a Multipath channel: Relationship Between
Bandwidth and Received Power (P.No: 181 To 191 of T1)
Small Scale Multipath Measurements: Direct RF Pulse System, Spread
Spectrum Sliding Correlator Channel Sounding, Frequency Domain
Channel Sounding (P.No: 192 To 197 of T1)
Parameters of Mobile Multipath Channels: Time Dispersion
Parameters, Coherence Bandwidth, Doppler Spread & Coherence Time
(P.No: 197 To 204 of T1) Types of Small Scale Fading: Fading Effects
Due to Multipath Time Delay Spread (P.No: 205 To 210 of T1)
Statistical Models for Multipath Fading Channels: Clarkes Model for
Flat Fading, Simulation of Clarke& Gans Fading Model, Level Crossing &
Fading Statistics, Two-ray Rayleigh Fading Model, Saleh & Valenzuela
Indoor Statistical Model, SIRCIM & SMRCIM Indoor & Out door
Statistical Model (P.No: 214 To 229 of T1)
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
CAT-I
Time in
minutes
Books
Referred
Teaching
Aids
50m
1,2
BB
50m
1,2
BB
50m
BB
50m
BB
50m
1,2
BB
50m
BB
50m
BB
50m
BB
50m
BB
DOC/LP/01/28.02.02
LESSON PLAN
LP-EC1451
LP Rev. No: 02
Sub Code & Name : EC1451 MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
Unit: III
Branch: EC
Semester: VIII
Date: 05/12/2009
Page 03 of 06
UNIT III Syllabus:
MODULATION TECHNIQUES AND EQUALIZATION
Modulation Techniques: Minimum Shift Keying, Gauss ion MSK, M-ary QAM, M-ary FSK, Orthogonal
Frequency Division Multiplexing, Performance of Digital Modulation in Slow-Flat Fading Channels and
Frequency Selective Mobile Channels. Equalization: Survey of Equalization Techniques, Linear Equalization,
Non-linear Equalization, Algorithms for Adaptive Equalization. Diversity Techniques, RAKE receiver.
Objective:
The students will get familiarized in knowing about the
1.
Modulation techniques such as BPSK, MSK, GMSK etc.
2.
Some equalization techniques such as Linear Equalization and Non-linear Equalization.
3.
Diversity Techniques, RAKE receiver.
Time in
minutes
Books
Referred
Teaching
Aids
50m
1.2,3
BB
50m
1,4
BB
50m
BB
Performance of digital modulation in slow-flat fading channels
(P.No: 340 To 344 of T1) and frequency selective mobile channels
(P.No: 344 To 346 of T1)
50m
BB
23
Introduction and fundamentals of equalization, Survey of Equalization
Techniques (P.No: 364 To 366 of T1)
50m
BB
24
Linear Equalization (P.No: 366 To 368 of T1)
50m
BB
25
Non-linear Equalization:
50m
BB
50m
BB
50m
1,2,3
BB
S.No
Topics to be covered
19
Constant envelope modulation:
Minimum Shift Keying (P.No: 314 To 318 of T1)
Gauss ion MSK (P.No: 318 To 323 of T1) (P.No: 300 of R3) (P.No: 120
To 121 of R2)
20
Combined Linear and Constant envelope modulation:
M-ary QAM (P.No: 325 To 328 of T1) (P.No: 190 To 196 of R4)
21
M-ay FSK, Orthogonal frequency division Multiplexing (P.No: 328
To 329 of T1)
22
Decision Feedback Equalization (DFE), Maximum Likelihood
Sequence Estimation (MLSE) Equalizer (P.No: 368 To 372 of T1)
26
Algorithms for Adaptive Equalization:
Zero Forcing Algorithm, LMS Algorithm, Recursive LMS
Algorithm, Summary of Algorithms (P.No: 372 To 379 of T1)
27
Diversity Techniques:
Derivation of Selection Diversity Improvement, Derivation of
Maximal Ratio Combining Improvement, Practical Space Diversity
Considerations, Polarization Diversity, Frequency Diversity, Time
Diversity (P.No: 380 To 391 of T1)
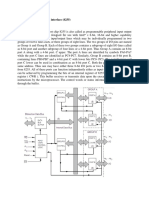
RAKE Receiver: (P.No: 391 To 393 of T1) (P.No: 438 of R2)
DOC/LP/01/28.02.02
LESSON PLAN
LP-EC1451
LP Rev. No: 02
Sub Code & Name : EC1451 MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
Unit: IV
Branch: EC
Semester: VIII
Date: 05/12/2009
Page 04 of 06
UNIT IV Syllabus:
CODING AND MULTIPLE ACCESS TECHNIQUES
Coding: Vocoders, Linear Predictive Coders, Selection of Speech Coders for Mobile Communication, GSM
Codec, RS codes for CDPD. Multiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, CDMA, SDMA, Capacity of
Cellular CDMA and SDMA.
Objective:
At the end of this unit, students are expected to be familiar with
1.
Speech coding principles.
2.
The time, frequency code division multiple access techniques as well as more recent multiple
access technique such as space division multiple access.
S.No
Topics to be covered
Time in
minutes
Books
Referred
Teaching
Aids
28
Vocoders:
Channel Vocoders, Formant Vocoders, Cepstrum Vocoders, Voice-Excited
Vocoders (P.No: 429 To 431 of T1) (P.No: 102 To 104 of R2)
50m
1,2
BB
Linear Predictive Coders:
LPC Vocoders, Multi Pulse Excited LPC, Code Excited LPC, Residual
Excited LPC (P.No: 431 To 436 of T1)
50m
BB
30
Selection of Speech Coders for Mobile Communication
(P.No: 436 To 440 of T1)
50m
BB
31
GSM Codec (P.No: 440 To 441 of T1)
50m
1,2,3
BB
32
RS codes for CDPD
50m
1,2,3
BB
33
FDMA (P.No: 449 To 453 of T1)
50m
1,2,3
BB
50m
1,2,3
BB
29
TDMA (P.No: 453 To 456 of T1), (P.No: 126 of R2)
Multiple Access Scheme (P.No: 511 To 558 of R3)
34
CDMA (P.No: 458 To 459 of T1) (P.No: 133 of R2)
SDMA (P.No: 461 To 462 of T1)
Multiple Access Scheme (P.No: 511 To 558 of R3)
35
Capacity of Cellular CDMA and SDMA Calculations
(P.No: 474 To 487 of T1)
50m
1,3
BB
36
Problems on Capacity of Cellular CDMA and SDMA Calculations
(P.No: 474 To 487 of T1)
50m
1,3
BB
CAT-II
DOC/LP/01/28.02.02
LESSON PLAN
LP-EC1451
LP Rev. No: 02
Sub Code & Name : EC1451 MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
Unit: V
Branch: EC
Semester: VIII
Date: 05/12/2009
Page 05 of 06
UNIT V Syllabus:
WIRELESS SYSTEMS AND STANDARDS
Second Generation and Third Generation Wireless Networks and Standards, WLL, Blue tooth. AMPS, GSM,
IS-95 and DECT
Objective:
From this unit the students will learn about the
1. Second generation and third generation wireless networks
2. Worldwide wireless standards.
S.No
Topics to be covered
37
Development of Wireless networks (P.No: 499 To 501 of T1)
38
Wireless systems and standards:
Time in
minutes
Books
Referred
Teaching
Aids
50m
BB
50m
1,2
BB
Key Specifications of 2G Technology
Evolution of 2.5G
2.5G & 3G Communication Standard (P.No: 25 To 40 of T1)
IMT 2000 Specification (P.No: 525 To 527 of R2)
39
WLL (P.No: 40 To 45 of T1) (P.No: 520 To 525 of R2)
50m
1,2
BB
40
Bluetooth (P.No: 52 To 54 of T1)
50m
BB
41
AMPS-AMPS system overview, call handling and AMPS air interface,
N-AMPS (P.No: 533 of T1) (P.No: 524 of R2)
50m
1,2
BB
42
GSM-Services and Features, System Architecture, Radio subsystem
(P.No: 549 To 566 of T1)
50m
BB
43
GSM-Channel types, GSM call, Frame structure, Signal processing
(P.No: 549 To 566 of T1)
50m
BB
44
CDMA Digital cellular standard (IS-95):
50m
1,2
BB
50m
BB
Frequency & Channel Specification, Forward CDMA Channel, Reverse
CDMA Channel, IS-95 with 14.4kbps Speech Coders
(P.No: 567 To 580 of T1) (P.No: 429 To 439 of R2)
45
DECT:
Digital
European
cordless
telephone-features,
Characteristics,
Architecture, Functional concept and radio link (P.No: 582 To 586 of T1)
CAT III
DOC/LP/01/28.02.02
LESSON PLAN
LP-EC1451
LP Rev. No: 02
Sub Code & Name : EC1451 MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS
Branch: EC
Date: 05/12/2009
Page 06 of 06
Semester: VIII
Course Delivery Plan:
Week
Units
10
11
12
13
I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II I II
C
C
C
1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 A 3 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 A 5 5 5 5 A
T
5 T
T
2
3
2
1
TEXT BOOK
1.
T.S.Rappaport, Wireless Communications: Principles and Practice, Second
Edition, Pearson Education/ Prentice Hall of India, Third Indian Reprint 2003.
REFERENCES
2.
R. Blake, Wireless Communication Technology, Thomson Delmar, 2003.
3.
W.C.Y.Lee, "Mobile Communications Engineering: Theory and applications,
Second Edition, McGraw-Hill International, 1998.
4.
Stephen G. Wilson, Digital Modulation and Coding, Pearson Education,
2003.
Prepared by
Approved by
Signature
Name
Dr.N.Venkateswaran
Mr.S.Senthil Rajan
Dr.R.Amutha
Designation
Professor
Senior Lecturer
HOD - ECE
También podría gustarte
- Wireless Communications and NetworksDocumento3 páginasWireless Communications and NetworksNaresh KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Sem 2Documento7 páginasSem 2Ajay KatageriAún no hay calificaciones
- Uni Structure Mob CommDocumento2 páginasUni Structure Mob Commanand_jha_309177Aún no hay calificaciones
- Performance Analysis of OFDM For 4G Wireless Systems Under Various Fading ChannelsDocumento4 páginasPerformance Analysis of OFDM For 4G Wireless Systems Under Various Fading ChannelsJuan Dela CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- B.tech ECE Syllabus 2017 FinalDocumento3 páginasB.tech ECE Syllabus 2017 FinalChandru RamaswamyAún no hay calificaciones
- Mishra and BeratingDocumento5 páginasMishra and BeratingMahmud JaafarAún no hay calificaciones
- Department of Ece Lesson Plan Subject: Subject Code: CLASS: IV Year A' & B'Documento5 páginasDepartment of Ece Lesson Plan Subject: Subject Code: CLASS: IV Year A' & B'Balasubramoniam ChokalingamAún no hay calificaciones
- Mobile Communication SlideDocumento251 páginasMobile Communication SlideVõ Thanh LiêmAún no hay calificaciones
- JNTUH Syllabus 2013 M.tech Communication SysDocumento26 páginasJNTUH Syllabus 2013 M.tech Communication SysSRINIVASA RAO GANTAAún no hay calificaciones
- 31 Ec647Documento2 páginas31 Ec647armen zarAún no hay calificaciones
- ECE Elective SyllabusDocumento34 páginasECE Elective SyllabusPratyush ChauhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Wireless Communication2171004Documento5 páginasWireless Communication2171004Aaryan AshokAún no hay calificaciones
- Cusat Btech Ece S8 SyllabusDocumento4 páginasCusat Btech Ece S8 SyllabusAmalAún no hay calificaciones
- Detail MIMO Wireless CommunicationsDocumento4 páginasDetail MIMO Wireless Communicationsshakeel1900Aún no hay calificaciones
- Performance Analysis of FBMC Prototype Filter Under The Effect of Variable Parameters For Physical Layer Cognitive RadioDocumento7 páginasPerformance Analysis of FBMC Prototype Filter Under The Effect of Variable Parameters For Physical Layer Cognitive RadioDr-Eng Imad A. ShaheenAún no hay calificaciones
- GITAM-ECE-4 TH Yr SyllabusDocumento41 páginasGITAM-ECE-4 TH Yr SyllabusSanthosh KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Performance Analysis of VBLAST MIMO-OFDM System For Intelligent Transportation SystemDocumento9 páginasPerformance Analysis of VBLAST MIMO-OFDM System For Intelligent Transportation SystemRakeshconclaveAún no hay calificaciones
- Dcrust ECE 4th YearDocumento16 páginasDcrust ECE 4th YearRahulPoriaAún no hay calificaciones
- ADC Lecture Contents 1-2-3 Dr. Samarth BorkarDocumento20 páginasADC Lecture Contents 1-2-3 Dr. Samarth Borkarpranavraikar1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationDe EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationAún no hay calificaciones
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsDe EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsAún no hay calificaciones
- Overview of Wireless Channel Models For UMTS and LTE: Abbas Mohammed and Asad MehmoodDocumento36 páginasOverview of Wireless Channel Models For UMTS and LTE: Abbas Mohammed and Asad MehmoodIgor MalianovAún no hay calificaciones
- Digital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsDe EverandDigital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsCalificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (2)
- Modern Communication TechnologiesDocumento3 páginasModern Communication TechnologiesSourabh VoraAún no hay calificaciones
- Cognitive Radio System Analysis Using MATLABDocumento4 páginasCognitive Radio System Analysis Using MATLABKennedy RonohAún no hay calificaciones
- Analog and DigitalcommunicationsDocumento139 páginasAnalog and DigitalcommunicationsPacha Praneeth35Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cross-Layer Design in Cognitive RadioDocumento6 páginasCross-Layer Design in Cognitive RadioAbhishek Pandey0% (1)
- Analog CommunicationsDocumento117 páginasAnalog CommunicationsSusmitha SambaAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics Communication SCH and Syla Pages DeletedDocumento6 páginasElectronics Communication SCH and Syla Pages DeletedAnanya AcharAún no hay calificaciones
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesDe EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- 5.another Format Paper 2Documento6 páginas5.another Format Paper 2iisteAún no hay calificaciones
- NptelDocumento3 páginasNptelAbhay GargAún no hay calificaciones
- Channel Estimation Techniques Over MIMO-OFDM SystemDocumento4 páginasChannel Estimation Techniques Over MIMO-OFDM SystemEditor IJRITCCAún no hay calificaciones
- Space-Time Block Coding (STBC) For Wireless NetworksDocumento13 páginasSpace-Time Block Coding (STBC) For Wireless NetworksijdpsAún no hay calificaciones
- Scheme of Examination of B.EDocumento12 páginasScheme of Examination of B.EDivay SawhneyAún no hay calificaciones
- Ec2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit IDocumento10 páginasEc2401 - Wireless Communication - Question Bank Unit Inazareth621Aún no hay calificaciones
- Wireless and Mobile Communications: InstructorDocumento43 páginasWireless and Mobile Communications: InstructorRaja Iftikhar HaiderAún no hay calificaciones
- ECE - MIMO-An Evolution - Abdul RashidDocumento6 páginasECE - MIMO-An Evolution - Abdul RashidTJPRC PublicationsAún no hay calificaciones
- Syll 6Documento7 páginasSyll 6BT21EE017 Gulshan RajAún no hay calificaciones
- Mobile Communication SyllabusDocumento2 páginasMobile Communication Syllabusflampard24Aún no hay calificaciones
- Wireless Receiver Architectures and Design: Antennas, RF, Synthesizers, Mixed Signal, and Digital Signal ProcessingDe EverandWireless Receiver Architectures and Design: Antennas, RF, Synthesizers, Mixed Signal, and Digital Signal ProcessingAún no hay calificaciones
- EE-402-E Wireless CommunicationDocumento4 páginasEE-402-E Wireless Communicationsanchi sethiAún no hay calificaciones
- Course Design Template Name of The Course: 21UEC959 Principles of CommunicationDocumento6 páginasCourse Design Template Name of The Course: 21UEC959 Principles of CommunicationDevika R ECEAún no hay calificaciones
- Wireless Lesson PlanDocumento1 páginaWireless Lesson PlanNadeem PashaAún no hay calificaciones
- ECE40 3 Wireless and Mobile Communication 3 0 0 3: Expected OutcomeDocumento2 páginasECE40 3 Wireless and Mobile Communication 3 0 0 3: Expected OutcomeAditya JainAún no hay calificaciones
- Master Thesis Long ProjectDocumento3 páginasMaster Thesis Long ProjectSreshta TricAún no hay calificaciones
- Radio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericDe EverandRadio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericAún no hay calificaciones
- A Review On SpectrumSensing For Cognitive RadioDocumento15 páginasA Review On SpectrumSensing For Cognitive RadioHamza DericheAún no hay calificaciones
- EC404 Advanced Communication SystemsDocumento2 páginasEC404 Advanced Communication SystemsanupvasuAún no hay calificaciones
- Koneru College B.Tech Mobile Communication SyllabusDocumento2 páginasKoneru College B.Tech Mobile Communication SyllabusNagarjuna JamullamudiAún no hay calificaciones
- Eeng360 Fall2010 2011 Course DescriptDocumento2 páginasEeng360 Fall2010 2011 Course DescriptEdmond NurellariAún no hay calificaciones
- WC Question Bank 10.10.17 STDocumento26 páginasWC Question Bank 10.10.17 STVigneswaran VigneshAún no hay calificaciones
- Survey On Throughput Enhancement Techniques For Real Time Wireless Link DeploymentDocumento17 páginasSurvey On Throughput Enhancement Techniques For Real Time Wireless Link DeploymentthiyagupsgAún no hay calificaciones
- Eight SemDocumento1 páginaEight Semapi-19497192Aún no hay calificaciones
- GTU Wireless Communication Course OverviewDocumento4 páginasGTU Wireless Communication Course OverviewMansi PatelAún no hay calificaciones
- Practical Guide to MIMO Radio Channel: with MATLAB ExamplesDe EverandPractical Guide to MIMO Radio Channel: with MATLAB ExamplesAún no hay calificaciones
- BOS Final - 4 Sem - 18EC42Documento4 páginasBOS Final - 4 Sem - 18EC42‡ ‡AnuRaG‡‡Aún no hay calificaciones
- MIMO OverviewDocumento22 páginasMIMO OverviewSaimaFakharAún no hay calificaciones
- Analog Digital CommunicationDocumento3 páginasAnalog Digital CommunicationHarsha M VAún no hay calificaciones
- Cep CommunicationDocumento13 páginasCep CommunicationMUHAMMAD BADAR ASHRAF RANAAún no hay calificaciones
- Proceedings of The Training Program Held On May 21, 2021Documento4 páginasProceedings of The Training Program Held On May 21, 2021Lokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- 30 April ProccDocumento4 páginas30 April ProccLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Session 5 Interfacing of Analog Digital IO Devices With NodeMCUDocumento18 páginasSession 5 Interfacing of Analog Digital IO Devices With NodeMCULokesh Sharma100% (1)
- Mininet VM: Kernel, Switch and Application Code, On A Single Machine (VM, Cloud or Native), in SecondsDocumento5 páginasMininet VM: Kernel, Switch and Application Code, On A Single Machine (VM, Cloud or Native), in SecondsAlbergica AldoAún no hay calificaciones
- Dr. Lokesh Sharma (MU - Jaipur) : CautionDocumento8 páginasDr. Lokesh Sharma (MU - Jaipur) : CautionLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- FDP On "Internet of Things": Session 1: Key Note SpeechDocumento17 páginasFDP On "Internet of Things": Session 1: Key Note SpeechLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sciencedirect: 6/Pphwulf.H/ (Qfu/Swlrq7Hfkqltxh$&Hooxodu$Xwrpdwdedvhg $Ssurdfklq:Luhohvv6Hqvru1HwzrunvDocumento7 páginasSciencedirect: 6/Pphwulf.H/ (Qfu/Swlrq7Hfkqltxh$&Hooxodu$Xwrpdwdedvhg $Ssurdfklq:Luhohvv6Hqvru1HwzrunvLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Dr. Ravi Kant Gupta (MU - Jaipur) : CautionDocumento2 páginasDr. Ravi Kant Gupta (MU - Jaipur) : CautionLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Dr. Lokesh Sharma (MU - Jaipur) : CautionDocumento8 páginasDr. Lokesh Sharma (MU - Jaipur) : CautionLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Central Board of Secondary Education, Delhi Roll Number Slip-Examination 2021 (Main)Documento1 páginaCentral Board of Secondary Education, Delhi Roll Number Slip-Examination 2021 (Main)Lokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- IoT For GECR RevisedDocumento55 páginasIoT For GECR RevisedLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Boanfied Certificate: Deputy Director Admissins Manipal University JaipurDocumento1 páginaBoanfied Certificate: Deputy Director Admissins Manipal University JaipurLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Floodlight Controller Tutorial - PradeepaDocumento8 páginasFloodlight Controller Tutorial - PradeepaLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- SDN Laboratory: Fabrizio GranelliDocumento39 páginasSDN Laboratory: Fabrizio GranelliLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Manipal University, Jaipur B.Tech., I Semester - 2018 Time Table Section:-J (Physics Group)Documento1 páginaManipal University, Jaipur B.Tech., I Semester - 2018 Time Table Section:-J (Physics Group)Lokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Build custom topologies using Mininet Python API and test performanceDocumento9 páginasBuild custom topologies using Mininet Python API and test performancebaskoroboAún no hay calificaciones
- Sec ADocumento1 páginaSec ALokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Day 01 - Session 03 - AICTE ATAL FDP On Internet of ThingsDocumento55 páginasDay 01 - Session 03 - AICTE ATAL FDP On Internet of ThingsLokesh Sharma100% (1)
- Application Original Degree CertificatesDocumento1 páginaApplication Original Degree CertificatesLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sensor NetworksDocumento68 páginasSensor NetworksLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 1 1 104 7910Documento22 páginas10 1 1 104 7910Lokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 s2.0 S1570870513002345 MainDocumento14 páginas1 s2.0 S1570870513002345 MainLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- 2008-04 Can Wireless Be SecuredDocumento31 páginas2008-04 Can Wireless Be SecuredLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Kumar 2012Documento7 páginasKumar 2012Lokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1687 1499 2013 109Documento13 páginas1687 1499 2013 109Lokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 6 Java Script - ArrayDocumento61 páginasLecture 6 Java Script - ArrayLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sem Che Dine 2016Documento4 páginasSem Che Dine 2016Lokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Impact of Variable Transmission Range An PDFDocumento8 páginasImpact of Variable Transmission Range An PDFLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mobile Communication and Computing CourseDocumento3 páginasMobile Communication and Computing CourseLokesh SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiplex Ticket Booking SystemDocumento23 páginasMultiplex Ticket Booking SystemMohit Kumar Lal100% (1)
- Programmable Peripheral Interface (8255) Architecture of 8255Documento15 páginasProgrammable Peripheral Interface (8255) Architecture of 8255shivaniAún no hay calificaciones
- DPH-20U 10U VoIP PhoneDocumento5 páginasDPH-20U 10U VoIP PhoneMillington MambweAún no hay calificaciones
- Fortigate Daily Security Report: Report Date: 2020-06-02 Data Range: Jun 01, 2020 (FW - Sm01)Documento17 páginasFortigate Daily Security Report: Report Date: 2020-06-02 Data Range: Jun 01, 2020 (FW - Sm01)David EstebanAún no hay calificaciones
- KOMATSU D65PX-15 Service ManualDocumento267 páginasKOMATSU D65PX-15 Service ManualLizardo Astudillo Cruz100% (8)
- Internsship - Project - Arjun Singh FinalDocumento78 páginasInternsship - Project - Arjun Singh FinalAnmol DubeyAún no hay calificaciones
- NG10 Manual 01 2011Documento164 páginasNG10 Manual 01 2011nknfiveAún no hay calificaciones
- Group 1 TCHE425 (23 24) 2.1 Mid Term International Financial ManagementDocumento34 páginasGroup 1 TCHE425 (23 24) 2.1 Mid Term International Financial Managementtran phankAún no hay calificaciones
- SOP - Rajarshi Das IT CoursesDocumento2 páginasSOP - Rajarshi Das IT CoursesNithinAún no hay calificaciones
- Portstation Breathing Apparatus Self Contained Breathing ApparatusDocumento1 páginaPortstation Breathing Apparatus Self Contained Breathing ApparatusFebriansyah Ar-rasyid AiniAún no hay calificaciones
- ACER 230V (LIFE) AC4R DL Motor Za Vrata UputstvaDocumento36 páginasACER 230V (LIFE) AC4R DL Motor Za Vrata UputstvaToni011973Aún no hay calificaciones
- Title Layout: SubtitleDocumento12 páginasTitle Layout: Subtitleriska augustAún no hay calificaciones
- Maemo - I - Introduction To MaemoDocumento15 páginasMaemo - I - Introduction To MaemoCatalin ConstantinAún no hay calificaciones
- Bored Piling Method Statement - Planning Engineer EstDocumento8 páginasBored Piling Method Statement - Planning Engineer EstboomiAún no hay calificaciones
- Wired (Bus) Electro-Installation: Technical CatalogueDocumento112 páginasWired (Bus) Electro-Installation: Technical CataloguevizanteaAún no hay calificaciones
- ReynoArch ACP LouversDocumento4 páginasReynoArch ACP LouversReynobond indiaAún no hay calificaciones
- ML Projects For Final YearDocumento7 páginasML Projects For Final YearAlia KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- A Procedure To Verify and Validate An FPGA Level Testing As Per DO-254Documento6 páginasA Procedure To Verify and Validate An FPGA Level Testing As Per DO-254sezgin bayramAún no hay calificaciones
- ConnectivityService network request notificationsDocumento47 páginasConnectivityService network request notificationsFwpAún no hay calificaciones
- Productivity Tools For AutoCAD Civil 3D 2015Documento1 páginaProductivity Tools For AutoCAD Civil 3D 2015Arturo Joel Polanco UrracaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tata Nifty India Digital Exchange Traded Fund - LeafletDocumento4 páginasTata Nifty India Digital Exchange Traded Fund - LeafletSatyam TiwariAún no hay calificaciones
- The Five Steps of Gemba KAIZENDocumento1 páginaThe Five Steps of Gemba KAIZENAbhinaya RamdassAún no hay calificaciones
- Digital Product Blueprint-1Documento56 páginasDigital Product Blueprint-1umarmukhtarabbaAún no hay calificaciones
- HVAC Essentials Andover ControlsDocumento120 páginasHVAC Essentials Andover ControlspujFierrosAún no hay calificaciones
- Meter Comparison Table: Powerlogic Power Monitoring and Control SystemsDocumento11 páginasMeter Comparison Table: Powerlogic Power Monitoring and Control SystemsRomi AntonAún no hay calificaciones
- Network-Simulator-2 Tutorial Learn About Ns2: What Is NS2Documento13 páginasNetwork-Simulator-2 Tutorial Learn About Ns2: What Is NS2chantyAún no hay calificaciones
- Satlink WS-6906 Manual - EnglisDocumento13 páginasSatlink WS-6906 Manual - Englisjrodrigues_90189Aún no hay calificaciones
- ABB Review - 01 - 2023 - Layout Complete - EN - 72-300dpi PDFDocumento82 páginasABB Review - 01 - 2023 - Layout Complete - EN - 72-300dpi PDFUsiAún no hay calificaciones
- Root BlueStacks Beta & Gain R/W Access in Under 10 StepsDocumento3 páginasRoot BlueStacks Beta & Gain R/W Access in Under 10 StepsSiddharth GoelAún no hay calificaciones
- Programación Módulo Confort Jetta MK4Documento8 páginasProgramación Módulo Confort Jetta MK4Rulas Palacios0% (1)