Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Nursing Med-Surg Chapter 34 Lewis
Cargado por
Lucas AskewDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Nursing Med-Surg Chapter 34 Lewis
Cargado por
Lucas AskewCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 9th Edition
Chapter 34
Rationales for Bridge to NCLEX Examination questions
1. Correct answers: b, c, d
Rationale: Atherosclerosis is the major cause of coronary artery disease (CAD) and is
characterized by a focal deposit of cholesterol and lipids, primarily within the intimal wall of the
artery. The endothelial lining of the coronary arteries becomes inflamed from the presence of
unstable plaques and the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Fibrous plaque
causes progressive changes in the endothelium of the arterial wall. The result is a narrowing of
the vessel lumen and a reduction in blood flow to the myocardial tissue.
2. Correct answer: a
Rationale: Risk factors for coronary artery disease include elevated serum levels of lipids,
elevated blood pressure, tobacco use, physical inactivity, obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome,
certain psychologic states, and elevated homocysteine levels. Weight lifting is not a
cardioprotective exercise. An example of health-promoting regular physical activity is brisk
walking (3 to 4 miles/hr) for at least 30 minutes five or more times each week.
3. Correct answer: b
Rationale: Chronic stable angina is chest pain that occurs intermittently over a long period with
the same pattern of onset, duration, and intensity of symptoms. The chest pain is relieved by rest
or by rest and medication (e.g., nitroglycerin). The ischemia is transient and does not cause
myocardial damage.
4. Correct answer: b
Rationale: Acute pericarditis is inflammation of the visceral and/or parietal pericardium; it often
occurs 2 to 3 days after an acute myocardial infarction. Chest pain may vary from mild to severe
and is aggravated by inspiration, coughing, and movement of the upper body. Sitting in a forward
position often relieves the pain. The pain is usually different from pain associated with a
myocardial infarction. Assessment of the patient with pericarditis may reveal a friction rub over
the pericardium.
5. Correct answers: a, b, e
Rationale: In addition to oxygen, several medications may be used to treat unstable angina
(UA): nitroglycerin, aspirin (chewable), and morphine. For patients with UA with negative
cardiac markers and ongoing angina, a combination of aspirin, heparin, and a glycoprotein
IIb/IIIa inhibitor (e.g., eptifibatide [Integrilin]) is recommended. Angiotensin-converting enzyme
(ACE) inhibitors decrease myocardial oxygen demand by producing vasodilation, reducing
blood volume, and slowing or reversing cardiac remodeling.
6. Correct answer: c
Rationale: Physical activity should be regular, rhythmic, and repetitive, with the use of large
muscles to build up endurance (e.g., walking, cycling, swimming, rowing). Physical activity
Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
Rationales for Bridge to NCLEX Examination questions
sessions should be at least 30 minutes long. Instruct the patient to begin slowly at personal
tolerance (perhaps only 5 to 10 minutes) and build up to 30 minutes.
7. Correct answer: c
Rationale: Left ventricular dysfunction (ejection fraction less than 30%) and ventricular
dysrhythmias after myocardial infarction are the strongest predictors of sudden cardiac death
(SCD).
Copyright 2014 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
También podría gustarte
- Unveiling the Unseen: A Journey Into the Hearts Labyrinth SeanDe EverandUnveiling the Unseen: A Journey Into the Hearts Labyrinth SeanAún no hay calificaciones
- Pulmonary Hypertension, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesDe EverandPulmonary Hypertension, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 4Documento8 páginasLec 4Sajjad FalahAún no hay calificaciones
- Pharmacotherapy of CADDocumento27 páginasPharmacotherapy of CADhams elaklamAún no hay calificaciones
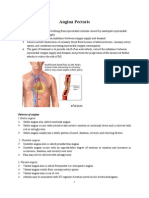
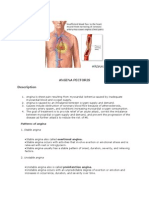
- Angina PectorisDocumento8 páginasAngina PectorisPrince DuAún no hay calificaciones
- Angina Pectoris: Class Activity Evoking AnginaDocumento4 páginasAngina Pectoris: Class Activity Evoking Anginamerin sunilAún no hay calificaciones
- Haad AnswersDocumento114 páginasHaad AnswersMohammadKhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiovascular ConditionsDocumento6 páginasCardiovascular ConditionsCJ ResabaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chronic Heart FailureDocumento11 páginasChronic Heart FailurelaydyAún no hay calificaciones
- 49 - Cardiac RehabilitationDocumento6 páginas49 - Cardiac RehabilitationMariaAún no hay calificaciones
- PrelimsDocumento11 páginasPrelimsJess Fabra100% (1)
- Chapter 30Documento16 páginasChapter 30NurseNancy93Aún no hay calificaciones
- Engage, Explore, and ExplainDocumento2 páginasEngage, Explore, and ExplainJohana Claire G. MoralesAún no hay calificaciones
- Angina Pectoris: Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocumento17 páginasAngina Pectoris: Ischemic Heart DiseaseMahum SohailAún no hay calificaciones
- MCQ SDocumento7 páginasMCQ Syousef.mohammed1015Aún no hay calificaciones
- CVD DiscussionDocumento6 páginasCVD Discussioncataleya mesaAún no hay calificaciones
- Coronary Heart DiseaseDocumento23 páginasCoronary Heart DiseaseBEA RADAAún no hay calificaciones
- Angina PectorisDocumento36 páginasAngina PectorisBardahWasaLamahAún no hay calificaciones
- ClaudicationDocumento6 páginasClaudicationdvenumohanAún no hay calificaciones
- Angina PectorisDocumento11 páginasAngina Pectorisjialin80% (5)
- Cardiopulmonary 3 2010 With AnswersDocumento14 páginasCardiopulmonary 3 2010 With AnswersWenzy Cruz100% (2)
- CGH Ed Reg Teaching Frcem Primary 1Documento20 páginasCGH Ed Reg Teaching Frcem Primary 1Maref JamalAún no hay calificaciones
- Angina Pectoris: Practice EssentialsDocumento11 páginasAngina Pectoris: Practice EssentialsAnonymous 6es4kViJ6KAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiovascular DiseasesDocumento67 páginasCardiovascular DiseasesokaciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Care of Patient With CADDocumento22 páginasCare of Patient With CADBader ZawahrehAún no hay calificaciones
- SG001 - Jore, Julianna RheavenDocumento9 páginasSG001 - Jore, Julianna RheavenJulianna Rheaven JoreAún no hay calificaciones
- SID For 4th YrsDocumento76 páginasSID For 4th YrsABREHAM BUKULOAún no hay calificaciones
- Lewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 8th EditionDocumento7 páginasLewis: Medical-Surgical Nursing, 8th EditionJoyzoeyAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiac Disorders HandoutDocumento14 páginasCardiac Disorders HandoutRizielle MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- AnginaDocumento12 páginasAnginaHermiie Joii Galang Maglaquii0% (1)
- Cardiovascular Practice Questions Answers and RationalesFALL2019-1Documento11 páginasCardiovascular Practice Questions Answers and RationalesFALL2019-1titilayo loveAún no hay calificaciones
- 9 CsaDocumento34 páginas9 Csaمحمد بن الصادقAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 4 Coronary Artery Disease and Ischaemic Heart Disease: StructureDocumento37 páginasUnit 4 Coronary Artery Disease and Ischaemic Heart Disease: StructurebtaleraAún no hay calificaciones
- Grupo 2 Practica 13Documento10 páginasGrupo 2 Practica 13Sadit Chauca VelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento17 páginasCoronary Artery DiseaseYulia ALAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 13 CirculationDocumento27 páginasChapter 13 CirculationHerman ZoletaAún no hay calificaciones
- Katzung 12th EditionDocumento1245 páginasKatzung 12th EditionAvin Guptha27% (88)
- Introduction To Ischemic Heart DiseasesDocumento8 páginasIntroduction To Ischemic Heart Diseasestiyavora2005Aún no hay calificaciones
- Heart Failure in ChildrenDocumento44 páginasHeart Failure in ChildrenRisna Ariani100% (2)
- Angina PectorisDocumento17 páginasAngina PectorisRacel HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Haad AnswersDocumento106 páginasHaad AnswersMohammadKhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Haad 1 AnswersDocumento10 páginasHaad 1 AnswersMariecar GarazaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiovascular LectureDocumento10 páginasCardiovascular LectureJaysonPangilinanAbanAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiac EmergencyDocumento34 páginasCardiac EmergencyRima HannaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Myocardial Ischemia: Dr. Wael H. Mansy, MDDocumento37 páginasMyocardial Ischemia: Dr. Wael H. Mansy, MDHaleema SultanAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Diagnose STEMI?Documento6 páginasHow To Diagnose STEMI?Adhie BadriAún no hay calificaciones
- Joy B. Johnson Department of PharmacologyDocumento55 páginasJoy B. Johnson Department of Pharmacologymatchees-gone rogueAún no hay calificaciones
- Med Surg Assignment 2Documento69 páginasMed Surg Assignment 2sham gowliAún no hay calificaciones
- Congestive Cardiac FailureDocumento24 páginasCongestive Cardiac FailureFarheen KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Angina PectorisDocumento7 páginasAngina PectorisTruptilata SahooAún no hay calificaciones
- Med Surg Unit 3 Exam ReviewDocumento10 páginasMed Surg Unit 3 Exam ReviewIfy OhansonAún no hay calificaciones
- NCP 2Documento5 páginasNCP 2Donna Co IgAún no hay calificaciones
- 1985-Cardiac Adaptations To Chronic ExerciseDocumento28 páginas1985-Cardiac Adaptations To Chronic ExerciseJavier Mora BaizAún no hay calificaciones
- NCM Disorders of Myocardial Perfusion-2Documento9 páginasNCM Disorders of Myocardial Perfusion-2Jeson Vien GuerraAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiogenic Shock: Submitted ToDocumento5 páginasCardiogenic Shock: Submitted Toal-obinay shereenAún no hay calificaciones
- Management & Nursing Care of Patient With Coronary Artery DiseasesDocumento49 páginasManagement & Nursing Care of Patient With Coronary Artery DiseaseslouradelAún no hay calificaciones
- Exercise Leadership in Cardiac Rehabilitation: An Evidence-Based ApproachDe EverandExercise Leadership in Cardiac Rehabilitation: An Evidence-Based ApproachAún no hay calificaciones
- Safety Environment and Bed Making (Group 5)Documento6 páginasSafety Environment and Bed Making (Group 5)Mira AurumtinAún no hay calificaciones
- Studi Kasus: Kehamilan Dengan: Dengan Katub Jantung Prostetik Mekanik Dan Penggunaan AntikoagulanDocumento10 páginasStudi Kasus: Kehamilan Dengan: Dengan Katub Jantung Prostetik Mekanik Dan Penggunaan AntikoagulanMonyet...Aún no hay calificaciones
- UCSD Internal Medicine Handbook 2011Documento142 páginasUCSD Internal Medicine Handbook 2011ak100007100% (5)
- Pharm 451-Historical Development of Chemotherapy 2021Documento22 páginasPharm 451-Historical Development of Chemotherapy 2021Akowuah SamuelAún no hay calificaciones
- Etiological Spectrum and Antimicrobial Resistance Among Bacterial Pathogen Association With Urinary Tract Infection in Wasit Governorate/ IraqDocumento11 páginasEtiological Spectrum and Antimicrobial Resistance Among Bacterial Pathogen Association With Urinary Tract Infection in Wasit Governorate/ IraqCentral Asian StudiesAún no hay calificaciones
- Holotrophic Breathwork Retreat 3-20-2011-1Documento9 páginasHolotrophic Breathwork Retreat 3-20-2011-1Jimmy WilsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Widal Test PDFDocumento2 páginasWidal Test PDFOctavia Putri KusumawardaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual of Obstetrics, 8e (Jun 25, 2014) - (1451186770) - (LWW) PDFDocumento766 páginasManual of Obstetrics, 8e (Jun 25, 2014) - (1451186770) - (LWW) PDFPrem100% (9)
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA (Kasus Mendalam 2)Documento4 páginasDAFTAR PUSTAKA (Kasus Mendalam 2)mkpnurdinAún no hay calificaciones
- Microsoft Word - Schuessler Salts FlyerDocumento2 páginasMicrosoft Word - Schuessler Salts Flyer4379100% (2)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 páginasAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationNurse NotesAún no hay calificaciones
- Treatment of Dengue Joe de LiveraDocumento11 páginasTreatment of Dengue Joe de Liverakrishna2205100% (1)
- Laporan Perencanaan Perbekalan FarmasiDocumento11 páginasLaporan Perencanaan Perbekalan FarmasikarinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Case Study BipolarDocumento12 páginasCase Study Bipolarapi-353954238Aún no hay calificaciones
- Medical BooksDocumento20 páginasMedical Booksapi-385347264% (14)
- The Pearson Guide To GPAT and o Umang H Shah SRJ Ilovepdf CompressedDocumento5 páginasThe Pearson Guide To GPAT and o Umang H Shah SRJ Ilovepdf CompressedDrSidharth MehanAún no hay calificaciones
- Norethisterone JournalDocumento29 páginasNorethisterone JournalAditya Syah PutraAún no hay calificaciones
- Admission Nursing AssessmentDocumento20 páginasAdmission Nursing Assessmentmonir61Aún no hay calificaciones
- Community DentistryDocumento3 páginasCommunity DentistryEkta Singh0% (1)
- Kawasaki Disease: A Comprehensive Review: Kamleshun Ramphul, Stephanie Gonzalez MejiasDocumento5 páginasKawasaki Disease: A Comprehensive Review: Kamleshun Ramphul, Stephanie Gonzalez MejiasAmarantoAún no hay calificaciones
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocumento44 páginasUrinary Tract Infectionstummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Bacterial Sinusitis in Children: AcuteDocumento11 páginasBacterial Sinusitis in Children: AcutefriscahalimAún no hay calificaciones
- Encopresis in Children An Overview of Recent FindiDocumento5 páginasEncopresis in Children An Overview of Recent FindiMaulana MalikAún no hay calificaciones
- Microbiology - Exercise 3e AntibiogramDocumento5 páginasMicrobiology - Exercise 3e Antibiogramapi-253346521Aún no hay calificaciones
- Competency Statement Compliance Criteria Validation Method Validated by DateDocumento4 páginasCompetency Statement Compliance Criteria Validation Method Validated by DateRosalinda Manuel VigiliaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tolerance - 2. Regulatory T Cells Why Tolerance Fails: Abul K. Abbas UcsfDocumento35 páginasTolerance - 2. Regulatory T Cells Why Tolerance Fails: Abul K. Abbas UcsfMeity ElvinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Idiopathic Hypersomnia Its All in Their HeadDocumento2 páginasIdiopathic Hypersomnia Its All in Their HeadSambo Pembasmi LemakAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Diagnosa PenyakitDocumento3 páginas10 Diagnosa PenyakitDiny Rachma Putri HAún no hay calificaciones
- Artikel 8 PDFDocumento8 páginasArtikel 8 PDFapryani lumban gaolAún no hay calificaciones
- Great Atlas of Dermatology IndexedDocumento73 páginasGreat Atlas of Dermatology Indexedjohn pauloAún no hay calificaciones