Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Ups Sefination
Cargado por
Shah JayTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Ups Sefination
Cargado por
Shah JayCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
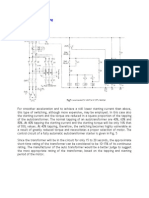
Off-line System in an off-line system, the critical load is powered from the raw
mains via the bypass line during normal operation. The load is transferred to t
he UPS inverter output if the mains fails or transgresses preset voltage limits.
On-line System in an on-line system, the critical load is fed by conditioned pow
er from the UPS inverter output during normal operation. If the mains power fail
s, the inverter continues to feed the load using DC power from the battery, with
no switching interruption. If the battery autonomy is exceeded, or the UPS fail
s, the load can be automatically switched to an alternative mains supply using a
static switch.
MTBF Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is a measure of the average time a device
will function before failing. MTBF ratings are measured in hours and indicate t
he reliability of hardware devices such as UPS equipment.
MTTR Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) measures the total time in hours from when a dev
ice fails until when it is restored to full operation. MTTR includes fault diagn
osis time, and any time necessary to obtain replacement parts, as well as the ac
tual repair work time.
Power Density the unit of power density is Watts/m. The power density of a UPS sy
stem is found by dividing its power output in Watts by the floor area it covers,
in square metres. A high power density figure is an important feature for UPS s
ystems.
Power Factor is a ratio defining the relationship between useable power in Watts
and total supplied power in VA (Volt Amperes). The power factor imposed by a lo
ad on a UPS system can be either lagging or leading. Traditional data centre loa
ds have been lagging, but blade servers, which impose a leading power factor, ar
e becoming increasingly popular because of their dense and flexible processing p
ower. The closer the power factor is to unity, the greater is the power efficien
cy of the UPS operation.
Rectifier/Charger the part of the UPS system that converts AC input power into D
C power for feeding the conditioning and inverter components, and charging the b
ack-up battery.
Redundancy for highly critical loads, it is essential to make the UPS system res
ilient to the failure of any single module. This can be achieved by connecting a
number of UPS modules in parallel to a common critical load bus. Redundancy exi
sts if the number of modules actually connected exceeds the number of modules ne
eded for the load. This means that if any one module fails, the remainder can co
ntinue to support the critical load without interruption.
Radio Frequency Interference electrical noise resulting from some parts of t
RFI
he equipment or wiring acting as a radio antenna. The noise may be large enough
to disrupt communications or cause computing errors.
THDi stands for the Total Harmonic Distortion of the input current waveform. It
is generally accepted that the THDi should be kept low to avoid excessive curren
t distortion at the point of common coupling within a building due to the cumula
tive effect of all connected equipment.
Transformerless Design UPS are now possible, due to advances in power semiconduc
tor technology and the introduction of the Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IG
BT) device. Transformerless design allows smaller, lighter and more efficient UP
S implementation. Other advantages include a higher input power factor, lower TH
Di, reduced capital and operating costs, lower audible noise and enhanced batter
y life.
UPS a UPS or Uninterruptible Power Supply is best defined as a backup power supp
ly that, in case of a power failure, allows enough time for an orderly shutdown
of a computer or other electronic equipment, or for a generator to take over. A
UPS therefore protects computers and other electronic equipment from mains fail
ures and power problems. If the mains voltage falls below a minimum level or fai
ls entirely, the UPS battery can maintain power to the load until either the mai
ns is restored or an orderly shutdown sequence is performed. Load protection fro
m mains borne spikes, surges and noise is also provided.
VRLA Battery VRLA or Valve Regulated Acid Batteries emit virtually no gas, requi
re no topping up and need no special ventilation apart from that required by loc
al building codes.
También podría gustarte
- ONAF Cooling of TransformerDocumento1 páginaONAF Cooling of TransformerShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Want To Learn Faster? : ONAN Cooling of TransformerDocumento4 páginasWant To Learn Faster? : ONAN Cooling of TransformerShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Autotransformer StarterDocumento1 páginaAutotransformer StarterShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Y DDocumento6 páginasY DShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Earthing in Electrical Network - Purpose, Methods and MeasurementDocumento12 páginasEarthing in Electrical Network - Purpose, Methods and MeasurementShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Power Flow Diagram of Induction Motor - 5Documento1 páginaPower Flow Diagram of Induction Motor - 5Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Starter DOLDocumento3 páginasStarter DOLShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Cooling Methods Available For Trans Former, We Will Now Explain One by OneDocumento1 páginaCooling Methods Available For Trans Former, We Will Now Explain One by OneShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Measurement of Earth Resistance (Three Point Method)Documento5 páginasMeasurement of Earth Resistance (Three Point Method)Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- DOL StarterDocumento2 páginasDOL StarterShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Ingress Protection IP Ratings - What Do They Mean?Documento1 páginaIngress Protection IP Ratings - What Do They Mean?Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Hazardous Area Classification GuideDocumento10 páginasHazardous Area Classification GuideShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Why LT Motors Are Delta Connected and HT Motors Are Star Connected - 4Documento2 páginasWhy LT Motors Are Delta Connected and HT Motors Are Star Connected - 4Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- STAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrincipleDocumento2 páginasSTAR DELTA Connection Diagram and Working PrinciplePrasant Kumar100% (5)
- Offshore Cathodic Protection 101: What It Is and How It WorksDocumento6 páginasOffshore Cathodic Protection 101: What It Is and How It WorksSaiful ArifAún no hay calificaciones
- Basics of Induction Motor - 1Documento2 páginasBasics of Induction Motor - 1Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Iec StandardsDocumento5 páginasIec StandardsShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Induction MotorDocumento6 páginasInduction MotorHafidah Mohd NoorAún no hay calificaciones
- Iec CodeDocumento14 páginasIec CodeShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Setting The Pickup Point - CT - PTDocumento4 páginasSetting The Pickup Point - CT - PTShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Autotransformer 6Documento5 páginasAutotransformer 6Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Lag, Lead, Lead-Lag - Compensation in Control SystemDocumento11 páginasLag, Lead, Lead-Lag - Compensation in Control SystemShah Jay100% (1)
- Practical Transformer 2Documento4 páginasPractical Transformer 2Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Compensator Design Using Bode PlotDocumento24 páginasCompensator Design Using Bode PlotShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- All Day Efficiency and Regulation - 5Documento8 páginasAll Day Efficiency and Regulation - 5Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- XCDocumento5 páginasXCPhuong PhamAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformer ProblemsDocumento4 páginasTransformer ProblemsShah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- Approximate Equivalent Circuits & Test - 3Documento6 páginasApproximate Equivalent Circuits & Test - 3Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Phase Transformer - 1Documento6 páginas3 Phase Transformer - 1Shah JayAún no hay calificaciones
- DC Generator ProjectDocumento10 páginasDC Generator ProjectMuhammad Asif Iqbal43% (7)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (119)
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2099)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- Sample Data Protection Policy TemplateDocumento8 páginasSample Data Protection Policy TemplateMarcelo Partes de OliveiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Maximabook PDFDocumento121 páginasMaximabook PDFWarley GramachoAún no hay calificaciones
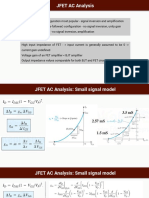
- JFET AC Equivalent CircuitsDocumento42 páginasJFET AC Equivalent Circuitssakuntala barikAún no hay calificaciones
- FoxMeyer's ERP Implementation Failure Case StudyDocumento30 páginasFoxMeyer's ERP Implementation Failure Case StudyNeo LiveAún no hay calificaciones
- V11 What's New and Changes PDFDocumento98 páginasV11 What's New and Changes PDFGAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture - 5: DC-AC Converters: Ug - ProgramDocumento54 páginasLecture - 5: DC-AC Converters: Ug - ProgramArife AbdulkerimAún no hay calificaciones
- Java Network ProjectDocumento20 páginasJava Network ProjectabbasmulaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Ipv4 Address Classes PDFDocumento2 páginasIpv4 Address Classes PDFAmol IngleAún no hay calificaciones
- QRQC / 8D Form: D 1. Description of The ProblemDocumento5 páginasQRQC / 8D Form: D 1. Description of The ProblemDearRed FrankAún no hay calificaciones
- Edward Malek's MBA Engineering ResumeDocumento1 páginaEdward Malek's MBA Engineering ResumeEdward Nicklaus MalekAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.tekla Structures 2016i Administrator's Release NotesDocumento48 páginas2.tekla Structures 2016i Administrator's Release NotesomerumeromerAún no hay calificaciones
- Android Voting System Synopsis Under 40 CharactersDocumento3 páginasAndroid Voting System Synopsis Under 40 CharactersShivshankar GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Billing Invoice Payment PlanDocumento7 páginasBilling Invoice Payment PlanyogeshAún no hay calificaciones
- ANSYS Parametric Design Language Guide 18.2Documento110 páginasANSYS Parametric Design Language Guide 18.2Panda HeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Carel Pco - SeriesDocumento84 páginasCarel Pco - SeriesAli Bin SaeedAún no hay calificaciones
- Fabrice CVDocumento2 páginasFabrice CVAnonymous 2v7rI0HjAún no hay calificaciones
- Development of A Buffer Monitoring DashboardDocumento47 páginasDevelopment of A Buffer Monitoring DashboardtelegenicsAún no hay calificaciones
- Divisors and representations of integersDocumento4 páginasDivisors and representations of integersAngeliePanerioGonzagaAún no hay calificaciones
- Alert Broadcasting Conferencing: Broadcasts and Alert NotificationsDocumento4 páginasAlert Broadcasting Conferencing: Broadcasts and Alert Notificationsdaniel.bpmAún no hay calificaciones
- Ghid Automatizari SchneiderDocumento372 páginasGhid Automatizari SchneidervalicanAún no hay calificaciones
- LENZE 8200 VectorDocumento290 páginasLENZE 8200 VectorAgus Itonk Suwardono100% (2)
- Register & Install Synthogy ProductsDocumento8 páginasRegister & Install Synthogy ProductsEduardo MontielAún no hay calificaciones
- JioBusiness-ILL Product Leaflet DigitalDocumento1 páginaJioBusiness-ILL Product Leaflet Digitaljitendermcse9816Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sunnxt AppDocumento8 páginasSunnxt ApppsiphoniphoneAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Guard PerformanceDocumento39 páginasData Guard Performancesrevenco srevencoAún no hay calificaciones
- One Pager v2Documento2 páginasOne Pager v2JuanCarlosMarrufoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 3: Computer Instructions: ObjectivesDocumento7 páginasChapter 3: Computer Instructions: ObjectivesSteffany RoqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Brachistochrone ProblemIPOPTinfoDocumento2 páginasBrachistochrone ProblemIPOPTinfoNumkang KangAún no hay calificaciones
- ISO 27001-2022 Transition BookDocumento20 páginasISO 27001-2022 Transition BookzghibAún no hay calificaciones
- AI QuestionsDocumento2 páginasAI QuestionsNarender SinghAún no hay calificaciones