Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
B 10 Ctsta 308
Cargado por
Andhi SoesiloTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
B 10 Ctsta 308
Cargado por
Andhi SoesiloCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Name
Class
Photosynthesis
Date
Chapter Test A
Multiple Choice
Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided.
_____ 1. Which of the following is NOT a true statement about ATP?
a. ATP consists of ribose, adenine, and three phosphate groups.
b. ADP is produced when ATP releases energy.
c. ATP provides energy for the mechanical functions of cells.
d. Used ATP is discarded by the cell as waste.
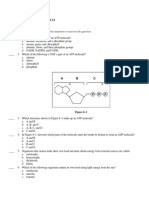
_____ 2. Look at Figure 81. All of the following are
parts of an ADP molecule EXCEPT
a. structure A.
b. structure B.
c. structure C.
d. structure D.
_____ 3. What happens during photosynthesis?
a. Heterotrophs consume ATP.
b. Heterotrophs produce ATP.
c. Autotrophs consume carbohydrates.
d. Autotrophs produce carbohydrates.
Figure 81
_____ 4. Plants gather the suns energy using molecules called
a. pigments.
b. thylakoids.
c. chloroplasts.
d. glucose.
_____ 5. Which structure in Figure 82 represents a
single thylakoid?
a. structure A
b. structure B
c. structure C
d. structure D
_____ 6. Where in the chloroplast is chlorophyll
found?
a. in the ATP
b. in the stroma
c. in the thylakoid membrane
d. in the thylakoid space
Figure 82
161
Name
Class
Date
Figure 83
_____ 7. Which chemical shown in Figure 83 is an electron carrier molecule?
a. H2O
c. NADP+
b. carbon dioxide
d. oxygen
_____ 8. Why are electron carriers needed for transporting electrons from one part of the chloroplast
to another?
a. High-energy electrons would be destroyed.
b. High-energy electrons are highly reactive.
c. High-energy electrons are not soluble in cytoplasm.
d. High-energy electrons get their energy from electron carriers.
_____ 9. Photosynthesis uses sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into
a. oxygen and carbon.
b. high-energy sugars and proteins.
c. ATP and oxygen.
d. oxygen and high-energy sugars.
Figure 84
_____ 10. In Figure 84, why might the candle in jar A burn longer than the candle in jar B?
a. Carbon dioxide produced by the plant allows the candle to burn longer.
b. Chlorophyll produced by the plant allows the candle to burn longer.
c. Glucose produced by the plant allows the candle to burn longer.
d. Oxygen produced by the plant allows the candle to burn longer.
162
Name
Class
Date
_____ 11. Which of the following is NOT a step in the light-dependent reactions?
a. High-energy electrons move through the electron transport chain.
b. Pigments in photosystem II absorb light.
c. ATP synthase allows H+ ions to pass through the thylakoid membrane.
d. ATP and NADPH are used to produce high-energy sugars.
_____ 12. Where are photosystems I and II found?
a. in the stroma
c. in the Calvin cycle
b. in the thylakoid membrane
d. in the cell membrane
_____ 13. Which pathway represents the flow of electrons during photosynthesis?
a. H2O Photosystem I Photosystem II
b. O2 ADP Calvin cycle
c. Photosystem I Calvin cycle NADP+
d. H2O NADP+ Calvin cycle
_____ 14. The Calvin cycle takes place in the
a. stroma.
b. photosystems.
c. thylakoid membranes.
d. chlorophyll molecules.
_____ 15. If you continue to increase the intensity of light that a plant receives, what happens?
a. The rate of photosynthesis increases indefinitely with light intensity.
b. The rate of photosynthesis decreases indefinitely with light intensity.
c. The rate of photosynthesis increases and then levels off .
d. The rate of photosynthesis does not change.
Completion
Complete each statement on the line provided.
16. Thylakoids are arranged in stacks known as
17. The area in Figure 85 labeled A is called the
18. A membrane protein called
allows
+
H ions to pass through the thylakoid membrane and into
the stroma.
19. During the Calvin cycle, molecules of
supply the carbon component of carbohydrates.
20. In many plants, the rate of photosynthesis
the weather becomes very cold.
when
Figure 85
163
Name
Class
Date
Short Answer
In complete sentences, write the answers to the questions on the lines provided.
Figure 86
21. Examine the food web in Figure 86 and identify whether each organism is an autotroph or a
heterotroph.
22. Why are six carbon dioxide molecules required to make one glucose molecule?
23. In what ways are photosystems I and II similar?
24. Why is it important that a membrane separate the cellular regions on either side of an ATP synthase
molecule in order for the protein to perform its function?
25. Describe the relationship between the light-dependent and the light-independent reactions.
164
Name
Class
Date
Using Science Skills
Use the diagram below to answer the following questions on the lines provided.
A student put together two different experimental setups as shown below.
Figure 87
26. Design an Experiment Look at Figure 87. What factor is the student varying? What might the
student be trying to test?
27. Control Variables Suggest an appropriate control for the experiment shown in Figure 87.
28. Predict In Figure 87, assume that the student placed Plant A in indirect sunlight for two days.
How would the rate of photosynthesis of this plant compare with that of a plant grown under
normal conditions?
29. Predict In Figure 87, assume that the student placed Plant B in indirect sunlight for two days.
How would the rate of photosynthesis of this plant compare with that of a plant grown under
normal conditions?
30. Predict Review the setups in Figure 87. Make a prediction about the effect of carbon dioxide on
starch production in plants.
165
Name
Class
Date
Essay
Write the answer to each question in the space provided.
31. Compare the storage capacity of ATP and glucose. How does the cell use each of these molecules
to store energy?
32. Describe the kinds of light that chlorophyll and carotene pigments absorb. What is the advantage
for a plant to have more than one kind of pigment?
33. Some people informally call the light-dependent reactions the light reactions and the lightindependent reactions the dark reactions. Why is this naming system misleading?
34. Identify three factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis and explain the effect of each.
35. Describe how photosynthesis in CAM plants differs from photosynthesis in more typical plants.
Why is it unlikely that you would find a CAM plant in an aquatic environment?
166
También podría gustarte
- Bio 10 Chapter 8 Study Test 10-11: Multiple ChoiceDocumento11 páginasBio 10 Chapter 8 Study Test 10-11: Multiple Choicegeorge linAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Chapter 8 (Due Jan. 18, Test Jan. 22)Documento9 páginasBiology Chapter 8 (Due Jan. 18, Test Jan. 22)عبدالرحمن شحاتهAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 Test Bank: Multiple ChoiceDocumento22 páginasChapter 8 Test Bank: Multiple ChoicePayalAún no hay calificaciones
- Grade 9 Biology Revision SheetDocumento11 páginasGrade 9 Biology Revision SheetLama AshiAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Choice Questions on Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocumento10 páginasMultiple Choice Questions on Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationLama AshiAún no hay calificaciones
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento7 páginasPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Multiple Choice Questionscarmela ambatAún no hay calificaciones
- Review 3: Metabolism Unit - Respiration & Photosynthesis A. Top "10" - If You Learned Anything From This Unit, You Should Have LearnedDocumento6 páginasReview 3: Metabolism Unit - Respiration & Photosynthesis A. Top "10" - If You Learned Anything From This Unit, You Should Have LearnedNguyen Thi Thien MinhAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 2.7 - Metabolism TestDocumento6 páginasUnit 2.7 - Metabolism TestEric ChiangAún no hay calificaciones
- Unlock SGCh08Documento8 páginasUnlock SGCh08SilaxAún no hay calificaciones
- ExamView - Ch. 8 ReviewDocumento4 páginasExamView - Ch. 8 ReviewJhe Hann BurcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Bank: Photosynthesis: A. B. C. EDocumento19 páginasTest Bank: Photosynthesis: A. B. C. ERaso bigAún no hay calificaciones
- SHS Biology Quarterly Assessment AnswersDocumento6 páginasSHS Biology Quarterly Assessment AnswersDiane GuilaranAún no hay calificaciones
- Worksheet No.9 MargalloDocumento12 páginasWorksheet No.9 Margalloaljon disabelleAún no hay calificaciones
- Photosynthesis Quiz MR ADocumento4 páginasPhotosynthesis Quiz MR Aapi-353447897100% (1)
- Unit Test 1 Grade 12 BioDocumento8 páginasUnit Test 1 Grade 12 BioSarah KwanAún no hay calificaciones
- Name: - Lilly Mack - Class Period: - 5 - Biology Summative Exam BDocumento3 páginasName: - Lilly Mack - Class Period: - 5 - Biology Summative Exam BLilly MackAún no hay calificaciones
- Summative Exam GEN - BIO 1Documento3 páginasSummative Exam GEN - BIO 1Paul VelardeAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Bank For Biology 9th Edition Peter Raven Full DownloadDocumento26 páginasTest Bank For Biology 9th Edition Peter Raven Full Downloadtimothybarberkscbxipoam100% (36)
- 2015pscrhw PacketDocumento7 páginas2015pscrhw Packetapi-235160519Aún no hay calificaciones
- Summative Exam 21st CenturyDocumento2 páginasSummative Exam 21st CenturyPaul VelardeAún no hay calificaciones
- Week 4 - Human and Social Biology - Third Form - Worksheet 1Documento5 páginasWeek 4 - Human and Social Biology - Third Form - Worksheet 1Miguel BonillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 Practice TestDocumento6 páginasChapter 8 Practice Testcrqin qinAún no hay calificaciones
- BIO CH09 L03 QuizDocumento4 páginasBIO CH09 L03 QuizFabiola PadillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Life On Earth 11Th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocumento38 páginasBiology Life On Earth 11Th Edition Audesirk Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFodetteisoldedfe100% (13)
- Chapter 10 Multiple Choice Practice: CO H O O PDocumento7 páginasChapter 10 Multiple Choice Practice: CO H O O PShaira CogollodoAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Practice PhotosynthesisDocumento7 páginasBiology Practice Photosynthesisbrowhocares121212Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lumbang Integrated National High SchoolDocumento3 páginasLumbang Integrated National High SchoolLorena DizonAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 1 4: ECOSYSTEM: Life EnergyDocumento9 páginasUnit 1 4: ECOSYSTEM: Life EnergyJono Asuncion0% (3)
- (Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration) : What I Know (Pre Test)Documento16 páginas(Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration) : What I Know (Pre Test)Maricar Feb MaturanAún no hay calificaciones
- Photosynthesis: Multiple ChoiceDocumento23 páginasPhotosynthesis: Multiple ChoiceValentina RumhizhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Pogil Track D - 5261224Documento11 páginasMark Marlatt - Photosynthesis Pogil Track D - 5261224api-544304176Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 Cellular Energy: Section 1: How Organisms Obtain Energy Section 2: PhotosynthesisDocumento31 páginasChapter 8 Cellular Energy: Section 1: How Organisms Obtain Energy Section 2: PhotosynthesisZ RashAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio 1 AssessmentDocumento7 páginasBio 1 AssessmentCamilla SenataAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15Th Edition Starr Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocumento35 páginasBiology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15Th Edition Starr Test Bank Full Chapter PDFBeckySmithnxro100% (8)
- Chapter 8 Study GuideDocumento8 páginasChapter 8 Study Guideamyjordan1Aún no hay calificaciones
- BIS 2A Midterm 1 UC DavisDocumento10 páginasBIS 2A Midterm 1 UC Daviscrahimi26Aún no hay calificaciones
- APBio 10 NotesDocumento5 páginasAPBio 10 Notes5377773Aún no hay calificaciones
- 4bioenergetics Utilization of EnergyDocumento7 páginas4bioenergetics Utilization of EnergyErica De Guzman AngelesAún no hay calificaciones
- Exam 2 Cells Membranes Energy Metabolism Biol101 f13Documento8 páginasExam 2 Cells Membranes Energy Metabolism Biol101 f13api-249772989Aún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Chapter 7 Solution Paper Grade 11 Advanced 2021 2022 1Documento8 páginasBiology Chapter 7 Solution Paper Grade 11 Advanced 2021 2022 1mallmazAún no hay calificaciones
- CRespiration and Photosynthesis Review KeyDocumento5 páginasCRespiration and Photosynthesis Review Keyvictoire BadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Photosyntesis Worksheet 3Documento5 páginasPhotosyntesis Worksheet 3Ryan De AlloAún no hay calificaciones
- BIO 9.3 - HomeworkDocumento4 páginasBIO 9.3 - HomeworkalradilaylaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.0.0.a - Pre-Test - Breathing On Mars - SWebsterDocumento6 páginas1.0.0.a - Pre-Test - Breathing On Mars - SWebsterJessa Lynn E. AcalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio 1 Finals 11 STEMDocumento3 páginasBio 1 Finals 11 STEMRosana De AsisAún no hay calificaciones
- Cellular Respiration Review WorksheetDocumento6 páginasCellular Respiration Review WorksheetTaniaBarrios-ChongAún no hay calificaciones
- PhotosynthesisDocumento4 páginasPhotosynthesisZul HakimAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Summative Test ReviewDocumento3 páginasBiology Summative Test ReviewKennedy Fieldad Vagay100% (2)
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocumento4 páginasPhotosynthesis WorksheetJustin Marju De VeraAún no hay calificaciones
- Energy and Life: Lesson QuizDocumento3 páginasEnergy and Life: Lesson QuizAya LutfiAún no hay calificaciones
- Energy and Life: Lesson QuizDocumento3 páginasEnergy and Life: Lesson QuizMarko DesnicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mana Barumsaa Bultii Addaa Waldaa Misooma OromiyaaDocumento8 páginasMana Barumsaa Bultii Addaa Waldaa Misooma OromiyaaNafiyaf BerhanuAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Practice TestDocumento13 páginasChapter 9: Cellular Respiration Practice TestDaniel ClementsAún no hay calificaciones
- 3rd Exam g11Documento3 páginas3rd Exam g11fe janduganAún no hay calificaciones
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: Quiz YourselfDocumento3 páginasPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: Quiz YourselfBenita ChickAún no hay calificaciones
- Summ Test 3 G9 ScienceDocumento1 páginaSumm Test 3 G9 ScienceAlexa RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15th Edition Starr Test BankDocumento38 páginasBiology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15th Edition Starr Test Bankapodaawlwortn3ae100% (7)
- Cellular Respiration ProcessesDocumento9 páginasCellular Respiration ProcessesVivian giducosAún no hay calificaciones
- Photosynthesis and cellular respiration practice questionsDocumento10 páginasPhotosynthesis and cellular respiration practice questionsSalah SalaqAún no hay calificaciones
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionDe EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- B 10 CTSTB 307Documento4 páginasB 10 CTSTB 307Andhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- IG 7 TopicBK For 2016 by PBDocumento29 páginasIG 7 TopicBK For 2016 by PBAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- B 10 Ctsta 834Documento6 páginasB 10 Ctsta 834Andhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- B 10 Ctsta 307Documento6 páginasB 10 Ctsta 307Andhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- B 10 Ctsta 309Documento6 páginasB 10 Ctsta 309Andhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- 31 Nervous System Chapter Test A Multiple Choice and Essay QuestionsDocumento6 páginas31 Nervous System Chapter Test A Multiple Choice and Essay QuestionsAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- B 10 Ctsta 309Documento6 páginasB 10 Ctsta 309Andhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- B 10 Ctsta 309Documento6 páginasB 10 Ctsta 309Andhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- 2003 James Ruse YearlyDocumento15 páginas2003 James Ruse YearlyAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- 2003 James Ruse YearlyDocumento15 páginas2003 James Ruse YearlyAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Resources for Teaching Biology in Bayelsa Secondary SchoolsDocumento9 páginasResources for Teaching Biology in Bayelsa Secondary SchoolsAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- 2003 James Ruse YearlyDocumento15 páginas2003 James Ruse YearlyAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 CirclesDocumento49 páginas10 CirclesAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Exercise MTTDocumento1 páginaExercise MTTAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Congr Uence ActivityDocumento3 páginasCongr Uence ActivityAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Jermyn 2003 - Women With A Mission - Lynda La Plante, DCI Jane Tennison and The Reconfiguration of TV Crime DramaDocumento19 páginasJermyn 2003 - Women With A Mission - Lynda La Plante, DCI Jane Tennison and The Reconfiguration of TV Crime DramaAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Dian Harapan Community Seeks To Honor God and The Quality of The School Community ThroughDocumento4 páginasDian Harapan Community Seeks To Honor God and The Quality of The School Community ThroughAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Assessment Rubric For Project Grade 8 SolidDocumento1 páginaAssessment Rubric For Project Grade 8 SolidAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Teach2-Documents-20 QuestionsDocumento3 páginasTeach2-Documents-20 Questionsapi-246926247Aún no hay calificaciones
- Reflecting on Elijah Lewis' English TestDocumento5 páginasReflecting on Elijah Lewis' English TestAndhi Soesilo100% (1)
- Webpage FirstRoundDetailsDocumento2 páginasWebpage FirstRoundDetailsAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Reflecting on Elijah Lewis' English TestDocumento5 páginasReflecting on Elijah Lewis' English TestAndhi Soesilo100% (1)
- Round 2 (Revised)Documento8 páginasRound 2 (Revised)Andhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Jermyn AnnotatedDocumento19 páginasJermyn AnnotatedAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Ingredients For Cupcakes (25) : Entrepreneur Recipes Chocolate Ganache Covered CupcakesDocumento1 páginaIngredients For Cupcakes (25) : Entrepreneur Recipes Chocolate Ganache Covered CupcakesAndhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Kuadrat 2010Documento46 páginasKuadrat 2010Andhi SoesiloAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell Biology: Structure and Functions of Plant and Animal CellsDocumento13 páginasCell Biology: Structure and Functions of Plant and Animal CellsRonnith NandyAún no hay calificaciones
- Photosynthesis 1Documento52 páginasPhotosynthesis 1Ella Mae CelestinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Biochemistry Free Easy 1Documento453 páginasBiochemistry Free Easy 1priyaprasad367792100% (5)
- Wbi14 01 Que 20221021Documento32 páginasWbi14 01 Que 20221021Johnieer Bassem MoferdAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 5 (The Fundamental Unit of Life) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Documento22 páginasUnit 5 (The Fundamental Unit of Life) : Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Nikhil SahuAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Test Bank DownloadDocumento37 páginasCell and Molecular Biology Concepts and Experiments 7th Edition Karp Test Bank DownloadBen Flott100% (21)
- Gbio 121 Week 11 19 by KuyajovertDocumento11 páginasGbio 121 Week 11 19 by KuyajovertAnonymous DZY4MvzkuAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Bank For Biology 9th Edition Peter Raven Full DownloadDocumento26 páginasTest Bank For Biology 9th Edition Peter Raven Full Downloadtimothybarberkscbxipoam100% (36)
- HTTP Wcedmis - Wcape.gov - Za Wcedmis Webadmin - Wwdoc Process - Process Download P File F11979 1032 1 Biology SG p1Documento11 páginasHTTP Wcedmis - Wcape.gov - Za Wcedmis Webadmin - Wwdoc Process - Process Download P File F11979 1032 1 Biology SG p1Hannes HelmieAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology: Biology Is The Scientific Study of LifeDocumento64 páginasBiology: Biology Is The Scientific Study of LifeJohn HenryAún no hay calificaciones
- IB HL Biology Photosynthesis NotesDocumento3 páginasIB HL Biology Photosynthesis NotesTiffani Choy100% (1)
- Atp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesDocumento6 páginasAtp and Coupled Reaction ProcessesJhondel GuirrenAún no hay calificaciones
- Melc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLLDocumento50 páginasMelc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLLphilip galizaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2: Cell Biology: Ck-12 Biology For High School Flexbook® 2.0 Answer KeyDocumento24 páginasChapter 2: Cell Biology: Ck-12 Biology For High School Flexbook® 2.0 Answer KeyKatherin FuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic 4. Photosynthesis PDFDocumento50 páginasTopic 4. Photosynthesis PDFJohn Michael LegaspiAún no hay calificaciones
- Self-Instructional ModuleDocumento19 páginasSelf-Instructional ModuleMarlon S. BarangganAún no hay calificaciones
- Activities (Ecosystem)Documento20 páginasActivities (Ecosystem)Rona Carmen LabradorAún no hay calificaciones
- Micropara: Chapter 5 NotesDocumento8 páginasMicropara: Chapter 5 NotesPatrick JuacallaAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Prelim Notes Module 1-4Documento54 páginasBiology Prelim Notes Module 1-4kkanaksingh124Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocumento24 páginasChapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesVassalyn Su ThatAún no hay calificaciones
- Photosynthesis Light Reaction QuestionsDocumento14 páginasPhotosynthesis Light Reaction QuestionsSevilay CaferogluAún no hay calificaciones
- AGR122 CHAPTER 4.3-PHOTOSYNTHESIS BaruDocumento38 páginasAGR122 CHAPTER 4.3-PHOTOSYNTHESIS BaruAisyah NabilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cell - The Unit of Life Line-By-Line NcertDocumento14 páginasCell - The Unit of Life Line-By-Line Ncertchandumenswear3Aún no hay calificaciones
- Eukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsDocumento1 páginaEukaryotic Cell Organelles and Their FunctionsShein GonzalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Immunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellDocumento20 páginasImmunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellJoia De LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Biology Investigatory ProjectDocumento18 páginasBiology Investigatory ProjectSekhar Sahoo100% (4)
- Extrachromosomal InheritanceDocumento13 páginasExtrachromosomal InheritancejazzyAún no hay calificaciones
- Keys 4 Success: Quick Revision: New Light InstituteDocumento41 páginasKeys 4 Success: Quick Revision: New Light Institutestudyloverx1234Aún no hay calificaciones
- Plant Kingdom: Cell Walls Central VacuoleDocumento10 páginasPlant Kingdom: Cell Walls Central VacuoleRishel Reign GasparAún no hay calificaciones
- Science 9 - Q1 - Mod5 - Ecosystem Life EnergyDocumento37 páginasScience 9 - Q1 - Mod5 - Ecosystem Life EnergyPaul Senen Didulo50% (2)