Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Drug Chart
Cargado por
starobinDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Drug Chart
Cargado por
starobinCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
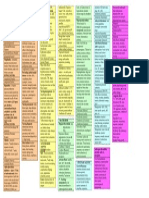
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 1
Pharmacology Drug Chart
Cholinergic Agonists
Drug Name
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Muscarinic
HR, CO and BP
Salivary Secretions
Secretions and Motility in the GIT
Bronchiolar Secretions
Miosis (Constriction of the Pupil)
Muscarinic
Stimulates the detrusor while relaxing
the trigone and sphincter causing
urination in Nonobstructive retention
i.e. postoperative and postpartum
Muscarinic
Similar to Bethanechol to treat urinary When used to treat Glaucoma there
retention
are little to no side effects b/c of direct
Used on the Eye to cause Miosis
administration
Intraocular Pressure to treat
Glaucoma
Muscarinic
Miosis
Intraocular Pressure in BOTH Narrow
and Wide angle Glaucoma
Acetylcholine
Bethanechol
Carbachol
Pilocarpine
Sweating, Salivation, Flushing, BP,
Nausea, Abdominal Pain, Diarrhea, and
Bronchospasam
Can enter the brain and cause CNS
disturbances
Sweating
Salivation
Anticholinesterases - Irreversible
Drug Name
Organophosphates
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Covalently bonds Chronic treatment of Open-angle
to AChase
Glaucoma
Adverse Effects
Death L
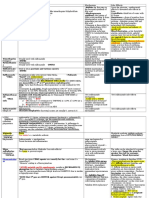
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 2
Anticholinesterases - Reversible
Drug Name
Physostigmine
Neostigmine
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Competitive
Inhibitor of
AChase
Intestinal Motility
Bladder Motility
Miosis
Intraocular Pressure
Used to treat an overdose of Atropine
Bradycardia
Can enter the CNS and high doses may
cause convulsions
Competitive
Inhibitor of
AChase
Intestinal Motility
Bladder Motility
Antidote for Tubocurarine
Treatment of Myasthenia Gravis
Sweating, Salivation, Flushing, BP,
Nausea, Abdominal Pain, Diarrhea, and
Bronchospasam
Cholinergic Antagonists
Drug Name
Atropine
Receptor
Non-specific
Muscarinic
Blocker via
Competitive
Binding
Therapeutic Uses
Mydriasis (Dilation of the Pupil)
Relaxes the GIT
Antispasmodic activity in the Bladder
Treatment of Organophosphate
overdose by blocking the effects of
excess ACh caused by Anti-AChase
Blocks secretions of the upper and
lower respiratory tract
Adverse Effects
Dry Mouth
Blurred Vision
Tachycardia
Constipation
Intraocular Pressure (Bad for
Glaucoma)
Enters the CNS to cause Confusion,
Hallucinations, Depression and
collapse of the Circulatory and
Respiratory systems
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 3
Ganglionic and Neuromuscular Blockers
Drug Name
Nicotine
Hexamethonium
(Trimethaphan)
Tubocurarine
Succinylcholine
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Low Dose - Ganglionic stimulation by
depolarization
High Dose - Ganglionic blockade
Sympathetic Stimulation followed by
paralysis of the ganglia
Adverse Effects
Irritability and Tremors
Intestinal Cramps and Diarrhea
HR
BP
Rate of Metabolism of other drugs Induction
Competitive
Used for the emergency lowering of BP
Nicotinic
Ganglionic
Blocker
Nondepolarizing Low Dose - Nicotinic Receptor and
Histamine Release
NM Blocker
competitively blocks the binding of ACh Ganglionic Blockade
High Dose - blocks the Ion Channels of BP
the End Plate
Used to relax skeletal muscle during
surgery
Depolarizing NM Rapid endothelial intubations
Blocker
Hyperthermia
Apnea due to the paralysis of the
Diaphragm
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 4
Direct Acting Adrenergic Agonists
Drug Name
Receptor
Low Dose
Med Dose D
High Dose
Epinephrine FIGHT OR FLIGHT
Therapeutic Uses
ACTIONS
Positive Inotropic 1
Positive Chronotropic 1
CO
TPR
Vasoconstriction in Skin and Viscera 1
Vasodilation in Liver and Skeletal
Muscle 2
Renal blood flow
Systolic Pressure
Diastolic Pressure
Bronchodilation 2
Glycogenolysis in Liver 2
Release of Glucagon 2
Release of Insulin 2
Lipolysis - Receptors in Adipose
Tissue
THERAPEUTIC USES
Intraocular Pressure ( Aqueous
Humor)
Used to treat Anaphylactic Shock
Used to treat acute Asthma
Adverse Effects
CNS Disturbances
Hemorrhage
Cardiac Arrhythmias
Pulmonary Edema
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 5
Norepinephrine
Isoproterenol /
Isoprenaline
Mostly
2 are for
Negative
Feedback
1
TPR
BP
Reflex Bradycardia
1 and 2
Decreased
Uptake
Positive Inotropic
Positive Chronotropic
Vasodilation of Skeletal Muscle
Bronchodilation
CNS Disturbances
Hemorrhage
Cardiac Arrhythmias
Pulmonary Edema
High Dose
Med Dose
Low Dose D
TPR
CO
TPR
Drug of choice for shock because it
Renal and Splanchnic blood flow
Treatment of CHF
Sympathetic Stimulation
Nausea
Hypertension
Arrhythmias
CO
Treatment of CHF
Use with caution in Atrial Fibrillation
because the drug atrioventricular
conduction
1 and 2 but
mostly 1
Resistant to COMT
Vasoconstriction
Systolic Pressure
Diastolic Pressure
Mydriasis
Reflex Bradycardia
Hypertensive Headache
Cardiac Irregularities
BP due to its action on the CNS
Treatment of Hypertension
Treatment for the withdrawal from
Opiates and Benzodiazepines
Dopamine
Dobutamine
Phenylephrine
Clonidine
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 6
Salbutamol
Bronchodilation
Treatment of Asthma
Reflex Tachycardia
2 Agonist
Treatment of Hypertension
TPR
BP
Organ Blood Flow is NOT Reduced
Sedation
Drowsiness
-Methyldopa
Indirect Acting Adrenergic Agonists
Drug Name
Receptor
, , CNS
Amphetamine
Therapeutic Uses
CNS stimulant in the treatment of
children with ADD
Also used in the treatment of
Depression, Narcolepsy and Appetite
Control
Adverse Effects
BP
HR
Mixed Acting Adrenergic Agonists
Drug Name
Receptor
, , CNS
Ephedrine
Therapeutic Uses
Resistant to COMT and MAO
Treatment of Asthma
Nasal Decongestant
Fatigue
Athletic Performance
Adverse Effects
BP
HR
Adrenergic Antagonists
Drug Name
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 7
1 and 2
Irreversible and
Noncompetitive
Treatment of Pheochromocytoma - a
catecholamine secreting tumor
Postural Hypotension
Epinephrine Reversal
Nasal Congestion
Nausea
Vomiting
May induce Tachycardia
Inhibits Ejaculation
1 and 2
Competitive
Used in the diagnosis of
Pheochromocytoma
Postural Hypotension
Tachycardia
Cardiac Stimulation
Epinephrine Reversal
Anginal Pain
Arrhythmias
1 Competitive
Treatment of Hypertension
TPR
Alternative to surgery in benign
Prostatic Hypertrophy thus improving
urine flow
First Dose Effect Syncope
Postural Hypotension
Lack of Energy
Nasal Congestion
Headache
Phenoxybenzamine
Phentolamine
Prazosin
Adrenergic Antagonists
Drug Name
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 8
1 and 2
Nonselective
Intraocular Pressure
Aqueous Humor
Treatment of Migraine
Curbing the effects of Hyperthyroidism
Treatment of STABLE Angina (NOT
ACUTE)
Can aid in the prevention a Second MI
Bronchoconstriction
Arrhythmias
Sexual Impairment (unclear as to why)
Glycogenolysis
Glucagon - Adverse of Insulin
dependent diabetics
1 Selective
Cardioselective
Treatment of
BP
Treatment of
Treatment of
Arrhythmia
Treatment of
May compromise respiratory activity in
Asthmatics
Propranolol
Atenolol
Hypertension
Angina
Atrial and Ventricular
Tachycardia
Vasodilation
1 Antagonist
Postural Hypotension 1
BP
1 Antagonist
Dizziness 1
2 Partial Agonist HR
Treatment of Hypertension - Especially
useful for patients with Asthma and
Diabetics due to the 2 partial agonist
effect
Labetalol
Drugs Affecting Neurotransmitter Release
Drug Name
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 9
Mg2+ / ATP
Dependent
Transporter
Reserpine
Guanethidine
Na+ / K+ ATPase
Cocaine
ACTION
Blocks the Mg2+ / ATP Dependent
transporter from transporting
Norepinephrine, Dopamine and
Serotonin from the cytoplasm into the
storage vesicles
THERAPEUTIC USES
Treatment of Hypertension
Causes the ultimate depletion of
Norepinephrine in the adrenergic
neuron
Sympathetic function is greatly
impaired
May cause Bradycardia
Mechanism 1 - Displaces
Norepinephrine from storage vesicles
Mechanism 2 - Blocks the release of
stored Norepinephrine
Treatment of Hypertension (Rarely
Used)
BP
HR
Postural Hypotension
Male sexual function interference
Hypertensive Crisis in patients with
Pheochromocytoma due to a
supersensitivity to Norepinephrine
Inhibits reuptake 1 of Norepinephrine
from the synaptic cleft by blocking
Na/K ATPase
Causes the accumulation of
Norepinephrine in the synaptic space
Causes an enhancement of
Sympathetic activity
Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Drug Name
Quinidine
Class IA
Na+ Channel
Blocker
Receptor
Binds to Open
and Inactive Na
Channels to
Prevent Influx
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Slows Phase 0 Depolarization
May cause SA and AV Block
Treatment of Atrial, AV, and Ventricular Asystole
Arrhythmias
May induce ventricular Tachycardia
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 10
Binds to Open
and Inactive Na
Channels to
Prevent Influx
Shortens Phase 3 Repolarization
Suppresses arrhythmias caused by
abnormal automaticity within the cells
Treatment of Ventricular Arrhythmias
during MI
Drug of choice for the emergency
treatment of Cardiac Arrhythmias Wide therapeutic to toxic ratio
Binds to Open
and Inactive Na
Channels to
Prevent Influx
Markedly Slows Phase 0 Depolarization Negative Inotropic
Treatment of Refractory Ventricular
Can aggravate CHF
Arrhythmias
Ventricular Tachycardia
Dizziness
Blurred Vision
Lidocaine
Class IB
Na+ Channel
Blocker
Flecainide
Class IC
Na+ Channel
Blocker
Drowsiness
Slurred Speech
Agitation
Confusion
Convulsions
Ventricular Arrhythmias
Does not slow down conduction
therefore it is not useful for AV junction
arrhythmias
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 11
1 and 2
Nonselective
Propranolol
Class II
Adrenorecepter
Blocker
REPEAT
Binds to K
Channels to
Diminish
Outward Current
Amiodarone
During
Class III
K+ Channel Blocker Repolarization
Suppresses Phase 4 Depolarization
cAMP causes Ca2+ Influx in Cardiac
Tissue which leads to CO
HR
Intraocular Pressure
Aqueous Humor
Treatment of Migraine
Curbing the effects of Hyperthyroidism
Treatment of STABLE Angina (NOT
ACUTE)
Treatment of arrhythmias caused by
sympathetic activity
Can aid in the prevention of a Second
MI
Bronchoconstriction
Arrhythmias
Sexual Impairment (unclear as to why)
Glycogenolysis
Glucagon
Prolongs Phase 3 Repolarization
Treatment of severe Supraventricular
and Ventricular Tachycardia
Has Class I, II, III, IV Effects
Interstitial Pulmonary Fibrosis
GI Intolerance
Hyper or Hypothyroidism
Liver Toxicity
Neuropathy
Muscle Weakness
Blue Skin (Iodine accumulation)
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 12
Verapamil
Class IV
Ca2+ Channel
Blocker
Diltiazem
Class IV
Ca2+ Channel
Blocker
Digoxin
Adenosine
Mg2+
Binds to Voltage
Gated Ca
Channels to
Decrease the
Inward Current
Shortens Action Potential
Greater effect on the heart than on
vascular smooth muscle
Treatment of Atrial Dysrhythmias
Treatment of Reentrant
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Reduction in Atrial Flutter
Treatment of Hypertension
Negative Inotropic
BP due to peripheral vasodilation
Binds to Voltage
Gated Ca
Channels to
Decrease the
Inward Current
Shortens Action Potential
Greater effect on the heart than on
vascular smooth muscle
Treatment of Atrial Dysrhythmias
Treatment of Reentrant
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Reduction in Atrial Flutter
Treatment of Hypertension
Negative Inotropic
BP due to peripheral vasodilation
Blocks Na/K
Channels and
Reverses Ca/Na
Antiport to
Intracellular Ca
Shortens the refractory period in both
the atria and the ventricles while
prolonging the effective refractory
period and decreasing the conduction
velocity
Can cause Ectopic ventricular beats
Ventricular Tachycardia or Fibrillation
Inhibits cAMP
Dependent Ca
and K
Conduction
(Hyperpolarizatio
n)
Unknown
Slows AV Nodal Conduction
Treatment of Supraventricular
Tachycardia
Flushing
Shortness of Breath
AV Block
Treatment of Digitalis Induced
Arrhythmias
Treatment of Ventricular Tachycardia
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 13
Cardiac Glycosides
Drug Name
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Reversibly Binds Digoxin is used in the treatment of
with the Na/K
severe left ventricular systolic
ATPase
dysfunction
Positive Inotropic - improved circulation
leads to TPR and eventually HR
Negative Chronotropic
Digitalis
Digoxin
Digitoxin
Adverse Effects
Progressively more severe Dysrhythmia
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Fibrillation
Complete Heart Block
Small therapeutic level before Digitalis
Toxicity - Ca overload together with
diuretics
Hyperkalemia
Anorexia, Nausea and Vomiting
Headache, Fatigue, Confusion, Blurred
Vision, Alteration of Color Perception
and Haloes
Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors
Drug Name
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 14
Milrinone /
Amnirone
Inhibits
cAMP causes Ca2+ Influx in Cardiac
Phosphodiestera Tissue which leads to
CO
se Enzyme
Vasodilation
Treatment of CHF
Toxicity and Death L
Antihypertensive Drugs
Drug Name
Receptor
Mechanism
Unknown
Thiazide Diuretics
Bendrofluazide
Loop Diuretics
Therapeutic Uses
Treatment of Hypertension
Water and Na Excretion
BP
TPR
CO
[Ca2+] in the Urine
Adverse Effects
Induce Hypokalemia and
Hyperuricemia
Can induce Hyperglycemia
Gout
Diabetics Mellitus
Cause Renal Vascular Resistance and
Renal Blood Flow
[Ca2+] in the Urine
Used on patients with poor renal
function rather than the Thiazide
Diuretics
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 15
1 and 2
Nonselective
Intraocular Pressure
Aqueous Humor
Treatment of Migraine
Curbing the effects of Hyperthyroidism
Treatment of STABLE Angina (NOT
ACUTE)
Can aid in the prevention of a Second
MI
Bronchoconstriction
Arrhythmias
Sexual Impairment (unclear as to why)
Glycogenolysis
Glucagon
1 Selective
Cardioselective
Treatment of
BP
Treatment of
Treatment of
Arrhythmia
Treatment of
May compromise respiratory activity in
Asthmatics
Propranolol
REPEAT
Atenolol
REPEAT
Labetalol
REPEAT
Angina
Atrial and Ventricular
Tachycardia
Vasodilation
1 Antagonist
Postural Hypotension 1
BP
1 Antagonist
Dizziness 1
2 Partial Agonist HR
Treatment of Hypertension - Especially
useful for patients with Asthma and
Diabetics due to the 2 partial agonist
effect
Blocks the ACE
enzyme
ACE Inhibitors
Captapril
Hypertension
Peripheral Vascular Resistance
without affecting CO, HR or
Contractility
Treatment of Hypertension
Dry Cough due to a diminished rate of
Bradykinin Inactivation
Renal Damage
Rashes
Fever
First Dose Effect Syncope
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 16
Angiotensin II
Antagonists:
Losartan
Highly Selective
Angiotensin II
Receptor Blocker
(AT1 Subtype)
Similar to ACE Inhibitors
Vasodilation
Blocks Aldosterone Secretion
No Dry cough because Bradykinin is
not affected
Improved of ACE Inhibitors
Fetotoxic
1 Competitive
Treatment of Hypertension
TPR
Alternative to surgery in benign
Prostatic Hypertrophy thus improving
urine flow
First Dose Effect Syncope
Postural Hypotension
Lack of Energy
Nasal Congestion
Headache
Binds to Ca
Channels to
Decrease the
Inward Current
Shortens Action Potential
Greater effect on the heart than on
vascular smooth muscle
Treatment of Atrial Dysrhythmias
Treatment of Reentrant
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Reduction in Atrial Flutter
Treatment of Hypertension
Negative Inotropic
BP due to peripheral vasodilation
Binds to Ca
Channels to
Decrease the
Inward Current
Shortens Action Potential
Greater effect on the heart than on
vascular smooth muscle
Treatment of Atrial Dysrhythmias
Treatment of Reentrant
Supraventricular Tachycardia
Reduction in Atrial Flutter
Treatment of Hypertension
Negative Inotropic
BP due to peripheral vasodilation
Prazosin
REPEAT
Verapamil
Class IV
Ca2+ Channel
Blocker
REPEAT
Diltiazem
Class IV
Ca2+ Channel
Blocker
REPEAT
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 17
2 Agonist
BP due to its action on the CNS
Treatment of Hypertension
Treatment for the withdrawal from
Opiates and Benzodiazepines
2 Agonist
Treatment of Hypertension
TPR
BP
Organ Blood Flow is NOT Reduced
Sedation
Drowsiness
Mg2+ / ATP
Dependent
Transporter
ACTION
Blocks the Mg2+ / ATP Dependent
transporter from transporting
Norepinephrine, Dopamine and
Serotonin from the cytoplasm into the
storage vesicles
THERAPEUTIC USES
Treatment of Hypertension
Causes the ultimate depletion of
Norepinephrine in the adrenergic
neuron
Sympathetic function is greatly
impaired
May cause Bradycardia
Clonidine
REPEAT
-Methyldopa
REPEAT
Reserpine
REPEAT
Vasodilators
Drug Name
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Hydralizine
Atrial Dilation
TPR
Treatment of Hypertension
Tachycardia
GI discomfort
Hirsuitism
Minoxidil
Atrial Dilation
TPR
Treatment of Hypertension
Tachycardia
GI discomfort
Hirsuitism
K+ Sparing Diuretics
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 18
Receptor
Drug Name
Competes with
Aldosterone
Receptors
Spirolactene
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Leads to Na Secretion and K Retention Hyperkalemia
Weak Diuretic
Autacoids
Drug Name
Prostaglandins
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Abortion
Peptic Ulcers
Inhibits the secretion of HCl in the
stomach
Erectile Dysfunction (Alprostadil)
Adverse Effects
With Alprostadil there is pain at the site
of injection
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 19
H1
H2
H1 and H2
Histamine
Bronchial and Intestinal Smooth Muscle
Contraction
NO
Production of Nasal and Bronchial
Mucus
Stimulates Itch and Pain and Sensory
Nerve Endings
Gastric HCl secretion
Systemic BP
Peripheral Resistance
Positive Inotropic (H1 and H2)
Positive Chronotropic (H2)
Capillary Permeability
Vasodilation
Triple Response - Wheal Formation,
Reddening and Halo
Respiratory Symptoms
Lung Capacity
Intestinal Cramps
Diarrhea
Antihistamines
Drug Name
Receptor
Therapeutic Uses
Adverse Effects
Pharmacology Drug Chart Page 20
H1 Receptor
Competitive
Treatment of Allergic Conditions
CANNOT treat Bronchial Asthma
Motion Sickness and Nausea
Treatment of Insomnia
H2 Receptor
Competitive
Treatment of Peptic Ulcers
Gastric HCl Secretion
H1 Receptor
Blockers
Chlorpheniramine
H2 Receptor
Blockers
Cimetidine
Sedation
Dry Mouth
Drug Interactions (MAO Inhibitors)
Overdose in Children
Tremor
Vertigo
También podría gustarte
- Musculoskeletal PharmacologyDocumento18 páginasMusculoskeletal PharmacologyBLEEMAGE100% (2)
- Revising basic and clinical pharmacology: eBookDe EverandRevising basic and clinical pharmacology: eBookAún no hay calificaciones
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocumento21 páginasReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresAún no hay calificaciones
- Northern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016Documento48 páginasNorthern Ireland Management of Infection Guidelines For Primary and Community Care 2016dreneavalentinstefanAún no hay calificaciones
- Anti Infective Drug ChartDocumento1 páginaAnti Infective Drug ChartJessica100% (1)
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocumento12 páginasCardiovascular DrugshannahcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Endocrine Drug ChartDocumento1 páginaEndocrine Drug ChartJessicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiac DrugsDocumento8 páginasCardiac Drugsdawggj100% (2)
- Pharmacology SummaryDocumento16 páginasPharmacology Summaryshenric16Aún no hay calificaciones
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocumento28 páginasA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudAún no hay calificaciones
- Antibiotics Chart 2Documento10 páginasAntibiotics Chart 2Vee MendAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug ClassDocumento13 páginasDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- Common infections and recommended antibioticsDocumento3 páginasCommon infections and recommended antibioticsNicole BerryAún no hay calificaciones
- Respiratory Drugs XL Chart 3Documento2 páginasRespiratory Drugs XL Chart 3cdp1587100% (1)
- Top-200-Drug ETSYDocumento31 páginasTop-200-Drug ETSYBetsy Brown ByersmithAún no hay calificaciones
- Cholinergics and AnticholinergicsDocumento5 páginasCholinergics and AnticholinergicscatislandbigredAún no hay calificaciones
- Brand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX ReviewDocumento72 páginasBrand Generic Class Other: NAPLEX Reviewbapimirab654Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pharma ChartsDocumento33 páginasPharma ChartsNooreen Hussain100% (1)
- Cholinergics and Cholinergic BlockersDocumento5 páginasCholinergics and Cholinergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (3)
- Pharm Drug ListDocumento17 páginasPharm Drug Listanon_523534678Aún no hay calificaciones
- Antiarrhythmic Drug Mechanisms and ClassificationDocumento3 páginasAntiarrhythmic Drug Mechanisms and ClassificationPatrick Tan100% (1)
- Drug of ChoiceDocumento2 páginasDrug of ChoiceRia Tiglao Fortugaliza100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Drugs XL ChartDocumento4 páginasCardiovascular Drugs XL Chartcdp158767% (3)
- Bumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2Documento1 páginaBumetanide Torsemide: Desmopressin - V2med testAún no hay calificaciones
- Cardiac Drugs HypertensionDocumento5 páginasCardiac Drugs HypertensionEciOwnsMeAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug of Choice List PDFDocumento2 páginasDrug of Choice List PDFHeceas Heceas0% (1)
- Drug of ChoiceDocumento16 páginasDrug of ChoiceVicky Vidhata100% (1)
- Respiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsDocumento21 páginasRespiratory and Cardiovascular DrugsCandace Flowers100% (3)
- Pharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsDocumento18 páginasPharmacology Drug Chart: Drug Name Receptor Therapeutic Uses Adverse EffectsPadmavathy Naidu Chokkapu100% (2)
- Psych Drugs Cheat SheetDocumento4 páginasPsych Drugs Cheat SheetHJ G100% (3)
- Total Pharmacy Notes TPN For EEDocumento1601 páginasTotal Pharmacy Notes TPN For EEClaire Cura100% (1)
- Antiinfectives Drug TableDocumento5 páginasAntiinfectives Drug Tablecdp1587100% (3)
- Cardiac Meds CompleteDocumento3 páginasCardiac Meds CompleteDanielle100% (2)
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocumento6 páginasCardiovascular Drugslhayes123488% (16)
- Clin Pharm Lile Antibacterial Classes and ExamplesDocumento4 páginasClin Pharm Lile Antibacterial Classes and ExamplesNicole BerryAún no hay calificaciones
- Git Drugs TablesDocumento3 páginasGit Drugs TablesSulochan Ssplendid Splinterr Lohani100% (1)
- Urinary Tract and Bladder DrugsDocumento2 páginasUrinary Tract and Bladder Drugslhayes1234100% (2)
- Endocrine PharmacologyDocumento42 páginasEndocrine PharmacologyAhmed El SharkawyAún no hay calificaciones
- Drugs WorksheetDocumento16 páginasDrugs Worksheetninja-2001Aún no hay calificaciones
- Naplex - Math Formulas 2Documento1 páginaNaplex - Math Formulas 2starobinAún no hay calificaciones
- Antibiotics ChartDocumento10 páginasAntibiotics Chartadom09Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEDocumento3 páginasPharmacology of Cardiac Diseases MINEMitu Miressa تAún no hay calificaciones
- Apha Naplex PDFDocumento408 páginasApha Naplex PDFsweetAún no hay calificaciones
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDocumento6 páginasMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- Drug TerminologyDocumento5 páginasDrug Terminologyimdaking123Aún no hay calificaciones
- Drug of Choice and First Line of TreatmentDocumento2 páginasDrug of Choice and First Line of Treatmentprinz1mendezAún no hay calificaciones
- Adrenergics & Adrenergic BlockersDocumento5 páginasAdrenergics & Adrenergic Blockersapi-3739910100% (4)
- NSAIDS and SteroidsDocumento2 páginasNSAIDS and Steroidsmed testAún no hay calificaciones
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)De EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesDe EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (2)
- Drug ListDocumento30 páginasDrug ListKristineAún no hay calificaciones
- Drugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemDocumento37 páginasDrugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemJah SuAún no hay calificaciones
- Drugs Acting on the Autonomic Nervous SystemDocumento68 páginasDrugs Acting on the Autonomic Nervous SystemjisooAún no hay calificaciones
- Pharma Drug Tables - 1st ShiftingDocumento29 páginasPharma Drug Tables - 1st ShiftingHei LeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Emergency Medications GuideDocumento7 páginasEmergency Medications Guidejohn72decAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Antimuscarinic AgentsDocumento13 páginas3 Antimuscarinic Agentsmatchees-gone rogueAún no hay calificaciones
- Drugs in ICUDocumento83 páginasDrugs in ICUJennifer DixonAún no hay calificaciones
- Vasopressors and Inotropes in Shock ManagementDocumento63 páginasVasopressors and Inotropes in Shock ManagementCraig DuHaney50% (2)
- Adrenergic DrugsDocumento33 páginasAdrenergic DrugsZsa Zsa FebryanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Practice Naplex 2015Documento160 páginasPractice Naplex 2015starobin100% (4)
- NAPLEX Drugs TableDocumento71 páginasNAPLEX Drugs Tablestarobin100% (3)
- Naplex - Math Formulas 2Documento1 páginaNaplex - Math Formulas 2starobinAún no hay calificaciones
- Simplified Version of Top 200Documento9 páginasSimplified Version of Top 200starobin100% (1)
- Top 300 DrugsDocumento97 páginasTop 300 Drugsstarobin0% (1)
- Nursing School Drug ChartDocumento13 páginasNursing School Drug ChartEve Lester100% (3)
- List of DrugdDocumento11 páginasList of Drugdstarobin100% (5)
- Generic Drug Suffix ChartDocumento19 páginasGeneric Drug Suffix ChartstarobinAún no hay calificaciones
- ErydgDocumento1 páginaErydgstarobinAún no hay calificaciones
- Veltri Drug Cards - Quiz 1Documento1 páginaVeltri Drug Cards - Quiz 1starobinAún no hay calificaciones
- Antibiotics Classification Guide for Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Fluoroquinolones and MoreDocumento1 páginaAntibiotics Classification Guide for Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Fluoroquinolones and MorestarobinAún no hay calificaciones
- Drug Cards Table 2Documento2 páginasDrug Cards Table 2starobinAún no hay calificaciones
- Refrigerate: Hives, RashDocumento5 páginasRefrigerate: Hives, RashstarobinAún no hay calificaciones
- Table 6Documento2 páginasTable 6starobinAún no hay calificaciones
- 2tak Vs 4takDocumento3 páginas2tak Vs 4takTaufiq AlhakimAún no hay calificaciones
- HTTP Verbs GET POST PUT PATCH DELETE (39Documento12 páginasHTTP Verbs GET POST PUT PATCH DELETE (39Jefferson EducacionAún no hay calificaciones
- Water System BOQ 16.12.2023 R0Documento144 páginasWater System BOQ 16.12.2023 R0moinu85Aún no hay calificaciones
- WHO Blocks Nanosilver Shipments to Treat Ebola in AfricaDocumento2 páginasWHO Blocks Nanosilver Shipments to Treat Ebola in AfricaTamas ZefferAún no hay calificaciones
- Research Article (Lavandula Angustifolia) Essential Oil On: Effect of Lavender Acute Inflammatory ResponseDocumento10 páginasResearch Article (Lavandula Angustifolia) Essential Oil On: Effect of Lavender Acute Inflammatory ResponseAndreeaAún no hay calificaciones
- Preparation and Evaluation of Orthodontic Setup PDFDocumento20 páginasPreparation and Evaluation of Orthodontic Setup PDFLiezty VioLen'sAún no hay calificaciones
- A Kitchen in The Corner of The HouseDocumento2 páginasA Kitchen in The Corner of The HousedanielrubarajAún no hay calificaciones
- HSS Article LimitState Plastification 0718 060120Documento3 páginasHSS Article LimitState Plastification 0718 060120clam2014Aún no hay calificaciones
- See Catalog: Get A QuoteDocumento4 páginasSee Catalog: Get A QuoteahnafAún no hay calificaciones
- Colistimethate Sodium 1 Million I.U. Powder For Solution For Injection - Colistin - (Emc)Documento8 páginasColistimethate Sodium 1 Million I.U. Powder For Solution For Injection - Colistin - (Emc)hakim shaikhAún no hay calificaciones
- Study Plan NCEPU PDFDocumento2 páginasStudy Plan NCEPU PDFAhsan100% (1)
- Starter Unit Basic Vocabulary: Smart Planet 3Documento21 páginasStarter Unit Basic Vocabulary: Smart Planet 3Rober SanzAún no hay calificaciones
- Real Possibility of Future ConditionDocumento3 páginasReal Possibility of Future ConditionHusAún no hay calificaciones
- Alternator NotesDocumento24 páginasAlternator Notesarunima arunimaAún no hay calificaciones
- 692pu 6 6Documento1 página692pu 6 6Diego GodoyAún no hay calificaciones
- M700-70 Series Programming Manual (M-Type) - IB1500072-F (ENG)Documento601 páginasM700-70 Series Programming Manual (M-Type) - IB1500072-F (ENG)Mert SertAún no hay calificaciones
- Return SectionDocumento1 páginaReturn SectionDaniel Pouso DiosAún no hay calificaciones
- Weekly Report 52Documento196 páginasWeekly Report 52Erceanu DanAún no hay calificaciones
- Production of Natural Bamboo Fibers-1: Experimental Approaches To Different Processes and AnalysesDocumento13 páginasProduction of Natural Bamboo Fibers-1: Experimental Approaches To Different Processes and AnalysesrabiulfAún no hay calificaciones
- User ManualDocumento14 páginasUser ManualKhaled BellegdyAún no hay calificaciones
- Alcon Capacitor AC Mp4aDocumento6 páginasAlcon Capacitor AC Mp4aDAC Secretary EEAún no hay calificaciones
- Installation & Testing of Fire Protection SystemsDocumento7 páginasInstallation & Testing of Fire Protection Systemssunny_84tAún no hay calificaciones
- Exogenous Driver Analysis Driver Relative GDP GrowthDocumento107 páginasExogenous Driver Analysis Driver Relative GDP GrowthBhagya FoodsAún no hay calificaciones
- Lock Out Tag Out ProceduresDocumento9 páginasLock Out Tag Out ProceduresyawarhassanAún no hay calificaciones
- US Army TV Course - Documentation Cinematography SS0536Documento49 páginasUS Army TV Course - Documentation Cinematography SS0536innerethosAún no hay calificaciones
- داينمك الملزمة كاملةDocumento79 páginasداينمك الملزمة كاملةarno assassin33% (3)
- Lisa - Add New Front: Process Matching/Installation and Qualification (IQ)Documento62 páginasLisa - Add New Front: Process Matching/Installation and Qualification (IQ)Thanh Vũ NguyễnAún no hay calificaciones
- Đánh giá chế độ ăn kiêng: Nhịn ăn gián đoạn để giảm cân- wed HarvardDocumento14 páginasĐánh giá chế độ ăn kiêng: Nhịn ăn gián đoạn để giảm cân- wed HarvardNam NguyenHoangAún no hay calificaciones
- General Guidelines For Design and Construction of Concrete Diaphram (Slurry) WallsDocumento108 páginasGeneral Guidelines For Design and Construction of Concrete Diaphram (Slurry) WallsharleyAún no hay calificaciones
- 4TWX4036 Service FactsDocumento4 páginas4TWX4036 Service FactsAlejandro OrdoñezAún no hay calificaciones