100% encontró este documento útil (1 voto)
1K vistas32 páginasAerial Photo Interpretation Principles
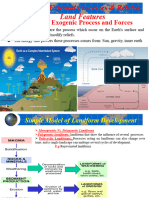
This document discusses the seven principles of aerial photo interpretation: 1) Shape, 2) Size, 3) Tone or color, 4) Texture, 5) Pattern, 6) Shadow, and 7) Association. It provides examples of how each principle can be used to identify natural and cultural features visible in aerial photographs. The principles help analysts determine attributes like an object's surface area, orientation, height and relationship to its surrounding environment. Understanding these principles is important for applications like soil surveys, geological mapping, and forestry management.
Cargado por
lucarsoDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd
100% encontró este documento útil (1 voto)
1K vistas32 páginasAerial Photo Interpretation Principles
This document discusses the seven principles of aerial photo interpretation: 1) Shape, 2) Size, 3) Tone or color, 4) Texture, 5) Pattern, 6) Shadow, and 7) Association. It provides examples of how each principle can be used to identify natural and cultural features visible in aerial photographs. The principles help analysts determine attributes like an object's surface area, orientation, height and relationship to its surrounding environment. Understanding these principles is important for applications like soil surveys, geological mapping, and forestry management.
Cargado por
lucarsoDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd