Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Introduction To LAN and WAN PDF
Cargado por
Ibra NazlaTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Introduction To LAN and WAN PDF
Cargado por
Ibra NazlaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Introduction
Different Networks
LAN
MAN
WAN
Internetwork
Networking Devices
WAN technologies
Dedicated
circuit switched
packet switched
narrowband - Analog modem, ISDN
broadband - DSL, Cable modem, SONET
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 1
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Networks Categories
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 2
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Local Area Networks
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 3
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Local Area Networks (II)
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 4
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Metropolitan Area Network
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 5
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
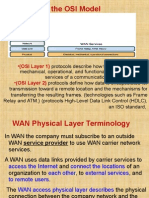
Wide Area Networks
Connect devices separated by
wide geographical areas
Use Carriers.
They use serial connections of
various types to access
bandwidth over large
geographic
Operate at the Physical and
Data Link layers (Layers 1 &
2).
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 6
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Internetwork
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 7
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
WAN Technologies
WAN Technologies Overview
Dedicated
T1, E1, T3, E3
xDSL
SONET
Switched
Circuit
Switched
POTS
ISDN
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
Analog
Dial-up modems
Cable modems
Wireless
Packet
Switched
X.25
Frame
Relay
page 8
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Networking Devices
Routers
offer many services, including internetworking and WAN interface ports
Switches
provide connectivity for voice, data, and video communication
Modems
Interface with voice-grade connection to convert analog signal to digital.
Also called CSU/DSUs (channel service units/digital service units) in data
service networks
Represents the DCE side of the DTE/DCE connection
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 9
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Circuit Switched: POTS
Plain Old Telephone System (POTS)
also known as Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN)
an important component of our communication infrastructure
It is still the standard for designing reliable networks
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 10
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Circuit Switched: POTS
Fixed Time Division Multiplex is used in POT network for users to
share transmission line in a rigid manner.
Each user may access the transmission line one by one, in different
time period. Each user is assigned a channel (sometime referred
as time slot) for him to transmit his data.
Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) is used to convert analogue voice
signal into digital form. PCM takes place at the telephone exchange
centers (or CO) where subscriber lines terminate.
Designed to carry analog information: voice
Can be used to carry digital data: require analog modem for
conversions
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 11
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Analog data Services
Dial-up Modems (switched analog)
Standard that can provides 56 kbps download speed and 33.6 kbps
upload speed.
With the download path, there is a
digital-to-analogue conversion at
the client side.
With the upload path, there is a
analogue-to-digital conversion at
the client side.A-to-D conversion
introduces quantization error
making the overall s/n ratio lower.
Hence, the upload path can not
support a data rate as high as the
download path
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 12
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Circuit Switched Services
B
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
D
Historically important--first dial-up digital serviceB
Max. bandwidth = 128 kbps for BRI (Basic Rate Interface)
2 B channels @ 64kps and 1 D channel @ 16kps
B channels are voice/data channels; D for signaling
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 13
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Packet Switched Services
X.25 (Connection-oriented)
Reliable--X.25 has been extensively debugged and is now very
stable--literally no errors in modern X.25 networks
Store & Forward--Since X.25 stores the whole frame to error check
it before forwarding it on to the destination, it has an inherent delay
(unlike Frame Relay) and requires large, expensive memory
buffering capabilities.
Frame Relay (Connectionless and/or Connection-oriented)
More efficient and much faster than X.25
Used mostly to forward LAN IP packets
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 14
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
WAN Data-Link
WAN data link protocols describe how frames are carried between
systems on a single data link.
They include protocols designed to operate over dedicated point-to-point,
multipoint, and multi-access switched services.
WAN standards are defined and managed by a number of recognized
authorities, including the following agencies: ITU-T, ISO, IETF, & EIA
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 15
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
WAN Data-Link Encapsulations
High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC)
Cisco default encapsulation; typically used between routers running
Cisco IOS
Streamlined: no windowing or flow control
may not be compatible with different vendors because of the way each
vendor has chosen to implement it.
HDLC supports both point-to-point and multipoint configurations
Frame Relay frame format
uses simplified framing with no error correction mechanisms
send Layer 2 information much more rapidly than other WAN protocols
PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol)
Developed by IETF; replacing SLIP
Contains a field to identify the network layer protocol
PPP can check for link quality during connection establishment
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 16
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Digital Subscriber Lines
Digital Subscriber Lines (xDSL); the x stands for a family of technologies
The Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
uses most of the bandwidth (up to 8 Mbps) for the downstream and
only a small bandwidth (up to 640 kbps) for the upstream
many Telcos have already installed high-speed digital wide-area
network.
The link between subscribers and network is still analog line from
plain old telephone service lines (POT).
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 17
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Cable Modems (Shared Analog)
Cable TV provides residential premises with a coaxial cable that has a bandwidth
of 750MHz
The bandwidth is divided into 6 MHz band using FDM for each TV channel
A "Cable Modem" is a device that allows high-speed data access (Internet) via
cable TV network.
A cable modem will typically have two connections because a splitter delivers the
TV bands to TV set and the internet access bands to PC via a cable box
The splitter delivers the TV bands to TV set and the internet access bands to PC
via a cable box
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 18
CS341: Introduction to LAN & WAN
Summary
LAN Basics
WAN Basics
Circuit Switch Network
POTS, PSTN, ISDN, leased line, majority of voice circuits, GSM
Packet Switch Network
X.25, FR, ATM, Ethernet, FastEthernet, ATM (cell switch)
WAN data link
Analog data service, ISDN, ADSL, Cable Model
Justinian Anatory Computer and Systems Engineering
page 19
También podría gustarte
- Wide-Area NetworksDocumento68 páginasWide-Area NetworksGorvam SaddarAún no hay calificaciones
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsDe EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroCalificación: 1 de 5 estrellas1/5 (1)
- Network Lesson 6Documento12 páginasNetwork Lesson 6Mesele BerhanuAún no hay calificaciones
- Handbook of Serial Communications Interfaces: A Comprehensive Compendium of Serial Digital Input/Output (I/O) StandardsDe EverandHandbook of Serial Communications Interfaces: A Comprehensive Compendium of Serial Digital Input/Output (I/O) StandardsCalificación: 1 de 5 estrellas1/5 (4)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)Documento36 páginasWide Area Network (WAN)Nikhil PatelAún no hay calificaciones
- Transmission and Media: Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MSC., PHDDocumento48 páginasTransmission and Media: Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MSC., PHDanurkumalaAún no hay calificaciones
- BCENT - Basic Cisco Entry Networking Technician: Introducing Wide-Area NetworksDocumento41 páginasBCENT - Basic Cisco Entry Networking Technician: Introducing Wide-Area NetworksmanuelAún no hay calificaciones
- Architecture of An ISPDocumento8 páginasArchitecture of An ISPSajad AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Computers Are Your Future: © 2005 Prentice-Hall, IncDocumento31 páginasComputers Are Your Future: © 2005 Prentice-Hall, IncAlex HaAún no hay calificaciones
- Protocol IP Address Ethernet MAC Address: OSI Model BytesDocumento10 páginasProtocol IP Address Ethernet MAC Address: OSI Model BytesRaka PoddarAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 2 Introduction To WANDocumento24 páginasLecture 2 Introduction To WANCalvinhoAún no hay calificaciones
- Part 3 Itroduction To Wan Ch1 Part2Documento22 páginasPart 3 Itroduction To Wan Ch1 Part2Marwan AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Broadband: - Networking Basics - Overview of NIB - Broadband Network - Installations OverviewDocumento64 páginasIntroduction To Broadband: - Networking Basics - Overview of NIB - Broadband Network - Installations OverviewsrshelkeAún no hay calificaciones
- WAN StandardsDocumento23 páginasWAN Standardsmanderin87Aún no hay calificaciones
- Optical EthernetDocumento19 páginasOptical EthernetEr Lingaraj Hiremath50% (4)
- Wide Area NetworksDocumento15 páginasWide Area NetworksSudhir MaherwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment ACNDocumento7 páginasAssignment ACNMukeshAún no hay calificaciones
- Frame Relay and X.25Documento63 páginasFrame Relay and X.25Mattew StevenAún no hay calificaciones
- CHAP 2bDocumento47 páginasCHAP 2bGANESAN AAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial 4Documento9 páginasTutorial 4susmita lamsalAún no hay calificaciones
- WAN Overview: Page - 1Documento3 páginasWAN Overview: Page - 1Mohamed MazharAún no hay calificaciones
- Borscht: Hook Refers To When The Handset Is Idle and Waiting For A Signal Indicating That Someone Wants ToDocumento10 páginasBorscht: Hook Refers To When The Handset Is Idle and Waiting For A Signal Indicating That Someone Wants ToNouman Asif100% (1)
- Introduction To Wan Technology and ServicesDocumento30 páginasIntroduction To Wan Technology and ServicesLaura TampubolonAún no hay calificaciones
- PTCL Internship Report-2015Documento26 páginasPTCL Internship Report-2015Hamza Shahid100% (1)
- Synopsis Frame RelayDocumento5 páginasSynopsis Frame RelayMohd Yasin KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Network System of PSTU PDFDocumento19 páginasNetwork System of PSTU PDFMohammad Zahid HasanAún no hay calificaciones
- Analysis of WAN Devices and FacilitiesDocumento11 páginasAnalysis of WAN Devices and FacilitiesBharat Kumar GatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes3 WANDocumento40 páginasNotes3 WANsamitha deshanAún no hay calificaciones
- EC2352 CN Notes - NPRDocumento150 páginasEC2352 CN Notes - NPRKarthick VijayanAún no hay calificaciones
- WAN Terms::-Wan Is Known As Wide Area Network and It Connects Two or More LAN Together Over LargeDocumento10 páginasWAN Terms::-Wan Is Known As Wide Area Network and It Connects Two or More LAN Together Over LargePankaj GargAún no hay calificaciones
- Networking Glossary: 150+ Words You Should KnowDocumento19 páginasNetworking Glossary: 150+ Words You Should KnowfranciscoAún no hay calificaciones
- Kimmo K. Saarela Tampere University of Technology Telecommunication Laboratory P.O. Box 553, 33101 Tampere, Finland Kks@cs - Tut. February 17, 1995Documento20 páginasKimmo K. Saarela Tampere University of Technology Telecommunication Laboratory P.O. Box 553, 33101 Tampere, Finland Kks@cs - Tut. February 17, 1995José AranibarAún no hay calificaciones
- ST 11 Teknologi-Jaringan-Akses PDFDocumento53 páginasST 11 Teknologi-Jaringan-Akses PDFSerpi PabungaAún no hay calificaciones
- Computer Network (CS610)Documento4 páginasComputer Network (CS610)Khansa MueenAún no hay calificaciones
- Analysis of WAN Devices and FacilitiesDocumento11 páginasAnalysis of WAN Devices and FacilitiesBharat Kumar GatlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lan ComponentsDocumento7 páginasLan ComponentsAbhishek DasAún no hay calificaciones
- Accessing The WAN - Chapter 2Documento85 páginasAccessing The WAN - Chapter 2Conrad TilburyAún no hay calificaciones
- 2Documento5 páginas2Krishna chhetriAún no hay calificaciones
- Lan Wan PresentationDocumento43 páginasLan Wan PresentationsonaltopiwalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ofc Assignment 02 ILSADocumento12 páginasOfc Assignment 02 ILSAIfra MalikAún no hay calificaciones
- Acrónim o Definición Términos Relacionados/dispositivos/ Ejemplos o Explicaciones AdicionalesDocumento7 páginasAcrónim o Definición Términos Relacionados/dispositivos/ Ejemplos o Explicaciones Adicionalesdaniel_087Aún no hay calificaciones
- Netacad and Quizlet CCNA4 Chapter 1 4Documento107 páginasNetacad and Quizlet CCNA4 Chapter 1 4ChoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture Two Introduction To WAN: by Dr. Alaa I. Al-Muttairi 2020/2021Documento32 páginasLecture Two Introduction To WAN: by Dr. Alaa I. Al-Muttairi 2020/2021Bashir Emad kadimAún no hay calificaciones
- WAN TechnologiesDocumento6 páginasWAN Technologiesolive360Aún no hay calificaciones
- 6-3emerging Network TechnologiesDocumento24 páginas6-3emerging Network TechnologiesBijay PoudelAún no hay calificaciones
- Metropolitan Area NetworksDocumento6 páginasMetropolitan Area NetworksKifaru Micro-electronicsAún no hay calificaciones
- CA Ex S1M09 EthernetDocumento136 páginasCA Ex S1M09 Ethernethttp://heiserz.com/Aún no hay calificaciones
- What Is ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) ?: How It WorksDocumento5 páginasWhat Is ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) ?: How It Workssoqylio mcbarAún no hay calificaciones
- CCN Class Assignment # 4 Solved 70067010Documento6 páginasCCN Class Assignment # 4 Solved 70067010HANNAN TARIQAún no hay calificaciones
- Digital Subscriber Line TechnologyDocumento9 páginasDigital Subscriber Line Technologypurushotham2009Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 02 03Documento53 páginasChapter 02 03Kjell15100% (2)
- Internet Access Via Cable TV NetworkDocumento25 páginasInternet Access Via Cable TV Networkankur_desaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To WAN Technologies: Dereje M. School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Hawassa Institute of TechnologyDocumento10 páginasIntroduction To WAN Technologies: Dereje M. School of Electrical & Computer Engineering, Hawassa Institute of TechnologymigadAún no hay calificaciones
- Siemens Power LinkDocumento14 páginasSiemens Power Linkarya_85Aún no hay calificaciones
- Data Communication and Networking Prelims ExamDocumento7 páginasData Communication and Networking Prelims ExamSagarAnchalkarAún no hay calificaciones
- Ethernet Industrial - Explicativo de Phoenix ContactDocumento48 páginasEthernet Industrial - Explicativo de Phoenix Contactluk@_sAún no hay calificaciones
- Power Line CommunicationDocumento62 páginasPower Line CommunicationPantech ProLabs India Pvt LtdAún no hay calificaciones
- WAN Technologies and ConfigsDocumento4 páginasWAN Technologies and ConfigsMusaAún no hay calificaciones
- Electromagnetic Waves & Antennas Solutions - 2008Documento137 páginasElectromagnetic Waves & Antennas Solutions - 2008DM250% (2)
- Digital Telecommunications: Semester II, 2008/2009Documento7 páginasDigital Telecommunications: Semester II, 2008/2009Ibra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- DistanceVectorRouting 5Documento122 páginasDistanceVectorRouting 5Ibra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic IOS ReviewDocumento64 páginasBasic IOS ReviewIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- TE312 01 April 22 2009.Documento32 páginasTE312 01 April 22 2009.Ibra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mid Term Exam SolutionsDocumento3 páginasMid Term Exam SolutionsIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- CS341 ProtocolsDocumento12 páginasCS341 ProtocolsIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Classless RoutingDocumento35 páginasIntroduction To Classless RoutingIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Analog and Digital Communications: 4. Sampling and Pulse Code ModulationDocumento18 páginasAnalog and Digital Communications: 4. Sampling and Pulse Code Modulationaditya_vyas_13Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lect NB NoiseDocumento8 páginasLect NB NoiseIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- COMM704 - Introduction PDFDocumento9 páginasCOMM704 - Introduction PDFIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lect SNR AfmDocumento12 páginasLect SNR AfmIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Analog and Digital Communications: 2. Amplitude ModulationDocumento17 páginasAnalog and Digital Communications: 2. Amplitude ModulationIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Signals and Operations: Continuous-TimeDocumento12 páginasIntroduction To Signals and Operations: Continuous-TimeIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- TE311 Lecture03 Fourier SeriesDocumento27 páginasTE311 Lecture03 Fourier SeriesIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nyquist Sampling, Pulse-Amplitude Modulation, and Time-Division MultiplexingDocumento10 páginasNyquist Sampling, Pulse-Amplitude Modulation, and Time-Division MultiplexingIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Communications Systems Tutorial3v1solDocumento2 páginasCommunications Systems Tutorial3v1solIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial Sheet 1 - Fourier SeriesDocumento1 páginaTutorial Sheet 1 - Fourier SeriesIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- TE311 Lecture03 Fourier SeriesDocumento27 páginasTE311 Lecture03 Fourier SeriesIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Examples of Time Division Multiplexed PAM and PCM SystemsDocumento9 páginasExamples of Time Division Multiplexed PAM and PCM SystemsEng IbontokoAún no hay calificaciones
- Workshop Number 1 - Matlab TutorialDocumento20 páginasWorkshop Number 1 - Matlab TutorialIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- TE311 Lecture09 SSB SC VSB ModulationDocumento20 páginasTE311 Lecture09 SSB SC VSB ModulationIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- TE311 Lecture07 AMDocumento29 páginasTE311 Lecture07 AMIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- TE311 Lecture08 DSB SC ModulationDocumento23 páginasTE311 Lecture08 DSB SC ModulationIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec13 Bandpass Modulation IDocumento28 páginasLec13 Bandpass Modulation IIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec 2 SamplingDocumento30 páginasLec 2 SamplingIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- TE312: Introduction To Digital Telecommunications: Lecture #4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Documento25 páginasTE312: Introduction To Digital Telecommunications: Lecture #4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Ibra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- TE311 Lecture07 AMDocumento29 páginasTE311 Lecture07 AMIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lec9 Error ProbabilityDocumento26 páginasLec9 Error ProbabilityIbra NazlaAún no hay calificaciones
- Topex VoibridgeDocumento36 páginasTopex VoibridgeFitim IsmailiAún no hay calificaciones
- Mod. PCM/EV: PCM Switching and Transmission SystemDocumento2 páginasMod. PCM/EV: PCM Switching and Transmission SystemShahoodulHassanAún no hay calificaciones
- SHLR Product DescriptionDocumento48 páginasSHLR Product DescriptionVoravit Satitviriyakul100% (1)
- Nepal TelecomDocumento18 páginasNepal TelecomManish JaiswalAún no hay calificaciones
- Vega Series Analog/Digital GatewaysDocumento2 páginasVega Series Analog/Digital GatewaysMiguel Andres VanegasAún no hay calificaciones
- Voice: FTTH Voice Service (B2C) Is As BelowDocumento8 páginasVoice: FTTH Voice Service (B2C) Is As BelowAung Thein OoAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 Evaluation of Switching System 240810newDocumento124 páginasChapter 2 Evaluation of Switching System 240810newSuleman Jamil100% (11)
- Unit 1Documento77 páginasUnit 1rashwin singhAún no hay calificaciones
- CIPT1 v8.0 VoD-SLIDESDocumento135 páginasCIPT1 v8.0 VoD-SLIDESPiyumal RajapaksheAún no hay calificaciones
- 2n Liftnet Manual en 1446v1.8.3Documento97 páginas2n Liftnet Manual en 1446v1.8.3Carlos RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- HONET UA5000 Oversea Enterprise BrochureV1Documento4 páginasHONET UA5000 Oversea Enterprise BrochureV1Irfan AslamAún no hay calificaciones
- ITU-T IP Related StudiesDocumento33 páginasITU-T IP Related StudiesCris To PherAún no hay calificaciones
- Hakin9 en TBO 01 2014 TeaserDocumento76 páginasHakin9 en TBO 01 2014 TeaserTom HallerAún no hay calificaciones
- Telecommunications Terms. A Glossary For Telecommunications Terms and Acronyms. - Vividfuture PDFDocumento16 páginasTelecommunications Terms. A Glossary For Telecommunications Terms and Acronyms. - Vividfuture PDFxavixeffAún no hay calificaciones
- BSNL Summer Traning ReportDocumento39 páginasBSNL Summer Traning ReportMohd MunzirAún no hay calificaciones
- Wisdom Risco Updown-Install UkDocumento48 páginasWisdom Risco Updown-Install UkDiego FRANCISCOAún no hay calificaciones
- IP Telephony Using CallManager Lab PortfolioDocumento319 páginasIP Telephony Using CallManager Lab PortfolioRehan S. Mirza50% (2)
- Multivoip: Gateways Have Been DiscontinuedDocumento4 páginasMultivoip: Gateways Have Been DiscontinuedCarlos Rumay DilasAún no hay calificaciones
- TelecommunicationDocumento81 páginasTelecommunicationhazlinatalib0% (1)
- Configuring CUC For SIPDocumento7 páginasConfiguring CUC For SIPmsteppAún no hay calificaciones
- Thesis 2023Documento69 páginasThesis 2023john kenneth FamoAún no hay calificaciones
- IP Over VoiceDocumento31 páginasIP Over VoiceHarish Kr SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Assign1 PDFDocumento2 páginasAssign1 PDFPrathiksha RavishankarAún no hay calificaciones
- Implementing Cisco Voice Gateways and GatekeepersDocumento7 páginasImplementing Cisco Voice Gateways and GatekeepersRonaldo RomeroAún no hay calificaciones
- EXO 2005 Step by StepDocumento119 páginasEXO 2005 Step by StepIbrahim AntarAún no hay calificaciones
- PT Programming ManualDocumento77 páginasPT Programming ManualpatriciaAún no hay calificaciones
- HTS Initial Set Up 2016 09 26Documento44 páginasHTS Initial Set Up 2016 09 26nboninaAún no hay calificaciones
- Borscht: Hook Refers To When The Handset Is Idle and Waiting For A Signal Indicating That Someone Wants ToDocumento10 páginasBorscht: Hook Refers To When The Handset Is Idle and Waiting For A Signal Indicating That Someone Wants ToNouman Asif100% (1)
- SIP To IP Architecture - Von9909 - EricssonDocumento22 páginasSIP To IP Architecture - Von9909 - EricssonduyckAún no hay calificaciones
- PSTN Connectivity For Microsoft Teams The Easy WayDocumento7 páginasPSTN Connectivity For Microsoft Teams The Easy WayRosanna ReynosoAún no hay calificaciones