Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
NESC
Cargado por
JLFDZDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
NESC
Cargado por
JLFDZCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
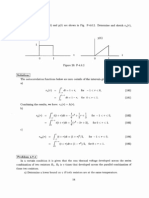
T-124-1A(m)
Part 1: Electric Supply Stations
T-124-1A(m)
Limite de
m
aproximacion
Table 124-1
segura de acuerdo
Clearances from live parts
PART ALow, medium, and high voltages (based on BIL factors) al NESC-2007
Column 1
Column C
Column 2
Column 3
Column 4
Maximum design
voltage between
phases
Basic impulse
insulation level t
(BIL)
Vertical clearance of
unguarded parts q
Horizontal
clearance of
unguarded parts q
Clearance guard
to live parts q
kV
kV
mm
0.3
Not specified
Not specified
Not specified
0.6
2.64
1.02
50
2.4
2.67
1.02
76
7.2
95
2.69
1.02
101
15
95
2.69
1.02
101
15
110
2.74
1.07
152
25
125
2.77
1.09
177
25
150
2.82
1.14
228
35
200
2.90
1.22
304
48
250
3.00
1.32
406
72.5
250
3.00
1.32
406
72.5
350
3.18
1.50
584
121
350
3.18
1.50
584
121
550
3.53
1.85
939
145
350
3.18
1.50
584
145
550
3.53
1.85
939
145
650
3.71
2.03
1117
169
550
3.53
1.85
939
169
650
3.71
2.03
1117
169
750
3.91
2.24
1320
242
550
3.53
1.85
939
242
650
3.71
2.03
1117
242
750
3.91
2.24
1320
242
900
4.19
2.51
1600
242
1050
4.52
2.84
1930
Copyright 2006 IEEE. All rights reserved.
43
Part 1: Electric Supply Stations
T-124-1D(ft)
125A2
Table 124-1 (continued)
PART D High voltage direct current (based on transient overvoltage)
ft
Column 1
Column A
Column B
Column 2
Column 3
Column 4
Maximum
design voltage
conductor to
ground
Transient
overvoltage
per unit r
Transient
overvoltage
line to grnd r
Vertical
clearance of
unguarded
parts q
Horizontal
clearance of
unguarded
parts q
Clearance
guard to live
partsq
kV
ft
in
ft
in
ft
in
kV
600
1.5 or below
900
20
10
15
12
600
1.6
960
22
16
13
600
1.7
1020
23
17
11
14
11
600
1.8
1080
24
10
19
16
750
1.5 or below
1125
25
11
20
17
750
1.6
1200
27
22
19
750
1.7
1275
29
24
21
750
1.8
1350
31
11
26
23
q Interpolate for intermediate values. The clearances in column 4 of this table are solely for guidance in installing
guards without definite engineering design and are not to be considered as a requirement for such engineering
design. For example, the clearances in the tables above are not intended to refer to the clearances between live
parts and the walls of the cells, compartments, or similar enclosing structures. They do not apply to the clearances
between bus bars and supporting structures nor to clearances between the blade of a disconnecting switch and its
base. However, where surge-protective devices are applied to protect the live parts, the vertical clearances,
column 2 of Table 124-1 Part A may be reduced provided the clearance is not less than 8.5 ft plus the electrical
clearance between energized parts and ground as limited by the surge-protective devices.
wClearances shall satisfy either switching-surge or BIL duty requirements, whichever are greater.
e Switching-surge factoran expression of the maximum switching-surge crest voltage in terms of the maximum
operating line-to-neutral crest voltage of the power system.
r The values of columns A, B, and C are power system design factors that shall correlate with selected clearances.
Adequate data to support these design factors should be available.
t The selection of station BIL shall be coordinated with surge-protective devices when BIL is used to determine
clearance. BILbasic impulse insulation levelfor definition and application, see IEEE Std 1313-1993.
125. Working space about electric equipment
A.
Working space (600 V or less)
Access and working space shall be provided and maintained about electric equipment to permit
ready and safe operation and maintenance of such equipment.
1.
Clear spaces
Working space required by this section shall not be used for storage. When normally enclosed
energized parts are exposed for inspection or servicing, the working space, if in a passageway
or general open space, shall be guarded.
2.
Access and entrance to working space
At least one entrance shall be provided to give access to the working space about electric
equipment.
Copyright 2006 IEEE. All rights reserved.
51
125A3
127
Part 1: Electric Supply Stations
3.
Working space
The working space in the direction of access to energized parts operating at 600 V or less that
require examination, adjustment, servicing, or maintenance while energized shall be not less
than indicated in Table 125-1. In addition to the dimensions shown in Table 125-1, the working
space shall be not less than 750 mm (30 in) wide in front of the electric equipment. Distances
shall be measured from the energized parts if such are exposed or from the enclosure front or
opening if such are enclosed. Concrete, brick, or tile walls shall be considered grounded.
4.
Headroom working space
The headroom of working spaces about switchboards or control centers shall be not less than
2.13 m (7 ft).
5.
Front working space
In all cases where there are energized parts normally exposed on the front of switchboards or
motor control centers, the working space in front of such equipment shall not be less than
900 mm (3 ft).
B.
Working space over 600 V
Working space shall be in accordance with Table 124-1.
Table 125-1Working space
Clear distance
Voltage to ground
Condition 1
Condition 2
Condition 3
mm
ft
mm
ft
mm
ft
0150
900
900
900
151600
900
1070
3-1/2
1200
Where the conditions are as follows:
1. Exposed energized parts on one side and no energized or grounded parts on the other side of the working space,
or exposed energized parts on both sides effectively guarded by suitable wood or other insulating materials. Insulated wire or insulated bus bars operating at not over 300 V shall not be considered energized parts.
2. Exposed energized parts on one side and grounded parts on the other side.
3. Exposed energized parts on both sides of the work space (not guarded as provided in Condition 1) with the operator between.
EXCEPTION: Working space shall not be required in back of assemblies, such as dead-front switchboards or motor
control centers where there are no renewable or adjustable parts such as fuses or switches on the back and where
all connections are accessible from locations other than the back.
Limite de
126. Equipment for work on energized parts
aproximacion
seguro de acuerdo
al NESC-2007
When it is necessary for personnel to move themselves, material, or tools within the guard zone of
unguarded energized parts, protective equipment shall be provided.
This protective equipment shall be periodically inspected, tested, and kept in a safe condition.
Protective equipment shall be rated for not less than the voltage involved. Refer to Section 3 for a
list of specifications for equipment.
127. Classified locations
Electrical installations in classified areas shall meet the requirements of the NEC, Articles 500
through 517. Areas classified in accordance with NEC Article 500 shall comply with the
52
Copyright 2006 IEEE. All rights reserved.
También podría gustarte
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Columbia Lxew High BayDocumento8 páginasColumbia Lxew High BayJLFDZAún no hay calificaciones
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5795)
- 038-706E TL85A OwnersManualDocumento20 páginas038-706E TL85A OwnersManualJLFDZAún no hay calificaciones
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- 8040 Series Gas Valves Features BenefitsDocumento1 página8040 Series Gas Valves Features BenefitsJLFDZAún no hay calificaciones
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Sags SwellsDocumento22 páginasSags SwellsIbrahim Mostafa FaragAún no hay calificaciones
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- Stremler Solution Part2Documento35 páginasStremler Solution Part2JLFDZAún no hay calificaciones
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (74)
- Worksheet 01: Software LAN Wi-Fi Attachments Virus Worm Resolves AntiDocumento7 páginasWorksheet 01: Software LAN Wi-Fi Attachments Virus Worm Resolves AntiAisha AnwarAún no hay calificaciones
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Azure DatalakeDocumento8 páginasAzure DatalakeRahaman AbdulAún no hay calificaciones
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- Regus Lakeview - Meeting Room Price ListDocumento1 páginaRegus Lakeview - Meeting Room Price ListJayaraj TAún no hay calificaciones
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- ZXDU68 B451 V6.0R20M02 DC Power System Quick Installation GuideDocumento7 páginasZXDU68 B451 V6.0R20M02 DC Power System Quick Installation GuideVictor ArticaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (400)
- ME302-Syllabus - ME-302 Mechanical Systems IIDocumento2 páginasME302-Syllabus - ME-302 Mechanical Systems IIد.محمد كسابAún no hay calificaciones
- Market Basket AnalysisDocumento15 páginasMarket Basket AnalysisAkanksha KadamAún no hay calificaciones
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (345)
- Manual Survey Pro For RangerDocumento337 páginasManual Survey Pro For RangerIni ChitozAún no hay calificaciones
- Renub Research: Published: May, 2012Documento12 páginasRenub Research: Published: May, 2012api-114525849Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- HP Moonshot Provisiong Manager User GuideDocumento44 páginasHP Moonshot Provisiong Manager User GuideBalasubramanian ReguramanAún no hay calificaciones
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- Introduction To MATLABDocumento33 páginasIntroduction To MATLABAbebayehu YohannesAún no hay calificaciones
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- Nebula - 150 User ManualDocumento94 páginasNebula - 150 User ManualSamuel MongeAún no hay calificaciones
- Rajesh Vasa - PHD ThesisDocumento252 páginasRajesh Vasa - PHD Thesisrajeshvasa100% (1)
- Operation Guide 5522: Things To Check Before Using The Watch About This ManualDocumento7 páginasOperation Guide 5522: Things To Check Before Using The Watch About This Manualfirdaus_stAún no hay calificaciones
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- Teachers Voices From Argentine ClassroomsDocumento69 páginasTeachers Voices From Argentine ClassroomsEmanuel AlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- Assignment 2 MIS Taha Ali KhanDocumento2 páginasAssignment 2 MIS Taha Ali KhanTaha Rizwan KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- ProjectWork Zaripova 2017Documento57 páginasProjectWork Zaripova 2017hieuAún no hay calificaciones
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- Zwave Compatibility ListDocumento2 páginasZwave Compatibility ListsupermanAún no hay calificaciones
- Agc 150 Designers Handbook 4189341188 UkDocumento398 páginasAgc 150 Designers Handbook 4189341188 UkMaicon ZagonelAún no hay calificaciones
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- Cheatsheet Supervised LearningDocumento4 páginasCheatsheet Supervised Learningan7l7aAún no hay calificaciones
- Research EditedDocumento7 páginasResearch Editedauko omondiAún no hay calificaciones
- Fda Ora Lab Manual Basics Statistics Data PresentationDocumento25 páginasFda Ora Lab Manual Basics Statistics Data PresentationDoaa KhalilAún no hay calificaciones
- Security SY0 501 Study GuideDocumento39 páginasSecurity SY0 501 Study GuidereAún no hay calificaciones
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- JNTU Old Question Papers 2007Documento8 páginasJNTU Old Question Papers 2007Srinivasa Rao GAún no hay calificaciones
- Domains (Meinberg) Install GuideDocumento21 páginasDomains (Meinberg) Install GuideManu DafonteAún no hay calificaciones
- Compiler Lab VivaDocumento6 páginasCompiler Lab VivaGaurav SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Harvard Apparatus, Model 44 Syringe Pump User ManualDocumento56 páginasHarvard Apparatus, Model 44 Syringe Pump User ManualthynameisraymondAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate Entrepreneurship - HowDocumento30 páginasCorporate Entrepreneurship - HowHoang Anh TuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Kassia Webb - Resume Updtd 11 Dec 2016Documento4 páginasKassia Webb - Resume Updtd 11 Dec 2016api-322501460Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2104)
- PYthon Class 21 TeluguDocumento4 páginasPYthon Class 21 TeluguTHE KINGAún no hay calificaciones
- Slides Adapted From: Foundations of Computer Science, Behrouz ForouzanDocumento21 páginasSlides Adapted From: Foundations of Computer Science, Behrouz Forouzanahmad alkasajiAún no hay calificaciones
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)