Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Light Dependent Resistor
Cargado por
antonerajDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Light Dependent Resistor
Cargado por
antonerajCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Light dependent resistor, photo resistor, or photocell
- Notes on the basics of a photoresistor, light dependent resistor or photocell including its construction, operation,
circuit symbol, and circuit applications
Resistor types includes:
Resistor types summary
Variable / adjustable resistor
Thermistor
LDR light dependent resistor
See also: SMT resistor MELF resistor
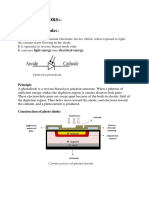
The light dependent resistor, LDR, is known by many names including the photoresistor, photo
resistor, photoconductor, photoconductive cell, or simply the photocell. It is probably the term
photocell that is most widely used in data and instruction sheets for domestic equipment.
The photo resistor, or light dependent resistor, LDR, finds many uses as a low cost photo sensitive
element and was used for many years in photographic light meters as well as in other applications such
as flame, smoke and burglar detectors, card readers and lighting controls for street lamps. Often within
the literature the photoresistor is called the photocell as a more generic term.
Photoresistor discovery
Photo-resistors, or light dependent resistors have been in use for very many years.
Photoresistors have been seen in early forms since the nineteenth century when photoconductivity in
selenium was discovered by Smith in 1873. Since then many variants of photoconductive devices have
been made.
Much useful work was conducted by T. W. Case in 1920 when he published a paper entitled
"Thalofide Cell - a new photo-electric cell".
Other substances including PbS, PbSe and PbTe were studied in the 1930s and 1940s, and then in
1952, Rollin and Simmons developed their photoconductors using silicon and germanium.
Light dependent resistor symbol
Light dependent resistor symbol used in circuit diagrams
The circuit symbol used for the light dependent resistor or photoresistor combines its resistor
action while indicating that it is sensitive to light. The basic light dependent resistor symbol has the
rectangle used to indicate its resistor action, and then has two incoming arrows - the same as those
used for photodiodes and phototransistors to indicate its light sensitivity.
For most applications, the light dependent resistor symbol used will be that with the resistor
with arrows, but in some instances those drawing circuit diagrams prefer to encase the resistor in a
circle. The more commonly used photoresistor symbol is the resistor without the circle around it.
Photoresistor mechanism
A photoresistor or photocell is a component that uses a photconductor between two contacts.
When this is exposed to light a change in resistance is noted.
Photoconductivity - the mechanism behind the photoresistor - results from the generation of mobile
carriers when photons are absorbed by the semiconductor material used for the photoconductor. While
the different types of material used for light dependent resistors are semiconductors, when used as a
photo-resistor, they are used only as a resistive element and there are no PN junctions. Accordingly the
device is purely passive.
There are two types of photoconductor and hence photoresistor:
Intrinsic photoresistor: This type of photoresistor uses a photoconductive material that involves
excitation of charge carriers from the valence bands to the conduction band.
Extrinsic photoresistor: This type of photoresistor uses a photoconductive material that involves
excitation of charge carriers between an impurity and the valence band or conduction band. It requires
shallow impurity dopants that are not ionised in the presence of light.
Extrinisc photoresistors or photocells are generally designed for long wavelength radiation - often
infra-red, but to avoid thermal generation they need to be operated at low temperatures.
Basic photoresistor structure
Although there are many ways in which light dependent resistors, or photo resistors can be
manufactured, there are naturally a few more common methods that are seen. Essentially the
photoresisitor or photocell consists of a resistive material sensitive to light that is exposed to light. The
photo resistive element comprises section of the material with contacts at either end.
A typical structure for a light dependent or photo resistor uses an active semiconductor layer that is
deposited on an insulating substrate. The semiconductor is normally lightly doped to enable it to have
the required level of conductivity. Contacts are then placed either side of the exposed area.
One form of photoresistor structure
Within the basic photoresistor or photocell structure, the resistance of the material itself is a key
issue. To ensure the resistance changes resulting from the light dominate, contact resistance is
minimised. To achieve this, the area around the contacts is normally heavily doped to reduce the
resistance in this region.
In many instances the area between the contacts is in the form of a zig zag, or interdigital pattern.
This maximises the exposed area and by keeping the distance between the contacts small it reduces the
spurious resistance levels and enhances the gain.
Photoresistor or photocell with interdigital contact pattern
It is also possible to use a polycrystalline semiconductor that is deposited onto a substrate such as
ceramic. This makes for a very low cost light dependent resistor
Applications
Photoresistors come in many types. Inexpensive cadmium sulphide cells can be found in many
consumer items such as camera light meters, street lights, clock radios, alarm devices, outdoor clocks,
solar street lamps and solar road studs, etc.
They are also used in some dynamic compressors together with a small incandescent lamp or light
emitting diode to control gain reduction and are also used in bed lamps, etc.
También podría gustarte
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento15 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEJerin JacobAún no hay calificaciones
- Phy IPDocumento13 páginasPhy IPJerin JacobAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Project - TO STUDY THE VARIATION IN CURRENT IN LDR CIRCUIT"Documento21 páginasPhysics Project - TO STUDY THE VARIATION IN CURRENT IN LDR CIRCUIT"aryanaryansen6Aún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent Resistor GuideDocumento6 páginasLight Dependent Resistor GuideMitran RonaldoAún no hay calificaciones
- Topic: Light Dependent Resistors and Their Applications: Physics Project ReportDocumento6 páginasTopic: Light Dependent Resistors and Their Applications: Physics Project ReportRimal KaurAún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent Resistor LDRDocumento5 páginasLight Dependent Resistor LDRAkshat GoelAún no hay calificaciones
- Phy ProjDocumento16 páginasPhy ProjpranavtsababayagaAún no hay calificaciones
- For LDRDocumento8 páginasFor LDRDeepu 5697Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento20 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEarunramarAún no hay calificaciones
- Sensors - FinalDocumento13 páginasSensors - Finalbob123Aún no hay calificaciones
- How photoresistors work to detect light intensityDocumento3 páginasHow photoresistors work to detect light intensityDezca NinditaAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento18 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEMannAún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent Resistance Project Report PhysicsDocumento23 páginasLight Dependent Resistance Project Report Physicsapi-342687563100% (1)
- What Is A Light Dependent Resistor or A Photo Resistor?: ResistivityDocumento4 páginasWhat Is A Light Dependent Resistor or A Photo Resistor?: Resistivitymani_vlsiAún no hay calificaciones
- Submitted by Aryan Patel Class XII ZDocumento21 páginasSubmitted by Aryan Patel Class XII Zaryan patelAún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent ResistorDocumento4 páginasLight Dependent ResistorShailesh RanawareAún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent ResistorDocumento7 páginasLight Dependent ResistorRUPALI MANKARAún no hay calificaciones
- Photoresistor - WikipediaDocumento12 páginasPhotoresistor - WikipediaSanyam JangraAún no hay calificaciones
- Acknowledgement 2Documento12 páginasAcknowledgement 2singhayushkumar2423Aún no hay calificaciones
- LDR: Light Dependent Resistor GuideDocumento4 páginasLDR: Light Dependent Resistor GuidehasnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Photo ResistorDocumento6 páginasPhoto Resistorsnehashissaha66Aún no hay calificaciones
- Physic Project LDRDocumento18 páginasPhysic Project LDRaPP bOssAún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent Resistor Circuit ExplainedDocumento37 páginasLight Dependent Resistor Circuit Explainedabhijeet deyAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is LDRDocumento5 páginasWhat Is LDRPrAkhar VermaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ec8252-Electronic Devices: Jothibasu M Ap (SR - GR) /ece PsgitechDocumento27 páginasEc8252-Electronic Devices: Jothibasu M Ap (SR - GR) /ece PsgitechJothibasu MarappanAún no hay calificaciones
- LDR Light Dependent Resistor Characteristics and ApplicationsDocumento3 páginasLDR Light Dependent Resistor Characteristics and ApplicationsMohammedAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture-2 2 2Documento14 páginasLecture-2 2 2Shubham JadhavAún no hay calificaciones
- Photo ResistorDocumento3 páginasPhoto ResistorHarish PrakashAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento21 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPESasmita KanungoAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Project: A.AravindDocumento24 páginasPhysics Project: A.Aravindasmiyaaslam062007Aún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent Resistance Project Report PhysicsDocumento23 páginasLight Dependent Resistance Project Report PhysicsAshwin RawatAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento23 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEyashAún no hay calificaciones
- (Redirected From) : Light Dependent ResistorDocumento3 páginas(Redirected From) : Light Dependent ResistorPeeyush MittalAún no hay calificaciones
- LDRDocumento12 páginasLDRRishabJaiswalAún no hay calificaciones
- GOSWAMIDocumento21 páginasGOSWAMIPrashant ChaudharyAún no hay calificaciones
- Swagata Deb BurmanDocumento9 páginasSwagata Deb Burmanvincent GamingAún no hay calificaciones
- Automatic lighting control with light dependent resistorsDocumento10 páginasAutomatic lighting control with light dependent resistorsAyush PattnaikAún no hay calificaciones
- Photo-Resistive Sensor: Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)Documento10 páginasPhoto-Resistive Sensor: Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)Narendra BhattAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit - V - Optoelectronics Devices MaterialsDocumento61 páginasUnit - V - Optoelectronics Devices MaterialsParth KhalasAún no hay calificaciones
- Detectors and Storage DevicesDocumento32 páginasDetectors and Storage Devices7t854s6wd2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent Resistor CircuitDocumento46 páginasLight Dependent Resistor Circuitkarthik srinivasanAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento21 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEMaverick ShadeAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento21 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEragg ss100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento21 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEdikshantdixit944Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Photoconductive CellDocumento4 páginasThe Photoconductive Cellfasdasd123Aún no hay calificaciones
- More On TransducersDocumento18 páginasMore On TransducersRand Ahmed BushnaqAún no hay calificaciones
- Light SensorDocumento15 páginasLight SensorVikal RajputAún no hay calificaciones
- PhotoresistorDocumento2 páginasPhotoresistorShashank AgarwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Physics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPEDocumento21 páginasPhysics Investigatory Project LIGHT DEPESasmita KanungoAún no hay calificaciones
- Priyanshu RajDocumento23 páginasPriyanshu RajSujal PandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Photodiode - WikipediaDocumento15 páginasPhotodiode - WikipediaIKENNAAún no hay calificaciones
- IR Transmitter Receiver Pair: Phototransistor StructureDocumento6 páginasIR Transmitter Receiver Pair: Phototransistor Structuresupport ubicuoAún no hay calificaciones
- Light Sensor (LDR) : Fig: LDR Symbol and SchematicDocumento3 páginasLight Sensor (LDR) : Fig: LDR Symbol and SchematicKarthik DmAún no hay calificaciones
- Light Dependent Resistor Automatic Switching CircuitDocumento25 páginasLight Dependent Resistor Automatic Switching Circuitkarthik srinivasanAún no hay calificaciones
- Photoelectric Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiDocumento32 páginasPhotoelectric Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamAún no hay calificaciones
- RajivDocumento19 páginasRajivpatilnagraj5622Aún no hay calificaciones
- IR Transmitter: Ir LedDocumento14 páginasIR Transmitter: Ir LedPragna ThatipelliAún no hay calificaciones
- LDR Guide: How Light Dependent Resistors WorkDocumento16 páginasLDR Guide: How Light Dependent Resistors WorkIndra Devi100% (1)
- INSTALL YOUR OWN Photovoltaic System: Hybrid, Stand Alone and Battery StorageDe EverandINSTALL YOUR OWN Photovoltaic System: Hybrid, Stand Alone and Battery StorageAún no hay calificaciones
- 8 X 8 Led DatasheetDocumento6 páginas8 X 8 Led DatasheetprAún no hay calificaciones
- Heavy Metals AnalysisDocumento14 páginasHeavy Metals AnalysisECRDAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamentals of Electromagnetic SpectrumDocumento14 páginasFundamentals of Electromagnetic SpectrumJacob AbrahamAún no hay calificaciones
- A Presentation By: L001: Hitakshi Arora L006: Yash Bhakkad L007: Varun Borkar L016: Shreya JainDocumento21 páginasA Presentation By: L001: Hitakshi Arora L006: Yash Bhakkad L007: Varun Borkar L016: Shreya JainHitakshi AroraAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 4 LaserDocumento22 páginasUnit 4 LaserAnshuman GhughutiyalAún no hay calificaciones
- Color Stability of Dental Composite Resin Materials For Crown and Bridge VeneersDocumento6 páginasColor Stability of Dental Composite Resin Materials For Crown and Bridge VeneersOsamaAliMoussaAún no hay calificaciones
- Alroy Feed BrochureDocumento12 páginasAlroy Feed BrochureNur FaiqahAún no hay calificaciones
- Rancangan Pengajaran Harian 2013: Topik CHAPTER 3 FORCES AND PRESSURE (Bernoulli's Principle) Objektif AM Objektif KhasDocumento11 páginasRancangan Pengajaran Harian 2013: Topik CHAPTER 3 FORCES AND PRESSURE (Bernoulli's Principle) Objektif AM Objektif KhasJubile A NelsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Uravi LampsDocumento6 páginasUravi LampsSurbhi GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Principles of IR SpectrosDocumento6 páginasPrinciples of IR SpectrosHemantAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial Letter 101/0/2020: Opto-Electronics IV (Theory)Documento17 páginasTutorial Letter 101/0/2020: Opto-Electronics IV (Theory)Vandiksha MaharajAún no hay calificaciones
- Bon SL Zoom Slit Lamp User and Service ManualDocumento20 páginasBon SL Zoom Slit Lamp User and Service ManualRoberto FalconeAún no hay calificaciones
- Cancer Cure That Worked PDFDocumento166 páginasCancer Cure That Worked PDFsurfsand100% (7)
- CPCAM KPC136A Camara BulletDocumento1 páginaCPCAM KPC136A Camara BulletTecnoSmartAún no hay calificaciones
- IR Spectroscopy: Dr. M. Saqlain TahirDocumento19 páginasIR Spectroscopy: Dr. M. Saqlain TahirAsif AliAún no hay calificaciones
- UEE Unit 3Documento29 páginasUEE Unit 3simbi arseneAún no hay calificaciones
- Fp4 Plus: Technical InformationDocumento8 páginasFp4 Plus: Technical InformationArkady YakhnisAún no hay calificaciones
- Science Module 5 PDFDocumento30 páginasScience Module 5 PDFerwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 1Documento53 páginasLecture 1Aalim KhanAún no hay calificaciones
- 650nm5mw Laser Diode FU-650LD-5Q-70Documento7 páginas650nm5mw Laser Diode FU-650LD-5Q-70allAún no hay calificaciones
- Wave Optics Animation - PpsDocumento20 páginasWave Optics Animation - Ppsaleena'Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lasers: An Introduction: Twenty-SixDocumento3 páginasLasers: An Introduction: Twenty-SixSwaroop ChAún no hay calificaciones
- Quantum Dots (Jacak)Documento176 páginasQuantum Dots (Jacak)MaxwellAún no hay calificaciones
- 2017 - Chapus Et Al. - Tunable SERS Platforms From Small Nanoparticle 3D Superlattices A Comparison Between Gold, Silver, and Copper - CDocumento10 páginas2017 - Chapus Et Al. - Tunable SERS Platforms From Small Nanoparticle 3D Superlattices A Comparison Between Gold, Silver, and Copper - CClaudio BiaginiAún no hay calificaciones
- ProjectDocumento11 páginasProjectMehak Parvez HamdaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Colour Vision AnomaliesDocumento27 páginasColour Vision AnomaliesGershon HayfordAún no hay calificaciones
- Phase-Shift Fizeau Interferometer in Presence of VibrationDocumento12 páginasPhase-Shift Fizeau Interferometer in Presence of VibrationMircea BujorAún no hay calificaciones
- Top Physical, Biological, Ergonomic and Chemical HazardsDocumento274 páginasTop Physical, Biological, Ergonomic and Chemical HazardsrwerwerwAún no hay calificaciones
- Antenna CharacteristicsDocumento43 páginasAntenna CharacteristicsbalambikaAún no hay calificaciones
- Corneal TransplantationDocumento12 páginasCorneal TransplantationnatanAún no hay calificaciones