Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Lecture 1
Cargado por
trannnen0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
48 vistas15 páginasSpreadsheet Modeling
& Decision Analysis
A Practical Introduction to Management Science
5th edition
Cliff T. Ragsdale
Título original
Lecture_1
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoSpreadsheet Modeling
& Decision Analysis
A Practical Introduction to Management Science
5th edition
Cliff T. Ragsdale
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
48 vistas15 páginasLecture 1
Cargado por
trannnenSpreadsheet Modeling
& Decision Analysis
A Practical Introduction to Management Science
5th edition
Cliff T. Ragsdale
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 15
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Spreadsheet Modeling
& Decision Analysis
A Practical Introduction to
Management Science
5
th
edition
Cliff T. Ragsdale
Introduction to Optimization
and Linear Programming
Lecture 1
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Introduction
We all face decision about how to use
limited resources such as:
Oil in the earth
Land for dumps
Time
Money
Workers
Mathematical Programming...
MP is a field of management science that
finds the optimal, or most efficient, way of
using limited resources to achieve the
objectives of an individual of a business.
a.k.a. Optimization
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Applications of Optimization
Determining Product Mix
Manufacturing
Routing and Logistics
Financial Planning
Characteristics of
Optimization Problems
Decisions
Constraints
Objectives
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
General Form of an Optimization Problem
MAX (or MIN): f
0
(X
1
, X
2
, , X
n
)
Subject to: f
1
(X
1
, X
2
, , X
n
)<=b
1
:
f
k
(X
1
, X
2
, , X
n
)>=b
k
:
f
m
(X
1
, X
2
, , X
n
)=b
m
Note: If all the functions in an optimization are linear,
the problem is a Linear Programming (LP) problem
Linear Programming (LP) Problems
MAX (or MIN): c
1
X
1
+ c
2
X
2
+ + c
n
X
n
Subject to: a
11
X
1
+ a
12
X
2
+ + a
1n
X
n
<= b
1
:
a
k1
X
1
+ a
k2
X
2
+ + a
kn
X
n
>=b
k
:
a
m1
X
1
+ a
m2
X
2
+ + a
mn
X
n
= b
m
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
An Example LP Problem
Blue Ridge Hot Tubs produces two types of hot
tubs: Aqua-Spas & Hydro-Luxes.
There are 200 pumps, 1566 hours of labor,
and 2880 feet of tubing available.
Aqua-Spa Hydro-Lux
Pumps 1 1
Labor 9 hours 6 hours
Tubing 12 feet 16 feet
Unit Profit $350 $300
5 Steps In Formulating LP Models:
1. Understand the problem.
2. Identify the decision variables.
X
1
=number of Aqua-Spas to produce
X
2
=number of Hydro-Luxes to produce
3. State the objective function as a linear
combination of the decision variables.
MAX: 350X
1
+ 300X
2
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
5 Steps In Formulating LP Models
(continued)
4. State the constraints as linear combinations
of the decision variables.
1X
1
+ 1X
2
<= 200 } pumps
9X
1
+ 6X
2
<= 1566 } labor
12X
1
+ 16X
2
<= 2880 } tubing
5. Identify any upper or lower bounds on the
decision variables.
X
1
>= 0
X
2
>= 0
LP Model for
Blue Ridge Hot Tubs
MAX: 350X
1
+ 300X
2
S.T.: 1X
1
+ 1X
2
<= 200
9X
1
+ 6X
2
<= 1566
12X
1
+ 16X
2
<= 2880
X
1
>= 0
X
2
>= 0
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Solving LP Problems:
An Intuitive Approach
Idea: Each Aqua-Spa (X
1
) generates the highest unit
profit ($350), so lets make as many of them as possible!
How many would that be?
Let X
2
= 0
1st constraint: 1X
1
<= 200
2nd constraint: 9X
1
<=1566 or X
1
<=174
3rd constraint: 12X
1
<= 2880 or X
1
<= 240
If X
2
=0, the maximum value of X
1
is 174 and the total
profit is $350*174 + $300*0 = $60,900
This solution is feasible, but is it optimal?
No!
Solving LP Problems:
A Graphical Approach
The constraints of an LP problem
defines its feasible region.
The best point in the feasible region is
the optimal solution to the problem.
For LP problems with 2 variables, it is
easy to plot the feasible region and find
the optimal solution.
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
(0, 200)
(200, 0)
boundary line of pump constraint
X
1
+ X
2
= 200
Plotting the First Constraint
X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
(0, 261)
(174, 0)
boundary line of labor constraint
9X
1
+ 6X
2
= 1566
Plotting the Second Constraint
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
(0, 180)
(240, 0)
boundary line of tubing constraint
12X
1
+ 16X
2
= 2880
Feasible Region
Plotting the Third Constraint
X
2
Plotting A Level Curve of the
Objective Function
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
(0, 116.67)
(100, 0)
objective function
350X
1
+ 300X
2
= 35000
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
A Second Level Curve of the
Objective Function X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
(0, 175)
(150, 0)
objective function
350X
1
+ 300X
2
= 35000
objective function
350X
1
+ 300X
2
= 52500
Using A Level Curve to Locate
the Optimal Solution
X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
objective function
350X
1
+ 300X
2
= 35000
objective function
350X
1
+ 300X
2
= 52500
optimal solution
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Calculating the Optimal Solution
The optimal solution occurs where the pumps and
labor constraints intersect.
This occurs where:
X
1
+ X
2
= 200 (1)
and 9X
1
+ 6X
2
= 1566 (2)
From (1) we have, X
2
= 200 -X
1
(3)
Substituting (3) for X
2
in (2) we have,
9X
1
+ 6 (200 -X
1
) = 1566
which reduces to X
1
= 122
So the optimal solution is,
X
1
=122, X
2
=200-X
1
=78
Total Profit = $350*122 + $300*78 = $66,100
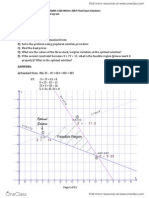
Enumerating The Corner Points
X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
(0, 180)
(174, 0)
(122, 78)
(80, 120)
(0, 0)
obj. value = $54,000
obj. value = $64,000
obj. value = $66,100
obj. value = $60,900 obj. value = $0
Note: This technique will not work if
the solution is unbounded.
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Summary of Graphical Solution
to LP Problems
1. Plot the boundary line of each constraint
2. Identify the feasible region
3. Locate the optimal solution by either:
a. Plotting level curves
b. Enumerating the extreme points
Understanding How Things Change
See file Fig2-8.xls
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Special Conditions in LP Models
A number of anomalies can occur in LP
problems:
Alternate Optimal Solutions
Redundant Constraints
Unbounded Solutions
Infeasibility
Example of Alternate Optimal Solutions
X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
450X
1
+ 300X
2
= 78300
objective function level curve
alternate optimal solutions
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Example of a Redundant Constraint
X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
boundary line of tubing constraint
Feasible Region
boundary line of pump constraint
boundary line of labor constraint
Example of an Unbounded Solution
X
2
X
1
1000
800
600
400
200
0
0 200
400 600 800 1000
X
1
+ X
2
= 400
X
1
+ X
2
= 600
objective function
X
1
+ X
2
= 800
objective function
-X
1
+ 2X
2
= 400
MANAGEMENT DECISION MAKING
International Executive MBA PGSM
Example of Infeasibility
X
2
X
1
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 50
100 150 200 250
X
1
+ X
2
= 200
X
1
+ X
2
= 150
feasible region for
second constraint
feasible region
for first
constraint
End of Chapter 2
También podría gustarte
- Spreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Practical Introduction To Management ScienceDocumento30 páginasSpreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Practical Introduction To Management ScienceTalha MaqsoodAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap1 2Documento23 páginasChap1 2Neeraj SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 4 - DSO 547 Linear Programming - DasguptaDocumento47 páginasLecture 4 - DSO 547 Linear Programming - DasguptaZhaohong WangAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear Programming Solution Techniques: Graphical and Computer MethodsDocumento120 páginasLinear Programming Solution Techniques: Graphical and Computer MethodsHarshal ParekhAún no hay calificaciones
- Industrial Engineering (IE)Documento22 páginasIndustrial Engineering (IE)محمد ناصر عليويAún no hay calificaciones
- We All Face Decision About How To Use Limited Resources Such As: Oil in The Earth Land For Dumps Time Money WorkersDocumento11 páginasWe All Face Decision About How To Use Limited Resources Such As: Oil in The Earth Land For Dumps Time Money WorkersGOHAR GHAFFARAún no hay calificaciones
- Mtse - 04.03.14Documento94 páginasMtse - 04.03.14santhosh90mechAún no hay calificaciones
- Mtse - 25.02.14Documento87 páginasMtse - 25.02.14santhosh90mechAún no hay calificaciones
- CHAPTER THREE Edited HandoutDocumento13 páginasCHAPTER THREE Edited Handoutasuasan151Aún no hay calificaciones
- LP Solved ProblemsDocumento5 páginasLP Solved ProblemsAaronLumibao100% (1)
- Session 2 - Wednesday 7th SeptemberDocumento12 páginasSession 2 - Wednesday 7th Septemberabdullah naveedAún no hay calificaciones
- 14, 42, 61 Or1 LPDocumento120 páginas14, 42, 61 Or1 LPPaola Pecolera100% (1)
- Spreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Practical Introduction To Management ScienceDocumento56 páginasSpreadsheet Modeling & Decision Analysis: A Practical Introduction To Management ScienceAmitoj Singh SainiAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2Documento29 páginasChapter 2Lyana JaafarAún no hay calificaciones
- CHE 536 Engineering Optimization: Course Policies and OutlineDocumento33 páginasCHE 536 Engineering Optimization: Course Policies and Outlineprasaad08Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 2Documento32 páginasLecture 2trannnenAún no hay calificaciones
- 02 Introduction To OptimizationDocumento14 páginas02 Introduction To Optimizationriya lakhotiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear ProgrammingDocumento70 páginasLinear ProgrammingAditya Risqi PratamaAún no hay calificaciones
- LPP Formulation & Graphical NewDocumento21 páginasLPP Formulation & Graphical NewManish Singh100% (1)
- Linear ProgrammingDocumento62 páginasLinear ProgrammingPayal ChauhanAún no hay calificaciones
- Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Solutions ManualDocumento44 páginasSpreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Solutions ManualTrevor feignarddAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Linear Programming ProblemDocumento35 páginas2 Linear Programming Problemangel190693100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Linear ProgrammingDocumento35 páginasChapter 3 Linear ProgrammingSaad ShaikhAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Linear ProgrammingDocumento56 páginasIntroduction To Linear Programmingreplyram123Aún no hay calificaciones
- Linear Programming: Model Formulation and Graphical SolutionDocumento65 páginasLinear Programming: Model Formulation and Graphical SolutionPatrice Elaine PillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Recent Chaos at Delhi Airport!Documento57 páginasRecent Chaos at Delhi Airport!Sahil ChaudharyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 2 Linear ProgrammingDocumento35 páginasLesson 2 Linear ProgrammingalecksgodinezAún no hay calificaciones
- IPandBIPDocumento30 páginasIPandBIPMritunjay HansdaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2: Linear Programming: Source: Tayloriii (2007)Documento52 páginasChapter 2: Linear Programming: Source: Tayloriii (2007)how_zheAún no hay calificaciones
- 3330 Winter 2007 Final Exam With SolutionsDocumento11 páginas3330 Winter 2007 Final Exam With SolutionsmaxzAún no hay calificaciones
- Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Solutions ManualDocumento46 páginasSpreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 8th Edition Ragsdale Solutions ManualShawnMitchellbfqyz93% (14)
- Assignment Group 04 LPPDocumento13 páginasAssignment Group 04 LPPAkshay BhatiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear Programming - Model Formulation, Graphical MethodDocumento48 páginasLinear Programming - Model Formulation, Graphical MethodJoseph George KonnullyAún no hay calificaciones
- 9 Edition by Bernard W. Taylor III: Introduction To Management ScienceDocumento42 páginas9 Edition by Bernard W. Taylor III: Introduction To Management ScienceMohd Akmal Md ZukiAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit I ORDocumento12 páginasUnit I ORsandy itAún no hay calificaciones
- Optimization TechniqueDocumento30 páginasOptimization Techniquerahuljiit100% (6)
- Linear Programming Model 2 MBADocumento44 páginasLinear Programming Model 2 MBABabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (1)
- Operres Case 1 - American Sporting Equipment PDFDocumento7 páginasOperres Case 1 - American Sporting Equipment PDFRed100% (1)
- 7 LP Sensitivity AnalysisDocumento9 páginas7 LP Sensitivity AnalysiszuluagagaAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear Programming: Graphical and Computer MethodsDocumento110 páginasLinear Programming: Graphical and Computer MethodschyonAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap 006 SDocumento26 páginasChap 006 SRana Gaballah100% (1)
- Introduction To Linear ProgrammingDocumento44 páginasIntroduction To Linear ProgrammingMohammad Faizal Azwar Annas100% (2)
- CMPG 312 Semester Test PreparationDocumento4 páginasCMPG 312 Semester Test PreparationAsemahleAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 - Linear ProrammingDocumento67 páginasChapter 2 - Linear ProrammingLetaAún no hay calificaciones
- Spreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 7th Edition Cliff Ragsdale Solutions ManualDocumento14 páginasSpreadsheet Modeling and Decision Analysis A Practical Introduction To Business Analytics 7th Edition Cliff Ragsdale Solutions ManualShawnMitchellbfqyz92% (12)
- Linear ProgrammingDocumento29 páginasLinear ProgrammingBrejohn McCrary100% (1)
- DS Linear ProgrammimgDocumento54 páginasDS Linear ProgrammimgKartik SharmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch. 1 Linear Programing Part 1Documento36 páginasCh. 1 Linear Programing Part 1Omar AlzayatAún no hay calificaciones
- Operations Management: William J. StevensonDocumento26 páginasOperations Management: William J. Stevensonaprian100% (4)
- OR - CH - 2Documento26 páginasOR - CH - 2gadisafufa81Aún no hay calificaciones
- Simplex Method AssignmentDocumento11 páginasSimplex Method AssignmentNurul Rizal100% (1)
- Decision Modeling Using SpreadsheetDocumento36 páginasDecision Modeling Using SpreadsheetamritaAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap02 Decision Modelling Using SpreadsheetDocumento36 páginasChap02 Decision Modelling Using SpreadsheetamritaAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 1 orDocumento2 páginasAssignment 1 orPiyush VirmaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear Programming Solution Techniques: Graphical and Computer MethodsDocumento100 páginasLinear Programming Solution Techniques: Graphical and Computer Methodsishuch24Aún no hay calificaciones
- OR RecordDocumento35 páginasOR RecordGOWTHAM H : CSBS DEPTAún no hay calificaciones
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"De EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Calificación: 2.5 de 5 estrellas2.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYDe EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 11 - Sheep and Goat Economics of Production and MarkeDocumento28 páginasChapter 11 - Sheep and Goat Economics of Production and MarkegavinilaaAún no hay calificaciones
- Create A Neural Network in 7 Steps - Neural DesignerDocumento11 páginasCreate A Neural Network in 7 Steps - Neural DesignerRamón RuizAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 5 (Duality Interpretation)Documento12 páginasLecture 5 (Duality Interpretation)RHEA MARISSA ROCHAún no hay calificaciones
- Supply Chain Management: An International Journal: Article InformationDocumento15 páginasSupply Chain Management: An International Journal: Article InformationFifi UmmahAún no hay calificaciones
- Agarwal CV PDFDocumento17 páginasAgarwal CV PDFlaharadeoAún no hay calificaciones
- Optimazation ProblemsDocumento17 páginasOptimazation ProblemsRichard Lorenzo BeloAún no hay calificaciones
- Design Optimisation Study of Solvent Extraction: Chemical Reaction, Mass Transfer and Mixer-Settler HydrodynamicsDocumento17 páginasDesign Optimisation Study of Solvent Extraction: Chemical Reaction, Mass Transfer and Mixer-Settler Hydrodynamicsnburn69Aún no hay calificaciones
- High-Quality and Efficient Volume ResamplingDocumento129 páginasHigh-Quality and Efficient Volume ResamplingBalazs DomonkosAún no hay calificaciones
- The Design of Extrusion Screws: An Optimization ApproachDocumento50 páginasThe Design of Extrusion Screws: An Optimization ApproachRicham HamzeAún no hay calificaciones
- SCGX Fino UserguideDocumento189 páginasSCGX Fino UserguideWashington JohnAún no hay calificaciones
- Notes On OptimizationDocumento55 páginasNotes On OptimizationSeshu BollineniAún no hay calificaciones
- Literature Review On Linear ProgrammingDocumento5 páginasLiterature Review On Linear Programmingea0kvft0100% (1)
- Fu 2014Documento90 páginasFu 2014David Esteban Meneses RendicAún no hay calificaciones
- 15MAT303 - I Ass - Jan 2019Documento1 página15MAT303 - I Ass - Jan 2019SURYA SPARKSAún no hay calificaciones
- Production Scheduling Using TWK and SLK Methods: January 2021Documento8 páginasProduction Scheduling Using TWK and SLK Methods: January 2021Fadoua LahnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Work Integrated Learning Programmes DigitalDocumento13 páginasBirla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Work Integrated Learning Programmes Digitalkansal611Aún no hay calificaciones
- Acusolve Hypermesh HyperstudyDocumento43 páginasAcusolve Hypermesh HyperstudyEfrain Diaz GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Simulink Design OptimizationDocumento686 páginasSimulink Design OptimizationGonzalo AlmeidaAún no hay calificaciones
- Optimizing The Use of Government AssetsDocumento10 páginasOptimizing The Use of Government AssetsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAún no hay calificaciones
- 5G DTA IntroductionDocumento4 páginas5G DTA IntroductionEmerson Eduardo RodriguesAún no hay calificaciones
- 3G Cluster Optimization by Drive TestingDocumento43 páginas3G Cluster Optimization by Drive Testingcorneliu.modilca71% (7)
- Tugas Integer Programming PO - Aldian Farabi - F34080001Documento4 páginasTugas Integer Programming PO - Aldian Farabi - F34080001Aldian FarabiAún no hay calificaciones
- Optislang Inside AnsysDocumento32 páginasOptislang Inside AnsysRaees SwatiAún no hay calificaciones
- Gurobi OptimizationDocumento26 páginasGurobi OptimizationAakriti AgarwalAún no hay calificaciones
- Python Exam Practice - ExercisesDocumento6 páginasPython Exam Practice - ExercisesAriyan JahanyarAún no hay calificaciones
- 01338475Documento6 páginas01338475api-3697505Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1 - V.good Lectures PDFDocumento89 páginas1 - V.good Lectures PDFrawadAún no hay calificaciones
- (U E in - Ppa) NotesDocumento28 páginas(U E in - Ppa) NotesSumedh Kakde100% (1)
- Compit2016 LecceDocumento492 páginasCompit2016 LecceAlessandro CastagnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Big Data Cyber Security PaperDocumento3 páginasBig Data Cyber Security PaperAbdul RazzakAún no hay calificaciones